Choose the Automation services in Azure
This article explains various Automation services offered in the Azure environment. These services can automate business and operational processes and solve integration problems among multiple services, systems, and processes. Automation services can define input, action, activity to be performed, conditions, error handling, and output generation. Using these services, you can run various activities on a schedule or do a manual demand-based execution. Each service has its unique advantages and target audience. Using these services, you can shift effort from manually performing operational tasks towards building automation for these tasks, including:
- Reduce time to perform an action
- Reduce risk in performing the action
- Increase human capacity for further innovation
- Standardize operations
Categories in Automation operations
Automation is required in three broad categories of operations:
Deployment and management of resources: Create and configure programmatically using automation or infrastructure as code tooling to deliver repeatable and consistent deployment and management of cloud resources. For example, an Azure Network Security Group can be deployed, and security group rules are created using an Azure Resource Manager template or an automation script.
Response to external events: Based on a critical external event, such as responding to database changes, acting as per the inputs given to a web page, and so on, you can diagnose and resolve issues.
Complex Orchestration: By integrating with first- or third-party products, you can define end-to-end automation workflows.
Azure services for Automation
Multiple Azure services can fulfill the above requirements. Each service has its benefits and limitations, and customers can use multiple services to meet their automation requirements.
Deployment and management of resources
- Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates with Bicep
- Azure Blueprints
- Azure Automation
- Azure Automanage (for machine configuration and management)
Responding to external events
- Azure Functions
- Azure Automation
- Azure Policy Guest Config (to take an action when there's a change in the compliance state of resource)
Complex orchestration and integration with first- or third-party products
- Azure Logic Apps
- Azure Functions or Azure Automation (Azure Logic app has over 400+ connectors to other services, including Azure Automation and Azure Functions, which could be used to meet complex automation scenarios)
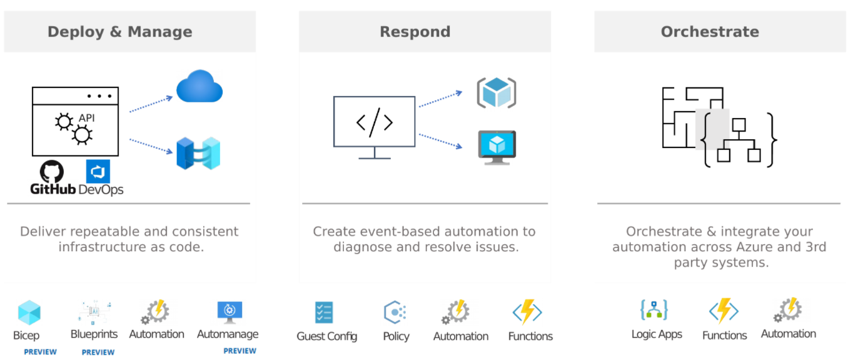
Deploy and manage Automation services
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template
Azure Resource Manager provides a language to develop repeatable and consistent deployment templates for Azure resources. The template is a JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) file that defines the infrastructure and configuration for your project. It uses declarative syntax, which lets you state what you intend to deploy without having to write the sequence of programming commands to create it. In the template, you specify the resources to deploy and the properties for those resources. Learn more.
Bicep
We introduced a new language named Bicep that offers the same capabilities as ARM templates but with a syntax that's easier to use. Each Bicep file is automatically converted to an ARM template during deployment. If you're considering infrastructure as code options, we recommend Bicep. For more information, see What is Bicep?
The following table describes the scenarios and users for ARM template and Bicep:
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Create, manage, and update infrastructure resources, such as virtual machines, networks, storage accounts, containers, and so on. Deploy apps, add tags, assign policies, and assign role-based access control all declaratively as code and integrated with your CI\CD tools. Manage multiple environments such as production, nonproduction, and disaster recovery. Deploy resources consistently and reliably at a scale. |
Application Developers, Infrastructure Administrators, DevOps Engineers using Azure for the first time or using Azure as their primary cloud. IT Engineer\Cloud Architect responsible for cloud infrastructure deployment. |
Azure Blueprints (Preview)
Note
On July 11, 2026, Azure Blueprints (Preview) will be deprecated. Learn more
Azure Blueprints (Preview) define a repeatable set of Azure resources that implements and adheres to an organization's standards, patterns, and requirements. Blueprints are a declarative way to orchestrate the deployment of various resource templates and other artifacts such as Role assignments, Policy assignments, ARM templates, and Resource groups. Learn more.
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Create, manage, and update infrastructure resources to ensure that the deployed infrastructure meets the organization compliance standards. Audit and track Azure deployments. |
Auditors and central information technology groups responsible to ensure that the deployed Azure infrastructure meets the organization compliance standards. |
Azure Automation
Azure Automation orchestrates repetitive processes using graphical, PowerShell, and Python runbooks in the cloud or hybrid environments. It provides persistent shared assets, including variables, connections, and objects, that allow orchestration of complex jobs. Learn more.
There are more than 3,000 modules in the PowerShell Gallery, and the PowerShell community continues to grow. Azure Automation based on PowerShell modules can work with multiple applications and vendors, both first- and third-party. As more application vendors release PowerShell modules for integration, extensibility, and automation tasks, you could use an existing PowerShell script as-is to execute it as a PowerShell runbook in an automation account without making any changes.
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Allows Automation to write an Automation PowerShell runbook that deploys an Azure resource by using an Azure Resource Manager template. Schedule tasks; for example, stop dev/test VMs or services at night and turn on during the day. Response to alerts such as system alerts, service alerts, high CPU/memory alerts, create ServiceNow tickets, and so on. Hybrid automation where you can manage to automate on-premises servers such as SQL Server, Active Directory, and so on. Azure resource life-cycle management and governance include resource provisioning, deprovisioning, adding correct tags, locks, NSGs, and so on. |
IT administrators, System administrators, IT operations administrators who are skilled at using PowerShell or Python-based scripting. Infrastructure administrators manage the on-premises infrastructure using scripts or executing long-running jobs such as month-end operations on servers running on-premises. |
Azure Automation based in-guest management
Configuration management : Collects inventory and tracks changes in your environment. Learn more. You can configure the desired state of your machines to discover and correct the configuration drift. Learn more.
Update management : Assess compliance of servers and schedule update installation on your machines. Learn more.
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Detect and alert on software, services, file, and registry changes to your machines, vigilant on everything installed in your servers. Assess and install updates on your servers using Azure Update management. Configure the desired state of your servers and ensure they stay compliant. |
Central IT\Infrastructure Administrators\Auditors looking for regulatory requirements at scale and ensuring that the end state of the servers looks as desired, patched, and audited. |
Azure Automanage (Preview)
Replaces repetitive, day-to-day operational tasks with an exception-only management model, where a healthy, steady state of VM is equal to hands-free management. Learn more.
Linux and Windows support
- Allows you to intelligently onboard virtual machines to select best practices Azure services
- Allows you to configure each service as per Azure best practices automatically
- Supports customization of best practice services through VM Best practices template for Dev\Test and Production workload
- Allows you to monitor for drift and correct it when detected
- Provides a simple experience (point, select, set, and forget)
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Automatically configures guest operating system as per Microsoft baseline configuration. Automatically detects for drift and corrects it across a VM's entire lifecycle. Aims at a hands-free management of machines. |
The IT Administrators, Infra Administrators, IT Operations Administrators are responsible for managing server workload, day-to-day admin tasks, such as backup, disaster recovery, security updates, responding to security threats, and so on, across Azure and on-premises. Developers who don't wish to manage servers or spend time on lower priority tasks. |
Respond to events in Automation workflow
Azure Policy based Guest Configuration
Azure Policy based Guest Configuration is the next iteration of Azure Automation State Configuration. Learn more.
You can check on what is installed in:
- The next iteration of Azure Automation State Configuration.
- For known-bad apps, protocols certificates, administrator privileges, and health of agents.
- For customer-authored content.
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Obtain compliance data that can include: The configuration of the operating system – files, registry, and services, Application configuration or presence, Check environment settings. Audit or deploy settings to all machines (Set) in scope either reactively to existing machines or proactively to new machines as they're deployed. Respond to policy events to provide remediation on demand or continuous remediation. |
The Central IT, Infrastructure Administrators, Auditors (Cloud custodians) are working towards the regulatory requirements at scale and ensuring that servers' end state looks as desired. The application teams validate compliance before releasing change. |
Azure Automation - Process Automation
Orchestrates repetitive processes using graphical, PowerShell, and Python runbooks in the cloud or hybrid environment. Learn more.
- Provides persistent shared assets, including variables, connections, and objects that allow orchestration of complex jobs
- Allows you to invoke a runbook based on Azure Monitor alert or through a webhook
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Respond to system alerts, service alerts, or high CPU/memory alerts from first- or third-party monitoring tools such as Splunk or ServiceNow, create ServiceNow tickets basis alerts, and so on. Hybrid automation scenarios where you can manage automation on on-premises servers such as SQL Server, Active Directory, and so on, based on an external event. Azure resource life cycle management and governance that includes Resource provisioning, deprovisioning, adding correct tags, locks, NSGs, and so on, based on Azure monitor alerts. |
IT administrators, System administrators, IT operations administrators who are skilled at using PowerShell or Python-based scripting. |
Azure functions
Provides a serverless, event-driven compute platform for automation that allows you to write code to react to critical events from various sources, third-party services, and on-premises systems. For example, an HTTP trigger without worrying about the underlying platform. Learn more.
- You can use a variety of languages to write functions in a language of your choice, such as C#, Java, JavaScript, PowerShell, or Python, and focus on specific pieces of code. Functions runtime is an open source.
- You can choose the hosting plan according to your function app scaling requirements, functionality, and resources required.
- You can orchestrate complex workflows through durable functions.
- You should avoid large and long-running functions that can cause unexpected timeout issues. Learn more.
- When you write PowerShell scripts within the Function Apps, you must tweak the scripts to define how the function behaves, such as how it's triggered and its input and output parameters. Learn more.
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Respond to events on resources such as add tags to resource group basis cost center when VM is deleted, and so on. Set scheduled tasks such as setting a pattern to stop and start a VM at a specific time, reading blob storage content at regular intervals, and so on. Process Azure alerts to send the team’s event when the CPU activity spikes to 90%. Orchestrate with external systems such as Microsoft 365. Respond to database changes. |
The Application developers who are skilled in coding languages such as C#, F#, PHP, Java, JavaScript, PowerShell, or Python. Cloud Architects who build serverless applications where Azure Functions could be part of a larger application workflow. |
Orchestrate complex jobs in Azure Automation
Azure logic apps
Logic Apps is a platform for creating and running complex orchestration workflows that integrate your apps, data, services, and systems. Learn more.
- Allows you to build smart integrations between first- and third-party apps, services and systems running across on-premises, hybrid and cloud native.
- Allows you to use managed connectors from a 450+ and growing Azure connectors ecosystem to use in your workflows.
- Provides a first-class support for enterprise integration and B2B scenarios.
- Allows flexibility to visually create and edit workflows - low code\no code approach
- Runs only on the cloud.
- Provides a large collection of ready-made actions and triggers.
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Schedule and send email notifications using Office 365 when a specific event happens. For example, a new file is uploaded. Route and process customer orders across on-premises systems and cloud services. Move uploaded files from an SFTP or FTP server to Azure Storage. Monitor tweets, analyze the sentiment, and create alerts or tasks for items that need review. |
The Pro integrators and developers, IT professionals who would want to use low code/no code option for advanced integration scenarios to external systems or APIs. |
Azure Automation - Process Automation
Orchestrates repetitive processes using graphical, PowerShell, and Python runbooks in the cloud or hybrid environment. It provides persistent shared assets, including variables, connections, and objects, that allow orchestration of complex jobs. Learn more.
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Azure resource life cycle management and governance, which includes resource provisioning, deprovisioning, adding correct tags, locks, NSGs, and so on, through runbooks that are triggered from ITSM alerts. Use hybrid worker as a bridge from cloud to on-premises, enabling resource\user management on-premises. Execute complex disaster recovery workflows through Automation runbooks. Execute automation runbooks as part of Logic apps workflow through Azure Automation Connector. |
IT administrators, System administrators, IT operations administrators who are skilled at using PowerShell or Python-based scripting. Infrastructure Administrators managing on-premises infrastructure using scripts or executing long running jobs such as month-end operations on servers running on-premises. |
Azure functions
Provides a serverless, event-driven compute platform for automation that allows you to write code to react to critical events from various sources, third-party services, and on-premises systems. For example, an HTTP trigger without worrying about the underlying platform Learn more.
- You can use a variety of languages to write functions in a language of your choice, such as C#, Java, JavaScript, PowerShell, or Python, and focus on specific pieces of code. Functions runtime is an open source.
- You can choose the hosting plan according to your function app scaling requirements, functionality, and resources required.
- You can orchestrate complex workflows through durable functions.
- You should avoid large and long-running functions that can cause unexpected timeout issues. Learn more.
- When you write PowerShell scripts within Function Apps, you must tweak the scripts to define how the function behaves, such as how it's triggered and its input and output parameters. Learn more.
| Scenarios | Users |
|---|---|
| Respond to events on resources such as add tags to resource group basis cost center when VM is deleted, and so on. Set scheduled tasks such as setting a pattern to stop and start a VM at a specific time, reading blob storage content at regular intervals, and so on. Process Azure alerts where you can send team's event when the CPU activity spikes to 90%. Orchestrate with external systems such as Microsoft 365. Executes Azure Function as part of Logic apps workflow through Azure Function Connector. |
Application Developers who are skilled in coding languages such as C#, F#, PHP, Java, JavaScript, PowerShell, or Python. Cloud Architects who build serverless applications where single or multiple Azure Functions could be part of a larger application workflow. |
Next steps
To learn on how to securely execute the automation jobs, see best practices for security in Azure Automation.