Nota
L-aċċess għal din il-paġna jeħtieġ l-awtorizzazzjoni. Tista’ tipprova tidħol jew tibdel id-direttorji.
L-aċċess għal din il-paġna jeħtieġ l-awtorizzazzjoni. Tista’ tipprova tibdel id-direttorji.
Controlled folder access helps you protect valuable data from malicious apps and threats, such as ransomware. Controlled folder access is included with Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server 2019. Controlled folder access is also included as part of the modern, unified solution for Windows Server 2012R2 and 2016.
You can enable controlled folder access by using any of these methods:
Tip
Exclusions don't work if you're using data loss prevention (DLP). Do the following steps to investigate:
- Download and install the Defender for Endpoint client analyzer.
- Run a trace for at least five minutes.
- In the resulting
MDEClientAnalyzerResult.zipoutput file, extract the contents of theEventLogsfolder, and search for instances ofDLP EAin the available.evtxlog files.
Prerequisites
Supported operating systems
Windows:
In the Microsoft Intune admin center at https://intune.microsoft.com, go to Endpoint security > Manage > Attack surface reduction. Or, to go directly to the Endpoint security | Attack surface reduction page, use https://intune.microsoft.com/#view/Microsoft_Intune_Workflows/SecurityManagementMenu/~/asr.
On the Policies tab of the Endpoint security | Attack surface reduction page, select Create policy.
On the Create a profile flyout that opens, configure the following settings:
- Platform: Select Windows.
- Profile: Select Attack surface reduction rules.
Select Create.
The Create policy wizard opens. On the Basics tab, configure the following settings:
- Name: Enter a unique, descriptive name for the policy.
- Description: Enter an optional description.
Select Next.
On the Configuration settings tab, scroll down to the Enable Controlled Folder Access section and configured the following settings:
In the box that says Not configured, select Audit Mode.
We recommend enabling controlled folder access in audit mode first to see how it works in your organization. You can set it to another mode, such as Enabled, later.
Controlled Folder Access Protected Folders: Optionally add folders that are protected. Files in these folders can't be modified or deleted by untrusted applications. Default system folders are automatically protected. You can view the list of default system folders in the Windows Security app on a Windows device. To learn more about this setting, see Policy CSP - Defender: ControlledFolderAccessProtectedFolders.
Controlled Folder Access Allowed Applications: Optionally add applications that are trusted to access protected folders. Microsoft Defender Antivirus automatically determines which applications are trusted. Only use this setting to specify more applications. To learn more about this setting, see Policy CSP - Defender: ControlledFolderAccessAllowedApplications.
When you're finished on the Configuration settings tab, select Next.
On the Scope tags tab, the scope tag named Default is select by default, but you can remove it and select other existing scope tags. When you're finished, select Next.
On the Assignments tab, click in the box, select All users, click in the box again, and then select select All Devices. Verify the Target type value is Include for both, and then select Next.
On the Review + create tab, verify the settings, and then select Save.
Note
Wildcards are supported for applications, but not for folders. Allowed apps continue to trigger events until they're restarted.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Use the ./Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config/ControlledFolderAccessProtectedFolders configuration service provider (CSP) to allow apps to make changes to protected folders.
Microsoft Configuration Manager
In Microsoft Configuration Manager, go to Assets and Compliance > Endpoint Protection > Windows Defender Exploit Guard.
Select Home > Create Exploit Guard Policy.
Enter a name and a description, select Controlled folder access, and select Next.
Choose whether block or audit changes, allow other apps, or add other folders, and select Next.
Note
Wildcard is supported for applications, but not for folders. Allowed apps continue to trigger events until they're restarted.
Review the settings and select Next to create the policy.
After the policy is created, Close.
For more information about Microsoft Configuration Manager and Controlled Folder Access, visit Controlled folder access policies and options.
Group Policy
On your Group Policy management device, open the Group Policy Management Console. Right-click the Group Policy Object you want to configure and select Edit.
In the Group Policy Management Editor, go to Computer configuration and select Administrative templates.
Expand the tree to Windows components > Microsoft Defender Antivirus > Microsoft Defender Exploit Guard > Controlled folder access.
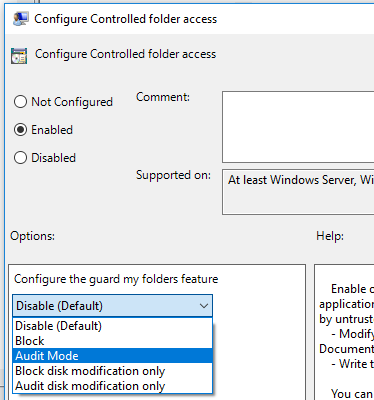
Double-click the Configure Controlled folder access setting and set the option to Enabled. In the options section, you must specify one of the following options:
- Enable - Malicious and suspicious apps aren't allowed to make changes to files in protected folders. A notification is provided in the Windows event log.
- Disable (Default) - The Controlled folder access feature won't work. All apps can make changes to files in protected folders.
- Audit Mode - Changes are allowed if a malicious or suspicious app attempts to make a change to a file in a protected folder. However, it's recorded in the Windows event log where you can assess the impact on your organization.
- Block disk modification only - Attempts by untrusted apps to write to disk sectors are logged in Windows Event log. These logs can be found in Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender > Operational > ID 1123.
- Audit disk modification only - Only attempts to write to protected disk sectors are recorded in the Windows event log (under Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender > Operational > ID 1124). Attempts to modify or delete files in protected folders won't be recorded.
Important
To fully enable controlled folder access, you must set the Group Policy option to Enabled and select Block in the options drop-down menu.
PowerShell
Type powershell in the Start menu, right-click Windows PowerShell and select Run as administrator.
Run the following command:
Set-MpPreference -EnableControlledFolderAccess EnabledYou can enable the feature in audit mode by specifying
AuditModeinstead ofEnabled. UseDisabledto turn off the feature.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see EnableControlledFolderAccess.
See also
- Protect important folders with controlled folder access
- Customize controlled folder access
- Evaluate Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Tech Community.