Native document support for Azure AI Language (preview)
Important
Native document support is a gated preview. To request access to the native document support feature, complete and submit the Apply for access to Language Service previews form.
Azure AI Language public preview releases provide early access to features that are in active development.
Features, approaches, and processes may change, prior to General Availability (GA), based on user feedback.
Azure AI Language is a cloud-based service that applies Natural Language Processing (NLP) features to text-based data. The native document support capability enables you to send API requests asynchronously, using an HTTP POST request body to send your data and HTTP GET request query string to retrieve the status results. Your processed documents are located in your Azure Blob Storage target container.
A native document refers to the file format used to create the original document such as Microsoft Word (docx) or a portable document file (pdf). Native document support eliminates the need for text preprocessing before using Azure AI Language resource capabilities. Currently, native document support is available for the following capabilities:
Personally Identifiable Information (PII). The PII detection feature can identify, categorize, and redact sensitive information in unstructured text. The
PiiEntityRecognitionAPI supports native document processing.Document summarization. Document summarization uses natural language processing to generate extractive (salient sentence extraction) or abstractive (contextual word extraction) summaries for documents. Both
AbstractiveSummarizationandExtractiveSummarizationAPIs support native document processing.
Supported document formats
Applications use native file formats to create, save, or open native documents. Currently PII and Document summarization capabilities supports the following native document formats:
| File type | File extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Text | .txt |
An unformatted text document. |
| Adobe PDF | .pdf |
A portable document file formatted document. |
| Microsoft Word | .docx |
A Microsoft Word document file. |
Input guidelines
Supported file formats
| Type | support and limitations |
|---|---|
| PDFs | Fully scanned PDFs aren't supported. |
| Text within images | Digital images with embedded text aren't supported. |
| Digital tables | Tables in scanned documents aren't supported. |
Document Size
| Attribute | Input limit |
|---|---|
| Total number of documents per request | ≤ 20 |
| Total content size per request | ≤ 1 MB |
Include native documents with an HTTP request
Let's get started:
For this project, we use the cURL command line tool to make REST API calls.
Note
The cURL package is pre-installed on most Windows 10 and Windows 11 and most macOS and Linux distributions. You can check the package version with the following commands: Windows:
curl.exe -VmacOScurl -VLinux:curl --versionIf cURL isn't installed, here are installation links for your platform:
An active Azure account. If you don't have one, you can create a free account.
An Azure Blob Storage account. You also need to create containers in your Azure Blob Storage account for your source and target files:
- Source container. This container is where you upload your native files for analysis (required).
- Target container. This container is where your analyzed files are stored (required).
A single-service Language resource (not a multi-service Azure AI services resource):
Complete the Language resource project and instance details fields as follows:
Subscription. Select one of your available Azure subscriptions.
Resource Group. You can create a new resource group or add your resource to a pre-existing resource group that shares the same lifecycle, permissions, and policies.
Resource Region. Choose Global unless your business or application requires a specific region. If you're planning on using a system-assigned managed identity (RBAC) for authentication, choose a geographic region like West US.
Name. Enter the name you chose for your resource. The name you choose must be unique within Azure.
Pricing tier. You can use the free pricing tier (
Free F0) to try the service, and upgrade later to a paid tier for production.Select Review + Create.
Review the service terms and select Create to deploy your resource.
After your resource successfully deploys, select Go to resource.
Retrieve your key and language service endpoint
Requests to the Language service require a read-only key and custom endpoint to authenticate access.
If you created a new resource, after it deploys, select Go to resource. If you have an existing language service resource, navigate directly to your resource page.
In the left rail, under Resource Management, select Keys and Endpoint.
You can copy and paste your
keyand yourlanguage service instance endpointinto the code samples to authenticate your request to the Language service. Only one key is necessary to make an API call.
Create Azure Blob Storage containers
Create containers in your Azure Blob Storage account for source and target files.
- Source container. This container is where you upload your native files for analysis (required).
- Target container. This container is where your analyzed files are stored (required).
Authentication
Your Language resource needs granted access to your storage account before it can create, read, or delete blobs. There are two primary methods you can use to grant access to your storage data:
Shared access signature (SAS) tokens. User delegation SAS tokens are secured with Microsoft Entra credentials. SAS tokens provide secure, delegated access to resources in your Azure storage account.
Managed identity role-based access control (RBAC). Managed identities for Azure resources are service principals that create a Microsoft Entra identity and specific permissions for Azure managed resources.
For this project, we authenticate access to the source location and target location URLs with Shared Access Signature (SAS) tokens appended as query strings. Each token is assigned to a specific blob (file).

- Your source container or blob must designate read and list access.
- Your target container or blob must designate write and list access.
Tip
Since we're processing a single file (blob), we recommend that you delegate SAS access at the blob level.
Request headers and parameters
| parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-X POST <endpoint> |
Specifies your Language resource endpoint for accessing the API. |
--header Content-Type: application/json |
The content type for sending JSON data. |
--header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key:<key> |
Specifies the Language resource key for accessing the API. |
-data |
The JSON file containing the data you want to pass with your request. |
The following cURL commands are executed from a BASH shell. Edit these commands with your own resource name, resource key, and JSON values. Try analyzing native documents by selecting the Personally Identifiable Information (PII) or Document Summarization code sample project:
PII Sample document
For this quickstart, you need a source document uploaded to your source container. You can download our Microsoft Word sample document or Adobe PDF for this project. The source language is English.
Build the POST request
Using your preferred editor or IDE, create a new directory for your app named
native-document.Create a new json file called pii-detection.json in your native-document directory.
Copy and paste the following Personally Identifiable Information (PII) request sample into your
pii-detection.jsonfile. Replace{your-source-container-SAS-URL}and{your-target-container-SAS-URL}with values from your Azure portal Storage account containers instance:
Request sample
{
"displayName": "Extracting Location & US Region",
"analysisInput": {
"documents": [
{
"language": "en-US",
"id": "Output-excel-file",
"source": {
"location": "{your-source-blob-with-SAS-URL}"
},
"target": {
"location": "{your-target-container-with-SAS-URL}"
}
}
]
},
"tasks": [
{
"kind": "PiiEntityRecognition",
"parameters":{
"excludePiiCategories" : ["PersonType", "Category2", "Category3"],
"redactionPolicy": "UseRedactionCharacterWithRefId"
}
}
]
}
The source
locationvalue is the SAS URL for the source document (blob), not the source container SAS URL.The
redactionPolicypossible values areUseRedactionCharacterWithRefId(default) orUseEntityTypeName. For more information, see PiiTask Parameters.
Run the POST request
Here's the preliminary structure of the POST request:
POST {your-language-endpoint}/language/analyze-documents/jobs?api-version=2023-11-15-previewBefore you run the POST request, replace
{your-language-resource-endpoint}and{your-key}with the values from your Azure portal Language service instance.Important
Remember to remove the key from your code when you're done, and never post it publicly. For production, use a secure way of storing and accessing your credentials like Azure Key Vault. For more information, see Azure AI services security.
PowerShell
cmd /c curl "{your-language-resource-endpoint}/language/analyze-documents/jobs?api-version=2023-11-15-preview" -i -X POST --header "Content-Type: application/json" --header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: {your-key}" --data "@pii-detection.json"command prompt / terminal
curl -v -X POST "{your-language-resource-endpoint}/language/analyze-documents/jobs?api-version=2023-11-15-preview" --header "Content-Type: application/json" --header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: {your-key}" --data "@pii-detection.json"Here's a sample response:
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted Content-Length: 0 operation-location: https://{your-language-resource-endpoint}/language/analyze-documents/jobs/f1cc29ff-9738-42ea-afa5-98d2d3cabf94?api-version=2023-11-15-preview apim-request-id: e7d6fa0c-0efd-416a-8b1e-1cd9287f5f81 x-ms-region: West US 2 Date: Thu, 25 Jan 2024 15:12:32 GMT
POST response (jobId)
You receive a 202 (Success) response that includes a read-only Operation-Location header. The value of this header contains a jobId that can be queried to get the status of the asynchronous operation and retrieve the results using a GET request:
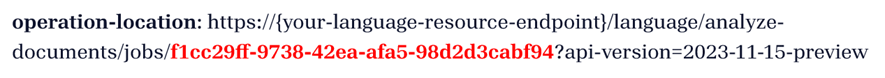
Get analyze results (GET request)
After your successful POST request, poll the operation-location header returned in the POST request to view the processed data.
Here's the preliminary structure of the GET request:
GET {your-language-endpoint}/language/analyze-documents/jobs/{jobId}?api-version=2023-11-15-previewBefore you run the command, make these changes:
Replace {jobId} with the Operation-Location header from the POST response.
Replace {your-language-resource-endpoint} and {your-key} with the values from your Language service instance in the Azure portal.
Get request
cmd /c curl "{your-language-resource-endpoint}/language/analyze-documents/jobs/{jobId}?api-version=2023-11-15-preview" -i -X GET --header "Content-Type: application/json" --header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: {your-key}"
curl -v -X GET "{your-language-resource-endpoint}/language/analyze-documents/jobs/{jobId}?api-version=2023-11-15-preview" --header "Content-Type: application/json" --header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: {your-key}"
Examine the response
You receive a 200 (Success) response with JSON output. The status field indicates the result of the operation. If the operation isn't complete, the value of status is "running" or "notStarted", and you should call the API again, either manually or through a script. We recommend an interval of one second or more between calls.
Sample response
{
"jobId": "f1cc29ff-9738-42ea-afa5-98d2d3cabf94",
"lastUpdatedDateTime": "2024-01-24T13:17:58Z",
"createdDateTime": "2024-01-24T13:17:47Z",
"expirationDateTime": "2024-01-25T13:17:47Z",
"status": "succeeded",
"errors": [],
"tasks": {
"completed": 1,
"failed": 0,
"inProgress": 0,
"total": 1,
"items": [
{
"kind": "PiiEntityRecognitionLROResults",
"lastUpdateDateTime": "2024-01-24T13:17:58.33934Z",
"status": "succeeded",
"results": {
"documents": [
{
"id": "doc_0",
"source": {
"kind": "AzureBlob",
"location": "https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/sample-input/input.pdf"
},
"targets": [
{
"kind": "AzureBlob",
"location": "https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/sample-output/df6611a3-fe74-44f8-b8d4-58ac7491cb13/PiiEntityRecognition-0001/input.result.json"
},
{
"kind": "AzureBlob",
"location": "https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/sample-output/df6611a3-fe74-44f8-b8d4-58ac7491cb13/PiiEntityRecognition-0001/input.docx"
}
],
"warnings": []
}
],
"errors": [],
"modelVersion": "2023-09-01"
}
}
]
}
}
Upon successful completion:
- The analyzed documents can be found in your target container.
- The successful POST method returns a
202 Acceptedresponse code indicating that the service created the batch request. - The POST request also returned response headers including
Operation-Locationthat provides a value used in subsequent GET requests.
Clean up resources
If you want to clean up and remove an Azure AI services subscription, you can delete the resource or resource group. Deleting the resource group also deletes any other resources associated with it.