Microsoft Defender Antivirus in the Windows Security app
Applies to:
Beginning with Windows 10, version 1703 and later, Microsoft Defender Antivirus settings are viewable in the Windows Security app. See Windows Security for more information about security features and settings that are built into Windows.
Important
Disabling the Windows Security app doesn't disable Microsoft Defender Antivirus or Windows Firewall. These capabilities are disabled or set to passive mode when non-Microsoft antivirus/antimalware software is installed on the device and kept up to date. If you do disable the Windows Security app, or configure its associated Group Policy settings to prevent it from starting or running, the Windows Security app might display stale or inaccurate information about any antivirus or firewall products that are installed on the device. It might also prevent Microsoft Defender Antivirus from re-enabling when you uninstall any non-Microsoft antivirus/antimalware software. Disabling the Windows Security app can significantly lower the level protection of your device and could lead to malware infection.
Review virus and threat protection settings in the Windows Security app
Open the Windows Security app by searching the start menu for Windows Security.
Select Virus & threat protection.
Use one or more of the subsequent sections to perform tasks using the Windows Security app.
Note
If these settings are configured and deployed using Group Policy, the settings described in this section are grayed-out and unavailable for use on individual endpoints. Changes made through a Group Policy Object must first be deployed to individual endpoints before the setting are updated in Windows Settings. The Configure end-user interaction with Microsoft Defender Antivirus topic describes how local policy override settings can be configured.
Run a scan with the Windows Security app
Open the Windows Security app by searching the start menu for Security, and then selecting Windows Security.
Select the Virus & threat protection tile (or the shield icon on the left menu bar).
Select Quick scan. Or, to run a full scan, select Scan options, and then select an option, such as Full scan.
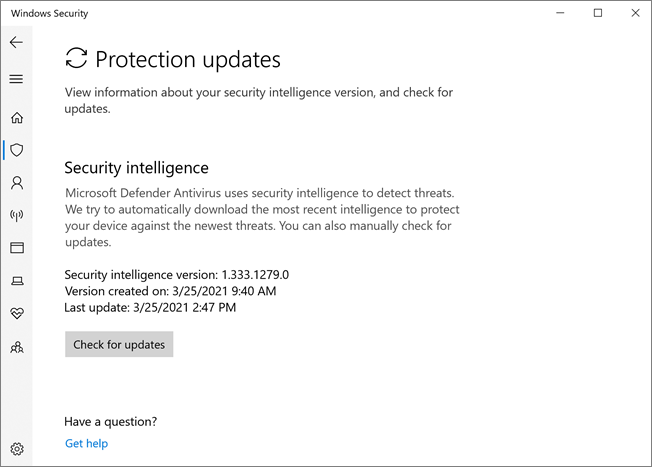
Review the security intelligence update version and download the latest updates in the Windows Security app
Open the Windows Security app by searching the start menu for Security, and then selecting Windows Security.
Select the Virus & threat protection tile (or the shield icon on the left menu bar).
Select Virus & threat protection updates. The currently installed version is displayed along with some information about when it was downloaded. You can check your current against the latest version available for manual download, or review the change log for that version. See Security intelligence updates for Microsoft Defender Antivirus and other Microsoft antimalware.
Select Check for updates to download new protection updates (if there are any).
Ensure Microsoft Defender Antivirus is enabled in the Windows Security app
Open the Windows Security app by searching the start menu for Security, and then selecting Windows Security.
Select the Virus & threat protection tile (or the shield icon on the left menu bar).
Select Virus & threat protection settings.
Toggle the Real-time protection switch to On.
Note
If you switch Real-time protection off, it will automatically turn back on after a short delay. This automatic enablement is to ensure you're protected from malware and threats. If you install another antivirus product, Microsoft Defender Antivirus automatically disables itself and is indicated as such in the Windows Security app. A setting appears that allows you to enable limited periodic scanning.
Add exclusions for Microsoft Defender Antivirus in the Windows Security app
Open the Windows Security app by searching the start menu for Security, and then selecting Windows Security.
Select the Virus & threat protection tile (or the shield icon on the left menu bar).
Under Virus & threat protection settings, select Manage settings.
Under Exclusions, select Add or remove exclusions.
Select the plus icon (+) to choose the type and set the options for each exclusion.
The following table summarizes exclusion types and what happens:
| Exclusion type | Defined by | What happens |
|---|---|---|
| File | Location Example: c:\sample\sample.test |
The specific file is skipped by Microsoft Defender Antivirus. |
| Folder | Location Example: c:\test\sample |
All items in the specified folder are skipped by Microsoft Defender Antivirus. |
| File type | File extension Example: .test |
All files with the .test extension anywhere on your device are skipped by Microsoft Defender Antivirus. |
| Process | Executable file path Example: c:\test\process.exe |
The specific process and any files that are opened by that process are skipped by Microsoft Defender Antivirus. |
To learn more, see the following resources:
- Configure and validate exclusions based on file extension and folder location
- Configure exclusions for files opened by processes
Review threat detection history in the Windows Defender app
Open the Windows Security app by searching the start menu for Security, and then selecting Windows Security.
Select the Virus & threat protection tile (or the shield icon on the left menu bar).
Select Protection history. Any recent items are listed.
Set ransomware protection and recovery options
Open the Windows Security app by searching the start menu for Security, and then selecting Windows Security.
Select the Virus & threat protection tile (or the shield icon on the left menu bar).
Under Ransomware protection, select Manage ransomware protection.
To change Controlled folder access settings, see Protect important folders with Controlled folder access.
To set up ransomware recovery options, select Set up under Ransomware data recovery and follow the instructions for linking or setting up your OneDrive account so you can easily recover from a ransomware attack.
See also
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Tech Community.