Note
Management (how to) changes for RDS in Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2
This wiki article main purpose is to provide administrators familiar with Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Services a quick overview of management changes in Windows Server 2012.It covers settings locations only and does not provide information about the technology used in each component
Windows Server 2012 introduced the Remote Desktop Management Service (RDMS) effectively removing the standard MMC consoles used to manage a Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Services server.
The RDMS is responsible for adding, removing and updating configuration for all of the servers comprising a Remote Desktop Services deployment. All of the configuration is now stored in the Connection Broker database.
Intro and lab configuration
In order to provide the best possible guidance in this article, two virtual machine based labs are being used to generate screenshots.
The first lab consists of a pure Windows Server 2008 R2 installation, the virtual machines used are the following:
- SRV2008DC / Windows Server 2008 R2 Domain Controller, DNS and DHCP
- SRV2008RDS1 / Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Session Host
- SRV2008Web1 / Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Services Web and Gateway Services
The second lab is a pure Windows Server 2012 R2 installation, the virtual machines used are the following:
- SRV2012DC /Windows Server 2012 R2 Domain Controller, DNS and DHCP
- SRV2012CB1 /Windows Server 2012 R2 Remote Desktop Services Connection Broker
- SRV2012RDS1 /Windows Server 2012 R2 Remote Desktop Services Session Host
- SRV2012Web1 /Windows Server 2012 R2 Remote Desktop Services Web and Gateway Services
A quick overview of consoles
In order to gain a better understanding of the administration in the previous release of Windows Server, I will quickly go through the MMC consoles used in order to configure the deployment options. The consoles used to manage the settings are the following:
Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration
The Remote Desktop Session Host configuration is used on a server running Remote Desktop Session Host to configure
RDP-Tcp server specific settings such as Color Depth, Session Settings, licensing options etc.
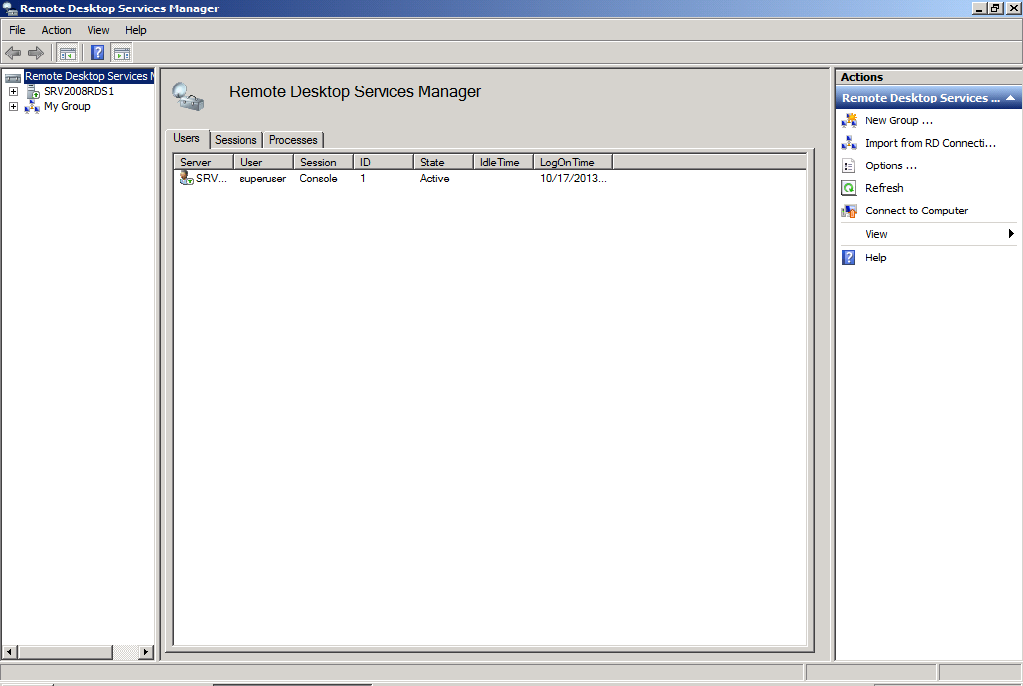
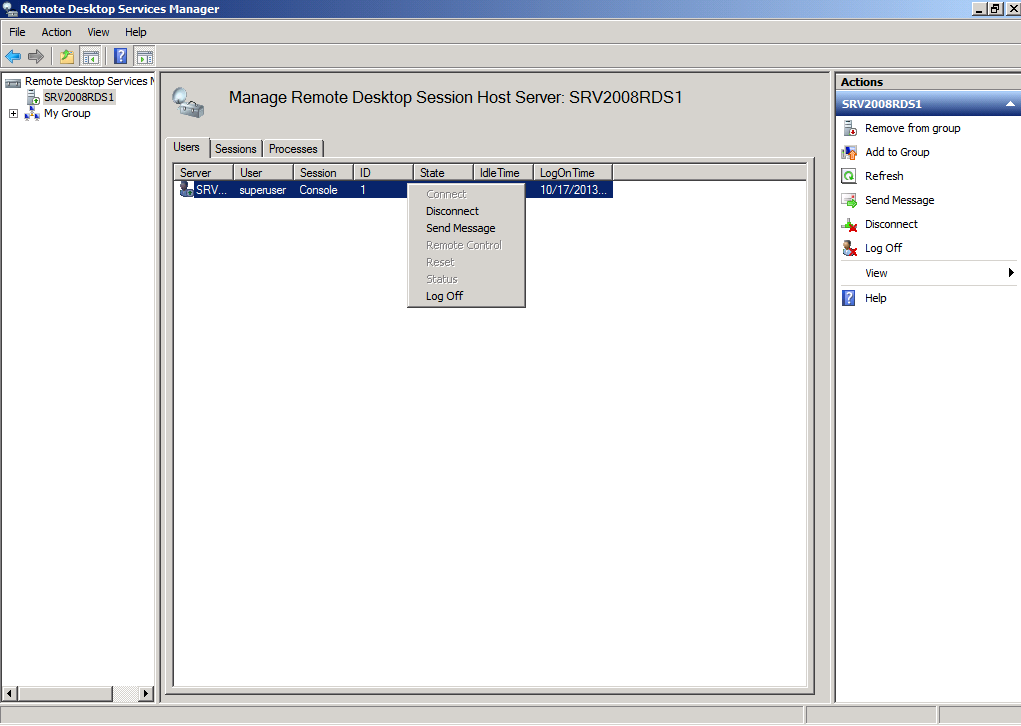
Remote Desktop Services Manager
The Remote Desktop Services Manager is used to manage the user connections like disconnect users and provide connection info.
RemoteAPP Manager
The RemoteAPP manager is used to publish and configure all of the remote application settings. Essentially this console provides the RDP Settings in each .rdp file. 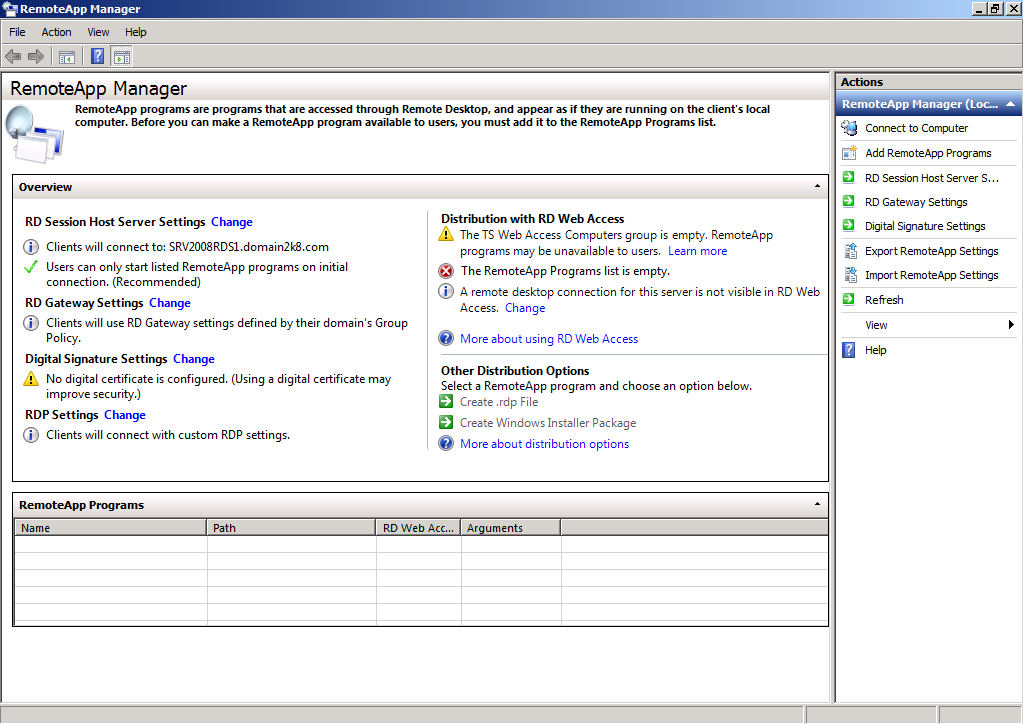
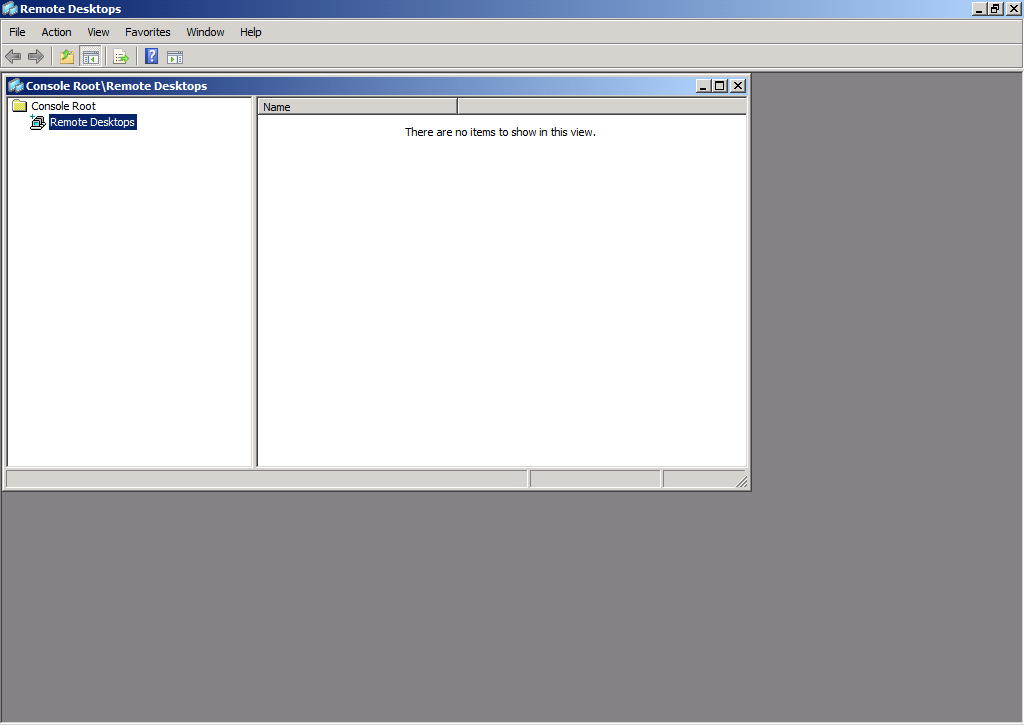
Remote Desktops
The Remote Desktops MMC is used to host connection information on a single pane providing administrators with quick access to Remote Desktop Servers instead of the Remote Desktop Services Client functionality. This console is no longer used in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2. An administrator can still use the Remote Desktop Client in order to connect to a Remote Desktop Server.
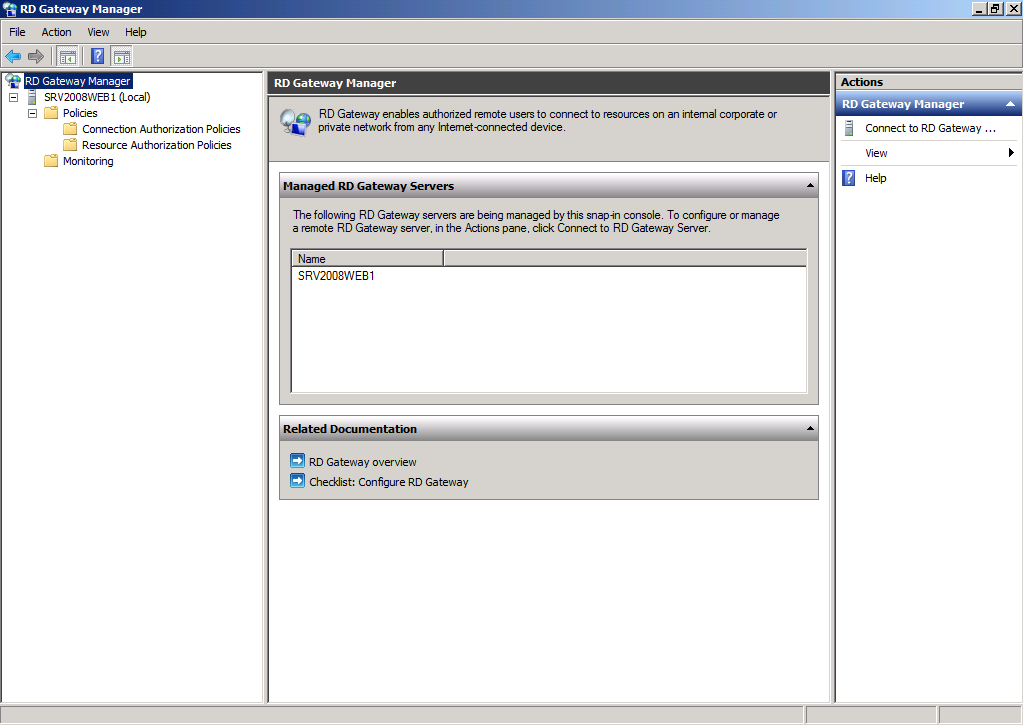
Remote Desktop Gateway Manager
The Remote Desktop Gateway Manager is the console used to manage Remote Desktop Services Gateway Settings.
Remote Desktop Licensing Manager
The Remote Desktop Licensing Manager is used to configure a License Server for the Remote Desktop Services Deployment. This console is unchanged in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
[
](resources/2742.6.png)
Remote Desktop Web Access Configuration
Finally the Remote Desktop Web Access Configuration is a web page with which we can configure the sources a Remote Desktop Services Web Access server can connect and provide Remote Desktop services to users. These settings are automatically configured by the Server Manager in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
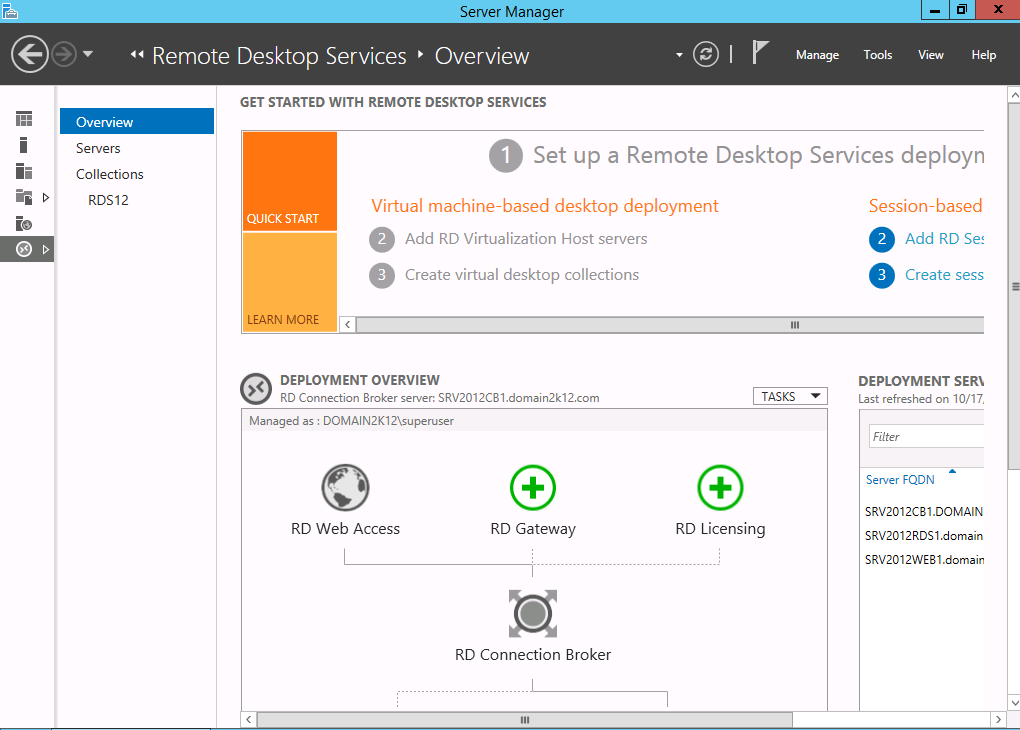
A brief description of Server Manager
The new unified administrative experience in Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2 is provided within Server Manager.
Server Manager hosts the Remote Desktop Services administration page for most of the settings an administrator need to configure. Some of the options in the previous release consoles are moved to either PowerShell or Group Policy.
This management change effectively pushes all of the configuration changes to the servers providing Remote Desktop functionality and eases the administrative burden of having to move through different consoles. It also provides an easy way to add or remove servers as needed empowering administrators with true scale out options.
Only Licensing and Gateway server consoles are available due to the fact that these roles can exist on different servers. For example a single Licensing server can provide licenses to both Windows Server 2008 R2 and Server 2012 R2 deployments and a Gateway server can reside on a DMZ.
Basic RDS Configuration
As installation completes on Windows Server 2008 R2 for the Remote Desktop Session Host, a number of settings would be revised by an administrator to provide users with optimal experience. This configuration was done through the Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration.
General Tab
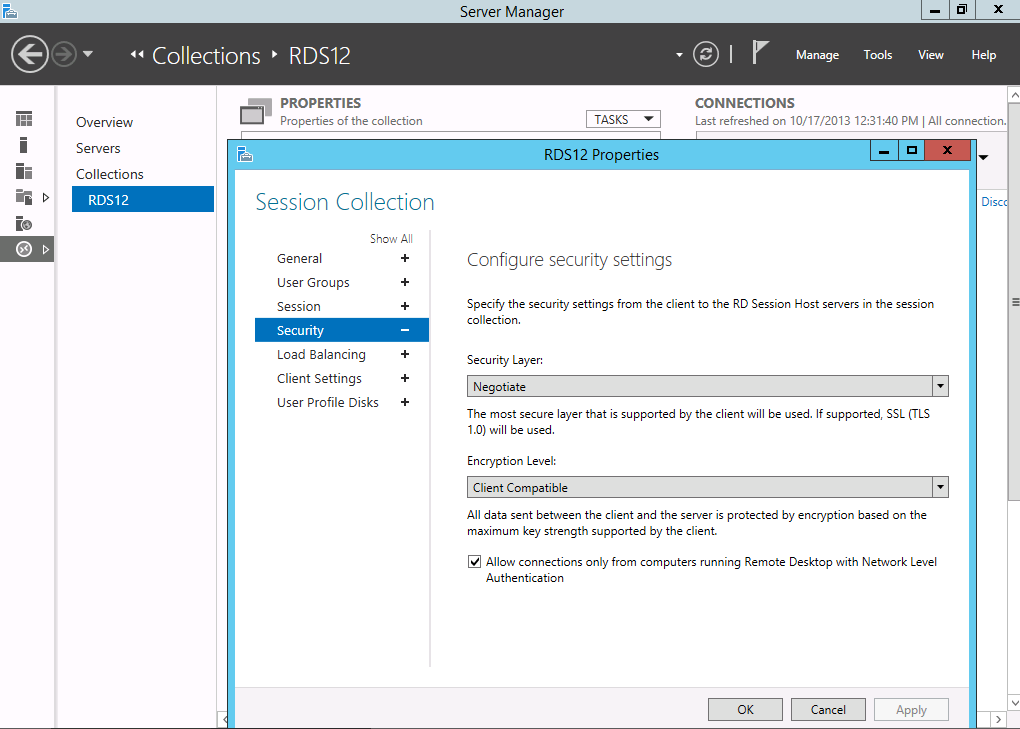
The first tab is the General Tab which is used to configure security settings and Certificate Settings on the RDP-Tcp Listener

The same functionality is provided by the Server Manager by navigating to the Collection, selecting Tasks->Edit Properties and then the Security Tab
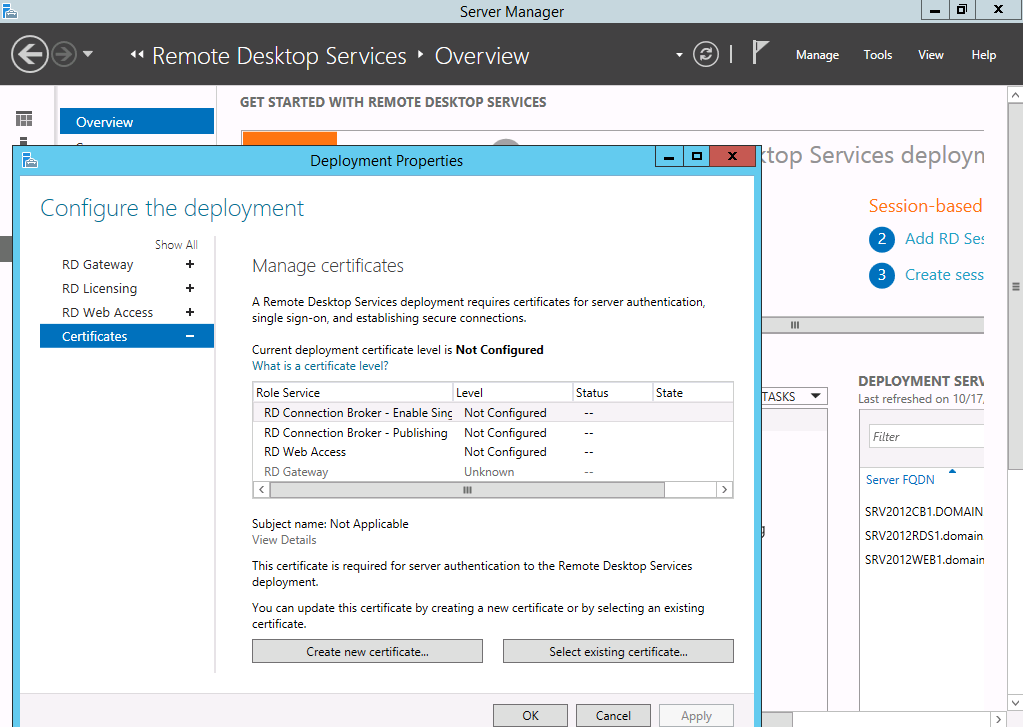
The certificate settings can be globally configured by navigating to Overview and selecting Edit Deployment Properties from the Tasks Button. On the deployment properties we can find the Certificates tab with which we can configure the certificates on all of the deployment.
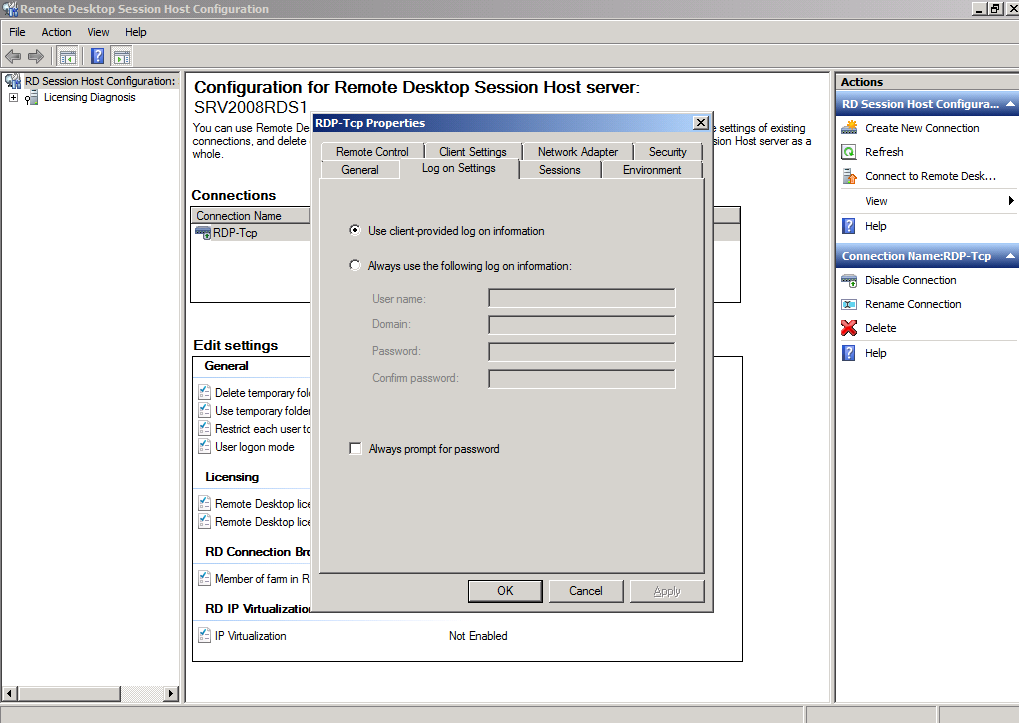
Log on settings
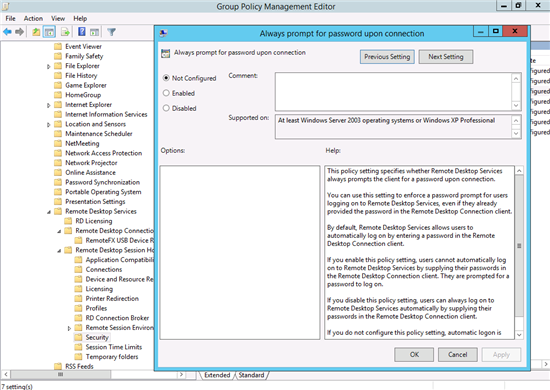
The Log on Settings Tab is deprecated in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
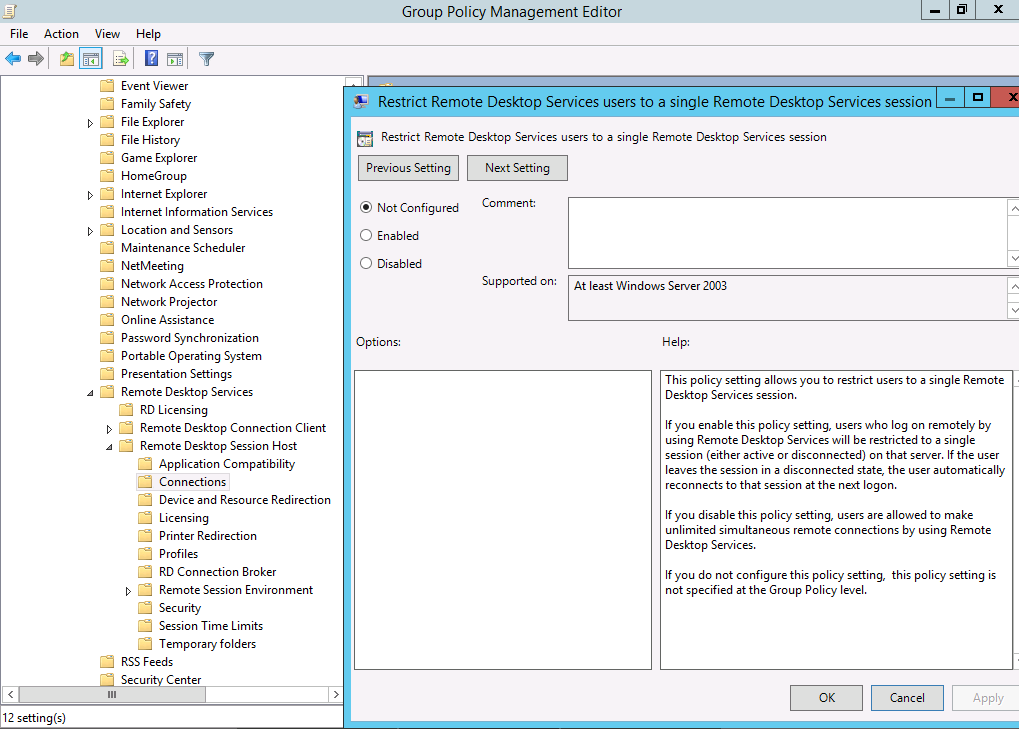
Although the Always prompt for password option is available in Group Policy. The setting can be found in Computer Configuration->Administrative Templates->Windows Components->Remote Desktop Services->Remote Desktop Session Host Security.
Sessions
The Sessions settings provide the options to disconnect or end sessions as needed.
The same functionality can be found by navigating to the Collection and then opening the Collection properties from the tasks button. The sessions tab contains the settings.
Environment
The Environment tab specifies an initial program to start when a user logs on.
The same functionality can be achieved through Group Policy for general settings or the Environment tab on the user property page in Active Directory Users and Computers for more granular control . The setting can be found in Computer Configuration->Administrative Templates->Windows Components->Remote Desktop Services->Remote Desktop Session Host->Remote Session Environment.
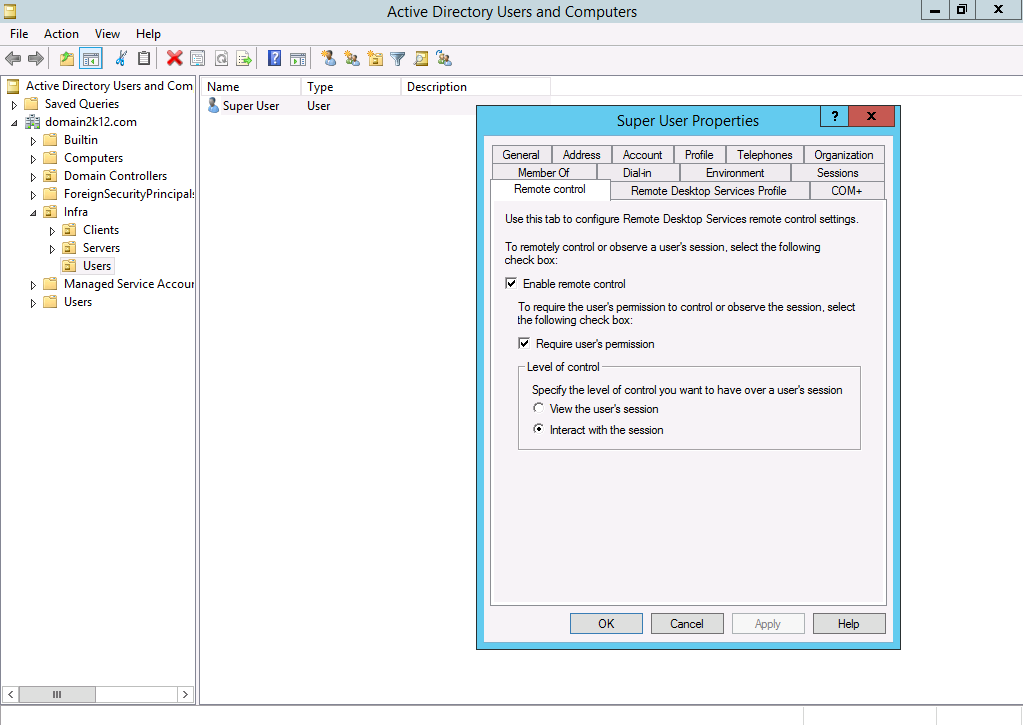
Remote Control
The Remote Control feature used in Windows 2008 R2 was added again in Windows Server 2012 R2.
The settings are now found in the users Remote Control tab in the Active Directory Users and Computers console.
**
 **
**
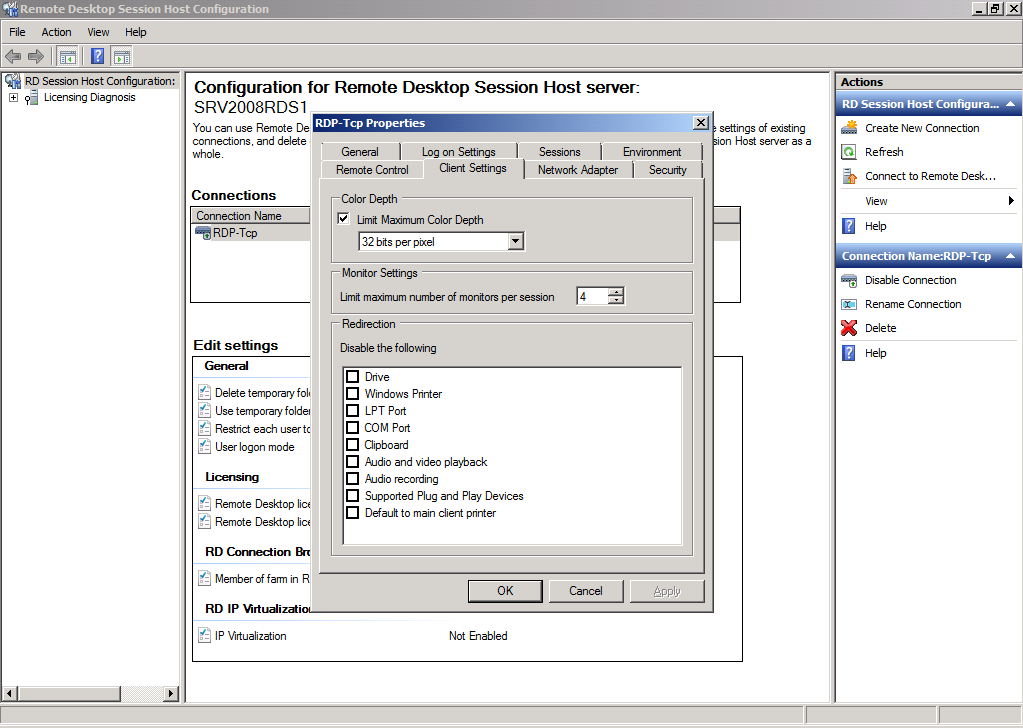
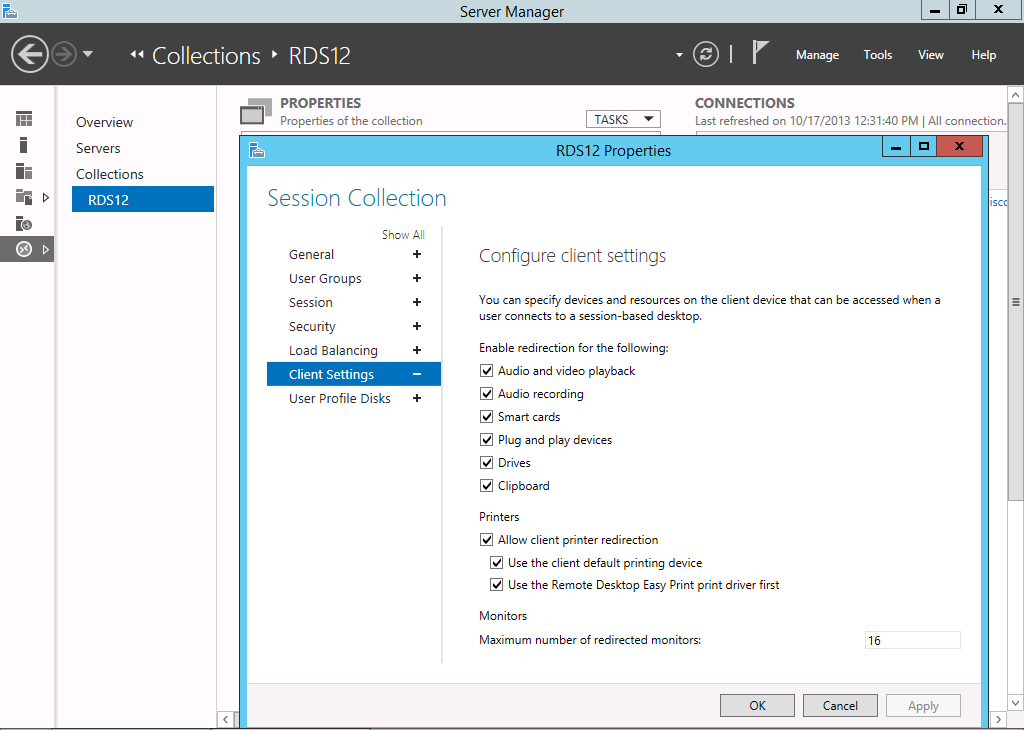
Client Settings
The Client Settings tab configures the options for the monitor redirection, maximum color depth and redirection settings.
These settings can be found at the Server Manager by editing the properties of the collection and navigating to Client Settings. Maximum color depth can be adjusted per RemoteApp by editing the custom rdp property “Session BPP” .
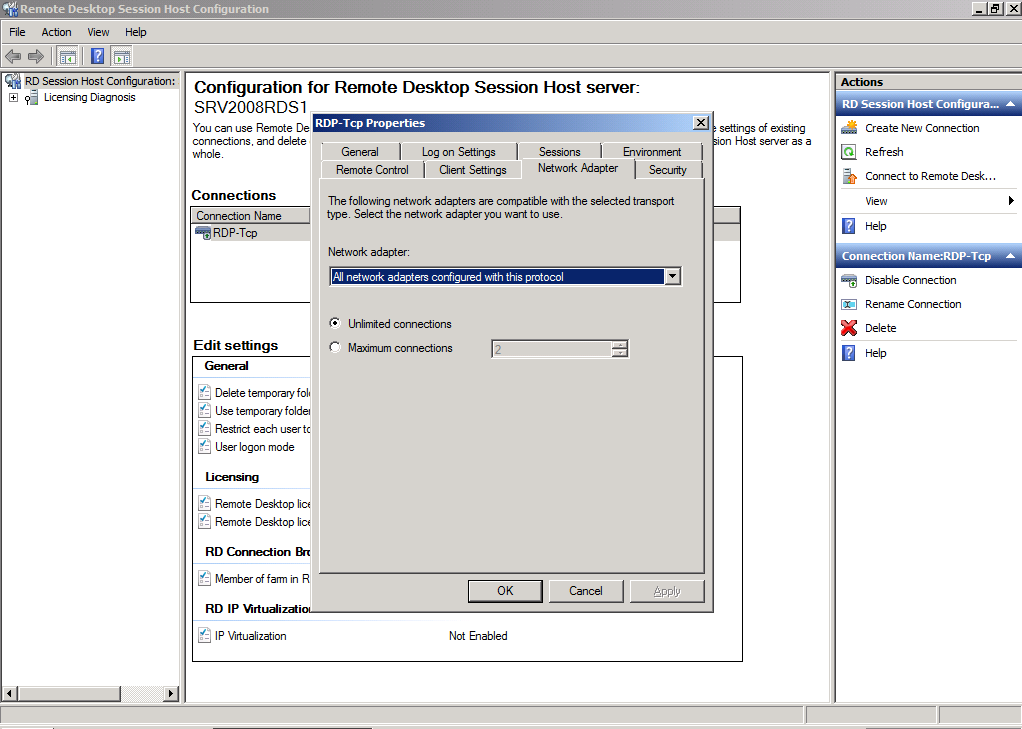
Network Adapter
The Network Adapter tab is does no longer exist in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
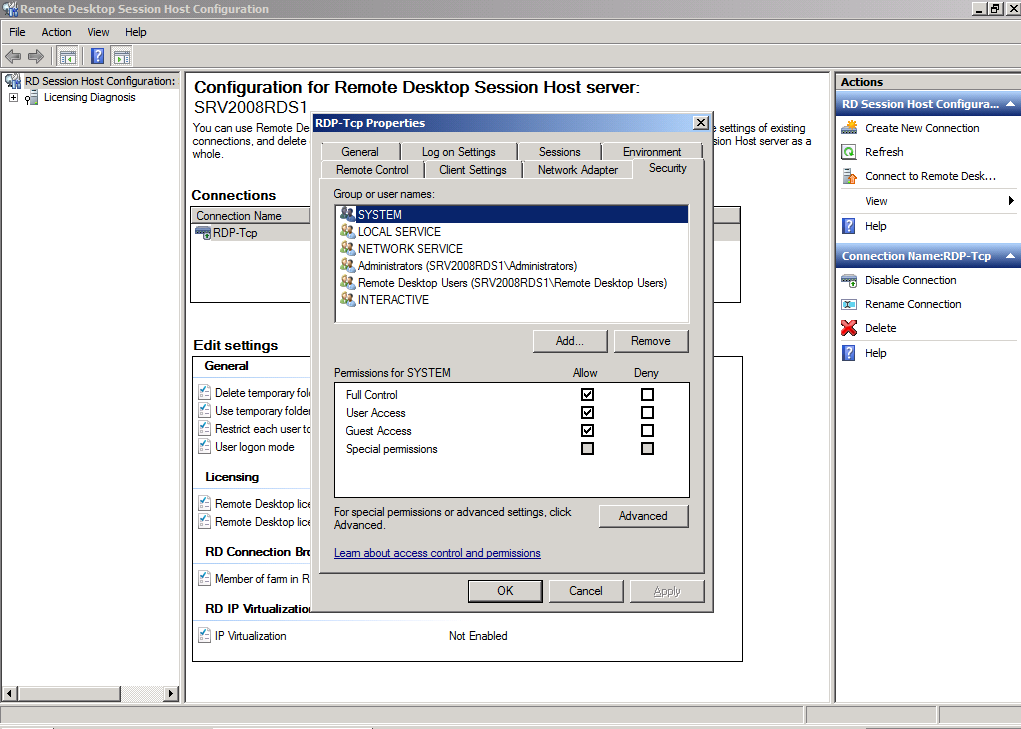
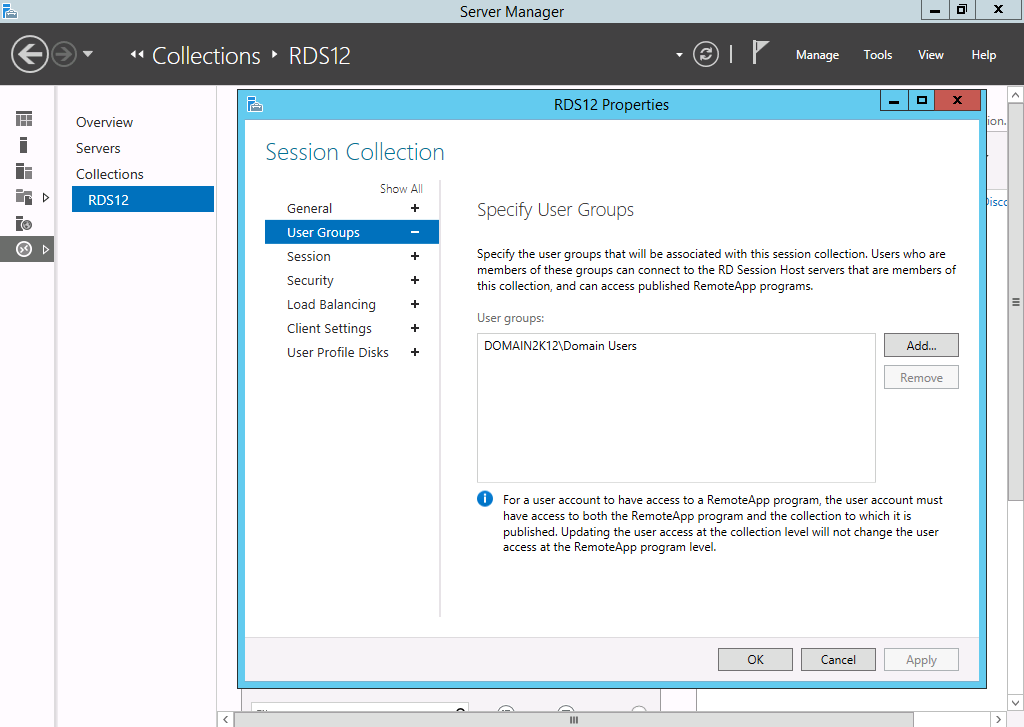
Security
The Security Tab on Windows Server 2008 R2 controls the access control lists
The same functionality is found on the Collection properties Users Group Tab and by editing each RemoteApp individually.
Remote Desktop Session Host General
On the general properties an administrator can configure the following tabs.
General
The General tab with which we can configure the temporary files behavior, the single session limit enforcement and the Remote Desktop Session Host drain mode.
The temporary files settings can be configured by navigating to the session collection properties and selecting the Session Tab.
The single session restriction can be enforced through Group Policy. The settings exists in Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections
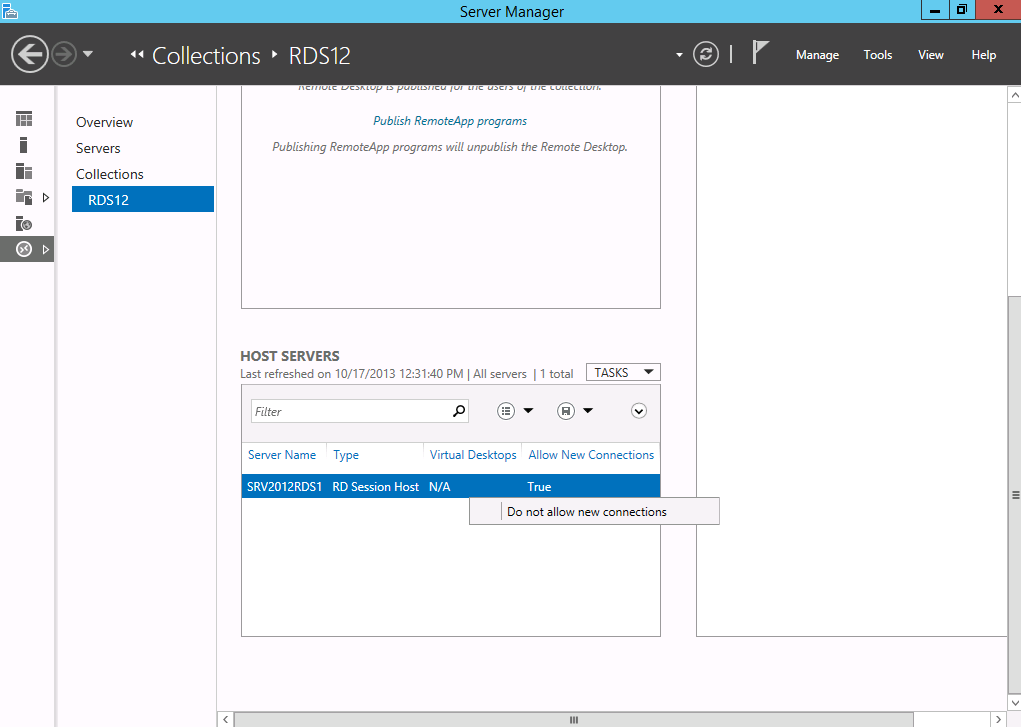
The Drain mode is much simpler. By right clicking a Remote Desktop Session Host in the specified collection , you can select Do not allow new connections.
Licensing
The Licensing tab allows you to configure a License server as well as the licensing mode. Either Per User or Per Device.
The same functionality can be found by editing the deployment properties from the Overview tab in Server Manager.
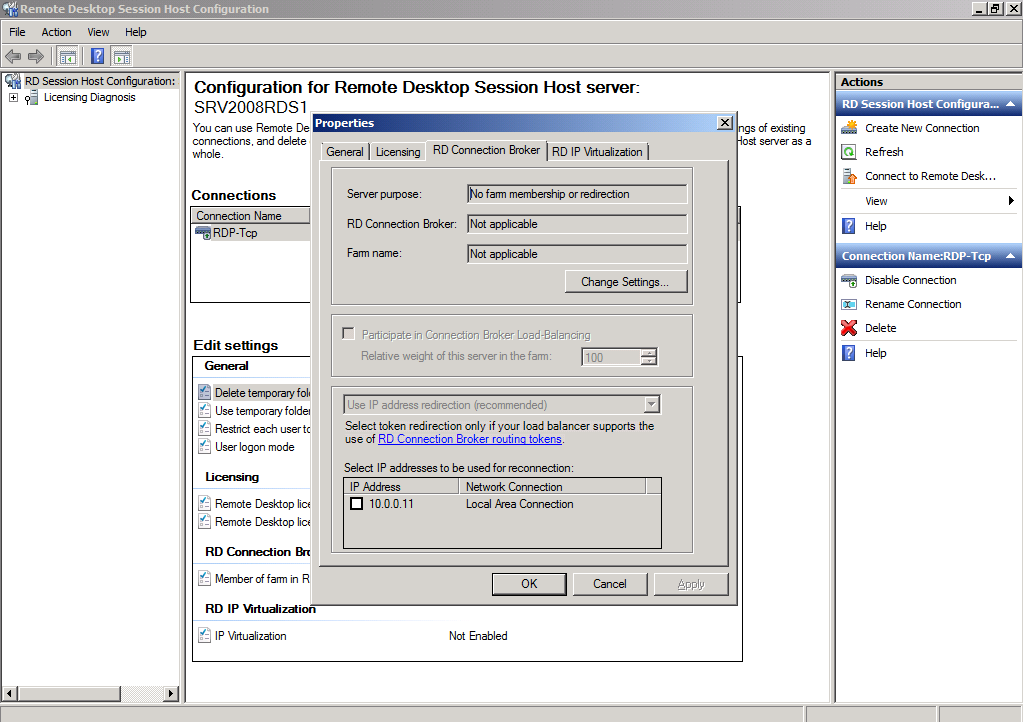
Connection Broker
The Connection Broker options allow you to configure the server role in a farm , the connection broker responsible for the redirections, the farm name and the redirection mode.
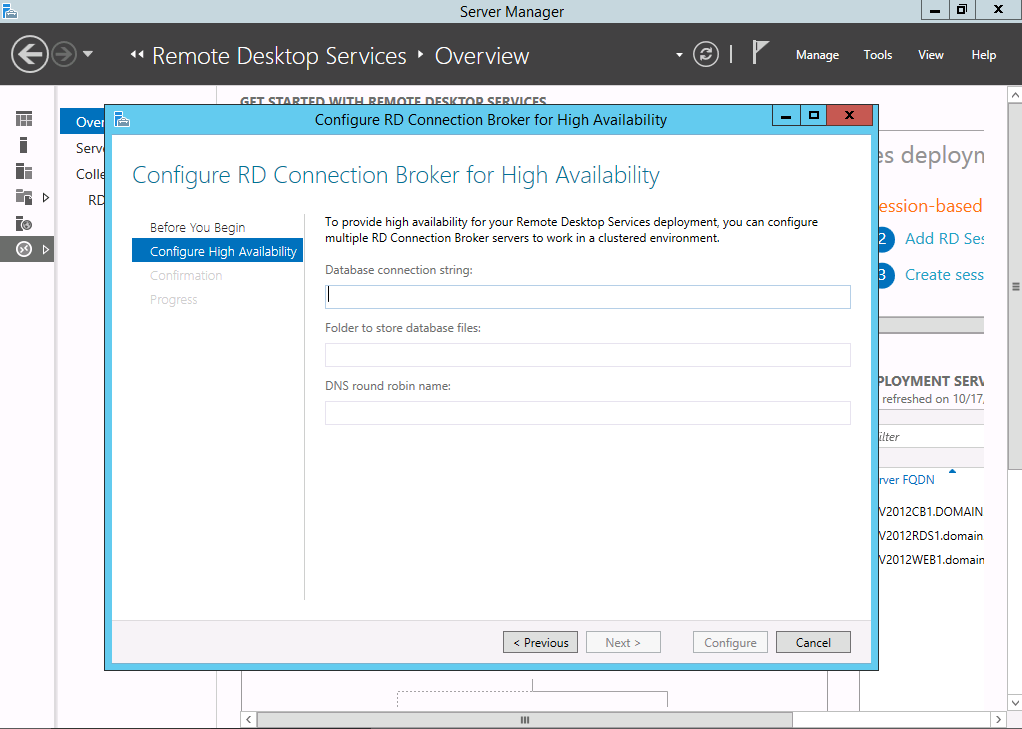
Since Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2 Remote Desktop Service rely on a Connection Broker, the role is configured automatically for each Session Host. However the DNS farm name in Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2 needs to be configured when you prepare high availability mode as in the screenshot below. If you need to change that name later you can use the PowerShell cmd-let Set-RDClientAccessName [[-ConnectionBroker] <String> ] [-ClientAccessName] <String> [ <CommonParameters>]
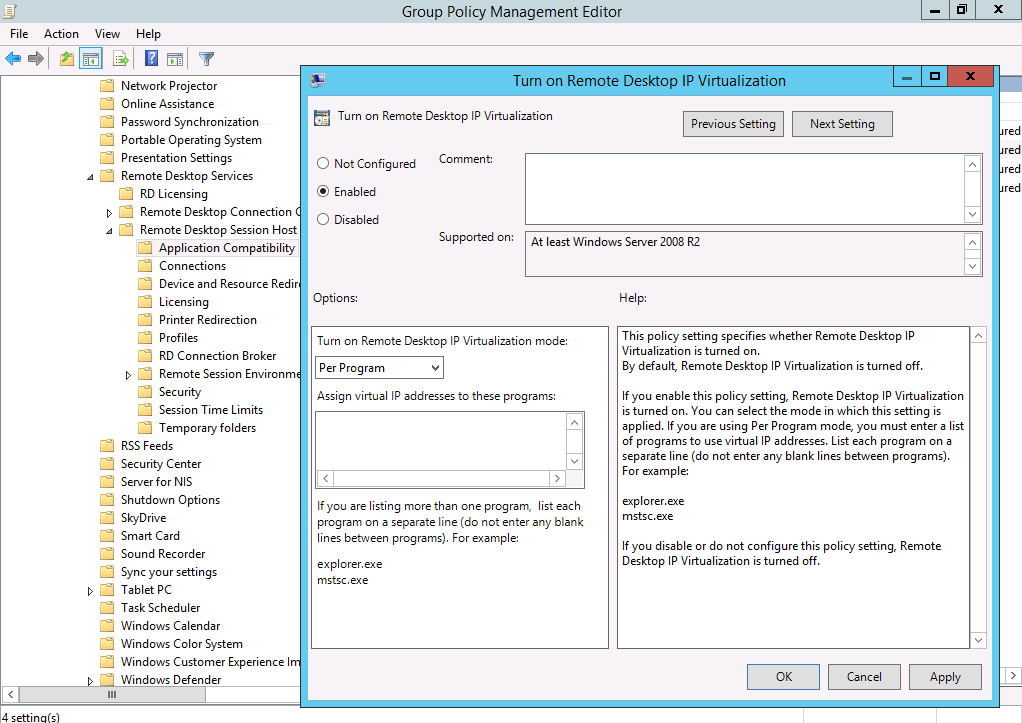
RD IP Virtualization
The RD IP Virtualization tab is used when we need to provide a virtual IP address per session or program. This is a requirement for some applications to work correctly.
These settings can now be configured through Group Policy. Navigate to Computer Configuration->Administrative Templates->Windows Components->Remote Desktop Services->Remote Desktop Session Host->Application Compatibility->Turn on Remote Desktop IP Virtualization.
Remote Desktop Services Manager
The Remote Desktop Services Manager allowed an administrator to act on user sessions like log off and disconnect by simply selecting a user session and right click upon it.
This Session administration is now moved to Server Manager. By navigating to a collection you can manage the user sessions on the right side of Server Manager in a widget-like tab named Connections.
The management scope extends to all collections by navigating to the Collection tab in Server Manager. Again on the right side you can manage the connections but this time collectively for all sessions on all of the available collections.
RemoteApp Manager
The RemoteAPP manager is used to publish and configure all of the remote application settings. Essentially this console provides the RDP Settings in each .rdp file.
RD Session Host Server
The first tab is the RD Session Host Server. On this tab you can configure the Server name , the rdp port as well as general access settings. Since Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 use a Connection broker the Server name and port is no longer needed.
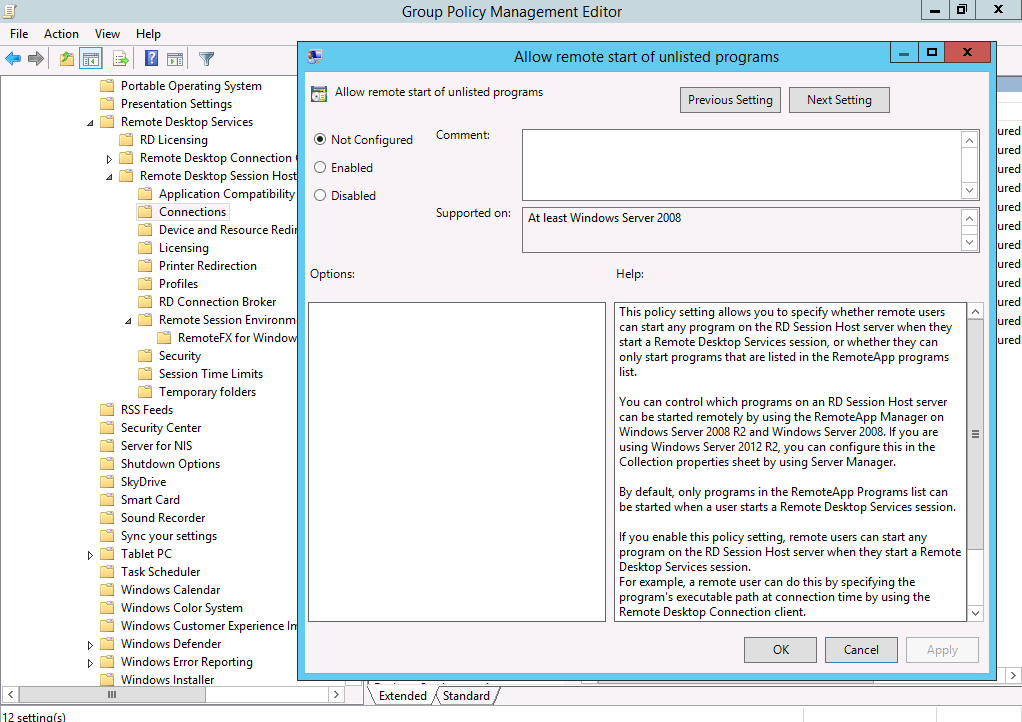
However the Access to unlisted programs can be found in Group Policy. Navigate to Computer Configuration->Administrative Templates->Windows Components->Remote Desktop Services->Connections->Allow remote start of unlisted programs, in order to select the appropriate setting.
RD Gateway
The same principle applies to the RD Gateway tab. Once a gateway server is configured through the Server Manager in Server 2012 and Server 2012 R2 it will automatically apply to all RemoteApp programs.
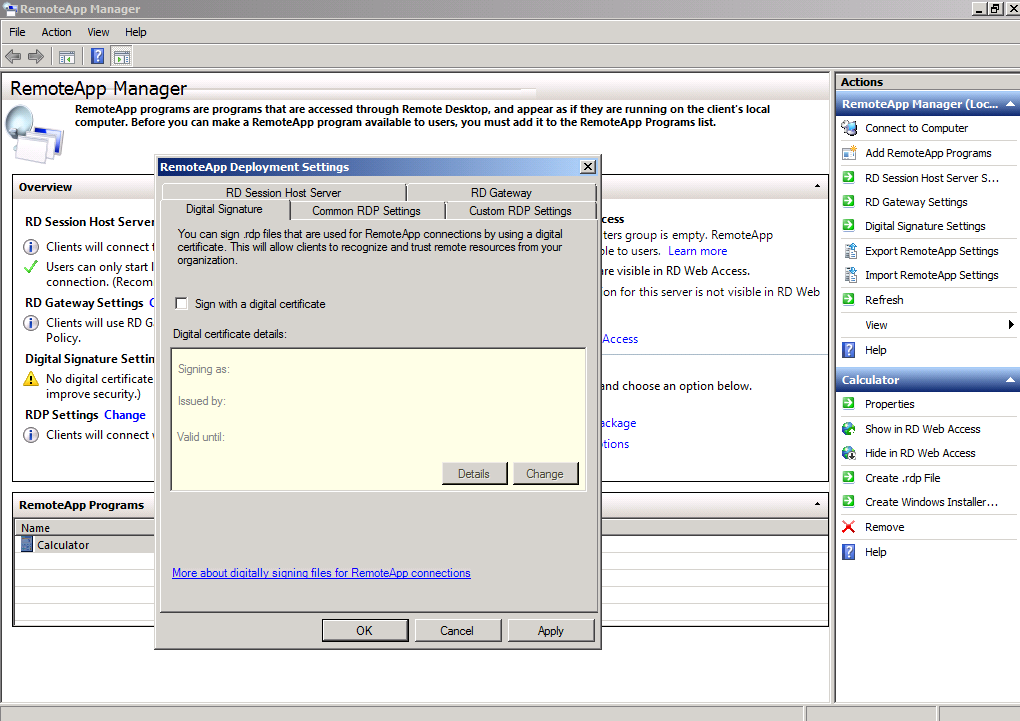
Digital Signature
The digital signature will derive from the certificate settings in the deployment properties.
Common / Custom RDP Settings
The Common RDP Settings and the Custom RDP Settings can be configured per Collection by using the powershell cmdlet Set-RDSessionCollectionConfiguration.
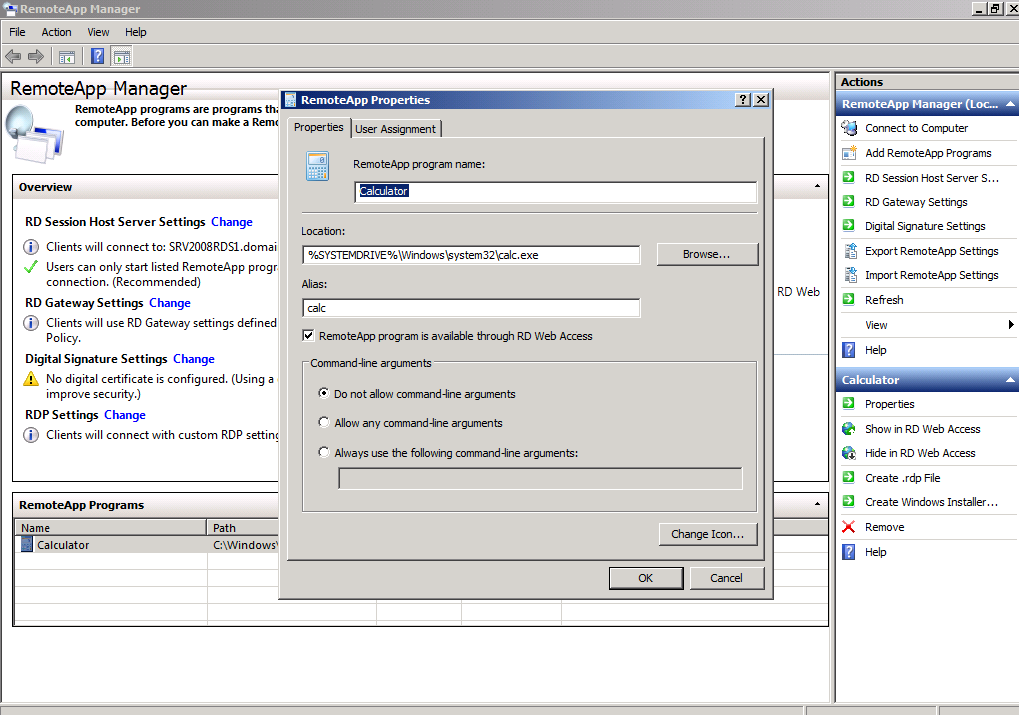
RemoteApp Settings
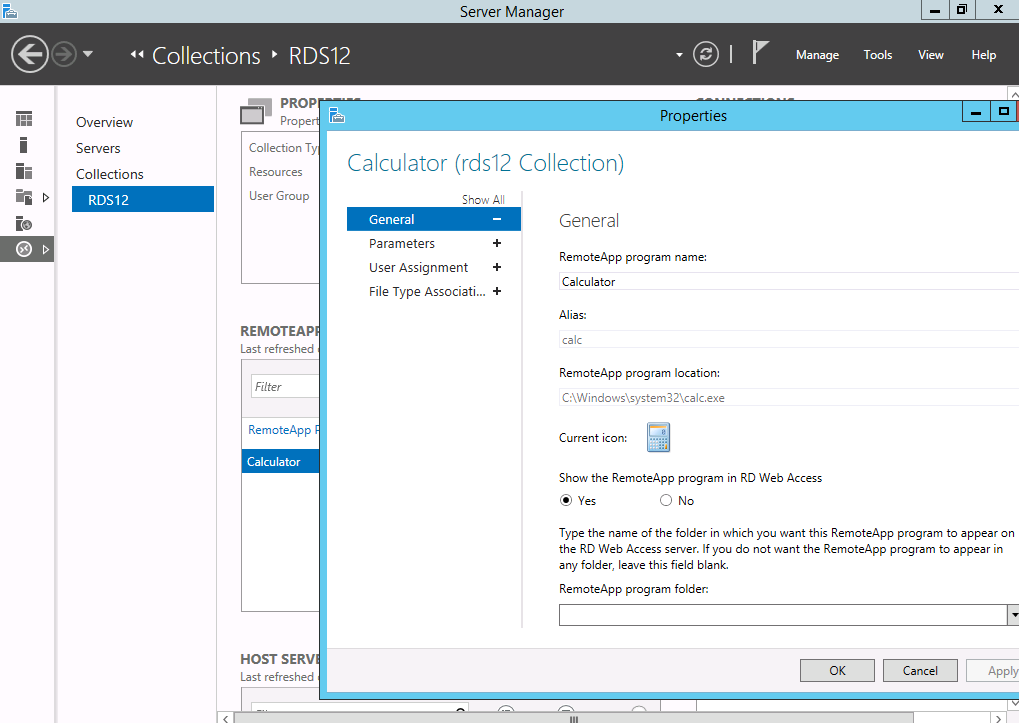
The RemoteApp settings control the Name, visibility and command line arguments as well as the User Assignment.
These settings also exist on Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2. Simply navigate to the collection and on the middle of the page select the RemoteApp you want to change the settings for, right click and choose the appropriate settings.