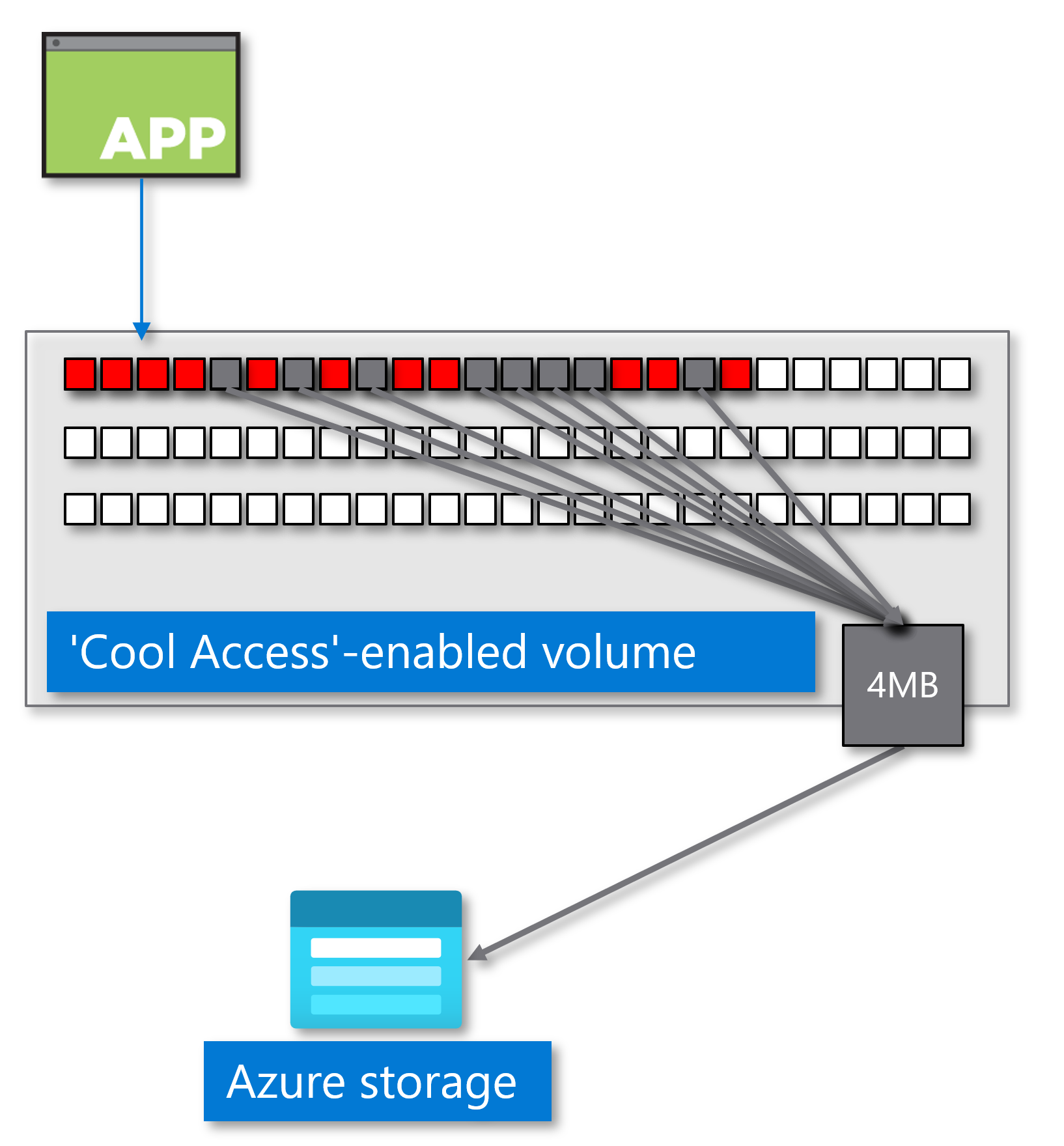
Azure NetApp Files storage with cool access
When you use Azure NetApp Files storage with cool access, you can configure inactive data to move from Azure NetApp Files storage (the hot tier) to an Azure storage account (the cool tier). Enabling cool access moves inactive data blocks from the volume and the volume's snapshots to the cool tier, which results in cost savings.
Most cold data is associated with unstructured data. It can account for more than 50% of the total storage capacity in many storage environments. Infrequently accessed data associated with productivity software, completed projects, and old datasets are an inefficient use of high-performance storage.
Azure NetApp Files supports cool access with three service levels: Standard, Premium, and Ultra.
The following diagram illustrates an application with a volume enabled for cool access.
In the initial write, data blocks are assigned a "warm" temperature value (in the diagram, red data blocks) and exist on the "hot" tier. Because the data resides on the volume, a temperature scan monitors the activity of each block. When a data block is inactive, the temperature scan decreases the value of the block until inactivity reaches the number of days specified in the coolness period. The coolness period lasts between 2 and 183 days. The default value is 31 days.
After data blocks are marked "cold," the tiering scan collects the blocks and packages them into 4-MB objects. Their move to Azure storage is transparent. To the application and users, the cool blocks still appear online. Tiered data appears to be online and continues to be available to users and applications by transparent and automated retrieval from the cool tier.
Note
When you enable cool access, data that satisfies the conditions set by the coolness period moves to the cool tier. For example, if the coolness period is set to 30 days, any data that was cool for at least 30 days moves to the cool tier when you enable cool access.
By default (unless cool access retrieval policy is configured otherwise), data blocks on the cool tier that are read randomly again become "warm" and are moved back to the hot tier. After the data blocks are marked as "warm," they're again subjected to the temperature scan. Large sequential reads (like index and antivirus scans) on inactive data in the cool tier don't "warm" the data. They also don't trigger inactive data so that it moves back to the hot tier.
Metadata is never cooled and always remains in the hot tier. Tiering doesn't affect the activities of metadata-intensive workloads like high file-count environments like chip design, version control systems, and home directories.
Supported regions
Azure NetApp Files storage with cool access is supported for the following regions:
- Australia Central
- Australia Central 2
- Australia East
- Australia Southeast
- Brazil South
- Brazil Southeast
- Canada Central
- Canada East
- Central India
- Central US
- East Asia
- East US
- East US 2
- France Central
- Germany North
- Germany West Central
- Israel Central
- Italy North
- Japan East
- Japan West
- Korea Central
- Korea South
- North Central US
- North Europe
- Norway East
- Norway West
- Qatar Central
- South Africa North
- South Central US
- South India
- Southeast Asia
- Spain Central
- Switzerland North
- Switzerland West
- Sweden Central
- UAE Central
- UAE North
- UK South
- UK West
- US Gov Arizona
- US Gov Texas
- US Gov Virginia
- West Europe
- West US
- West US 2
- West US 3
Metrics
Cool access offers performance metrics to understand usage patterns on a per-volume basis:
- Volume cool tier size
- Volume cool tier data read size
- Volume cool tier data write size
Billing
You can enable tiering at the volume level for a newly created capacity pool. How you're billed is based on:
- The capacity and the service level.
- Unallocated capacity within the capacity pool.
- The capacity in the cool tier.
- Network transfer between the hot tier and the cool tier. The markup on top of the transaction cost (
GETandPUTrequests) on blob storage and private link transfer in either direction between the hot tiers determines the rate.
Billing calculation for a capacity pool is at the hot-tier rate for the data that isn't tiered to the cool tier. Unallocated capacity within the capacity pool is included. When you enable tiering for volumes, the capacity in the cool tier is at the rate of the cool tier. The remaining capacity is at the rate of the hot tier. The rate of the cool tier is lower than the hot tier's rate.
Examples of billing structure
Assume that you created a 4-TiB Standard capacity pool. The billing structure is at the Standard capacity tier rate for the entire 4 TiB.
When you create volumes in the capacity pool and start tiering data to the cool tier, the following scenarios explain the billing structure that applies:
Assume that you create three volumes with 1 TiB each. You don't enable tiering at the volume level. The billing calculation is:
- 3 TiB of allocated capacity at the hot tier rate.
- 1 TiB of unallocated capacity at the hot tier rate.
- Zero capacity at the cool tier rate.
- Zero network transfer between the hot tier and the cool tier. The markup on top of the transaction cost (
GET,PUT) on blob storage and private link transfer in either direction between the hot tiers determines the rate.
Assume that you create four volumes with 1 TiB each. Each volume has 0.25 TiB of the volume capacity on the hot tier and 0.75 TiB of the volume capacity in the cool tier. The billing calculation is:
- 1-TiB capacity at the hot tier rate.
- 3-TiB capacity at the cool tier rate.
- Network transfer between the hot tier and the cool tier. The markup on top of the transaction cost (
GET,PUT) on blob storage and private link transfer in either direction between the hot tiers determines the rate.
Assume that you create two volumes with 1 TiB each. Each volume has 0.25 TiB of the volume capacity on the hot tier and 0.75 TiB of the volume capacity in the cool tier. The billing calculation is:
- 0.5-TiB capacity at the hot tier rate.
- 2 TiB of unallocated capacity at the hot tier rate.
- 1.5-TiB capacity at the cool tier rate.
- Network transfer between the hot tier and the cool tier. The markup on top of the transaction cost (
GET,PUT) on blob storage and private link transfer in either direction between the hot tiers determines the rate.
Assume that you create one volume with 1 TiB. The volume has 0.25 TiB of the volume capacity on the hot tier and 0.75 of the volume capacity in the cool tier. The billing calculation is:
- 0.25-TiB capacity at the hot tier rate.
- 0.75-TiB capacity at the cool tier rate.
- Network transfer between the hot tier and the cool tier. The markup on top of the transaction cost (
GET,PUT) on blob storage and private link transfer in either direction between the hot tiers determines the rate.
Examples of cost calculations with varying coolness periods
This section shows you examples of storage and network transfer costs with varying coolness periods.
In these examples, assume that:
- The hot tier storage cost is $0.000202/GiB/hr. The cool tier storage cost is $0.000082/GiB/hr.
- Network transfer cost (including read or write activities from the cool tier) is $0.020000/GiB.
- A 5-TiB capacity pool with cool access is enabled.
- One TiB of unallocated capacity is within the capacity pool.
- A 4-TiB volume is enabled for cool access.
- After the coolness period, 3 TiB of the 4 TiB is moved to the cool tier.
- Each month, you read or write 20% of data from the cool tier.
- Each month is 30 days or 730 hours. So each day is 730/30 hours.
Important
- Use these calculations only as a reference estimate and not for validating the exact bill amount.
- The rates considered in the examples are for an example region and might be different for your intended region of deployment.
- If data is read from or written to the cool tier, it causes the percentage of data distribution in the hot tier and cool tier to change. The calculations in this article demonstrate initial percentage distribution in the hot and cool tiers, and not after the 20% of data was moved to or from the cool tier.
The following examples include 1 TiB of unallocated space in the capacity pool to show how unallocated space is charged when cool access is enabled. To maximize your savings, the capacity pool size should be reduced to eliminate unallocated pool capacity.
Example 1: Coolness period is set to seven days
Your storage cost for the first month:
| Cost | Description | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Unallocated storage cost for days 1~30 (30 days) | 1 TiB of unallocated storage | 1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 |
| Storage cost for days 1~7 (seven days) | 4 TiB of active data (hot tier) | 4 TiB x 1024 x 7 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $140.93 |
| Storage cost for days 8~30 (23 days) | 1 TiB of active data (hot tier) 3 TiB of inactive data (cool tier) |
1 TiB x 1024 x 23 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $115.77 3 TiB x 1024 x 23 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000082/GiB/hr. = $140.98 |
| Network transfer cost | Moving inactive data to cool tier 20% of data read/write from cool tier |
3 TiB x 1024 x $0.020000/GiB = $61.44 3 TiB x 1024 x 20% x $0.020000/GiB = $12.29 |
| First month total | $622.41 |
Your monthly storage cost for the second and subsequent months:
| Cost | Description | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Storage cost for 30 days | 1 TiB of unallocated storage 1 TiB of active data (hot tier) 3 TiB of inactive data (cool tier) |
1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 3 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000082/GiB/hr. = $183.89 |
| Network transfer cost | 20% of data read/write from cool tier | 3 TiB x 1024 x 20% x $0.020000/GiB = $12.29 |
| Second and subsequent monthly total | $498.18 |
Your first six-month savings:
- Cost without cool access: 5 TiB x 1024 x $0.000202/GiB/hr. x 730 hrs. x 6 months = $4,529.97
- Cost with cool access: First month + Second month + … + Sixth month = $622.41 + (5x $498.18) = $3,113.31
- Savings using cool access: 31.27%
Your first 12-month savings:
- Cost without cool access: 5 TiB x 1024 x $0.000202/GiB/hr. x 730 hrs. x 12 months = $9,059.94
- Cost with cool access: First month + Second month + … + twelfth month = $622.41 + (11 x $498.18) = $6,102.39
- Savings using cool access: 32.64%
Example 2: Coolness period is set to 35 days
All 5 TiB is active data (in hot tier) for the first month. Your storage cost for the first month:
5 TiB x 1024 x 730hr. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $755.00
Your storage cost for the second month:
| Cost | Description | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Unallocated storage cost for days 1~30 (30 days) | 1 TiB of unallocated storage | 1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 |
| Storage cost for days 1~5 (five days) | 4 TiB of active data (hot tier) | 4 TiB x 1024 x 5 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $100.67 |
| Storage cost for days 6~30 (25 days) | 1 TiB of active data (hot tier) 3 TiB of inactive data (cool tier) |
1 TiB x 1024 x 25 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $125.83 3 TiB x 1024 x 25 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000082/GiB/hr. = $153.24 |
| Network transfer cost | Moving inactive data to cool tier 20% of data read/write from cool tier |
3 TiB x 1024 x $0.020000 /GiB = $61.44 3 TiB x 1024 x 20% x $0.020000/GiB = $12.29 |
| Second month total | $604.47 |
Your monthly storage cost for third and subsequent months:
| Cost | Description | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Storage cost for 30 days | 1 TiB of unallocated storage 1 TiB of active data (hot tier) 3 TiB of inactive data (cool tier) |
1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 3 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000082/GiB/hr. = $183.89 |
| Network transfer cost | 20% of data read/write from cool tier | 3 TiB x 1024 x 20% x $0.020000/GiB = $12.29 |
| Third and subsequent monthly total | $498.18 |
Your first six-month savings:
- Cost without cool access: 5 TiB x 1024 x $0.000202/GiB/hr. x 730 hrs. x 6 months = $4,529.97
- Cost with cool access: First month + Second month + … + Sixth month = $755.00 + $604.47 + (4 x $498.18) = $3,352.19
- Savings using cool access: 25.99%
Your first 12-month savings:
- Cost without cool access: 5 TiB x 1024 x $0.000202/GiB/hr. x 730 hrs. x 12 months = $9,059.94
- Cost with cool access: First month + Second month + … + twelfth month = $755.00 + $604.47 + (10 x $498.18) = $6,341.27
- Savings using cool access: 30.00%
Example 3: Coolness period is set to 63 days
All 5 TiB is active data (in hot tier) for the first two months. Your monthly storage cost for the first and second months: 5 TiB x 1024 x 730hr. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $755.00
Your storage cost for the third month:
| Cost | Description | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Unallocated storage cost for days 1~30 (30 days) | 1 TiB of unallocated storage | 1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 |
| Storage cost for days 1~3 (three days) | 4 TiB of active data (hot tier) | 4 TiB x 1024 x 3 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $60.40 |
| Storage cost for days 4~30 (27 days) | 1 TiB of active data (hot tier) 3 TiB of inactive data (cool tier) |
1 TiB x 1024 x 27 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $135.90 3 TiB x 1024 x 27 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000082/GiB/hr. = $165.50 |
| Network transfer cost | Moving inactive data to cool tier 20% of data read/write from cool tier |
3 TiB x 1024 x $0.020000/GiB = $61.44 3 TiB x 1024 x 20% x $0.020000/GiB = $12.29 |
| Third month total | $586.52 |
Your monthly storage cost for the fourth and subsequent months:
| Cost | Description | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Storage cost for 30 days | 1 TiB of unallocated storage 1 TiB of active data (hot tier) 3 TiB of inactive data (cool tier) |
1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 1 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000202/GiB/hr. = $151.00 3 TiB x 1024 x 30 days x 730/30 hrs. x $0.000082/GiB/hr. = $183.89 |
| Network transfer cost | 20% of data read/write from cool tier | 3 TiB x 1024 x 20% x $0.020000/GiB = $12.29 |
| Fourth and subsequent monthly total | $498.18 |
Your first six-month savings:
- Cost without cool access: 5 TiB x 1024 x $0.000202/GiB/hr. x 730 hrs. x 6 months = $4,529.97
- Cost with cool access: First month + Second month + … + Sixth month = (2 x $755.00) + $586.52 + (3 x $498.18) = $3,591.06
- Savings using cool access: 20.73%
Your first 12-month savings:
- Cost without cool access: 5 TiB x 1024 x $0.000202/GiB/hr. x 730 hrs. x 12 months = $9,059.94
- Cost with cool access: First month + Second month + … + twelfth month = (2 x $755.00) + $586.52 + (9 x $498.18) = $6,580.14
- Savings using cool access: 27.37%
Tip
You can use the Azure NetApp Files storage with cool access cost savings estimator to interactively estimate cost savings based on changeable input parameters.