適用対象: SQL Server 2017 (14.x) 以降のバージョン
この記事では、SQL Server Machine Learning Services で外部 Python スクリプトを実行するための Python 拡張機能について説明します。 拡張機能により、次のものが追加されます。
- Python 実行環境
- Python 3.5 ランタイムおよびインタープリターを使用した Anaconda ディストリビューション
- 標準ライブラリとツール
- Microsoft Python パッケージ:
- 大規模な分析のための revoscalepy。
- 機械学習アルゴリズム用の microsoftml。
Python 3.5 ランタイムとインタープリターのインストールにより、標準的な Python ソリューションとのほぼ完全な互換性が確保されます。 Python は SQL Server とは別のプロセスで実行されるので、データベース操作に支障はありません。
Python コンポーネント
SQL Server には、オープンソース パッケージと専用パッケージの両方が含まれています。 セットアップによってインストールされる Python ランタイムは、Python 3.5 を含む Anaconda 4.2 です。 Python ランタイムは、SQL ツールとは別にインストールされ、機能拡張フレームワークのコア エンジン プロセスの外部で実行されます。 Machine Learning Services と Python のインストールの一環として、GNU Public License の条項に同意する必要があります。
SQL Server では、Python 実行可能ファイルは変更されませんが、セットアップによってインストールされたバージョンの Python を使用する必要があります。これは、専用パッケージがビルドおよびテストされているバージョンであるためです。 Anaconda ディストリビューションでサポートされているパッケージの一覧については、Continuum 分析サイト「Anaconda package list」(Anaconda パッケージ リスト) を参照してください。
特定のデータベース エンジン インスタンスに関連付けられている Anaconda ディストリビューションは、そのインスタンスに関連付けられているフォルダーで見つけることができます。 たとえば、SQL Server 2017 データベース エンジンと共に Machine Learning Services および Python を既定のインスタンスにインストールした場合は、C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\PYTHON_SERVICES を確認します。
Microsoft が並列ワークロードと分散ワークロード用に追加した Python パッケージには、次のライブラリが含まれます。
| ライブラリ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| revoscalepy | データ ソース オブジェクトとデータの探索、操作、変換、視覚化をサポートします。 リモート コンピューティング コンテキスト、およびさまざまなスケーラブルな機械学習モデル (rxLinMod など) の作成をサポートします。 詳細については、SQL Server での revoscalepy モジュールに関するページをご覧ください。 |
| microsoftml | 速度と精度のために最適化された機械学習アルゴリズムに加え、テキストとイメージを操作するためのインライン変換も含まれています。 詳細については、SQL Server での microsoftml モジュールに関するページを参照してください。 |
microsoftml と revoscalepy は密結合されています。microsoftml で使用されるデータ ソースは、revoscalepy オブジェクトとして定義されています。 revoscalepy でコンピューティング コンテキストの制限は microsoftml に転送されます。 つまり、ローカル操作ではすべての機能を使用できますが、リモート コンピューティング コンテキストに切り替えるには RxInSqlServer が必要です。
SQL Server での Python の使用
ご利用の Python コードに revoscalepy モジュールをインポートしてから、他の Python 関数と同様に、モジュールから関数を呼び出します。
サポートされているデータ ソースには、ODBC データベース、SQL Server、他のソースまたは R ソリューションとデータを交換するための XDF ファイル形式があります。 Python に対する入力データは表形式とする必要があります。 Python の結果はすべて、Pandas データ フレームの形式で返される必要があります。
サポートされているコンピューティング コンテキストには、ローカルまたはリモートの SQL Server コンピューティング コンテキストが含まれます。 リモート コンピューティング コンテキストとは、ワークステーションなどの 1 台のコンピューターで起動するコード実行を指しますが、その後、スクリプトの実行はリモート コンピューターに切り替えられます。 コンピューティング コンテキストを切り替えるには、両方のシステムに同じ revoscalepy ライブラリが用意されている必要があります。
ご想像のとおり、ローカルのコンピューティング コンテキストには、データベース エンジン インスタンスと同じサーバー上での Python コードの実行に加え、T-SQL 内のコードまたはストアド プロシージャに埋め込まれたコードの実行も含まれます。 また、リモートのコンピューティング コンテキストを定義することにより、ローカルの Python IDE からコードを実行し、SQL Server コンピューター上でスクリプトを実行することもできます。
実行アーキテクチャ
以下の図は、サポートされている各シナリオでの SQL Server コンポーネントと Python ランタイムとのやりとりを示しています。そのシナリオとは、SQL Server コンピューティング コンテキストを使用したデータベース内のスクリプトの実行と Python ターミナルからのリモート実行です。
データベース内で実行される Python スクリプト
SQL Server の "内部で" Python を実行する場合は、Python スクリプトを特殊なストアド プロシージャである sp_execute_external_script にカプセル化する必要があります。
ストアド プロシージャにスクリプトが埋め込まれたら、ストアド プロシージャを呼び出すことができる任意のアプリケーションで、Python コードの実行を開始できます。 その後は、SQL Server により、次の図にまとめたように、コードの実行が管理されます。
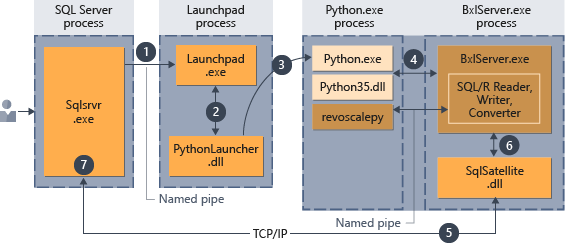
- ストアド プロシージャに渡されたパラメーター
@language='Python'によって、Python ランタイムに対する要求が示されます。 この要求は SQL Server からスタート パッド サービスに送信されます。 Linux の場合、SQL ではスタート パッド サービスを使用して、ユーザーごとに個別のスタート パッド プロセスとの通信が行われます。 詳細については、機能拡張アーキテクチャの図を参照してください。 - スタート パッド サービスによって適切なランチャーが起動されます (この場合は PythonLauncher)。
- PythonLauncher によって外部の Python35 プロセスが開始されます。
- BxlServer と Python ランタイムとの連携により、データ交換や、作業結果の保存が管理されます。
- SQL サテライトでは、関連するタスクやプロセスについての SQL Server との通信が管理されます。
- BxlServer では、SQL サテライトを使用して、状態と結果が SQL Server に通知されます。
- SQL Server では、結果が取得され、関連するタスクとプロセスが終了されます。
リモート クライアントから実行される Python スクリプト
次の条件が満たされている場合は、ラップトップなどのリモート コンピューターから Python スクリプトを実行し、SQL Server コンピューターのコンテキストでそれらを実行することができます。
- あなたはスクリプトを適切に設計します。
- リモート コンピューターには、Machine Learning Services で使用される機能拡張ライブラリがインストールされています。 リモート コンピューティング コンテキストを使用するには、revoscalepy パッケージが必要です。
次の図は、リモート コンピューターからスクリプトが送信される場合の全体的なワークフローをまとめたものです。
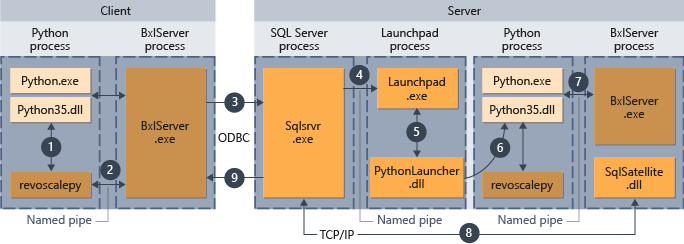
- revoscalepy でサポートされている関数の場合、Python ランタイムによってリンク関数が呼び出され、続いてこの関数によって BxlServer が呼び出されます。
- BxlServer は Machine Learning Services (データベース内) に含まれており、Python ランタイムとは別のプロセスで実行されます。
- BxlServer では接続のターゲットが決定され、ODBC を使用して接続が開始され、Python スクリプト内の接続文字列の一部として提供された資格情報が渡されます。
- BxlServer によって、SQL Server インスタンスへの接続が開かれます。
- 外部スクリプト ランタイムが呼び出されると、スタート パッド サービスが呼び出され、続いて適切なランチャー (この場合は、PythonLauncher.dll) が起動されます。 その後、Python コードの処理は、T-SQL のストアド プロシージャから Python コードが呼び出される場合と同様のワークフローで処理されます。
- PythonLauncher では、SQL Server コンピューターにインストールされている Python のインスタンスへの呼び出しが行われます。
- 結果が BxlServer に返されます。
- SQL サテライトでは、SQL Server との通信と、関連するジョブ オブジェクトのクリーンアップが管理されます。
- SQL Server からクライアントに結果が返されます。