警告
セマンティック カーネル プロセス フレームワーク は、まだ開発中であり、変更される可能性があります。
概要
前のセクションでは、新しい製品のドキュメントの作成を自動化するためのプロセスを構築しました。 このプロセスでは、製品に固有のドキュメントを生成できるようになり、校正と編集のサイクルを通じて実行することで、品質バーを満たすことができます。 このセクションでは、公開前にドキュメントを承認または拒否するよう人間に要求することで、そのプロセスをもう一度改善します。 プロセス フレームワークの柔軟性は、これを行うにはいくつかの方法があることを意味しますが、この例では、承認を要求するための外部 pubsub システムとの統合を示します。
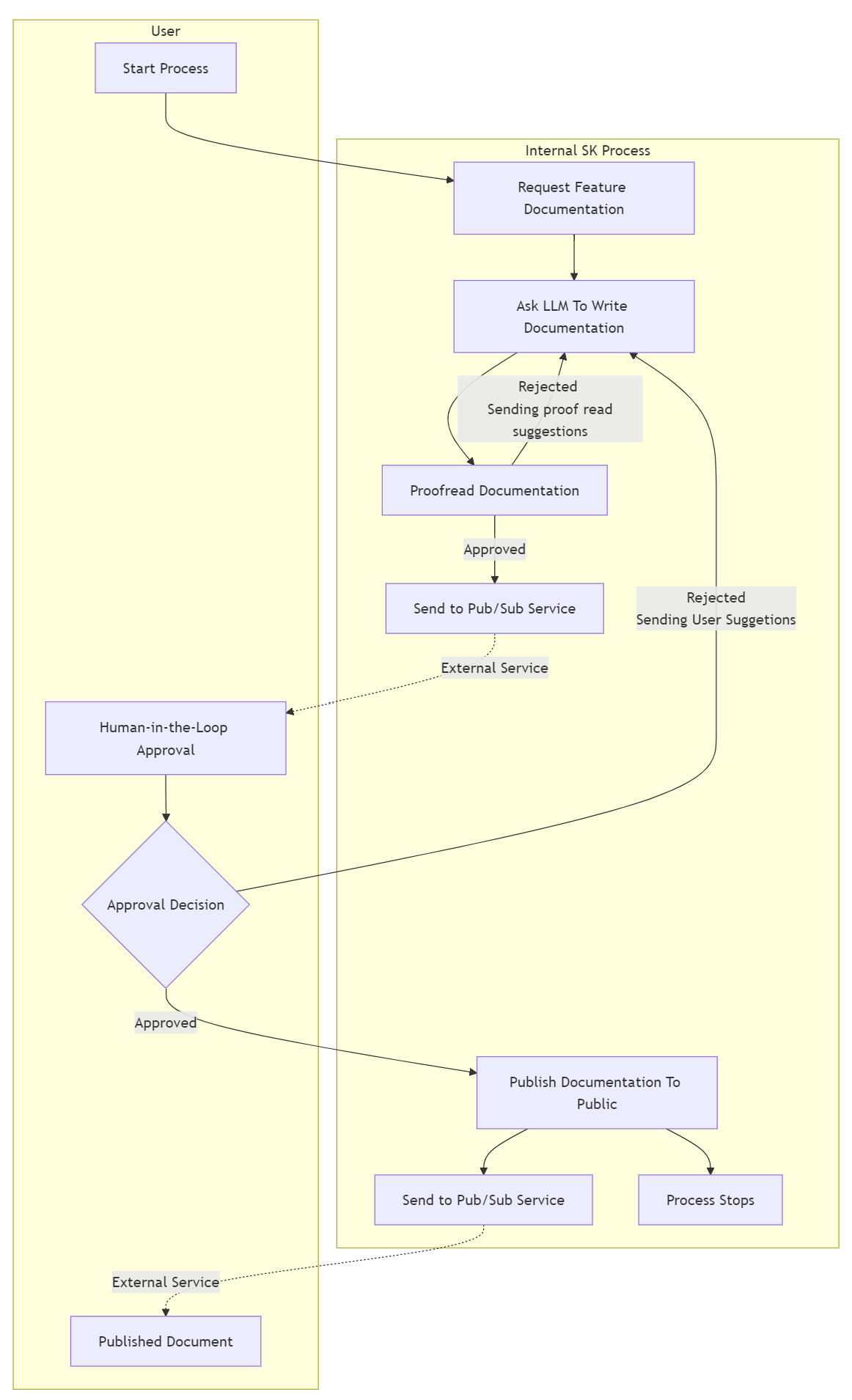
公開を承認待ちにする
プロセスに対して最初に行う必要がある変更は、ドキュメントを公開する前に、発行手順が承認を待つようすることです。 1 つのオプションは、PublishDocumentationの PublishDocumentationStep 関数に承認用の 2 つ目のパラメーターを追加することです。 これは、ステップ内の KernelFunction が呼び出されるのは、必要なすべてのパラメーターが指定されている場合のみであるためです。
// A process step to publish documentation
public class PublishDocumentationStep : KernelProcessStep
{
[KernelFunction]
public DocumentInfo PublishDocumentation(DocumentInfo document, bool userApproval) // added the userApproval parameter
{
// Only publish the documentation if it has been approved
if (userApproval)
{
// For example purposes we just write the generated docs to the console
Console.WriteLine($"[{nameof(PublishDocumentationStep)}]:\tPublishing product documentation approved by user: \n{document.Title}\n{document.Content}");
}
return document;
}
}
Python Human-in-the-loop プロセス動作のサポートは近日公開予定です。
上記のコードでは、生成されたドキュメントが PublishDocumentation パラメーターに送信され、承認の結果が PublishDocumentationStep パラメーターに送信された場合にのみ、document の userApproval 関数が呼び出されます。
ProofreadStepステップの既存のロジックを再利用して、新しい要求があることを人間の承認者に通知するイベントを外部 pubsub システムに追加で出力できるようになりました。
// A process step to publish documentation
public class ProofReadDocumentationStep : KernelProcessStep
{
...
if (formattedResponse.MeetsExpectations)
{
// Events that are getting piped to steps that will be resumed, like PublishDocumentationStep.OnPublishDocumentation
// require events to be marked as public so they are persisted and restored correctly
await context.EmitEventAsync("DocumentationApproved", data: document, visibility: KernelProcessEventVisibility.Public);
}
...
}
Proofread エージェントによって承認されたときに、新しく生成されたドキュメントを発行するため、承認されたドキュメントは発行手順でキューに登録されます。 さらに、最新のドキュメントの更新を含む外部 pubsub システムを介して、人間に通知されます。 この新しい設計に合わせてプロセス フローを更新しましょう。
Python Human-in-the-loop プロセス動作のサポートは近日公開予定です。
// Create the process builder
ProcessBuilder processBuilder = new("DocumentationGeneration");
// Add the steps
var infoGatheringStep = processBuilder.AddStepFromType<GatherProductInfoStep>();
var docsGenerationStep = processBuilder.AddStepFromType<GenerateDocumentationStepV2>();
var docsProofreadStep = processBuilder.AddStepFromType<ProofreadStep>();
var docsPublishStep = processBuilder.AddStepFromType<PublishDocumentationStep>();
// internal component that allows emitting SK events externally, a list of topic names
// is needed to link them to existing SK events
var proxyStep = processBuilder.AddProxyStep(["RequestUserReview", "PublishDocumentation"]);
// Orchestrate the events
processBuilder
.OnInputEvent("StartDocumentGeneration")
.SendEventTo(new(infoGatheringStep));
processBuilder
.OnInputEvent("UserRejectedDocument")
.SendEventTo(new(docsGenerationStep, functionName: "ApplySuggestions"));
// When external human approval event comes in, route it to the 'isApproved' parameter of the docsPublishStep
processBuilder
.OnInputEvent("UserApprovedDocument")
.SendEventTo(new(docsPublishStep, parameterName: "userApproval"));
// Hooking up the rest of the process steps
infoGatheringStep
.OnFunctionResult()
.SendEventTo(new(docsGenerationStep, functionName: "GenerateDocumentation"));
docsGenerationStep
.OnEvent("DocumentationGenerated")
.SendEventTo(new(docsProofreadStep));
docsProofreadStep
.OnEvent("DocumentationRejected")
.SendEventTo(new(docsGenerationStep, functionName: "ApplySuggestions"));
// When the proofreader approves the documentation, send it to the 'document' parameter of the docsPublishStep
// Additionally, the generated document is emitted externally for user approval using the pre-configured proxyStep
docsProofreadStep
.OnEvent("DocumentationApproved")
// [NEW] addition to emit messages externally
.EmitExternalEvent(proxyStep, "RequestUserReview") // Hooking up existing "DocumentationApproved" to external topic "RequestUserReview"
.SendEventTo(new(docsPublishStep, parameterName: "document"));
// When event is approved by user, it gets published externally too
docsPublishStep
.OnFunctionResult()
// [NEW] addition to emit messages externally
.EmitExternalEvent(proxyStep, "PublishDocumentation");
var process = processBuilder.Build();
return process;
最後に、インターフェイス IExternalKernelProcessMessageChannel の実装は、新しい ProxyStepによって内部的に使用されるため提供する必要があります。 このインターフェイスは、外部からメッセージを出力するために使用されます。 このインターフェイスの実装は、使用している外部システムによって異なります。 この例では、作成したカスタム クライアントを使用して、外部 pubsub システムにメッセージを送信します。
// Example of potential custom IExternalKernelProcessMessageChannel implementation
public class MyCloudEventClient : IExternalKernelProcessMessageChannel
{
private MyCustomClient? _customClient;
// Example of an implementation for the process
public async Task EmitExternalEventAsync(string externalTopicEvent, KernelProcessProxyMessage message)
{
// logic used for emitting messages externally.
// Since all topics are received here potentially
// some if else/switch logic is needed to map correctly topics with external APIs/endpoints.
if (this._customClient != null)
{
switch (externalTopicEvent)
{
case "RequestUserReview":
var requestDocument = message.EventData.ToObject() as DocumentInfo;
// As an example only invoking a sample of a custom client with a different endpoint/api route
this._customClient.InvokeAsync("REQUEST_USER_REVIEW", requestDocument);
return;
case "PublishDocumentation":
var publishedDocument = message.EventData.ToObject() as DocumentInfo;
// As an example only invoking a sample of a custom client with a different endpoint/api route
this._customClient.InvokeAsync("PUBLISH_DOC_EXTERNALLY", publishedDocument);
return;
}
}
}
public async ValueTask Initialize()
{
// logic needed to initialize proxy step, can be used to initialize custom client
this._customClient = new MyCustomClient("http://localhost:8080");
this._customClient.Initialize();
}
public async ValueTask Uninitialize()
{
// Cleanup to be executed when proxy step is uninitialized
if (this._customClient != null)
{
await this._customClient.ShutdownAsync();
}
}
}
最後に、プロセス ProxyStep が IExternalKernelProcessMessageChannel 実装を利用できるようにするには、この場合 MyCloudEventClient、適切にパイプする必要があります。
ローカル ランタイムを使用する場合は、StartAsync クラスでKernelProcessを呼び出すときに、実装されたクラスを渡すことができます。
KernelProcess process;
IExternalKernelProcessMessageChannel myExternalMessageChannel = new MyCloudEventClient();
// Start the process with the external message channel
await process.StartAsync(kernel, new KernelProcessEvent
{
Id = inputEvent,
Data = input,
},
myExternalMessageChannel)
Dapr ランタイムを使用する場合は、プロジェクトのプログラムセットアップで依存関係の挿入を通じて配管を行う必要があります。
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
...
// depending on the application a singleton or scoped service can be used
// Injecting SK Process custom client IExternalKernelProcessMessageChannel implementation
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IExternalKernelProcessMessageChannel, MyCloudEventClient>();
Python Human-in-the-loop プロセス動作のサポートは近日公開予定です。
プロセス フローに対して次の 2 つの変更が行われました。
-
HumanApprovalResponseステップのuserApprovalパラメーターにルーティングされるdocsPublishStepという名前の入力イベントを追加しました。 -
docsPublishStepの KernelFunction には 2 つのパラメーターがあるため、既存のルートを更新して、documentのパラメーター名を指定する必要があります。
前と同じようにプロセスを実行し、今度は校正者が生成されたドキュメントを承認し、それを document ステップの docPublishStep パラメーターに送信すると、userApproval パラメーターを待機しているため、ステップが呼び出されなくなります。 この時点でプロセスはアイドル状態になります。呼び出す準備ができているステップがなく、プロセスを開始するために行った呼び出しが返されます。 このプロセスは、"human-in-the-loop" が発行要求を承認または拒否するためのアクションを実行するまで、このアイドル状態のままになります。 これが発生し、結果がプログラムに伝達されたら、結果を使用してプロセスを再開できます。
// Restart the process with approval for publishing the documentation.
await process.StartAsync(kernel, new KernelProcessEvent { Id = "UserApprovedDocument", Data = true });
Python Human-in-the-loop プロセス動作のサポートは近日公開予定です。
プロセスが UserApprovedDocument で再度開始されると、中断した場所から再開され、docsPublishStep が userApproval に設定された true が呼び出され、ドキュメントが公開されます。
UserRejectedDocumentイベントで再度開始された場合、プロセスはApplySuggestionsステップでdocsGenerationStep関数を開始し、プロセスは以前と同様に続行されます。
これでプロセスが完了し、プロセスに人間のループステップが正常に追加されました。 これで、このプロセスを使用して、製品のドキュメントを生成し、それを校正し、人間によって承認された後に公開することができます。