Azure Databases: SQL vs NoSQL
Introduction
By reading this post, we will be able to compare and choose the right one service for our database deployments (SQL or NoSQL).
Definition
**SQL: **A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a program that lets you create, update, and administer a relational database.
**NoSQL: **NoSQL is a class of database management systems (DBMS) that do not follow all of the rules of a relational DBMS and cannot use traditional SQL to query data.
Types Of Databases
At the tables below we can see the types of SQL and NoSQL databases that are available.
SQL
There are three SQL type of databases SQL Managed Instance, Azure Elastic databases and Azure databases.
| SQL Database Managed Instance | Azure SQL Elastic Database | Azure Database |
| Almost 100% compact with on-premises | Database share resources (CPU, IO, Memory) | Built-in high availability, Disaster Recovery, upgrade |
| Fully Managed PaaS | Good choice for heavy usage or performance peaks | An on-premises application can access data |
| Full Isolation & Security | 3 elastic pools service tiers (Basic, Standard, Premium) | Eliminates hardware and administrative costs |
NoSQL
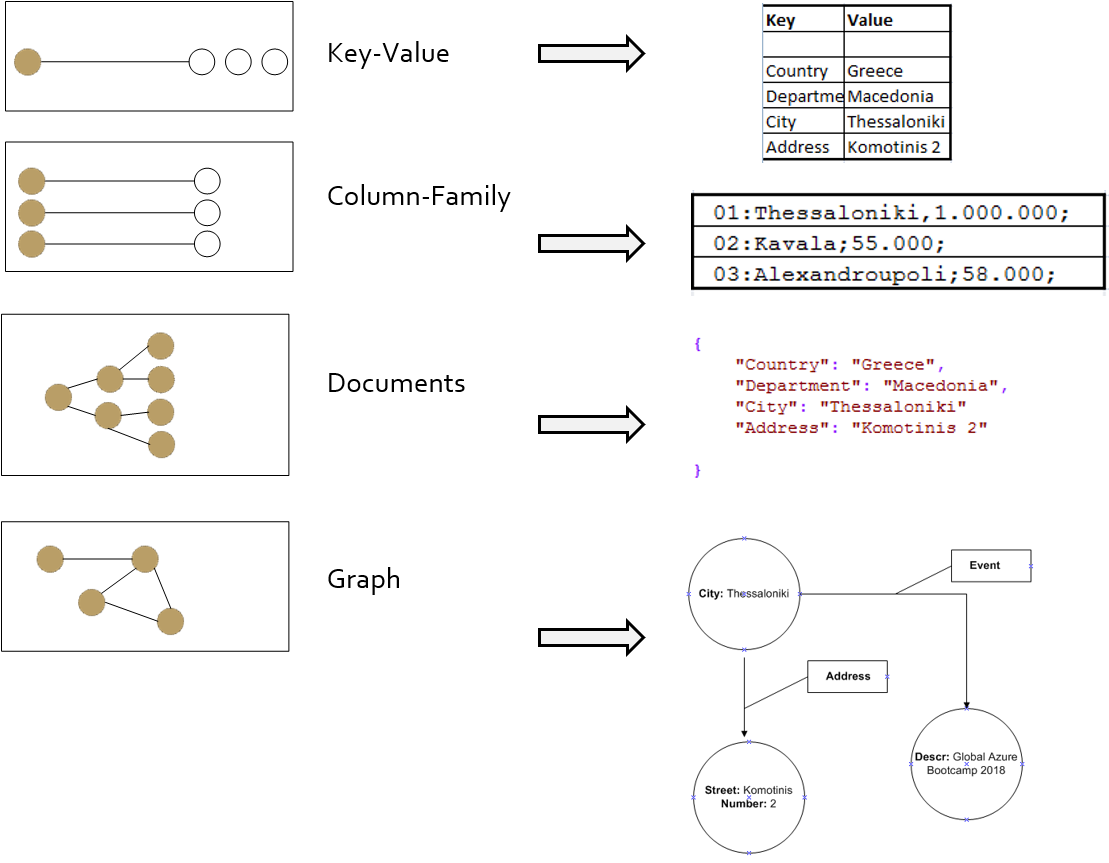
Most common NoSQL types of databases are four, Key Value Store, Document, Column Store, and Graph Database.
|
Key Value Store |
Document |
Column Store | Graph Database |
| Every record is stored as a {key} with a value. | Records stored as “documents”. Key is always strings and values can be string, numeric, Boolean, arrays etc. | Store and process very large amounts of data distributed over many machines | Graph Databases are built with nodes, relationships between nodes and the properties of nodes |
| Mappings are usually accompanied by cache mechanisms to maximize performance | Semi-structured documents can be XML or JSON formatted | Keys point to multiple columns | |
| API is typically simple | Documents can be retrieved with queries |
NoSQL Database Types Diagrams
SQL vs NoSQL
At the table below we can find the differents between SQL and NoSQL databases.
| SQL | NoSQL | |
| Type | Relational | Non-Relational |
| Data | Structured Data stored in Tables | Un-structured stored in JSON files.
** Graph Database support relationship |
| Schema | Static | Dynamic |
| Language | Structure Query Language | Un-Structured Query Language |
| Scalability | Vertical (Scale-up || Scale-down) | Horizontal (Scale-in || Scale-out) |
| Joins | Allow to design complex queries | Do not allow complex queries |
| OLTP | Comfortable | |
| Support | Great Support | Community dependent, they are expanding the support model |
| Integrated Caching | Support In-line memory | Supports Integrated caching |
| Flexible | ||
| Transaction | ACID (Atomic, Consistent, Isolated, Durable) | BASE Compatibility |
| Auto Elasticity | Requires downtime in most cases | Automatic, No outage required |
Benefits
At the tables below we can read about the benefits that SQL and NoSQL databases are offers.
SQL
| SQL | |
| Management | Microsoft offers Performance Dashboard, which allows the visualisation of the database performance |
| Elastic Groups | A database can be scaled up for an intensive process and scaled back after the process has completed. |
| Security | Microsoft integrates security features first in the cloud, e.g. Always Encrypted, Row-level security, Dynamic data masking, authentication, authorization, threat detection, auditing etc. |
| Backup | Automatic Backup, Restore database to point-in-time when TDE is enabled, backups are also encrypted. |
| Performance | Performance is measured in database DTUs (Data Transaction Units = a blended measure of CPU, Memory, I/O) |
| Enterprise Features | New features are added much faster on cloud than on-premise. These features can be, Online indexing, partitioning, compression, column store indexes, in-memory capabilities etc. |
NoSQL
| NoSQL | |
| Scalability | Horizontal scale-out, easy way to reduce capacity quickly |
| Performance | By simply adding resources, enterprises can increase performance NoSQL database. |
| High Availability | NoSQL is by design high available databases, without complexity |
| Global Availability | By automatically replicating data across multiple servers, this minimizes latency and ensure consistent application experience. |
| Flexible Data Modelling | Developers can leverage the data types and query options that are most fit to their application. It offers a more agile development. |
| Pricing | NoSQL databases are a low cost solution in comparison SQL databases. |
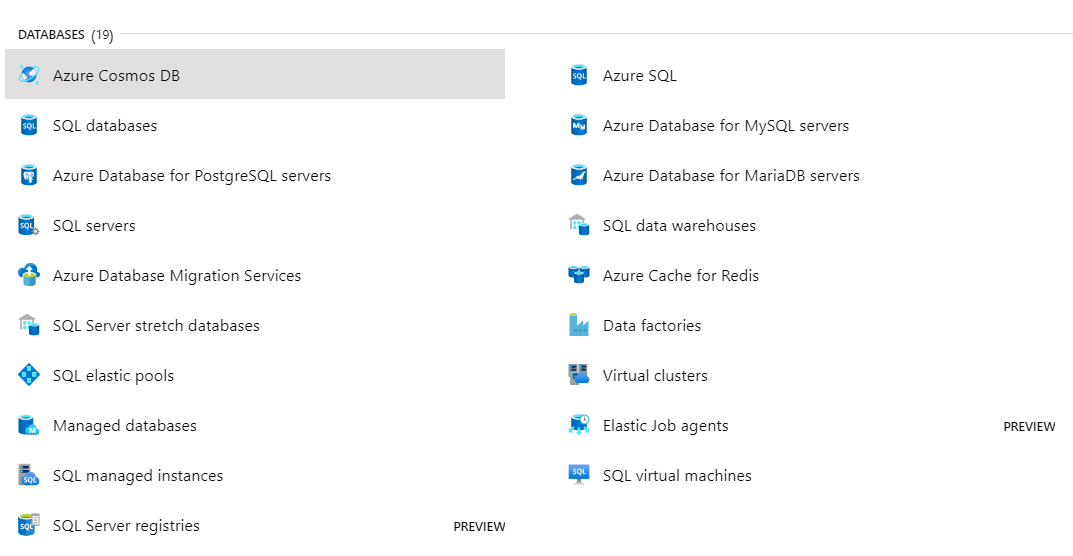
What Azure Offers
At the image below we can see what Database services Azure offers.
NoSQL Azure Databases
- Storage Tables: The Azure Storage service offers highly available storage. Within the Storage service, there is a Tables feature that allows users to create NoSQL entities within a key-value store.
- Azure Cosmos DB: Azure Cosmos DB is an Azure-native database service that focuses on providing a high-performance database regardless of your selected API or data model. Azure Cosmos DB offers multiple APIs and models that can be used interchangeably for various application scenarios.
- Redis Cache: Redis Cache is an implementation of the Redis Database engine that is offered as a service on Azure. Using the Redis Cache service, one could create a cache instance quickly using the key-value based store.
SQL Azure Databases
- Azure SQL Database: Azure SQL Database is a DaaS (Database As A Service) cloud offering by Microsoft. In this service Azure is responsible for database common administration tasks, hypervisors, networking, bare-metal hardware etc. offers automating scale up and scale down resources on demand and finally, the user pays according to their usage of the service.
- **Azure SQL Managed Instance:**This is a fully managed SQL Server instance hosted in Azure Cloud, communicates with on-premise LAN or Azure VNet and provides most SQL Server features to applications.<
- Azure Elastic Pool: Elastic Pool is a set of databases which they shared the resources. This is a quite cost-effective service for deployments with a large number of databases.
How to understand what service to choose
There are three basic questions that we can ask ourselves to get an answer for the type of database that it is better to use on our deployment.
- Does the application work with relatively simple data?
- Did we want a low-cost managed service?
- Does the app need to work with a large amount of data?