Overview of Microsoft Defender for Storage (classic)
Note
Upgrade to the new Microsoft Defender for Storage plan. It includes new features like Malware Scanning and Sensitive Data Threat Detection. This plan also provides a more predictable pricing structure for better control over coverage and costs. Additionally, all new Defender for Storage features will only be released in the new plan. Migrating to the new plan is a simple process, read here about how to migrate from the classic plan. If you're using Defender for Storage (classic) with per-transaction or per-storage account pricing, you'll need to migrate to the new Defender for Storage (classic) plan to access these features and pricing. Learn about the benefits of migrating to the new Defender for Storage plan.
Microsoft Defender for Storage (classic) is an Azure-native layer of security intelligence that detects unusual and potentially harmful attempts to access or exploit your storage accounts. It uses advanced threat detection capabilities and Microsoft Threat Intelligence data to provide contextual security alerts. Those alerts also include steps to mitigate the detected threats and prevent future attacks.
You can enable Microsoft Defender for Storage (classic) at either the subscription level (recommended) or the resource level.
Defender for Storage (classic) continually analyzes the data stream generated by the Azure Blob Storage, Azure Files, and Azure Data Lake Storage services. When potentially malicious activities are detected, security alerts are generated. These alerts are displayed in Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Any details of suspicious activity along with the relevant investigation steps, remediation actions, and security recommendations are presented here.
Analyzed data of Azure Blob Storage includes operation types such as Get Blob, Put Blob, Get Container ACL, List Blobs, and Get Blob Properties. Examples of analyzed Azure Files operation types include Get File, Create File, List Files, Get File Properties, and Put Range.
Defender for Storage (classic) doesn't access the Storage account data and has no effect on its performance.
You can learn more by watching this video from the Defender for Cloud in the Field video series:
For more clarification about Defender for Storage (classic), see the commonly asked questions.
Availability
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Release state: | General availability (GA) |
| Pricing: | Microsoft Defender for Storage (classic) is billed as shown on the pricing page |
| Protected storage types: | Blob Storage (Standard/Premium StorageV2, Block Blobs) Azure Files (over REST API and SMB) Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (Standard/Premium accounts with hierarchical namespaces enabled) |
| Clouds: |
What are the benefits of Microsoft Defender for Storage (classic)?
Defender for Storage (classic) provides:
Azure-native security - With 1-click enablement, Defender for Storage (classic) protects data stored in Azure Blob, Azure Files, and Data Lakes. As an Azure-native service, Defender for Storage (classic) provides centralized security across all data assets that Azure manages and is integrated with other Azure security services such as Microsoft Sentinel.
Rich detection suite - Powered by Microsoft Threat Intelligence, the detections in Defender for Storage (classic) cover the top storage threats such as unauthenticated access, compromised credentials, social engineering attacks, data exfiltration, privilege abuse, and malicious content.
Response at scale - Defender for Cloud's automation tools make it easier to prevent and respond to identified threats. Learn more in Automate responses to Defender for Cloud triggers.

Security threats in cloud-based storage services
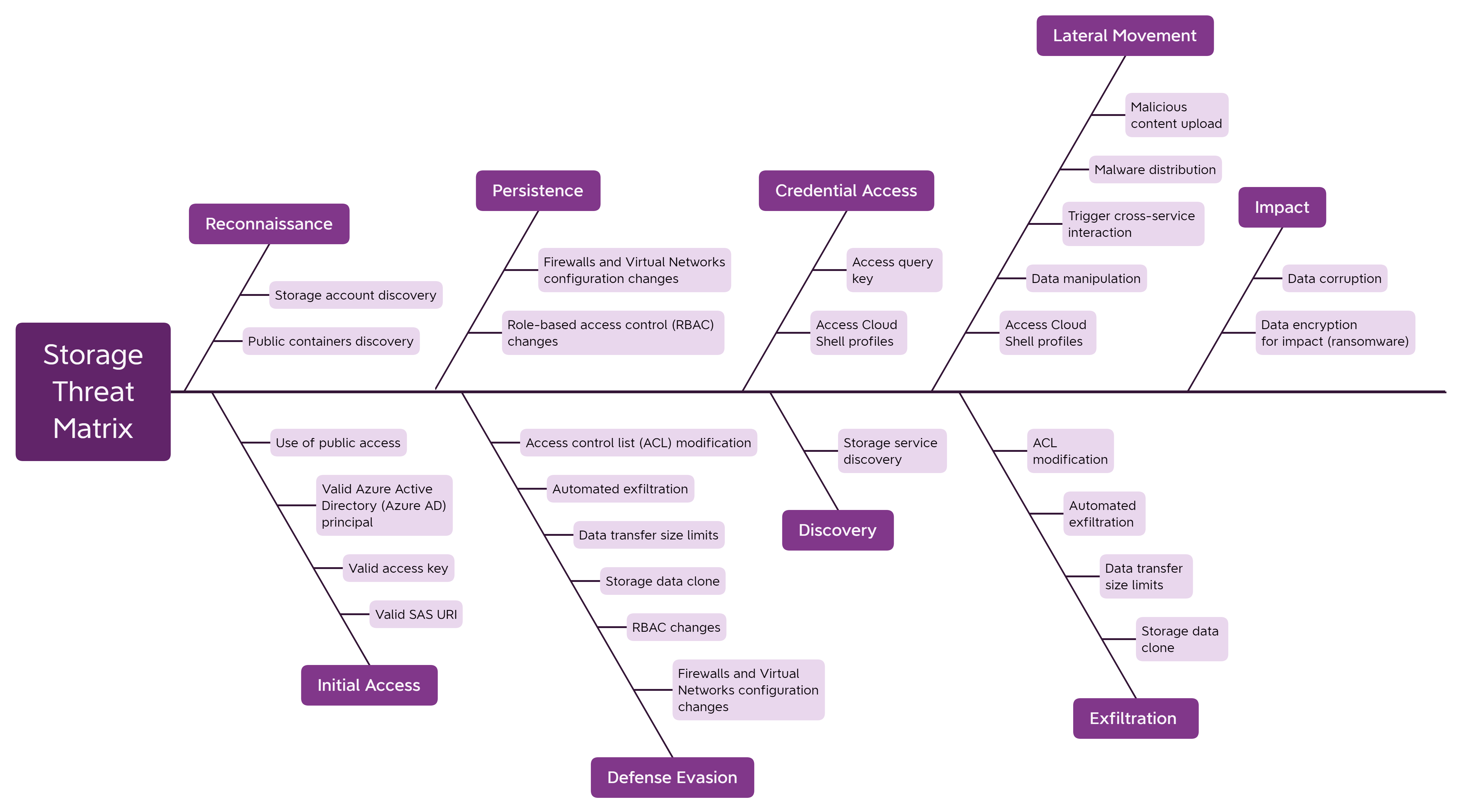
Microsoft security researchers have analyzed the attack surface of storage services. Storage accounts can be subject to data corruption, exposure of sensitive content, malicious content distribution, data exfiltration, unauthorized access, and more.
The potential security risks are described in the threat matrix for cloud-based storage services and are based on the MITRE ATT&CK® framework, a knowledge base for the tactics and techniques employed in cyberattacks.
What kind of alerts does Microsoft Defender for Storage (classic) provide?
Security alerts are triggered for the following scenarios (typically from 1-2 hours after the event):
| Type of threat | Description |
|---|---|
| Unusual access to an account | For example, access from a TOR exit node, suspicious IP addresses, unusual applications, unusual locations, and anonymous access without authentication. |
| Unusual behavior in an account | Behavior that deviates from a learned baseline. For example, a change of access permissions in an account, unusual access inspection, unusual data exploration, unusual deletion of blobs/files, or unusual data extraction. |
| Hash reputation based Malware detection | Detection of known malware based on full blob/file hash. Which can help detect ransomware, viruses, spyware, and other malware uploaded to an account, prevent it from entering the organization, and spreading to more users and resources. See also Limitations of hash reputation analysis. |
| Unusual file uploads | Unusual cloud service packages and executable files that have been uploaded to an account. |
| Public visibility | Potential break-in attempts by scanning containers and pulling potentially sensitive data from publicly accessible containers. |
| Phishing campaigns | When content that's hosted on Azure Storage is identified as part of a phishing attack that's impacting Microsoft 365 users. |
Tip
For a comprehensive list of all Defender for Storage (classic) alerts, see the alerts reference page. It is essential to review the prerequisites, as certain security alerts are only accessible under the new Defender for Storage plan. The information in the reference page is beneficial for workload owners seeking to understand detectable threats and enables Security Operations Center (SOC) teams to familiarize themselves with detections prior to conducting investigations. Learn more about what's in a Defender for Cloud security alert, and how to manage your alerts in Manage and respond to security alerts in Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Alerts include details of the incident that triggered them, and recommendations on how to investigate and remediate threats. Alerts can be exported to Microsoft Sentinel or any other third-party SIEM or any other external tool. Learn more in Stream alerts to a SIEM, SOAR, or IT classic deployment model solution.
Limitations of hash reputation analysis
Tip
If you're looking to have your uploaded blobs scanned for malware in near real-time, we recommend that you upgrade to the new Defender for Storage plan. Learn more about Malware Scanning.
Hash reputation isn't deep file inspection - Microsoft Defender for Storage (classic) uses hash reputation analysis supported by Microsoft Threat Intelligence to determine whether an uploaded file is suspicious. The threat protection tools don’t scan the uploaded files; rather they analyze the data generated from the Blobs Storage and Files services. Defender for Storage (classic) then compares the hashes of newly uploaded files with hashes of known viruses, trojans, spyware, and ransomware.
Hash reputation analysis isn't supported for all files protocols and operation types - Some, but not all, of the data logs contain the hash value of the related blob or file. In some cases, the data doesn't contain a hash value. As a result, some operations can't be monitored for known malware uploads. Examples of such unsupported use cases include SMB file-shares and when a blob is created using Put Block and Put blocklist.
Next steps
In this article, you learned about Microsoft Defender for Storage (classic).
- Enable Defender for Storage (classic)
- Check out common questions about Defender for Storage classic.