Nota
L-aċċess għal din il-paġna jeħtieġ l-awtorizzazzjoni. Tista’ tipprova tidħol jew tibdel id-direttorji.
L-aċċess għal din il-paġna jeħtieġ l-awtorizzazzjoni. Tista’ tipprova tibdel id-direttorji.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides a SQL simulated alert feature that helps organizations and security teams validate deployment and test the preparedness of security teams detection, response, and automation workflows without creating actual security risks.
The simulation injects telemetry records on target machines (Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) or Arc-connected machines) through a custom script extension named Sql-SimulateAlert. The simulated alerts include full runtime context such as host, SQL instance, database, and process information, so you can validate your end-to-end security response flows. This process is safe and non-intrusive, ensuring your resources remain secure.
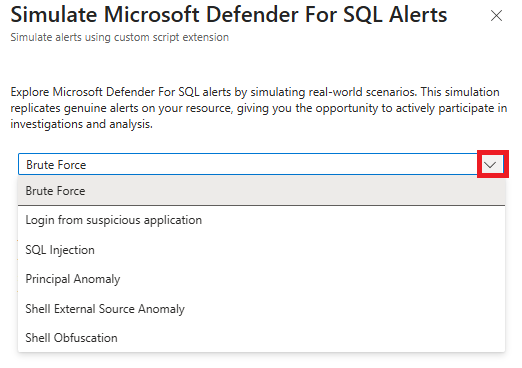
You can simulate the following security scenarios:
- Brute force authentication
- Authentication from suspicious application
- SQL injection
- Principal anomaly
- Shell external source anomaly
- Shell obfuscation
The simulation runs locally on the machine through the Custom Script Extension without executing external malicious payloads. All generated alerts contain complete machine and resource identifiers, SQL instance names, database information, process details, and telemetry data required by playbooks and security automation workflows.
Prerequisites
Enable SQL Servers on Machines plan for Defender for Databases.
Ensure that the target machine, whether a SQL VM or Arc‑connected machine, is successfully protected.
Must have the following role and permission:
- Create an ARM deployment and to write VM extensions: Security Admin or Contributor in the target subscription.
- Contributor permission and Resource Policy contributor to the resource
Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/writeandMicrosoft.Resources/deployments/*.
The SQL Server instance must be configured to allow SQL Authentication for simulation scenarios that require a username and password (some simulation types accept user credentials).
Note
Use an appropriate test SQL username and password rather than a production account.
Simulate alerts
The SqlAlertSimulationClient extracts template parameters from the target resource, including subscription, resource group, machine name, location, and the presence of the Defender extension.
SqlAlertSimulationClient builds an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template that deploys or re-uses a custom script extension on the machine. The extension runs a PowerShell command that invokes the Defender for SQL simulate helper with the requested attack parameters. The helper generates alert telemetry that flows into Defender for Cloud, triggering alerts that downstream automation and mobilization connectors can consume.
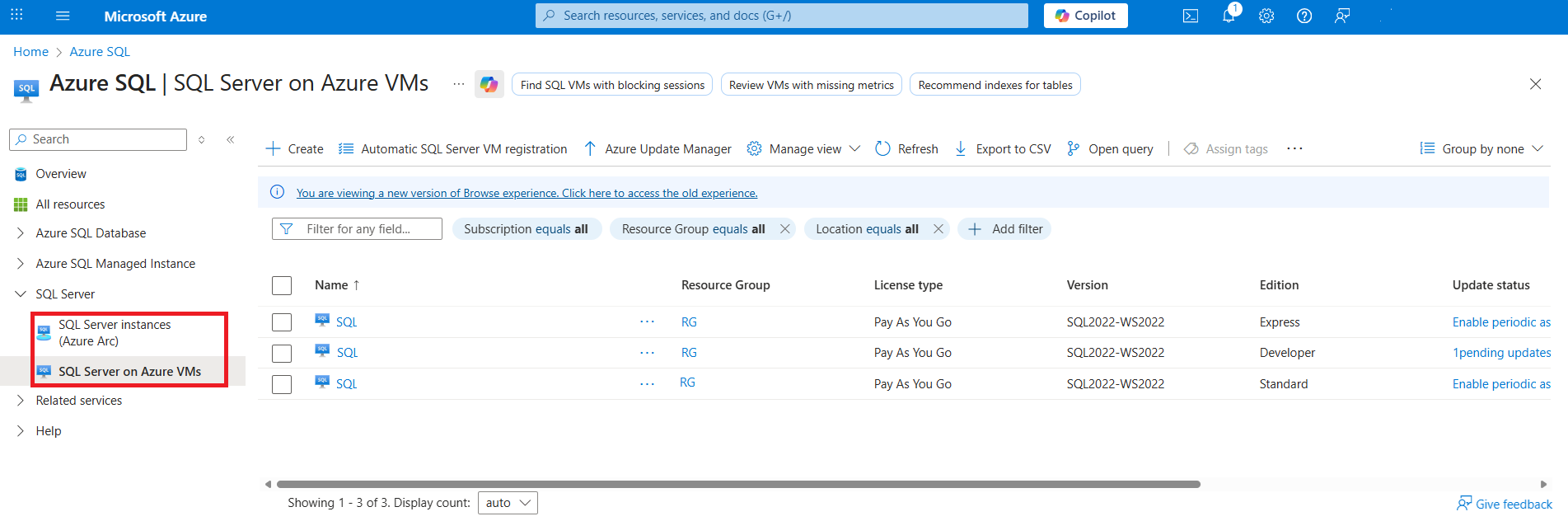
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Search for and select Azure SQL.
Select SQL Server on Azure VMS or SQL Server instances (Azure Arc).
Select the relevant database.
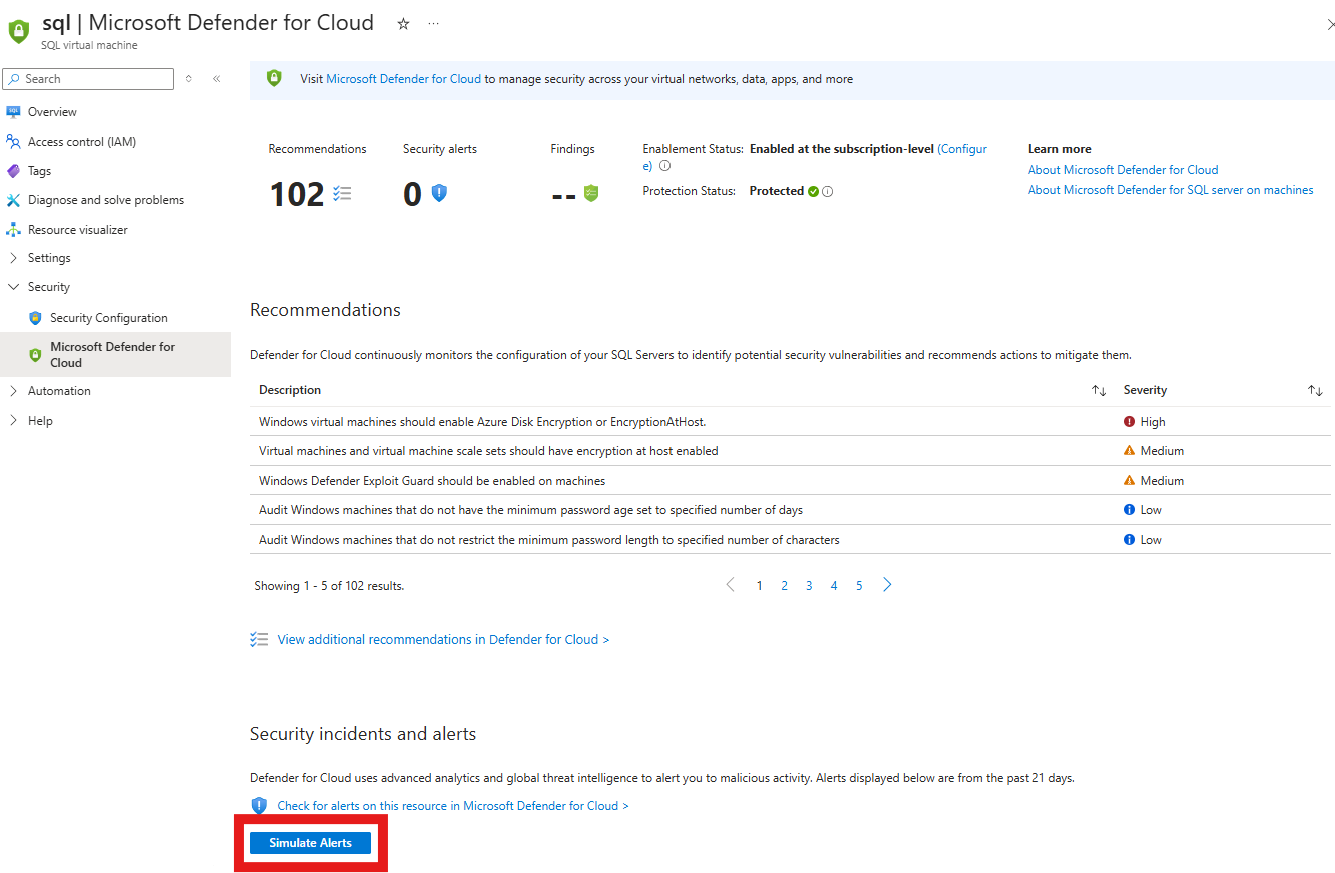
Select Security > Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Select Simulate alert.
Select an alert type.
Enter the required information for the selected alert type. For example, username and password for authentication attacks.
Select Simulate Alert.
The alert appears after a few minutes and you can use it to validate your security monitoring setup.
Verify that the alert is generated
After you simulate an alert, verify that the alert is generated.
In the Azure portal, search for and select Azure SQL.
Select SQL Server on Azure VMS or SQL Server instances (Azure Arc).
Select the relevant database.
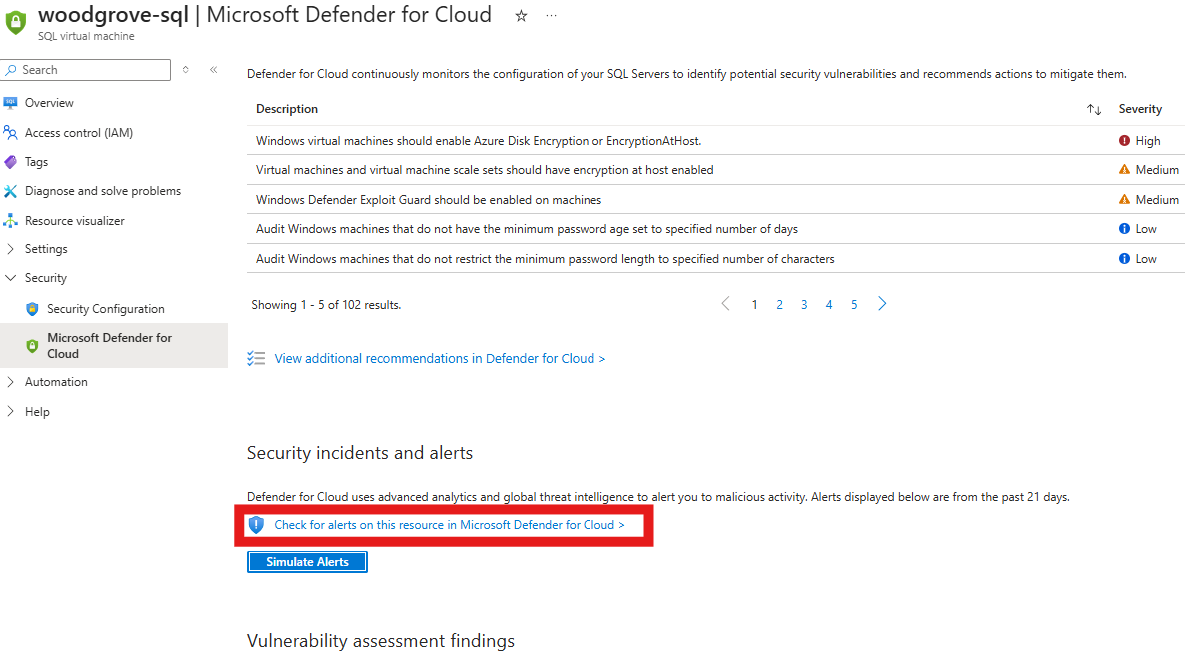
Select Security > Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Select Check for alerts on this resource in Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Verify that the simulated alert appears in the list of alerts for the resource and manage and respond to the security alert.