Nota
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare ad accedere o modificare le directory.
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare a modificare le directory.
Stima il numero di valori distinti di expr per le righe in cui il predicato restituisce true.
I valori Null vengono ignorati e non vengono inseriti nel calcolo.
Sintassi
dcountif
(
expr, predicato, [,accuratezza])
Altre informazioni sulle convenzioni di sintassi.
Parametri
| Nome | Digita | Obbligatorio | Descrizione |
|---|---|---|---|
| expr | string |
✔️ | Espressione utilizzata per il calcolo dell'aggregazione. |
| predicato | string |
✔️ | Espressione utilizzata per filtrare le righe. |
| accuratezza | int |
Controllo tra velocità e accuratezza. Se non specificato, il valore predefinito è 1. Vedere Accuratezza della stima per i valori supportati. |
Valori restituiti
Restituisce una stima del numero di valori distinti di expr per le righe in cui il predicato restituisce true.
Suggerimento
dcountif() può restituire un errore nei casi in cui tutte o nessuna delle righe passa l'espressione Predicate.
Esempi
Nell'esempio seguente viene illustrato il numero di tipi di eventi di tempesta irreversibili che si sono verificati in ogni stato.
StormEvents
| summarize DifferentFatalEvents=dcountif(EventType,(DeathsDirect + DeathsIndirect)>0) by State
| where DifferentFatalEvents > 0
| order by DifferentFatalEvents
La tabella dei risultati mostrata include solo le prime 10 righe.
| Provincia | DifferentFatalEvents |
|---|---|
| CALIFORNIA | 12 |
| TEXAS | 12 |
| OKLAHOMA | 10 |
| ILLINOIS | 9 |
| KANSAS | 9 |
| NEW YORK | 9 |
| NEW JERSEY | 7 |
| WASHINGTON | 7 |
| MICHIGAN | 7 |
| MISSOURI | 7 |
| ... | ... |
Accuratezza della stima
Questa funzione usa una variante dell'algoritmo HyperLogLog (HLL), che esegue una stima stocastica della cardinalità set. L'algoritmo fornisce una "manopola" che può essere usata per bilanciare l'accuratezza e il tempo di esecuzione in base alle dimensioni della memoria:
| Precisione | Errori (%) | Numero di voci |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.6 | 212 |
| 1 | 0,8 | 214 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 216 |
| 3 | 0.28 | 217 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 218 |
Nota
La colonna "Numero di voci" corrisponde al numero di contatori di 1 byte nell'implementazione di HLL.
L'algoritmo include alcune clausole per eseguire un conteggio perfetto (zero errori) se la cardinalità del set è sufficientemente piccola:
- Se il livello di accuratezza è
1, vengono restituiti 1000 valori - Se il livello di accuratezza è
2, vengono restituiti 8000 valori
Il limite di errore è probabilistico, non teorico. Il valore è la deviazione standard della distribuzione degli errori (sigma) e il 99,7% delle stime avrà un errore relativo inferiore a 3 x sigma.
L'immagine seguente mostra la funzione di distribuzione delle probabilità di errore relativo nella stima, in percentuali, per tutte le impostazioni di accuratezza supportate:
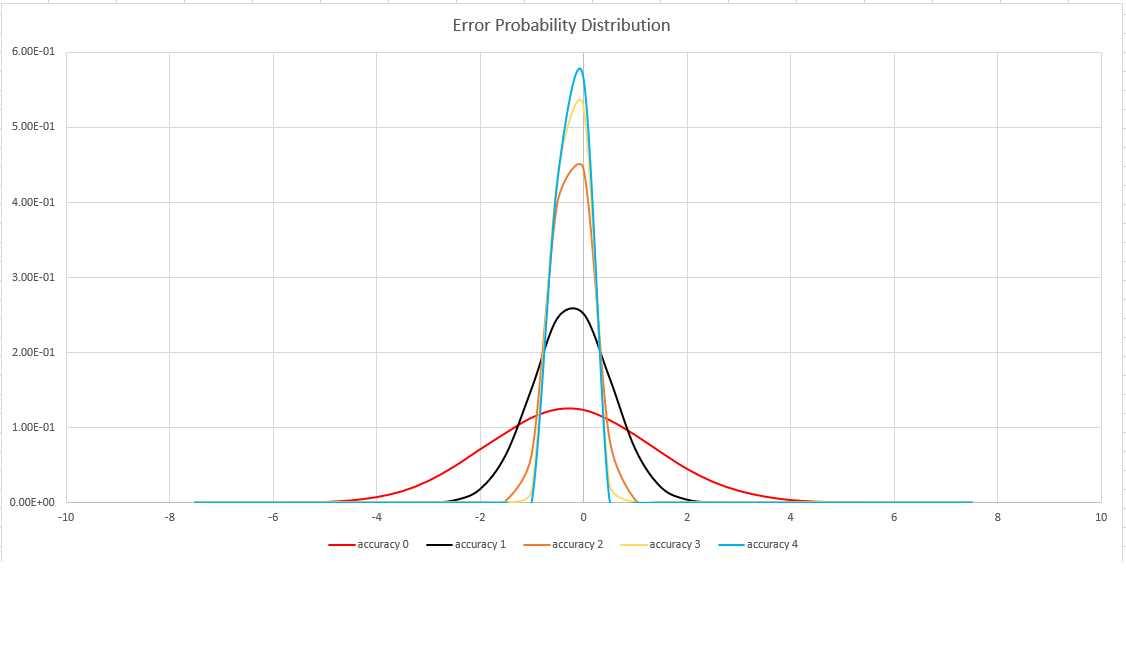
Contenuto correlato
- tipi di funzione Aggregazione a colpo d'occhio
- dcount() (funzione di aggregazione)
- countif() (funzione di aggregazione)
- count_distinctif() (funzione di aggregazione)