Microsoft Connected Cache with Configuration Manager
Applies to: Configuration Manager (current branch)
You can install a Microsoft Connected Cache server on your distribution points. By caching this content on-premises, your clients can benefit from the Delivery Optimization feature that can help to protect WAN links.
This cache server acts as an on-demand transparent cache for content downloaded by Delivery Optimization. Use client settings to make sure this server is offered only to the members of the local Configuration Manager boundary group.
This cache is separate from Configuration Manager's distribution point content. If you choose the same drive as the distribution point role, it stores content separately.
Supported scenarios
Connected Cache supports the following three primary scenarios:
Traditional Configuration Manager clients that communicate with on-premises distribution points.
Co-managed clients that get Win32 apps from Microsoft Intune. For more information, see Support for Intune Win32 apps.
Cloud-only devices, such as Intune-enrolled devices without the Configuration Manager client. For more information, see Support for cloud-managed devices.
Supported content types
When clients download cloud-managed content, they use Delivery Optimization from the cache server installed on your distribution point. Cloud-managed content includes the following types:
Microsoft Store apps (UWP)
If you enable Windows Update for Business policies: Windows feature and quality updates
-
Windows Update for Business: Windows feature and quality updates
Office Click-to-Run apps: Microsoft 365 Apps and updates
Client apps: Microsoft Store apps (UWP) and updates
Endpoint Protection: Windows Defender definition updates
Intune Win32 apps
For a complete list visit: Types of download content supported by Delivery Optimization and Microsoft Connected Cache
Note
Connected Cache doesn't support content that Configuration Manager manages, like software updates with an integrated software update point.
How it works
When you configure clients to use the Connected Cache server, they no longer request Microsoft cloud-managed content from the internet. Clients request this content from the cache server installed on the distribution point. The on-premises server caches this content using the IIS feature for Application Request Routing (ARR). Then the cache server can quickly respond to any future requests for the same content. If the Connected Cache server is unavailable, clients download the content from the internet. Clients also use Delivery Optimization to download portions of the content from peers in their network.
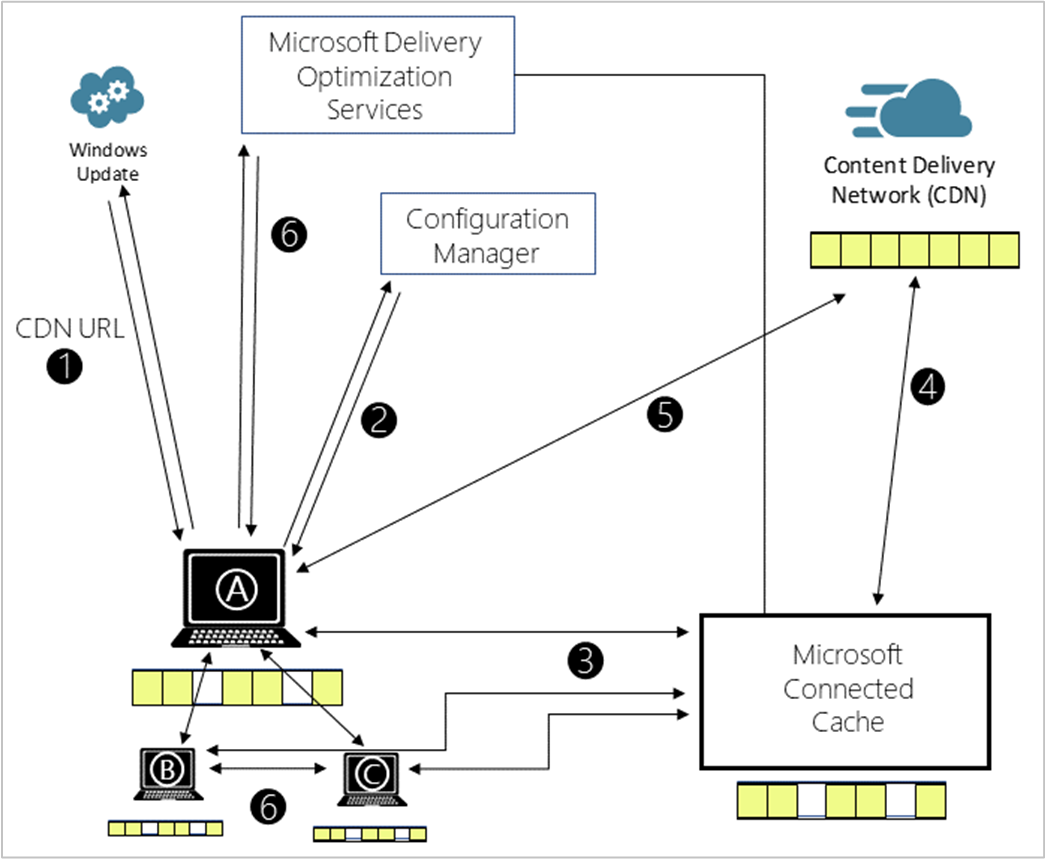
Client checks for updates and gets the address for the content delivery network (CDN).
Configuration Manager configures Delivery Optimization (DO) settings on the client, including the cache server name.
Client A requests content from the Connected Cache server.
If the cache doesn't include the content, then the Connected Cache server gets it from the CDN.
If the cache server fails to respond, the client downloads the content from the CDN. To delay this behavior, set the DelayCacheServerFallbackForeground/DelayCacheServerFallbackBackground setting(s) to avoid the immediate fallback.
Clients will also use DO to get pieces of the content from peers, such as client B and client C.
Prerequisites and limitations
Note
Additional prerequisites apply to the scenario for co-managed clients and Intune Win32 apps. For more information, see Support for Intune Win32 apps.
Supported clients
Connected Cache and Delivery Optimization only support clients running a supported version of Windows 10 or later.
Licensing
You need one of the following license subscriptions for each device that gets content from a Connected Cache-enabled distribution point:
Windows Enterprise E3 or E5, included in Microsoft 365 F3, E3, or E5
Windows Education A3 or A5, included in Microsoft 365 A3 or A5
Windows Virtual Desktop Access (VDA) E3 or E5
Distribution point
Connected Cache with Configuration Manager requires an on-premises distribution point, with the following configurations:
Running a currently supported version of Windows Server.
Microsoft .NET Framework version 4.7.2 or later. For more information, see .NET Framework system requirements.
The default web site enabled on port 80.
Don't preinstall the IIS Application Request Routing (ARR) feature. Connected Cache installs ARR and configures its settings. Microsoft can't guarantee that the Connected Cache's ARR configuration won't conflict with other applications on the server that also use this feature.
The Connected Cache application can use an unauthenticated proxy server for internet access. For more information, see Configure the proxy for a site system server.
Don't use a distribution point that has other site roles, for example, a management point. Enable Connected Cache on a site system server that only has the distribution point role.
Network access requirements
The distribution point requires internet access to the Microsoft cloud. The specific URLs can vary depending upon the specific cloud-enabled content. Make sure to also allow the endpoints for delivery optimization. For more information, see Internet access requirements.
For co-managed clients and Intune Win32 apps, allow the distribution point to access the endpoints for that scenario. For more information, see Network requirements for PowerShell scripts and Win32 apps.
Clients technically only need access to the distribution point with the Connected Cache. Although it's best to also give clients access to the internet endpoints for the content, in case they need to fall back to the original source.
Enable Connected Cache
In the Configuration Manager console, go to the Administration workspace, and select the Distribution Points node.
Select an on-premises distribution point, and then in the ribbon select Properties.
In the properties of the distribution point role, on the General tab, configure the following settings:
Enable the option to Enable this distribution point to be used as Microsoft Connected Cache server
Review the list of required license subscriptions, and then confirm your licenses.
Local drive to be used: Select the disk to use for the cache. Automatic is the default value, which uses the disk with the most free space.Note 1
Note
You can change this drive later. Any cached content is lost, unless you copy it to the new drive.
Disk space: Select the amount of disk space to reserve in GB or a percentage of the total disk space. By default, this value is 100 GB.
Note
The default cache size should be sufficient for most customers. You can adjust the cache size later.
If the cache size on disk exceeds the allocated space, ARR clears space by removing content based on its built-in heuristics.
Retain cache when disabling the Connected Cache server: If you remove the cache server, and you enable this option, the server keeps the cache's content on the disk.
In client settings, in the Delivery Optimization group, configure the setting to Enable devices managed by Configuration Manager to use Microsoft Connected Cache servers for content download.
Note 1: About drive selection
If you select Automatic, when Configuration Manager installs the Connected Cache component, it honors the NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS file. For example, the distribution point has the file C:\NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS. Even if the C: drive has the most free space, Configuration Manager configures Connected Cache to use another drive for its cache.
If you select a specific drive that already has the NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS file, Configuration Manager ignores the file. Configuring Connected Cache to use that drive is an explicit intent. For example, the distribution point has the file F:\NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS. When you explicitly configure the distribution point properties to use the F: drive, Configuration Manager configures Connected Cache to use the F: drive for its cache.
To change the drive after you install Connected Cache:
Manually configure the distribution point properties to use a specific drive letter.
If set to automatic, first create the NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS file. Then make some change to the distribution point properties to trigger a configuration change.
Automation
Automation via Windows PowerShell
Starting in version 2010, use the following parameters of the Set-CMDistributionPoint cmdlet to configure the Connected Cache:
- EnableDoinc
- DiskSpaceUnit
- DiskSpaceDoinc
- LocalDriveDoinc
- RetainDoincCache
- AgreeDoincLicense
For more information, see the 2010 release notes.
Automation via the Configuration Manager SDK
You can use the Configuration Manager SDK to automate the configuration of Microsoft Connected Cache settings on a distribution point. As is the case for all site roles, use the SMS_SCI_SysResUse WMI class. For more information, see Programming the site roles.
When you update the SMS_SCI_SysResUse instance for the distribution point, set the following properties:
- AgreeDOINCLicense: Set to
1to accept the license terms. - Flags: Enable
|= 4, disable&= ~4 - DiskSpaceDOINC: Set to
PercentageorGB - RetainDOINCCache: Set to
0or1 - LocalDriveDOINC: Set to
Automatic, or a specific drive letter, such asC:orD:
Verify
On supported versions of Windows 10 or later, verify this behavior with the Get-DeliveryOptimizationStatus Windows PowerShell cmdlet. In the cmdlet output, review the BytesFromCacheServer value. For more information, see Monitor Delivery Optimization.
If the cache server returns any HTTP failure, the Delivery Optimization client falls back to the original cloud source.
For more detailed information, see Troubleshoot Microsoft Connected Cache with Configuration Manager.
Support for Intune Win32 apps
When you enable Connected Cache on your Configuration Manager distribution points, they can serve Microsoft Intune Win32 apps to co-managed clients.
Tip
All other content that Intune-managed devices download from Microsoft with Delivery Optimization can also be cached on Microsoft Connected Cache. This content includes software updates for Windows, Microsoft 365 apps, and Microsoft Edge.
Prerequisites
Client
Update the client to the latest version.
For Delivery Optimization peer-to-peer: the client device needs to have at least 4 GB of memory.
Tip
Use the following group policy setting: Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Delivery Optimization > Minimum RAM capacity (inclusive) required to enable use of Peer Caching (in GB).
Site
For Microsoft Connected Cache:
Enable Connected Cache on a distribution point.
The client and the Connected Cache-enabled distribution point need to be in the same boundary group. If a client isn't in a boundary group with a Connected Cache-enabled distribution point, it won't download content from a Connected Cache-enabled distribution point in a neighbor or site default boundary group.
Enable the following client settings in the Delivery Optimization group:
- Enable devices managed by Configuration Manger to use Microsoft Connected Cache servers for content download
For Delivery Optimization peer-to-peer:
- Enable the following client settings in the Delivery Optimization group:
- Use Configuration Manager Boundary Groups for Delivery Optimization Group ID:
- Enable Allow peer downloads in this boundary group option for the Boundary Group that contains the client and the distribution point. For more information, see Boundary Group options.
Tip
You do not need to set the options that enable Delivery Optimization peer-to-peer in order to use Microsoft Connected Cache.
Intune
For apps managed in Intune, this feature only supports the Intune Win32 app type.
- Create and assign (deploy) a new app in Intune for this purpose. (Apps created before Intune version 1811 don't work.) For more information, see Win32 app management in Microsoft Intune.
Enable co-management, and switch the Client apps workload to Pilot Intune or Intune. For more information, see the following articles:
-
If in pilot, add the client to the pilot collection for Client Apps.
Support for cloud-managed devices
When you install a Microsoft Connected Cache on a Configuration Manager distribution point, cloud-managed devices can use the on-premises cache. For example, a device that's managed by Intune, but connects to the on-premises network. As long as the device can communicate with the server, the cache is available to deliver content to these devices.
To configure the device to use the Microsoft Connected Cache, configure the DOCacheHost policy. Set it to the FQDN or IP address of the Configuration Manager distribution point. For more information on this policy, see Policy CSP - DeliveryOptimization. To use Intune to configure this policy, use the Cache server host names setting. For more information, see Delivery Optimization settings for Windows devices in Intune.
When you enable this policy for cloud-managed devices, either type of device can request the server to cache content, and either can download the content. If multiple devices request the same content, no matter their management authority, they download supported and available content from the Microsoft Connected Cache.
Next steps
Optimize Windows updates with Delivery Optimization
Troubleshoot Microsoft Connected Cache with Configuration Manager