Configure and access audit logs in the Azure portal
Important
Azure Database for MariaDB is on the retirement path. We strongly recommend that you migrate to Azure Database for MySQL. For more information about migrating to Azure Database for MySQL, see What's happening to Azure Database for MariaDB?.
You can configure the Azure Database for MariaDB audit logs and diagnostic settings from the Azure portal.
Prerequisites
To step through this how-to guide, you need:
Configure audit logging
Important
It is recommended to only log the event types and users required for your auditing purposes to ensure your server's performance is not heavily impacted.
Enable and configure audit logging.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select your Azure Database for MariaDB server.
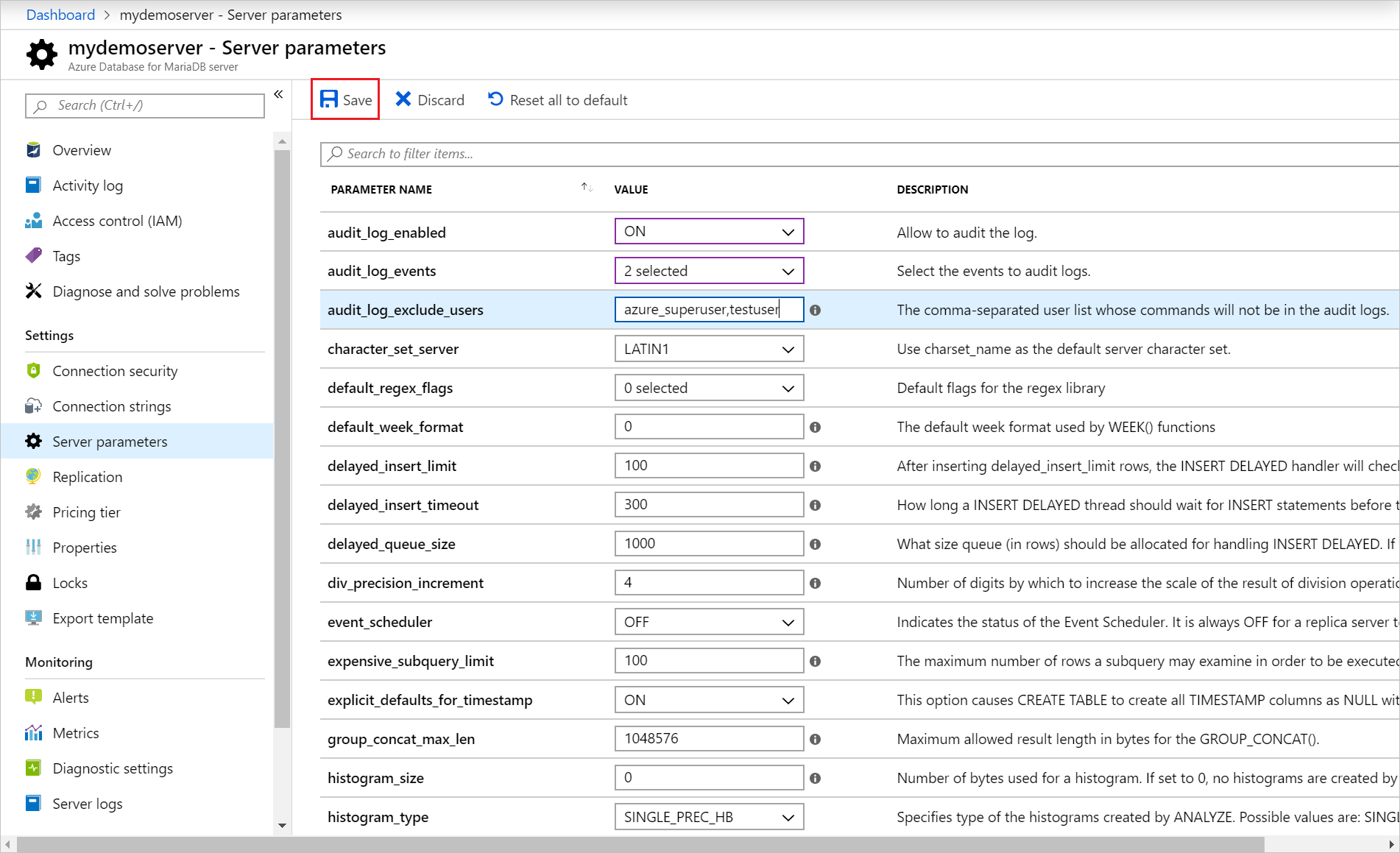
Under the Settings section in the sidebar, select Server parameters.
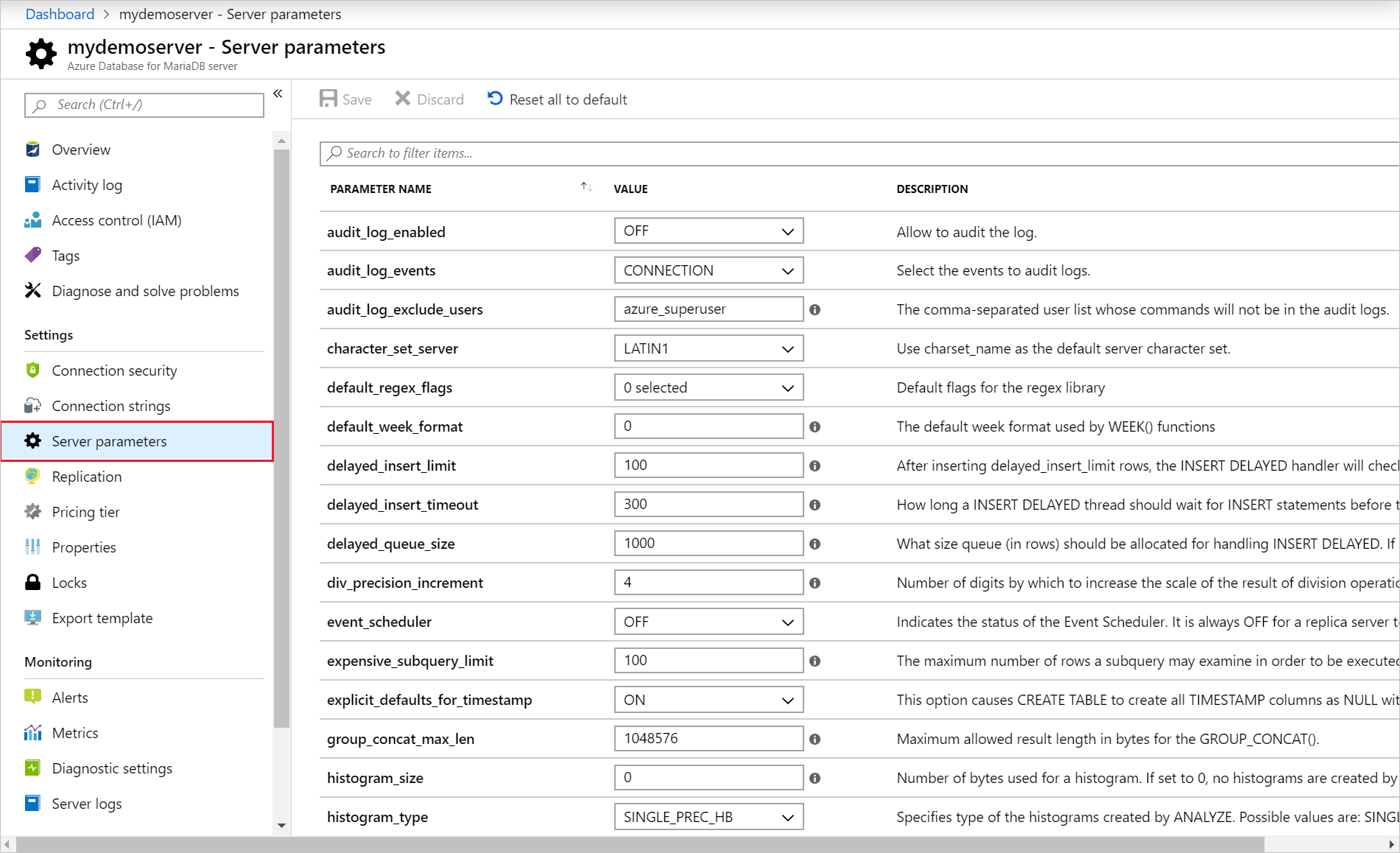
Update the audit_log_enabled parameter to ON.
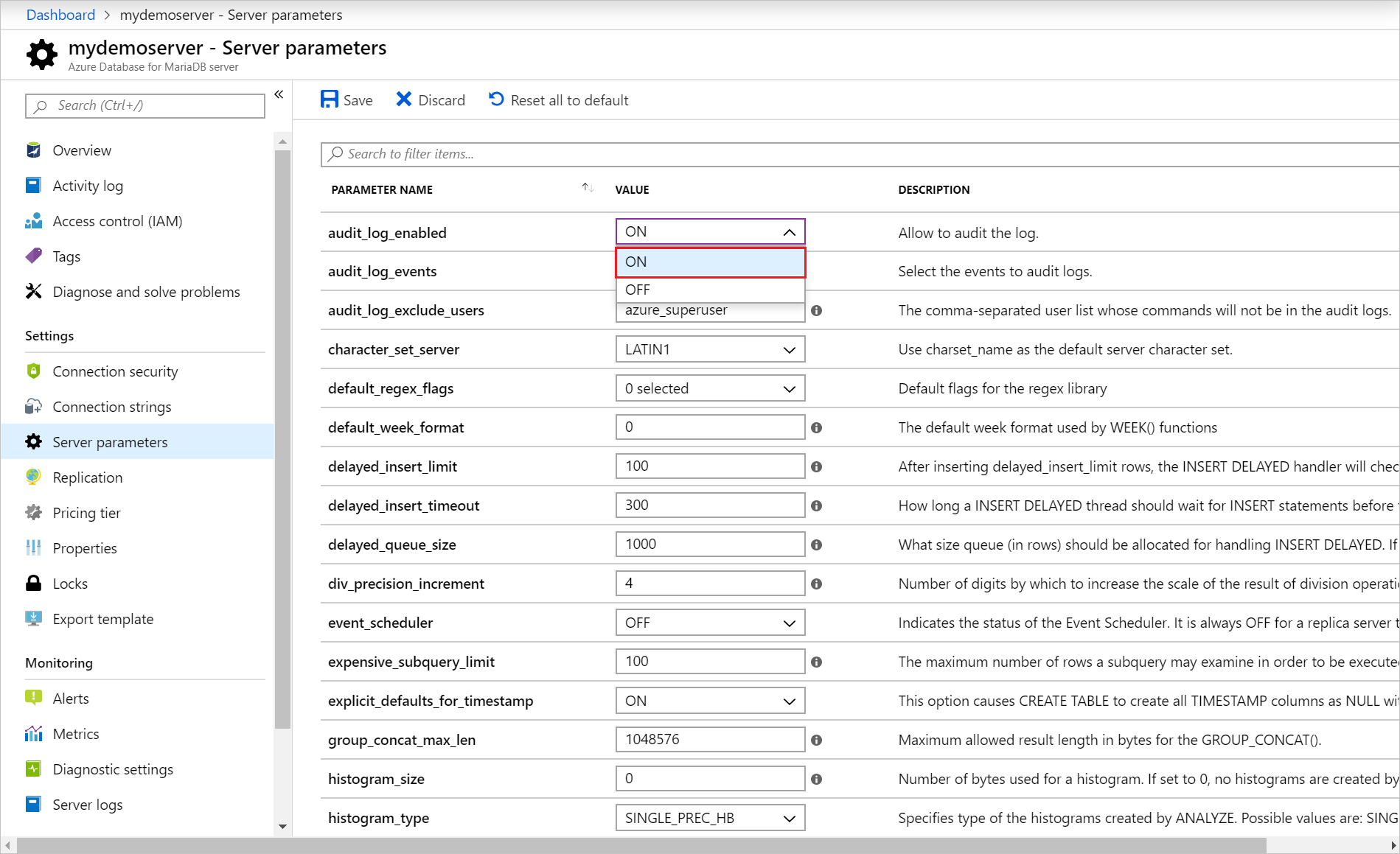
Select the event types to be logged by updating the audit_log_events parameter.
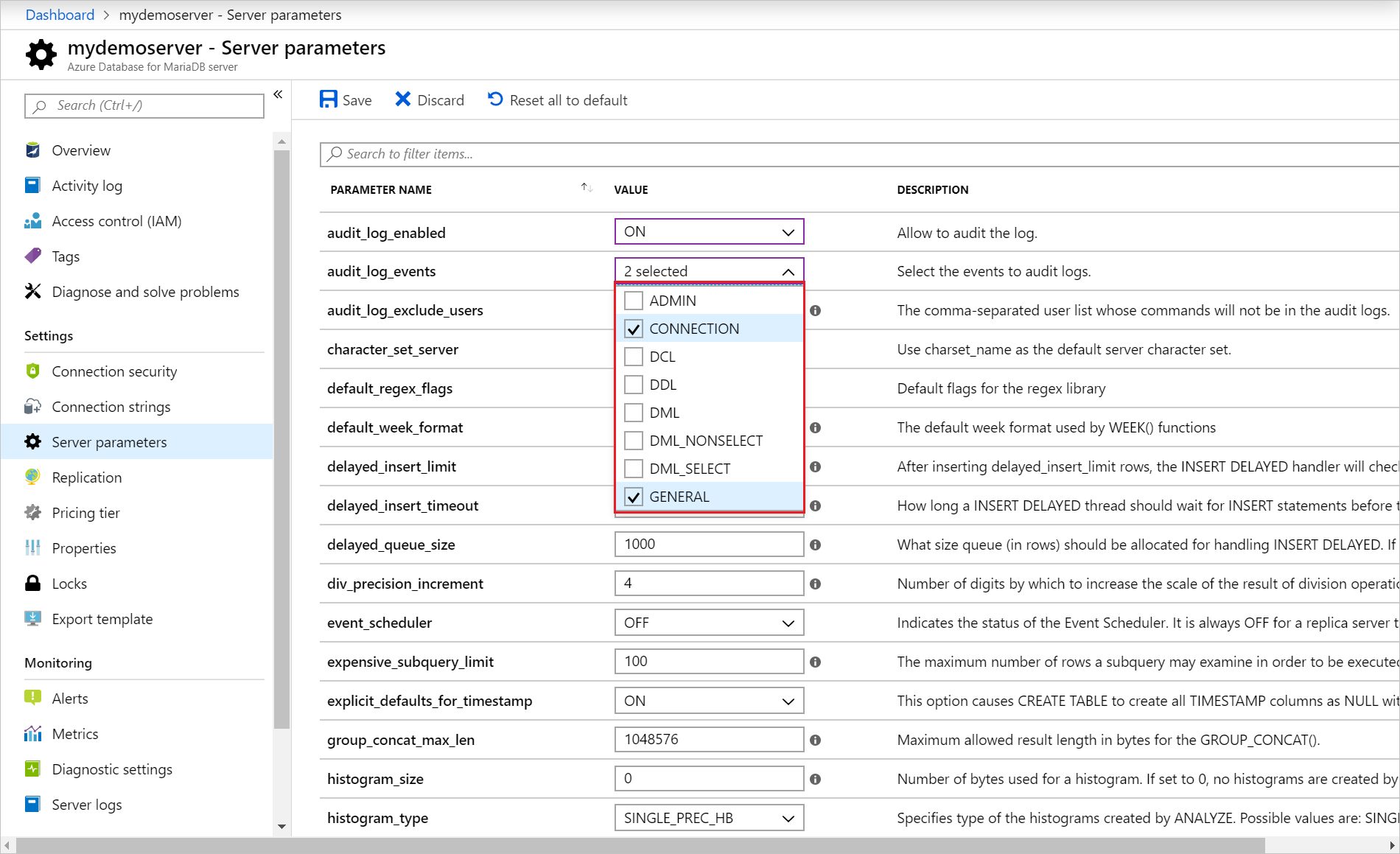
Add any MariaDB users to be excluded from logging by updating the audit_log_exclude_users parameter. Specify users by providing their MariaDB user name.
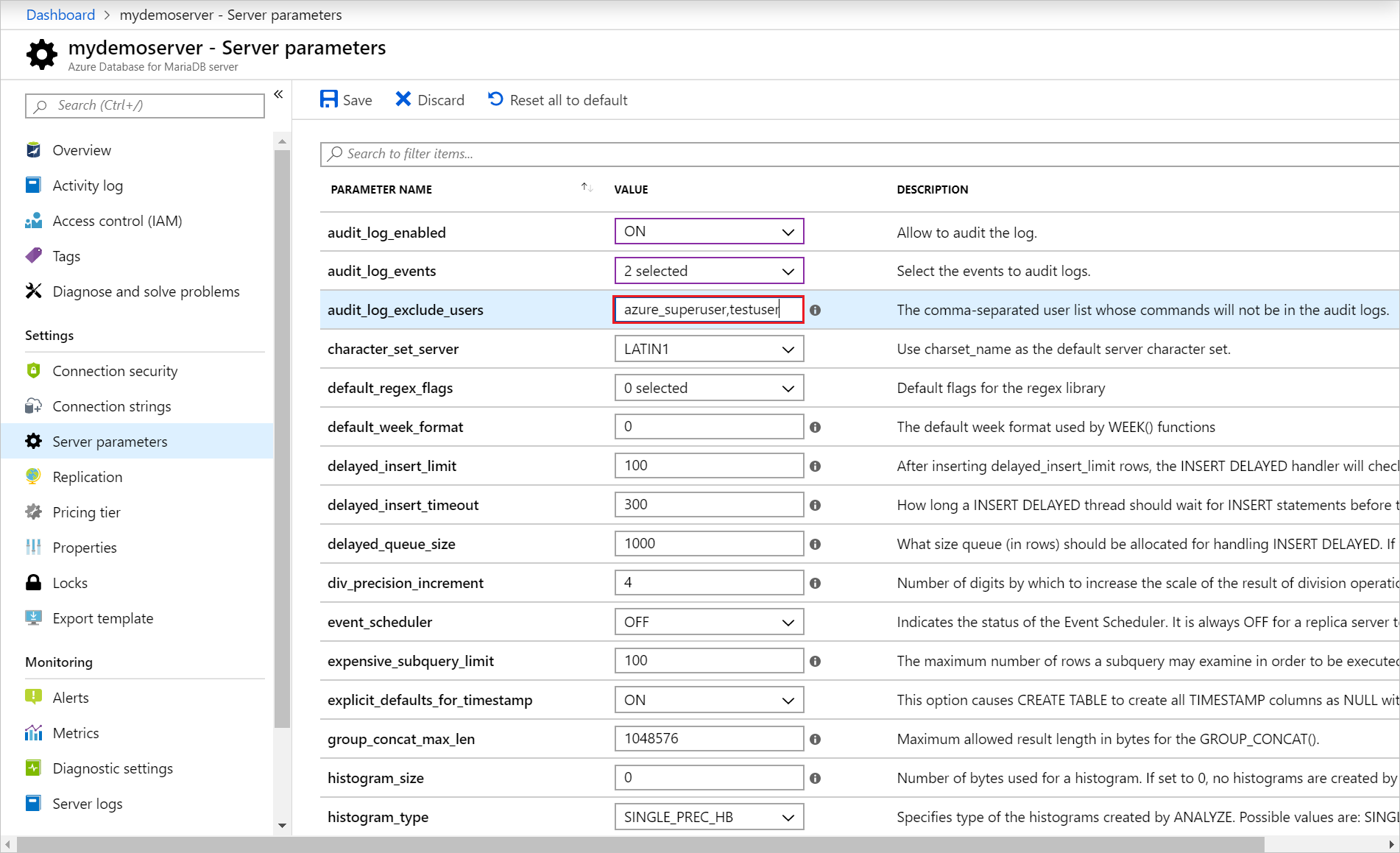
Once you have changed the parameters, you can select Save. Or you can Discard your changes.
Set up diagnostic logs
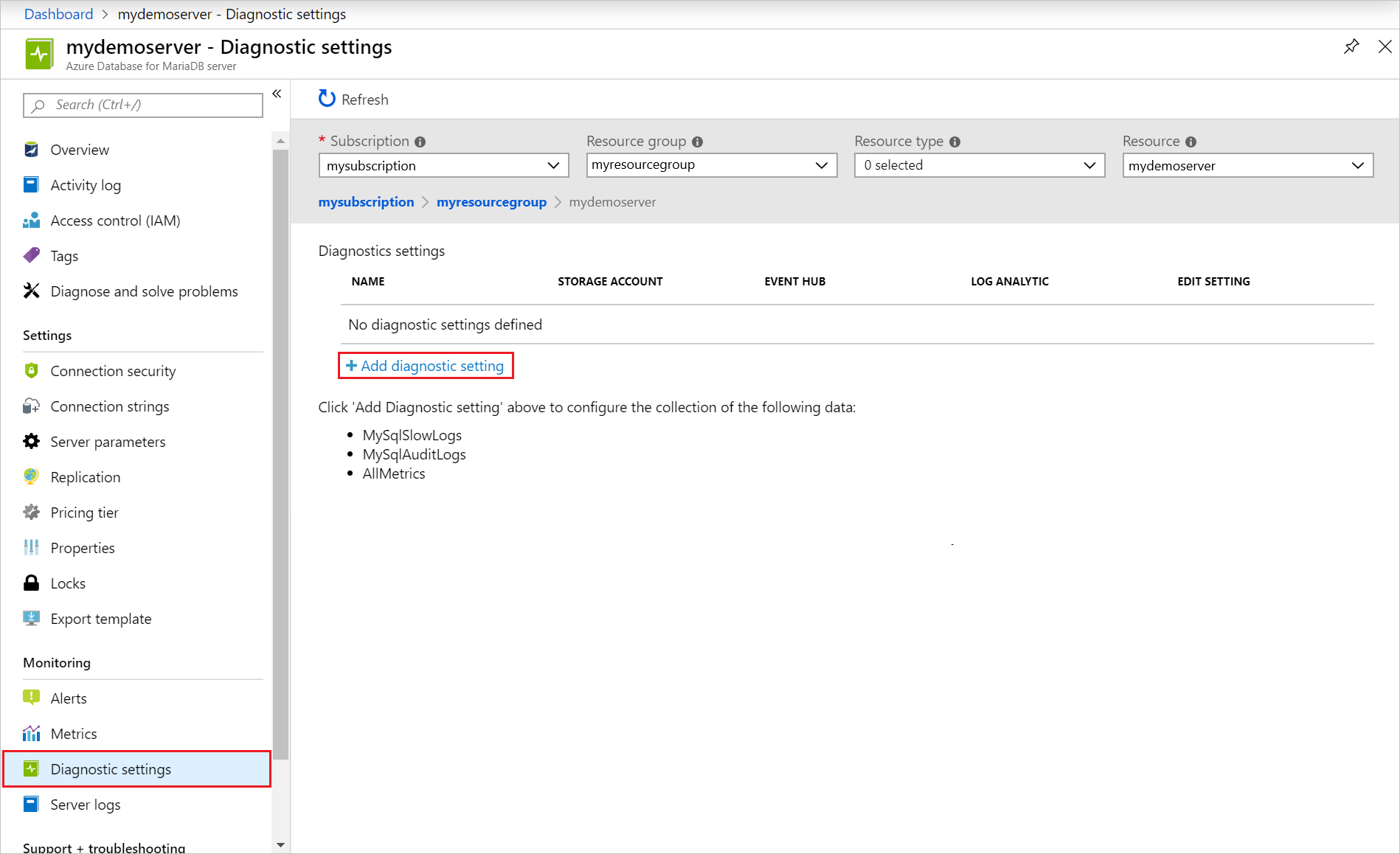
Under the Monitoring section in the sidebar, select Diagnostic settings.
Select on "+ Add diagnostic setting"
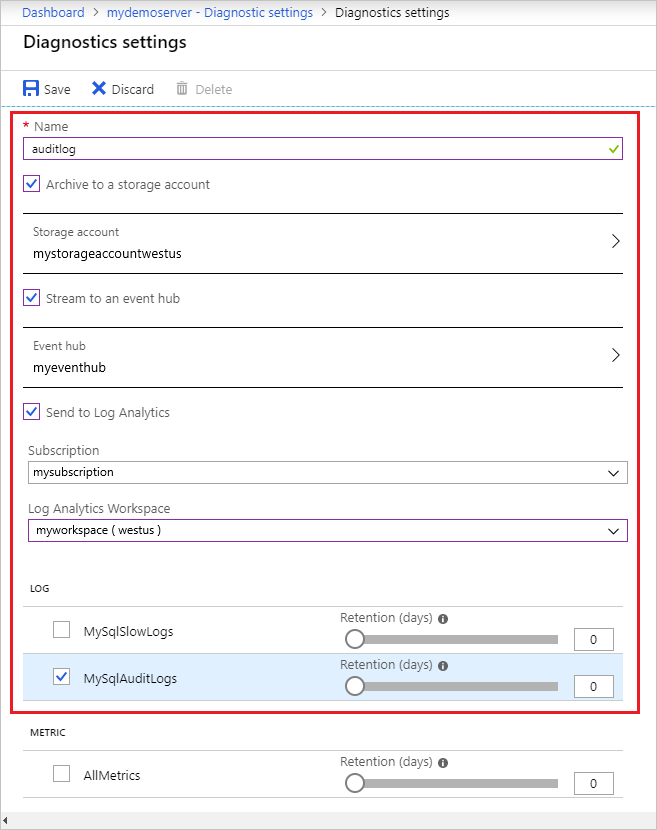
Provide a diagnostic setting name.
Specify which data sinks to send the audit logs (storage account, event hub, and/or Log Analytics workspace).
Select "MySqlAuditLogs" as the log type.
Once you've configured the data sinks to pipe the audit logs to, you can select Save.
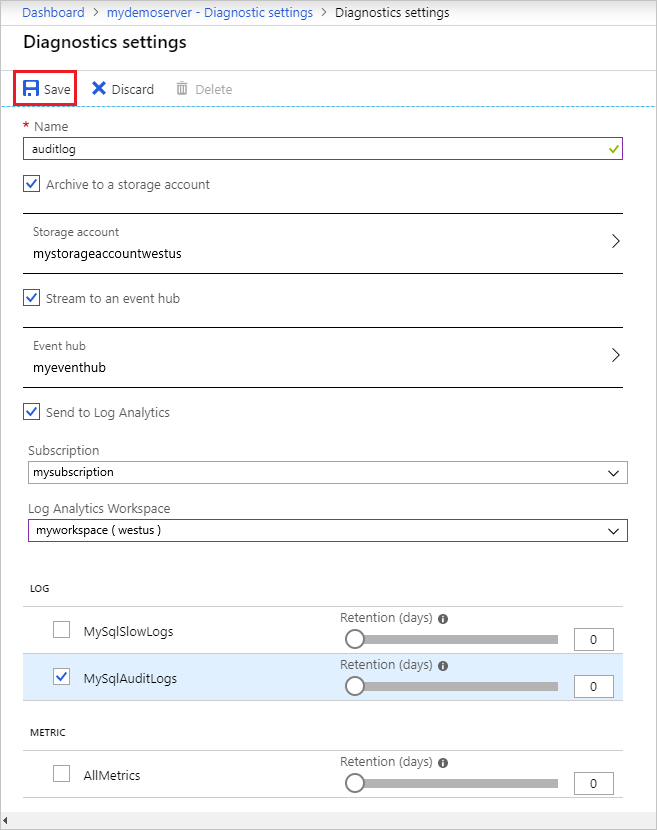
Access the audit logs by exploring them in the data sinks you configured. It may take up to 10 minutes for the logs to appear.
Next steps
- Learn more about audit logs in Azure Database for MariaDB
- Learn how to configure audit logs in the Azure CLI