Nóta
Teastaíonn údarú chun rochtain a fháil ar an leathanach seo. Is féidir leat triail a bhaint as shíniú isteach nó eolairí a athrú.
Teastaíonn údarú chun rochtain a fháil ar an leathanach seo. Is féidir leat triail a bhaint as eolairí a athrú.
This tutorial shows how to create and run a .NET console application by using Visual Studio Code.
In this tutorial, you:
- Launch Visual Studio Code with a C# development environment.
- Create a "HelloWorld" .NET console application.
- Enhance the app to prompt the user for their name and display it in the console window.
This tutorial shows how to create and run a .NET console application by using GitHub Codespaces.
In this tutorial, you:
- Launch a GitHub Codespace with a C# development environment.
- Create a "HelloWorld" .NET single-file app.
- Enhance the app to prompt the user for their name and display it in the console window.
Prerequisites
- The latest .NET SDK
- Visual Studio Code editor
- The C# DevKit
Installation instructions
On Windows, this WinGet configuration file to install all prerequisites. If you already have something installed, WinGet will skip that step.
- Download the file and double-click to run it.
- Read the license agreement, type y, and select Enter when prompted to accept.
- If you get a flashing User Account Control (UAC) prompt in your Taskbar, allow the installation to continue.
On other platforms, you need to install each of these components separately.
- Download the recommended installer from the .NET SDK download page and double-click to run it. The download page detects your platform and recommends the latest installer for your platform.
- Download the latest installer from the Visual Studio Code home page and double click to run it. That page also detects your platform and the link should be correct for your system.
- Click the "Install" button on the C# DevKit extension page. That opens Visual Studio code, and asks if you want to install or enable the extension. Select "install".
- A GitHub account to use GitHub Codespaces. If you don't already have one, you can create a free account at GitHub.com.
Create the app
Create a .NET console app project named "HelloWorld".
Start Visual Studio Code.
Go to the Explorer view and select Create .NET Project. Alternatively, you can bring up the Command Palette using Ctrl+Shift+P (Command+Shift+P on MacOS) and then type ".NET" and find and select the .NET: New Project command.
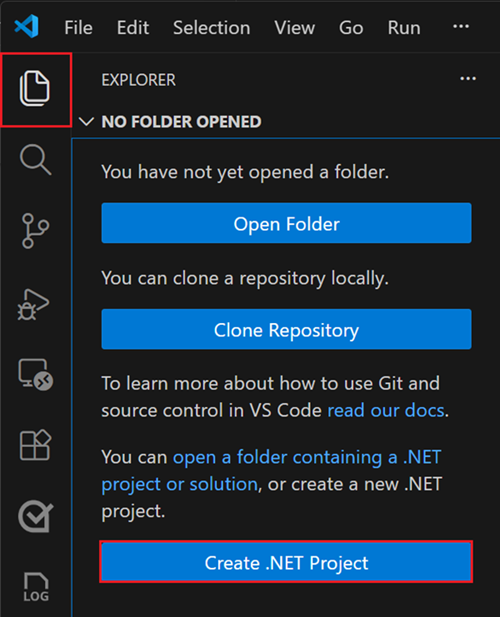
After selecting the command, you need to choose the project template. Choose Console App.
Select the location where you would like the new project to be created.
Give your new project a name, "HelloWorld".
Select .sln for the solution file format.
Select Create Project.
The project is created and the Program.cs file opens. You see the simple application created by the template:
// See https://aka.ms/new-console-template for more information Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!");The code defines a class,
Program, that calls the Console.WriteLine(String) method to display a message in the console window.
Open Codespaces
Start a GitHub Codespace with the tutorial environment.
Open a browser window and navigate to the tutorial codespace repository.
Select the green Code button, and then the Codespaces tab.
Select the
+sign or the green Create codespace on main button to create a new Codespace using this environment.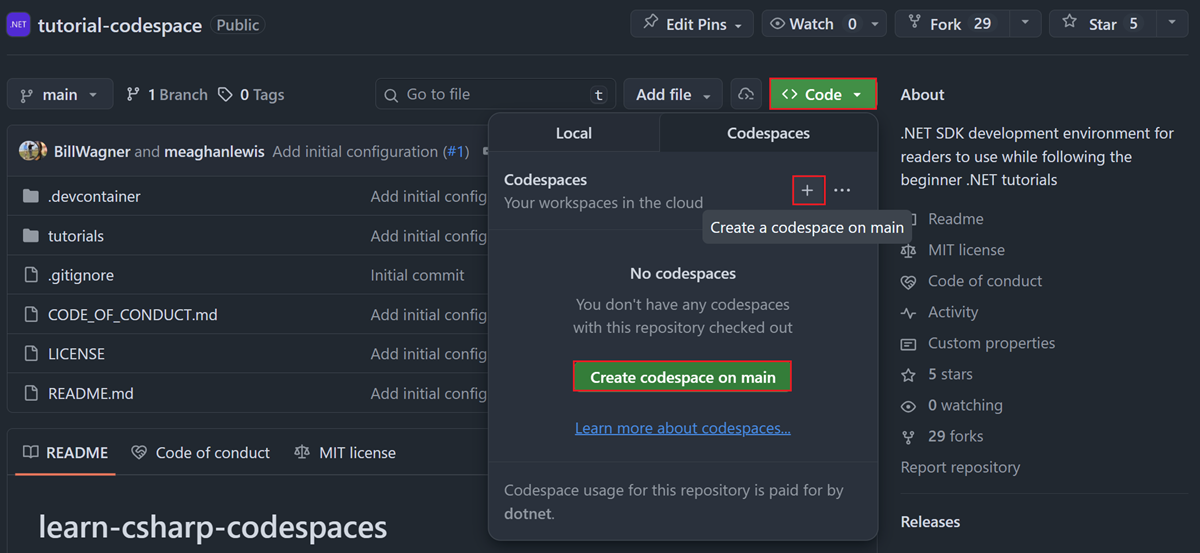
Create a .NET file-based app
In Codespaces, you'll create a file-based app. File-based apps let you build .NET applications from a single C# file without creating a traditional project file.
When your codespace loads, right-click on the tutorials folder and select New File.... Enter the name HelloWorld.cs and then press Enter.
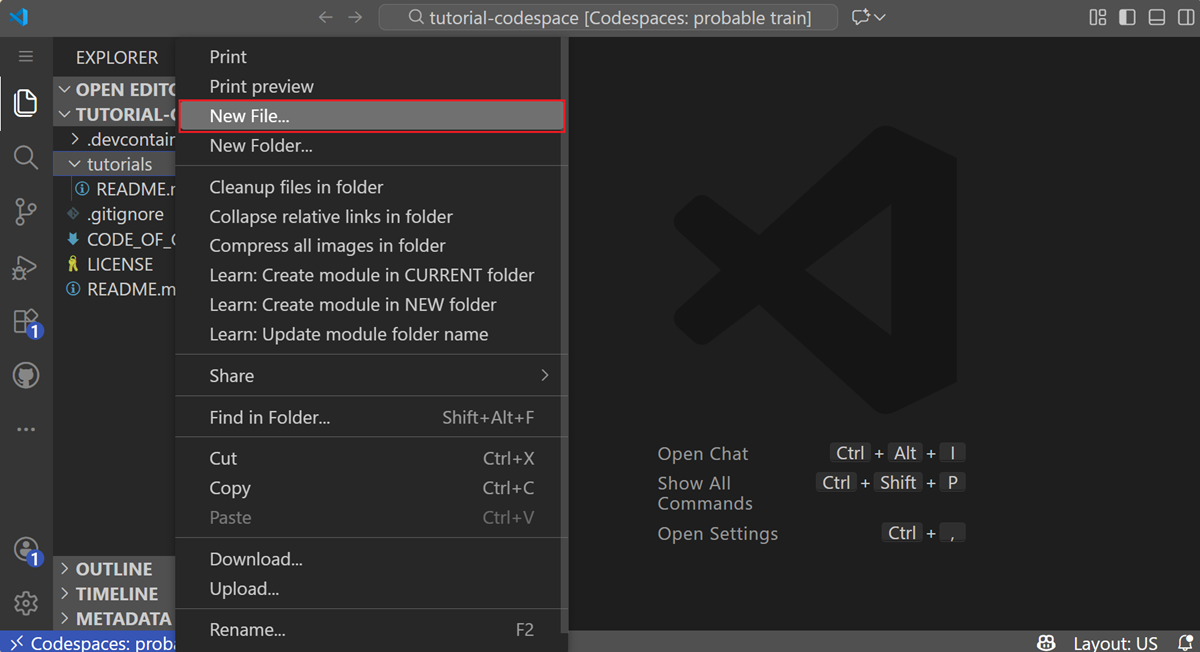
HelloWorld.cs opens in the editor. Type or copy the following code into the file:
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!");
Run the app
To run your app, select Run > Run without Debugging in the upper menu, or use the keyboard shortcut (Ctrl+F5).
If asked to select a debugger, select C# as the debugger, then select C#: Debug Active File as the Launch configuration.
The program displays "Hello, World!" and ends.
In the terminal window, make sure the tutorials folder is the current folder, and run your program:
cd tutorials
dotnet HelloWorld.cs
The program displays "Hello, World!" and ends.
Enhance the app
Enhance the application to prompt the user for their name and display it along with the date and time.
Open Program.cs.
Replace the contents of the class with the following code:
Console.WriteLine("What is your name?"); var name = Console.ReadLine(); var currentDate = DateTime.Now; Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}!"); Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press Enter to exit..."); Console.Read();This code displays a prompt in the console window and waits until the user enters a string followed by the Enter key. It stores this string in a variable named
name. It also retrieves the value of the DateTime.Now property, which contains the current local time, and assigns it to a variable namedcurrentDate. And it displays these values in the console window. Finally, it displays a prompt in the console window and calls the Read() method to wait for user input.NewLine is a platform-independent and language-independent way to represent a line break.
The dollar sign (
$) in front of a string lets you put expressions such as variable names in curly braces in the string. The expression value is inserted into the string in place of the expression. This syntax is referred to as interpolated strings.Save your changes.
Important
In Visual Studio Code, you have to explicitly save changes. Unlike Visual Studio, file changes are not automatically saved when you build and run an app.
Select Run>Run without debugging.
Respond to the prompt by entering a name and pressing the Enter key.
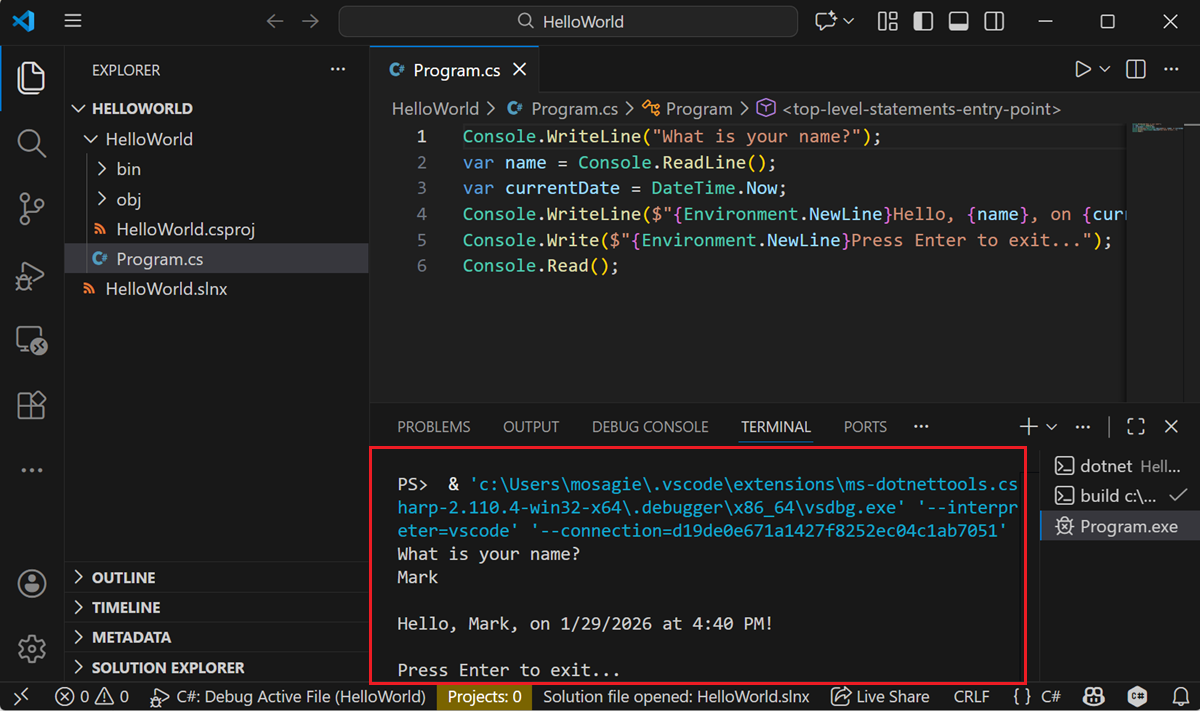
Press Enter to exit the program.
Update HelloWorld.cs with the following code:
Console.WriteLine("What is your name?"); var name = Console.ReadLine(); var currentDate = DateTime.Now; Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}!"); Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press Enter to exit..."); Console.Read();This code displays a prompt in the console window and waits until the user enters a string followed by the Enter key. It stores this string in a variable named
name. It also retrieves the value of the DateTime.Now property, which contains the current local time, and assigns it to a variable namedcurrentDate. And it displays these values in the console window. Finally, it displays a prompt in the console window and calls the Read() method to wait for user input.NewLine is a platform-independent and language-independent way to represent a line break.
The dollar sign (
$) in front of a string lets you put expressions such as variable names in curly braces in the string. The expression value is inserted into the string in place of the expression. This syntax is referred to as interpolated strings.Run the updated app using the following command:
dotnet HelloWorld.csRespond to the prompt by entering a name and pressing the Enter key.
You'll see output similar to the following:
What is your name? Mark Hello, Mark, on 1/29/2026 at 4:40 PM! Press Enter to exit...Press Enter to exit the program.
Additional resources
Cleanup resources
GitHub automatically deletes your Codespace after 30 days of inactivity. If you plan to explore more tutorials in this series, you can leave your Codespace provisioned. If you're ready to visit the .NET site to download the .NET SDK, you can delete your Codespace. To delete your Codespace, open a browser window and navigate to your Codespaces. You see a list of your codespaces in the window. Select the three dots (...) in the entry for the learn tutorial codespace. Then select "delete".
Next steps
In this tutorial, you created a .NET console application. In the next tutorial, you debug the app.
