Avviare l'app predefinita per un file
API importanti
Informazioni su come avviare l'app predefinita per un file. Molte app devono lavorare con i file che non possono gestire da sé. Ad esempio, le app di posta elettronica ricevono un'ampia gamma di tipi di file e richiedono un modo per avviare questi file nei gestori predefiniti. Questi passaggi illustrano come usare l'API Windows.System.Launcher per avviare il gestore predefinito per un file che l'app non può gestire autonomamente.
Recuperare l'oggetto file
Prima di tutto, ottenere un Windows.Storage.StorageFile oggetto per il file.
Se il file è incluso nel pacchetto per l'app, puoi usare la proprietà Package.InstalledLocation per ottenere l'oggetto Windows.Storage.StorageFolder e il metodo Windows.Storage.StorageFolder.GetFileAsync per ottenere l'oggetto StorageFile.
Se il file si trova in una cartella nota, è possibile utilizzare le proprietà della classe Windows.Storage.KnownFolders per ottenere una StorageFolder e il metodo GetFileAsync per ottenere l'oggetto StorageFile.
Avviare il file
Windows offre diverse opzioni per l'avvio del gestore predefinito per un file. Queste opzioni sono descritte in questo grafico e nelle sezioni che seguono.
| Opzione | metodo | Descrizione |
|---|---|---|
| Avvio predefinito | LaunchFileAsync(IStorageFile) | Avviare il file specificato con il gestore predefinito. |
| Aprire con avvio | LaunchFileAsync(IStorageFile, LauncherOptions) | Avviare il file specificato consentendo all'utente di selezionare il gestore tramite la finestra di dialogo Apri con. |
| Avviare con un fallback dell'app consigliato | LaunchFileAsync(IStorageFile, LauncherOptions) | Avviare il file specificato con il gestore predefinito. Se nel sistema non è installato alcun gestore, consigliare all'utente un'app nello Store. |
| Avviare con una visualizzazione rimanente desiderata | LaunchFileAsync(I Archiviazione File, LauncherOptions) (solo Windows) | Avviare il file specificato con il gestore predefinito. Specificare una preferenza per rimanere sulla schermata dopo l'avvio e richiedere una dimensione della finestra specifica. LauncherOptions.DesiredRemainingView non è supportato nella famiglia di dispositivi mobili. |
Avvio predefinito
Chiamare il metodo Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(IStorageFile) per avviare l'app predefinita. In questo esempio viene usato il metodo Windows.Storage.StorageFolder.GetFileAsync per avviare un file immagine, test.png, incluso nel pacchetto dell'app.
async void DefaultLaunch()
{
// Path to the file in the app package to launch
string imageFile = @"images\test.png";
var file = await Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(imageFile);
if (file != null)
{
// Launch the retrieved file
var success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(file);
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
}
async Sub DefaultLaunch()
' Path to the file in the app package to launch
Dim imageFile = "images\test.png"
Dim file = await Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(imageFile)
If file IsNot Nothing Then
' Launch the retrieved file
Dim success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(file)
If success Then
' File launched
Else
' File launch failed
End If
Else
' Could not find file
End If
End Sub
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncAction MainPage::DefaultLaunch()
{
auto installFolder{ Windows::ApplicationModel::Package::Current().InstalledLocation() };
Windows::Storage::StorageFile file{ co_await installFolder.GetFileAsync(L"images\\test.png") };
if (file)
{
// Launch the retrieved file
bool success = co_await Windows::System::Launcher::LaunchFileAsync(file);
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
}
void MainPage::DefaultLaunch()
{
auto installFolder = Windows::ApplicationModel::Package::Current->InstalledLocation;
concurrency::task<Windows::Storage::StorageFile^getFileOperation(installFolder->GetFileAsync("images\\test.png"));
getFileOperation.then([](Windows::Storage::StorageFile^ file)
{
if (file != nullptr)
{
// Launch the retrieved file
concurrency::task<bool> launchFileOperation(Windows::System::Launcher::LaunchFileAsync(file));
launchFileOperation.then([](bool success)
{
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
});
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
});
}
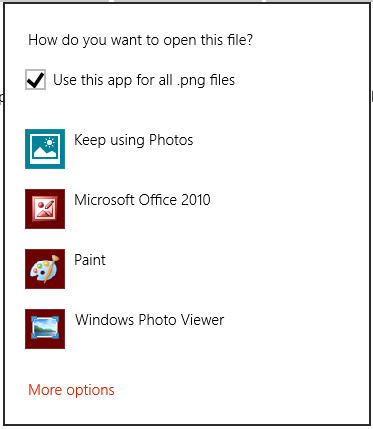
Aprire con avvio
Chiamare il metodo Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(IStorageFile, LauncherOptions) con LauncherOptions.DisplayApplicationPicker set to true per avviare l'app selezionata dall'utente nella finestra di dialogo Apri con.
È consigliabile usare la finestra di dialogo Apri con quando l'utente potrebbe voler selezionare un'app diversa dall'impostazione predefinita per un determinato file. Ad esempio, se l'app consente all'utente di avviare un file immagine, è probabile che il gestore predefinito sia un'app visualizzatore. In alcuni casi, l'utente potrebbe voler modificare l'immagine anziché visualizzarla. Usare l'opzione Apri con insieme a un comando alternativo in AppBar o in un menu di scelta rapida per consentire all'utente di visualizzare la finestra di dialogo Apri con e selezionare l'app editor in questi tipi di scenari.
async void DefaultLaunch()
{
// Path to the file in the app package to launch
string imageFile = @"images\test.png";
var file = await Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(imageFile);
if (file != null)
{
// Set the option to show the picker
var options = new Windows.System.LauncherOptions();
options.DisplayApplicationPicker = true;
// Launch the retrieved file
bool success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(file, options);
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
}
async Sub DefaultLaunch()
' Path to the file in the app package to launch
Dim imageFile = "images\test.png"
Dim file = await Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(imageFile)
If file IsNot Nothing Then
' Set the option to show the picker
Dim options = Windows.System.LauncherOptions()
options.DisplayApplicationPicker = True
' Launch the retrieved file
Dim success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(file)
If success Then
' File launched
Else
' File launch failed
End If
Else
' Could not find file
End If
End Sub
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncAction MainPage::DefaultLaunch()
{
auto installFolder{ Windows::ApplicationModel::Package::Current().InstalledLocation() };
Windows::Storage::StorageFile file{ co_await installFolder.GetFileAsync(L"images\\test.png") };
if (file)
{
// Set the option to show the picker
Windows::System::LauncherOptions launchOptions;
launchOptions.DisplayApplicationPicker(true);
// Launch the retrieved file
bool success = co_await Windows::System::Launcher::LaunchFileAsync(file, launchOptions);
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
}
void MainPage::DefaultLaunch()
{
auto installFolder = Windows::ApplicationModel::Package::Current->InstalledLocation;
concurrency::task<Windows::Storage::StorageFile^> getFileOperation(installFolder->GetFileAsync("images\\test.png"));
getFileOperation.then([](Windows::Storage::StorageFile^ file)
{
if (file != nullptr)
{
// Set the option to show the picker
auto launchOptions = ref new Windows::System::LauncherOptions();
launchOptions->DisplayApplicationPicker = true;
// Launch the retrieved file
concurrency::task<bool> launchFileOperation(Windows::System::Launcher::LaunchFileAsync(file, launchOptions));
launchFileOperation.then([](bool success)
{
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
});
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
});
}
Avviare con un fallback dell'app consigliato
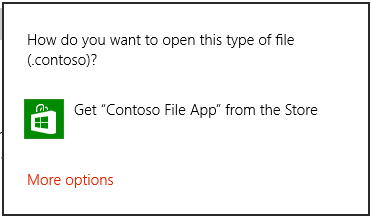
In alcuni casi l'utente potrebbe non avere un'app installata per gestire il file che si sta avviando. Per impostazione predefinita, Windows gestirà questi casi fornendo all'utente un collegamento per cercare un'app appropriata nello Store. Se si vuole fornire all'utente una raccomandazione specifica per quale app acquisire in questo scenario, si può farlo passando tale raccomandazione insieme al file che si sta avviando. A tale scopo, chiamare il metodo Windows.System.Launcher.launchFileAsync(IStorageFile, LauncherOptions) con LauncherOptions.PreferredApplicationPackageFamilyName impostato sul nome della famiglia di pacchetti dell'app nello Store che si vuole consigliare. Impostare quindi LauncherOptions.PreferredApplicationDisplayName sul nome dell'app. Windows userà queste informazioni per sostituire l'opzione generale per cercare un'app nello Store con un'opzione specifica per acquisire l'app consigliata dallo Store.
Nota
È necessario impostare entrambe queste opzioni per consigliare un'app. L'impostazione di una senza l'altra comporterà un errore.
async void DefaultLaunch()
{
// Path to the file in the app package to launch
string imageFile = @"images\test.contoso";
// Get the image file from the package's image directory
var file = await Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(imageFile);
if (file != null)
{
// Set the recommended app
var options = new Windows.System.LauncherOptions();
options.PreferredApplicationPackageFamilyName = "Contoso.FileApp_8wknc82po1e";
options.PreferredApplicationDisplayName = "Contoso File App";
// Launch the retrieved file pass in the recommended app
// in case the user has no apps installed to handle the file
bool success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(file, options);
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
}
async Sub DefaultLaunch()
' Path to the file in the app package to launch
Dim imageFile = "images\test.contoso"
' Get the image file from the package's image directory
Dim file = await Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(imageFile)
If file IsNot Nothing Then
' Set the recommended app
Dim options = Windows.System.LauncherOptions()
options.PreferredApplicationPackageFamilyName = "Contoso.FileApp_8wknc82po1e";
options.PreferredApplicationDisplayName = "Contoso File App";
' Launch the retrieved file pass in the recommended app
' in case the user has no apps installed to handle the file
Dim success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(file)
If success Then
' File launched
Else
' File launch failed
End If
Else
' Could not find file
End If
End Sub
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncAction MainPage::DefaultLaunch()
{
auto installFolder{ Windows::ApplicationModel::Package::Current().InstalledLocation() };
Windows::Storage::StorageFile file{ co_await installFolder.GetFileAsync(L"images\\test.png") };
if (file)
{
// Set the recommended app
Windows::System::LauncherOptions launchOptions;
launchOptions.PreferredApplicationPackageFamilyName(L"Contoso.FileApp_8wknc82po1e");
launchOptions.PreferredApplicationDisplayName(L"Contoso File App");
// Launch the retrieved file, and pass in the recommended app
// in case the user has no apps installed to handle the file.
bool success = co_await Windows::System::Launcher::LaunchFileAsync(file, launchOptions);
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
}
void MainPage::DefaultLaunch()
{
auto installFolder = Windows::ApplicationModel::Package::Current->InstalledLocation;
concurrency::task<Windows::Storage::StorageFile^> getFileOperation(installFolder->GetFileAsync("images\\test.contoso"));
getFileOperation.then([](Windows::Storage::StorageFile^ file)
{
if (file != nullptr)
{
// Set the recommended app
auto launchOptions = ref new Windows::System::LauncherOptions();
launchOptions->PreferredApplicationPackageFamilyName = "Contoso.FileApp_8wknc82po1e";
launchOptions->PreferredApplicationDisplayName = "Contoso File App";
// Launch the retrieved file pass, and in the recommended app
// in case the user has no apps installed to handle the file.
concurrency::task<bool> launchFileOperation(Windows::System::Launcher::LaunchFileAsync(file, launchOptions));
launchFileOperation.then([](bool success)
{
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
});
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
});
}
Avviare con una visualizzazione rimanente desiderata (solo Windows)
Le app di origine che chiamano LaunchFileAsync possono richiedere che rimangano sullo schermo dopo l'avvio di un file. Per impostazione predefinita, Windows tenta di condividere lo spazio disponibile in modo uniforme tra l'app di origine e l'app di destinazione che gestisce il file. Le app di origine possono usare la proprietà pesiredRemainingView per indicare al sistema operativo che preferiscono che la finestra dell'app occupa più o meno dello spazio disponibile. DesiredRemainingView può anche essere usato per indicare che l'app di origine non deve rimanere sullo schermo dopo l'avvio del file e può essere completamente sostituita dall'app di destinazione. Questa proprietà specifica solo le dimensioni della finestra preferite dell'app chiamante. Non specifica il comportamento di altre app che possono verificarsi sullo schermo contemporaneamente.
Nota
Windows tiene conto di più fattori diversi quando determina le dimensioni finali della finestra dell'app di origine, ad esempio la preferenza dell'app di origine, il numero di app sullo schermo, l'orientamento dello schermo e così via. Impostando DesiredRemainingView, non è garantito un comportamento specifico di finestra per l'app di origine.
**Famiglia di dispositivi mobili: **LauncherOptions.DesiredRemainingView non è supportato nella famiglia di dispositivi mobili.
async void DefaultLaunch()
{
// Path to the file in the app package to launch
string imageFile = @"images\test.png";
var file = await Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(imageFile);
if (file != null)
{
// Set the desired remaining view
var options = new Windows.System.LauncherOptions();
options.DesiredRemainingView = Windows.UI.ViewManagement.ViewSizePreference.UseLess;
// Launch the retrieved file
bool success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(file, options);
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
}
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncAction MainPage::DefaultLaunch()
{
auto installFolder{ Windows::ApplicationModel::Package::Current().InstalledLocation() };
Windows::Storage::StorageFile file{ co_await installFolder.GetFileAsync(L"images\\test.png") };
if (file)
{
// Set the desired remaining view.
Windows::System::LauncherOptions launchOptions;
launchOptions.DesiredRemainingView(Windows::UI::ViewManagement::ViewSizePreference::UseLess);
// Launch the retrieved file.
bool success = co_await Windows::System::Launcher::LaunchFileAsync(file, launchOptions);
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
}
void MainPage::DefaultLaunch()
{
auto installFolder = Windows::ApplicationModel::Package::Current->InstalledLocation;
concurrency::task<Windows::Storage::StorageFile^> getFileOperation(installFolder->GetFileAsync("images\\test.png"));
getFileOperation.then([](Windows::Storage::StorageFile^ file)
{
if (file != nullptr)
{
// Set the desired remaining view.
auto launchOptions = ref new Windows::System::LauncherOptions();
launchOptions->DesiredRemainingView = Windows::UI::ViewManagement::ViewSizePreference::UseLess;
// Launch the retrieved file.
concurrency::task<bool> launchFileOperation(Windows::System::Launcher::LaunchFileAsync(file, launchOptions));
launchFileOperation.then([](bool success)
{
if (success)
{
// File launched
}
else
{
// File launch failed
}
});
}
else
{
// Could not find file
}
});
}
Osservazioni:
L'app non può selezionare l'app avviata. L'utente determina l'app avviata. L'utente può selezionare un'app piattaforma UWP (Universal Windows Platform) (UWP) o un'app desktop di Windows.
Quando si avvia un file, l'app deve essere l'app in primo piano, ovvero deve essere visibile all'utente. Questo requisito consente di garantire che l'utente rimanga in controllo. Per soddisfare questo requisito, assicurarsi di associare tutti i lanci di file direttamente all'interfaccia utente dell'app. Molto probabilmente, l'utente deve sempre eseguire un'azione per avviare un file.
Non è possibile avviare tipi di file che contengono codice o script se vengono eseguiti automaticamente dal sistema operativo, ad esempio, file .exe, .msi e .js. Questa limitazione protegge gli utenti da file potenzialmente dannosi che potrebbero modificare il sistema operativo. È possibile usare questo metodo per avviare i tipi di file che possono contenere script se vengono eseguiti da un'app che isola lo script, ad esempio file .docx. Le app come Microsoft Word impediscono allo script di file .docx di modificare il sistema operativo.
Se si tenta di avviare un tipo di file con limitazioni, l'avvio avrà esito negativo e verrà richiamato il callback di errore. Se l'app gestisce molti tipi diversi di file e ci si aspetta che si verifichi questo errore, è consigliabile offrire un'esperienza di fallback all'utente. Ad esempio, è possibile concedere all'utente un'opzione per salvare il file sul desktop e aprirlo lì.