Nota
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare ad accedere o modificare le directory.
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare a modificare le directory.
In questa guida introduttiva si apprenderà come usare TypeSpec per progettare, generare e implementare un'applicazione API RESTful. TypeSpec è un linguaggio open source per descrivere le API del servizio cloud e genera codice client e server per più piattaforme. Seguendo questa guida introduttiva si apprenderà come definire il contratto API una sola volta e generare implementazioni coerenti, consentendo di creare servizi API più gestibili e ben documentati.
Questa guida introduttiva spiega come:
- Definire l'API usando TypeSpec
- Creare un'applicazione server API
- Integrare Azure Cosmos DB per l'archiviazione permanente
- Eseguire e testare l'API in locale
- Eseguire la distribuzione in App Azure Container
Prerequisites
- Un account Azure attivo. Crea gratuitamente un account se non ne hai uno.
- .NET 9 SDK
- Node.js LTS installato nel sistema.
- Visual Studio Code con le seguenti estensioni:
- Estensione TypeSpec
- Facoltativo: distribuzione con l'interfaccia della riga di comando per sviluppatori di Azure
Sviluppo con TypeSpec
TypeSpec definisce l'API in modo indipendente dal linguaggio e genera il server API e la libreria client per più piattaforme. Questa funzionalità consente di:
- Definire il contratto API una sola volta
- Generare codice client e server coerenti
- Concentrarsi sull'implementazione della logica di business anziché sull'infrastruttura API
TypeSpec fornisce la gestione dei servizi API:
- Linguaggio di definizione API
- Middleware di routing lato server per l'API
- Librerie client per l'utilizzo dell'API
Tu fornisci richieste client e integrazioni server:
- Implementare la logica di business nel middleware, ad esempio i servizi di Azure per database, archiviazione e messaggistica
- Server di hosting per l'API (in locale o in Azure)
- Script di implementazione per il provisioning e l'implementazione ripetibili
Creare una nuova applicazione TypeSpec
Creare una nuova cartella per contenere il server API e i file TypeSpec.
mkdir my_typespec_quickstart cd my_typespec_quickstartInstallare il compilatore TypeSpec a livello globale:
npm install -g @typespec/compilerControllare TypeSpec installato correttamente:
tsp --versionInizializzare il progetto TypeSpec:
tsp initRispondere alle istruzioni seguenti con le risposte fornite:
- Inizializzare un nuovo progetto qui? Y
- Selezionare un modello di progetto? API REST generica
- Immettere un nome di progetto: Widget
- Quali emettitori vuoi usare?
- Documento OpenAPI 3.1
- Stub del server C#
Gli emettitori TypeSpec sono librerie che utilizzano varie API del compilatore di TypeSpec per interagire con il processo di compilazione di TypeSpec e generare artefatti.
Attendere il completamento dell'inizializzazione prima di continuare.
Run tsp compile . to build the project. Please review the following messages from emitters: @typespec/http-server-csharp: Generated ASP.Net services require dotnet 9: https://dotnet.microsoft.com/download Create an ASP.Net service project for your TypeSpec: > npx hscs-scaffold . --use-swaggerui --overwrite More information on getting started: https://aka.ms/tsp/hscs/startCompilare il progetto:
tsp compile .TypeSpec genera il progetto predefinito in
./tsp-output, creando due cartelle separate:- schema
- server
Aprire il file
./tsp-output/schema/openapi.yaml. Notate che le poche righe in./main.tsphanno generato per voi oltre 200 righe della specifica OpenApi.Aprire la cartella
./tsp-output/server/aspnet. Si noti che i file .NET generati automaticamente includono:-
./generated/operations/IWidgets.csdefinisce l'interfaccia per i metodi widget. -
./generated/controllers/WidgetsController.csimplementa l'integrazione con i metodi Widgets. Qui si inserisce la logica aziendale. -
./generated/modelsdefinisce i modelli per l'API Widget.
-
Configurare gli emettitori TypeSpec
Usare i file TypeSpec per configurare la generazione del server API.
tsconfig.yamlAprire e sostituire la configurazione esistente con il codice YAML seguente:emit: - "@typespec/openapi3" - "@typespec/http-server-csharp" options: "@typespec/openapi3": emitter-output-dir: "{cwd}/server/wwwroot" openapi-versions: - 3.1.0 "@typespec/http-server-csharp": emitter-output-dir: "{cwd}/server/" use-swaggerui: true overwrite: true emit-mocks: "mocks-and-project-files"Questa configurazione proietta diverse modifiche necessarie per un server API .NET completamente generato:
-
emit-mocks: crea tutti i file di progetto necessari per il server. -
use-swaggerui: integrare l'interfaccia utente di Swagger in modo che sia possibile usare l'API in modo semplice da browser. -
emitter-output-dir: impostare la directory di output per la generazione del server e la generazione della specifica OpenApi. - Generare tutti gli elementi in
./server.
-
Ricompilare il progetto:
tsp compile .Passare alla nuova
/serverdirectory:cd serverCreare un certificato per sviluppatore predefinito se non ne è già disponibile uno:
dotnet dev-certs httpsEseguire il progetto:
dotnet runAttendere che la notifica venga aperta nel browser.
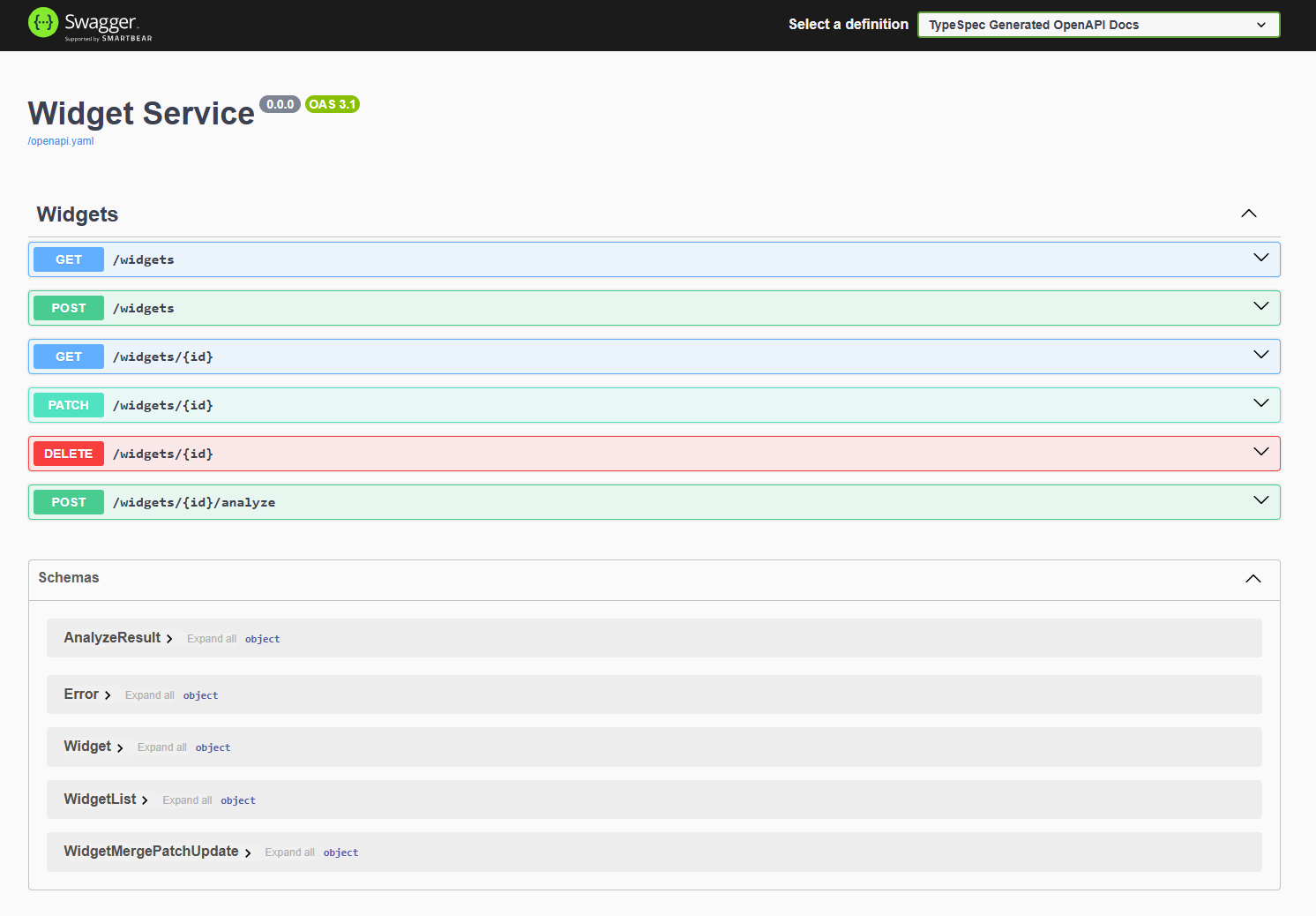
Aprire il browser e aggiungere il percorso Swagger UI,
/swagger.L'API TypeSpec predefinita e il server funzionano entrambi.
Informazioni sulla struttura dei file dell'applicazione
La struttura del progetto per il server generato include il server API basato su controller .NET, i file .NET per la compilazione del progetto e il middleware per l'integrazione di Azure.
├── appsettings.Development.json
├── appsettings.json
├── docs
├── generated
├── mocks
├── Program.cs
├── Properties
├── README.md
├── ServiceProject.csproj
└── wwwroot
-
Aggiungere la logica di business: in questo esempio iniziare con il
./server/mocks/Widget.csfile . L'oggetto generatoWidget.csfornisce metodi predefiniti. -
Aggiornare il server: aggiungere eventuali configurazioni del server specifiche a
./program.cs. -
Usare la specifica OpenApi: TypeSpec ha generato il file OpenApi3.json nel
./server/wwwrootfile e lo ha reso disponibile per l'interfaccia utente di Swagger durante lo sviluppo. Questo fornisce un'interfaccia utente per la vostra specifica. È possibile interagire con l'API senza dover fornire un meccanismo di richiesta, ad esempio un client REST o un front-end Web.
Modifica la persistenza in Azure Cosmos DB NoSQL
Ora che il server API Widget di base funziona, aggiornare il server per lavorare con Azure Cosmos DB per un archivio dati permanente.
./serverNella directory aggiungere Azure Cosmos DB al progetto:dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.CosmosAggiungere la libreria di identità di Azure per l'autenticazione in Azure:
dotnet add package Azure.IdentityAggiornare le
./server/ServiceProject.csprojimpostazioni di integrazione per Cosmos DB:<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web"> <PropertyGroup> ... existing settings ... <EnableSdkContainerSupport>true</EnableSdkContainerSupport> </PropertyGroup> <ItemGroup> ... existing settings ... <PackageReference Include="Newtonsoft.Json" Version="13.0.3" /> </ItemGroup> </Project>- EnableSdkContainerSupport consente di usare il supporto predefinito per la compilazione di contenitori di .NET SDK (dotnet publish –-container) senza scrivere un Dockerfile.
- Newtonsoft.Json aggiunge il serializzatore JSON .NET usato da Cosmos DB SDK per convertire gli oggetti .NET in e da JSON.
Creare un nuovo file
./azure/CosmosDbRegistrationdi registrazione per gestire la registrazione di Cosmos DB:using Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using System; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Azure.Identity; using DemoService; namespace WidgetService.Service { /// <summary> /// Registration class for Azure Cosmos DB services and implementations /// </summary> public static class CosmosDbRegistration { /// <summary> /// Registers the Cosmos DB client and related services for dependency injection /// </summary> /// <param name="builder">The web application builder</param> public static void RegisterCosmosServices(this WebApplicationBuilder builder) { // Register the HttpContextAccessor for accessing the HTTP context builder.Services.AddHttpContextAccessor(); // Get configuration settings var cosmosEndpoint = builder.Configuration["Configuration:AzureCosmosDb:Endpoint"]; // Validate configuration ValidateCosmosDbConfiguration(cosmosEndpoint); // Configure Cosmos DB client options var cosmosClientOptions = new CosmosClientOptions { SerializerOptions = new CosmosSerializationOptions { PropertyNamingPolicy = CosmosPropertyNamingPolicy.CamelCase }, ConnectionMode = ConnectionMode.Direct }; builder.Services.AddSingleton(serviceProvider => { var credential = new DefaultAzureCredential(); // Create Cosmos client with token credential authentication return new CosmosClient(cosmosEndpoint, credential, cosmosClientOptions); }); // Initialize Cosmos DB if needed builder.Services.AddHostedService<CosmosDbInitializer>(); // Register WidgetsCosmos implementation of IWidgets builder.Services.AddScoped<IWidgets, WidgetsCosmos>(); } /// <summary> /// Validates the Cosmos DB configuration settings /// </summary> /// <param name="cosmosEndpoint">The Cosmos DB endpoint</param> /// <exception cref="ArgumentException">Thrown when configuration is invalid</exception> private static void ValidateCosmosDbConfiguration(string cosmosEndpoint) { if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(cosmosEndpoint)) { throw new ArgumentException("Cosmos DB Endpoint must be specified in configuration"); } } } }È importante notare la variabile di ambiente per l'endpoint:
var cosmosEndpoint = builder.Configuration["Configuration:AzureCosmosDb:Endpoint"];Creare una nuova classe Widget,
./azure/WidgetsCosmos.csper fornire la logica aziendale da integrare con Azure Cosmos DB per il tuo archivio persistente.using System; using System.Net; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; // Use generated models and operations using DemoService; namespace WidgetService.Service { /// <summary> /// Implementation of the IWidgets interface that uses Azure Cosmos DB for persistence /// </summary> public class WidgetsCosmos : IWidgets { private readonly CosmosClient _cosmosClient; private readonly ILogger<WidgetsCosmos> _logger; private readonly IHttpContextAccessor _httpContextAccessor; private readonly string _databaseName = "WidgetDb"; private readonly string _containerName = "Widgets"; /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the WidgetsCosmos class. /// </summary> /// <param name="cosmosClient">The Cosmos DB client instance</param> /// <param name="logger">Logger for diagnostic information</param> /// <param name="httpContextAccessor">Accessor for the HTTP context</param> public WidgetsCosmos( CosmosClient cosmosClient, ILogger<WidgetsCosmos> logger, IHttpContextAccessor httpContextAccessor) { _cosmosClient = cosmosClient; _logger = logger; _httpContextAccessor = httpContextAccessor; } /// <summary> /// Gets a reference to the Cosmos DB container for widgets /// </summary> private Container WidgetsContainer => _cosmosClient.GetContainer(_databaseName, _containerName); /// <summary> /// Lists all widgets in the database /// </summary> /// <returns>Array of Widget objects</returns> public async Task<WidgetList> ListAsync() { try { var queryDefinition = new QueryDefinition("SELECT * FROM c"); var widgets = new List<Widget>(); using var iterator = WidgetsContainer.GetItemQueryIterator<Widget>(queryDefinition); while (iterator.HasMoreResults) { var response = await iterator.ReadNextAsync(); widgets.AddRange(response.ToList()); } // Create and return a WidgetList instead of Widget[] return new WidgetList { Items = widgets.ToArray() }; } catch (Exception ex) { _logger.LogError(ex, "Error listing widgets from Cosmos DB"); throw new Error(500, "Failed to retrieve widgets from database"); } } /// <summary> /// Retrieves a specific widget by ID /// </summary> /// <param name="id">The ID of the widget to retrieve</param> /// <returns>The retrieved Widget</returns> public async Task<Widget> ReadAsync(string id) { try { var response = await WidgetsContainer.ReadItemAsync<Widget>( id, new PartitionKey(id)); return response.Resource; } catch (CosmosException ex) when (ex.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotFound) { _logger.LogWarning("Widget with ID {WidgetId} not found", id); throw new Error(404, $"Widget with ID '{id}' not found"); } catch (Exception ex) { _logger.LogError(ex, "Error reading widget {WidgetId} from Cosmos DB", id); throw new Error(500, "Failed to retrieve widget from database"); } } /// <summary> /// Creates a new widget from the provided Widget object /// </summary> /// <param name="body">The Widget object to store in the database</param> /// <returns>The created Widget</returns> public async Task<Widget> CreateAsync(Widget body) { try { // Validate the Widget if (body == null) { throw new Error(400, "Widget data cannot be null"); } if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(body.Id)) { throw new Error(400, "Widget must have an Id"); } if (body.Color != "red" && body.Color != "blue") { throw new Error(400, "Color must be 'red' or 'blue'"); } // Save the widget to Cosmos DB var response = await WidgetsContainer.CreateItemAsync( body, new PartitionKey(body.Id)); _logger.LogInformation("Created widget with ID {WidgetId}", body.Id); return response.Resource; } catch (CosmosException ex) when (ex.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.Conflict) { _logger.LogError(ex, "Widget with ID {WidgetId} already exists", body.Id); throw new Error(409, $"Widget with ID '{body.Id}' already exists"); } catch (Exception ex) when (!(ex is Error)) { _logger.LogError(ex, "Error creating widget in Cosmos DB"); throw new Error(500, "Failed to create widget in database"); } } /// <summary> /// Updates an existing widget with properties specified in the patch document /// </summary> /// <param name="id">The ID of the widget to update</param> /// <param name="body">The WidgetMergePatchUpdate object containing properties to update</param> /// <returns>The updated Widget</returns> public async Task<Widget> UpdateAsync(string id, TypeSpec.Http.WidgetMergePatchUpdate body) { try { // Validate input parameters if (body == null) { throw new Error(400, "Update data cannot be null"); } if (body.Color != null && body.Color != "red" && body.Color != "blue") { throw new Error(400, "Color must be 'red' or 'blue'"); } // First check if the item exists Widget existingWidget; try { var response = await WidgetsContainer.ReadItemAsync<Widget>( id, new PartitionKey(id)); existingWidget = response.Resource; } catch (CosmosException ex) when (ex.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotFound) { _logger.LogWarning("Widget with ID {WidgetId} not found for update", id); throw new Error(404, $"Widget with ID '{id}' not found"); } // Apply the patch updates only where properties are provided bool hasChanges = false; if (body.Weight.HasValue) { existingWidget.Weight = body.Weight.Value; hasChanges = true; } if (body.Color != null) { existingWidget.Color = body.Color; hasChanges = true; } // Only perform the update if changes were made if (hasChanges) { // Use ReplaceItemAsync for the update var updateResponse = await WidgetsContainer.ReplaceItemAsync( existingWidget, id, new PartitionKey(id)); _logger.LogInformation("Updated widget with ID {WidgetId}", id); return updateResponse.Resource; } // If no changes, return the existing widget _logger.LogInformation("No changes to apply for widget with ID {WidgetId}", id); return existingWidget; } catch (Error) { // Rethrow Error exceptions throw; } catch (Exception ex) { _logger.LogError(ex, "Error updating widget {WidgetId} in Cosmos DB", id); throw new Error(500, "Failed to update widget in database"); } } /// <summary> /// Deletes a widget by its ID /// </summary> /// <param name="id">The ID of the widget to delete</param> public async Task DeleteAsync(string id) { try { await WidgetsContainer.DeleteItemAsync<Widget>(id, new PartitionKey(id)); _logger.LogInformation("Deleted widget with ID {WidgetId}", id); } catch (CosmosException ex) when (ex.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotFound) { _logger.LogWarning("Widget with ID {WidgetId} not found for deletion", id); throw new Error(404, $"Widget with ID '{id}' not found"); } catch (Exception ex) { _logger.LogError(ex, "Error deleting widget {WidgetId} from Cosmos DB", id); throw new Error(500, "Failed to delete widget from database"); } } /// <summary> /// Analyzes a widget by ID and returns a simplified analysis result /// </summary> /// <param name="id">The ID of the widget to analyze</param> /// <returns>An AnalyzeResult containing the analysis of the widget</returns> public async Task<AnalyzeResult> AnalyzeAsync(string id) { try { // First retrieve the widget from the database Widget widget; try { var response = await WidgetsContainer.ReadItemAsync<Widget>( id, new PartitionKey(id)); widget = response.Resource; } catch (CosmosException ex) when (ex.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotFound) { _logger.LogWarning("Widget with ID {WidgetId} not found for analysis", id); throw new Error(404, $"Widget with ID '{id}' not found"); } // Create the analysis result var result = new AnalyzeResult { Id = widget.Id, Analysis = $"Weight: {widget.Weight}, Color: {widget.Color}" }; _logger.LogInformation("Analyzed widget with ID {WidgetId}", id); return result; } catch (Error) { // Rethrow Error exceptions throw; } catch (Exception ex) { _logger.LogError(ex, "Error analyzing widget {WidgetId} from Cosmos DB", id); throw new Error(500, "Failed to analyze widget from database"); } } } }Creare il file per l'autenticazione
./server/services/CosmosDbInitializer.csin Azure:using System; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; namespace WidgetService.Service { /// <summary> /// Hosted service that initializes Cosmos DB resources on application startup /// </summary> public class CosmosDbInitializer : IHostedService { private readonly CosmosClient _cosmosClient; private readonly ILogger<CosmosDbInitializer> _logger; private readonly IConfiguration _configuration; private readonly string _databaseName; private readonly string _containerName = "Widgets"; public CosmosDbInitializer(CosmosClient cosmosClient, ILogger<CosmosDbInitializer> logger, IConfiguration configuration) { _cosmosClient = cosmosClient; _logger = logger; _configuration = configuration; _databaseName = _configuration["CosmosDb:DatabaseName"] ?? "WidgetDb"; } public async Task StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken) { _logger.LogInformation("Ensuring Cosmos DB database and container exist..."); try { // Create database if it doesn't exist var databaseResponse = await _cosmosClient.CreateDatabaseIfNotExistsAsync( _databaseName, cancellationToken: cancellationToken); _logger.LogInformation("Database {DatabaseName} status: {Status}", _databaseName, databaseResponse.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Created ? "Created" : "Already exists"); // Create container if it doesn't exist (using id as partition key) var containerResponse = await databaseResponse.Database.CreateContainerIfNotExistsAsync( new ContainerProperties { Id = _containerName, PartitionKeyPath = "/id" }, throughput: 400, // Minimum RU/s cancellationToken: cancellationToken); _logger.LogInformation("Container {ContainerName} status: {Status}", _containerName, containerResponse.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Created ? "Created" : "Already exists"); } catch (Exception ex) { _logger.LogError(ex, "Error initializing Cosmos DB"); throw; } } public Task StopAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken) { return Task.CompletedTask; } } }Aggiornare l'
./server/program.csper utilizzare Cosmos DB e permettere l'utilizzo della Swagger UI in una distribuzione di produzione. Copiare nell'intero file:// Generated by @typespec/http-server-csharp // <auto-generated /> #nullable enable using TypeSpec.Helpers; using WidgetService.Service; var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews(options => { options.Filters.Add<HttpServiceExceptionFilter>(); }); builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer(); builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen(); // Replace original registration with the Cosmos DB one CosmosDbRegistration.RegisterCosmosServices(builder); var app = builder.Build(); // Configure the HTTP request pipeline. if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); // The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts. app.UseHsts(); } // Swagger UI is always available app.UseSwagger(); app.UseSwaggerUI(c => { c.DocumentTitle = "TypeSpec Generated OpenAPI Viewer"; c.SwaggerEndpoint("/openapi.yaml", "TypeSpec Generated OpenAPI Docs"); c.RoutePrefix = "swagger"; }); app.UseHttpsRedirection(); app.UseStaticFiles(); app.Use(async (context, next) => { context.Request.EnableBuffering(); await next(); }); app.MapGet("/openapi.yaml", async (HttpContext context) => { var externalFilePath = "wwwroot/openapi.yaml"; if (!File.Exists(externalFilePath)) { context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status404NotFound; await context.Response.WriteAsync("OpenAPI spec not found."); return; } context.Response.ContentType = "application/json"; await context.Response.SendFileAsync(externalFilePath); }); app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.MapControllerRoute( name: "default", pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); app.Run();Compilare il progetto:
dotnet buildOra il progetto viene sviluppato con l'integrazione di Cosmos DB. Creare gli script di distribuzione per creare le risorse di Azure e distribuire il progetto.
Creare un'infrastruttura di distribuzione
Creare i file necessari per una distribuzione ripetibile con l'interfaccia della riga di comando per sviluppatori di Azure e i modelli Bicep.
Alla radice del progetto TypeSpec, crea un
azure.yamlfile di definizione della distribuzione e incolla il seguente contenuto:# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-dev/main/schemas/v1.0/azure.yaml.json name: azure-typespec-scaffold-dotnet metadata: template: azd-init@1.14.0 services: api: project: ./server host: containerapp language: dotnet pipeline: provider: githubSi noti che questa configurazione fa riferimento al percorso del progetto generato (
./server). Assicurarsi che./tspconfig.yamlcorrisponda al percorso specificato in./azure.yaml.Nella radice del progetto TypeSpec creare una
./infradirectory.Creare un
./infra/main.bicepparamfile e copiarlo nel modo seguente per definire i parametri necessari per la distribuzione:using './main.bicep' param environmentName = readEnvironmentVariable('AZURE_ENV_NAME', 'dev') param location = readEnvironmentVariable('AZURE_LOCATION', 'eastus2') param deploymentUserPrincipalId = readEnvironmentVariable('AZURE_PRINCIPAL_ID', '')Questo elenco di parametri fornisce i parametri minimi necessari per questa distribuzione.
Creare un
./infra/main.bicepfile e copiarlo nel modo seguente per definire le risorse di Azure per il provisioning e la distribuzione:metadata description = 'Bicep template for deploying a GitHub App using Azure Container Apps and Azure Container Registry.' targetScope = 'resourceGroup' param serviceName string = 'api' var databaseName = 'WidgetDb' var containerName = 'Widgets' @minLength(1) @maxLength(64) @description('Name of the environment that can be used as part of naming resource convention') param environmentName string @minLength(1) @description('Primary location for all resources') param location string @description('Id of the principal to assign database and application roles.') param deploymentUserPrincipalId string = '' var resourceToken = toLower(uniqueString(resourceGroup().id, environmentName, location)) var tags = { 'azd-env-name': environmentName repo: 'https://github.com/typespec' } module managedIdentity 'br/public:avm/res/managed-identity/user-assigned-identity:0.4.1' = { name: 'user-assigned-identity' params: { name: 'identity-${resourceToken}' location: location tags: tags } } module cosmosDb 'br/public:avm/res/document-db/database-account:0.8.1' = { name: 'cosmos-db-account' params: { name: 'cosmos-db-nosql-${resourceToken}' location: location locations: [ { failoverPriority: 0 locationName: location isZoneRedundant: false } ] tags: tags disableKeyBasedMetadataWriteAccess: true disableLocalAuth: true networkRestrictions: { publicNetworkAccess: 'Enabled' ipRules: [] virtualNetworkRules: [] } capabilitiesToAdd: [ 'EnableServerless' ] sqlRoleDefinitions: [ { name: 'nosql-data-plane-contributor' dataAction: [ 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/readMetadata' 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlDatabases/containers/items/*' 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlDatabases/containers/*' ] } ] sqlRoleAssignmentsPrincipalIds: union( [ managedIdentity.outputs.principalId ], !empty(deploymentUserPrincipalId) ? [deploymentUserPrincipalId] : [] ) sqlDatabases: [ { name: databaseName containers: [ { name: containerName paths: [ '/id' ] } ] } ] } } module containerRegistry 'br/public:avm/res/container-registry/registry:0.5.1' = { name: 'container-registry' params: { name: 'containerreg${resourceToken}' location: location tags: tags acrAdminUserEnabled: false anonymousPullEnabled: true publicNetworkAccess: 'Enabled' acrSku: 'Standard' } } var containerRegistryRole = subscriptionResourceId( 'Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions', '8311e382-0749-4cb8-b61a-304f252e45ec' ) module registryUserAssignment 'br/public:avm/ptn/authorization/resource-role-assignment:0.1.1' = if (!empty(deploymentUserPrincipalId)) { name: 'container-registry-role-assignment-push-user' params: { principalId: deploymentUserPrincipalId resourceId: containerRegistry.outputs.resourceId roleDefinitionId: containerRegistryRole } } module logAnalyticsWorkspace 'br/public:avm/res/operational-insights/workspace:0.7.0' = { name: 'log-analytics-workspace' params: { name: 'log-analytics-${resourceToken}' location: location tags: tags } } module containerAppsEnvironment 'br/public:avm/res/app/managed-environment:0.8.0' = { name: 'container-apps-env' params: { name: 'container-env-${resourceToken}' location: location tags: tags logAnalyticsWorkspaceResourceId: logAnalyticsWorkspace.outputs.resourceId zoneRedundant: false } } module containerAppsApp 'br/public:avm/res/app/container-app:0.9.0' = { name: 'container-apps-app' params: { name: 'container-app-${resourceToken}' environmentResourceId: containerAppsEnvironment.outputs.resourceId location: location tags: union(tags, { 'azd-service-name': serviceName }) ingressTargetPort: 8080 ingressExternal: true ingressTransport: 'auto' stickySessionsAffinity: 'sticky' scaleMaxReplicas: 1 scaleMinReplicas: 1 corsPolicy: { allowCredentials: true allowedOrigins: [ '*' ] } managedIdentities: { systemAssigned: false userAssignedResourceIds: [ managedIdentity.outputs.resourceId ] } secrets: { secureList: [ { name: 'azure-cosmos-db-nosql-endpoint' value: cosmosDb.outputs.endpoint } { name: 'user-assigned-managed-identity-client-id' value: managedIdentity.outputs.clientId } ] } containers: [ { image: 'mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/samples:aspnetapp-9.0' name: serviceName resources: { cpu: '0.25' memory: '.5Gi' } env: [ { name: 'CONFIGURATION__AZURECOSMOSDB__ENDPOINT' secretRef: 'azure-cosmos-db-nosql-endpoint' } { name: 'AZURE_CLIENT_ID' secretRef: 'user-assigned-managed-identity-client-id' } ] } ] } } output CONFIGURATION__AZURECOSMOSDB__ENDPOINT string = cosmosDb.outputs.endpoint output CONFIGURATION__AZURECOSMOSDB__DATABASENAME string = databaseName output CONFIGURATION__AZURECOSMOSDB__CONTAINERNAME string = containerName output AZURE_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_ENDPOINT string = containerRegistry.outputs.loginServerLe variabili di output consentono di usare le risorse cloud di cui è stato effettuato il provisioning con lo sviluppo locale.
Il tag containerAppsApp utilizza la variabile serviceName (impostata su
apiall'inizio del file) e la variabileapispecificata in./azure.yaml. Questa connessione indica all'interfaccia della riga di comando per sviluppatori di Azure dove distribuire il progetto .NET nella risorsa di hosting di App Azure Container....bicep... module containerAppsApp 'br/public:avm/res/app/container-app:0.9.0' = { name: 'container-apps-app' params: { name: 'container-app-${resourceToken}' environmentResourceId: containerAppsEnvironment.outputs.resourceId location: location tags: union(tags, { 'azd-service-name': serviceName }) <--------- `API` ...bicep..
Struttura progetto
La struttura finale del progetto include i file dell'API TypeSpec, il server di Express.js e i file di distribuzione di Azure:
├── infra
├── tsp-output
├── .gitignore
├── .azure.yaml
├── Dockerfile
├── main.tsp
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
├── tspconfig.yaml
| Area | File/Directory |
|---|---|
| TypeSpec |
main.tsp, tspconfig.yaml |
| serverExpress.js |
./tsp-output/server/ (include i file generati come controllers/, models/, ServiceProject.csproj) |
| Distribuzione dell'interfaccia della riga di comando per sviluppatori di Azure |
./azure.yaml,./infra/ |
Distribuire l'applicazione in Azure
È possibile distribuire questa applicazione in Azure usando App Azure Container:
Eseguire l'autenticazione nell'interfaccia della riga di comando per sviluppatori di Azure:
azd auth loginDistribuire su Azure Container Apps usando la CLI per sviluppatori di Azure.
azd up
Usare l'applicazione nel browser
Dopo la distribuzione, puoi:
- Accedere all'interfaccia utente di Swagger per testare l'API all'indirizzo
/swagger. - Usare la funzionalità Prova ora in ogni API per creare, leggere, aggiornare ed eliminare widget tramite l'API.
Espandere l'applicazione
Ora che l'intero processo end-to-end funziona, continuare a compilare l'API:
- Scopri di più sul linguaggio TypeSpec per aggiungere ulteriori API e funzionalità del livello API in
./main.tsp. - Aggiungere altri emettitori e configurare i relativi parametri in
./tspconfig.yaml. - Man mano che si aggiungono altre funzionalità nei file TypeSpec, supportare tali modifiche con il codice sorgente nel progetto server.
- Continuare a usare l'autenticazione senza password con Identità di Azure.
Pulire le risorse
Al termine di questa guida introduttiva, è possibile rimuovere le risorse di Azure:
azd down
In alternativa, eliminare il gruppo di risorse direttamente dal portale di Azure.