Enable Azure AI Custom Translator through Azure Virtual Network
In this article, we show you how to set up and use VNet service endpoints with Custom Translator.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) service endpoints securely connect your Azure service resources to your virtual networks over an optimized route via the Azure global network. Service endpoints enable private IP addresses within your virtual network to reach the endpoint of an Azure service without the need for a public IP address on the virtual network.
For more information, see Azure Virtual Network overview
Note
Before you start, review how to use virtual networks with Azure AI services.
To set up a Translator resource for VNet service endpoint scenarios, you need the resources:
- A regional Translator resource (global isn't supported).
VNetand networking settings for the Translator resource.
Configure virtual networks resource networking settings
To start, you need to add all virtual networks that are allowed access via the service endpoint to the Translator resource networking properties. To enable access to a Translator resource via the VNet, you need to enable the Microsoft.CognitiveServices service endpoint type for the required subnets of your virtual network. Doing so routes all subnet traffic related to Azure AI services through the private global network. If you intend to access any other Azure AI services resources from the same subnet, make sure these resources are also configured to allow your virtual network.
Note
- If a virtual network isn't added as allowed in the Translator resource networking properties, it doesn't have access to the Translator resource via the service endpoint, even if the
Microsoft.CognitiveServicesservice endpoint is enabled for the virtual network. - If the service endpoint is enabled but the virtual network isn't allowed, the Translator resource isn't accessible for the virtual network through a public IP address. This restriction applies regardless of your other network security settings.
- Enabling the
Microsoft.CognitiveServicesendpoint routes all traffic related to Azure AI services through the private global network. Thus, the virtual network should be explicitly allowed to access the resource. - This guidance applies for all Azure AI services resources, not just for Translator resources.
Let's get started:
Navigate to the Azure portal and sign in to your Azure account.
Select a regional Translator resource.
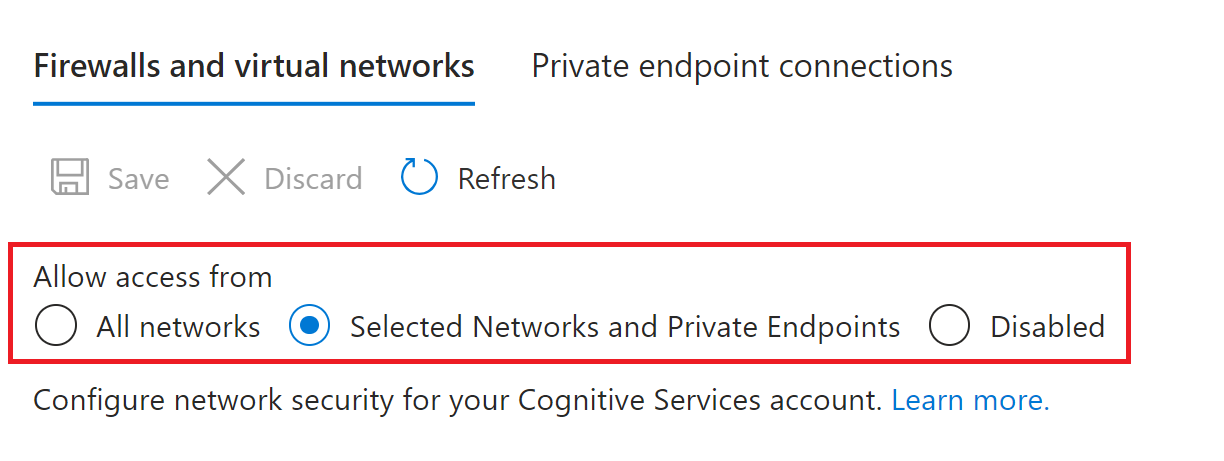
From the Resource Management group in the left side panel, select Networking.
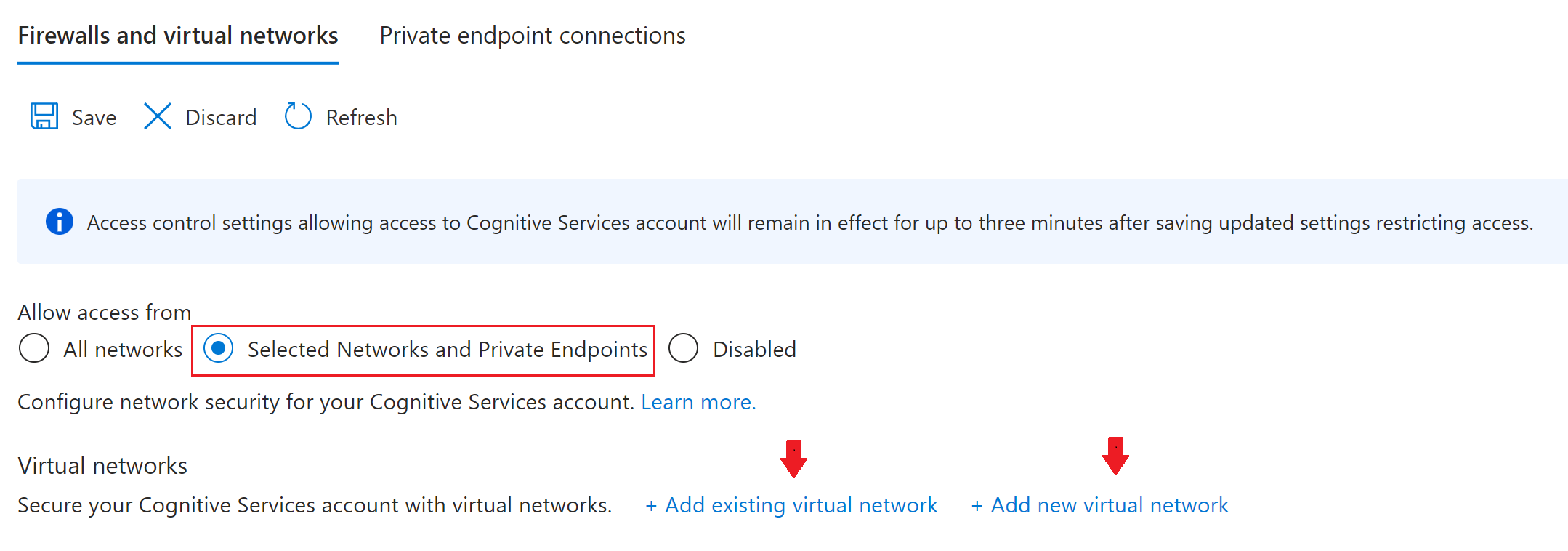
From the Firewalls and virtual networks tab, choose Selected Networks and Private Endpoints.
Note
To use Virtual Network service endpoints, you need to select the Selected Networks and Private Endpoints network security option. No other options are supported.
Select Add existing virtual network or Add new virtual network and provide the required parameters.
Complete the process by selecting Add for an existing virtual network or Create for a new one.
If you add an existing virtual network, the
Microsoft.CognitiveServicesservice endpoint is automatically enabled for the selected subnets.If you create a new virtual network, the default subnet is automatically configured to the
Microsoft.CognitiveServicesservice endpoint. This operation can take few minutes.
Note
As described in the previous section, when you configure a virtual network as allowed for the Translator resource, the
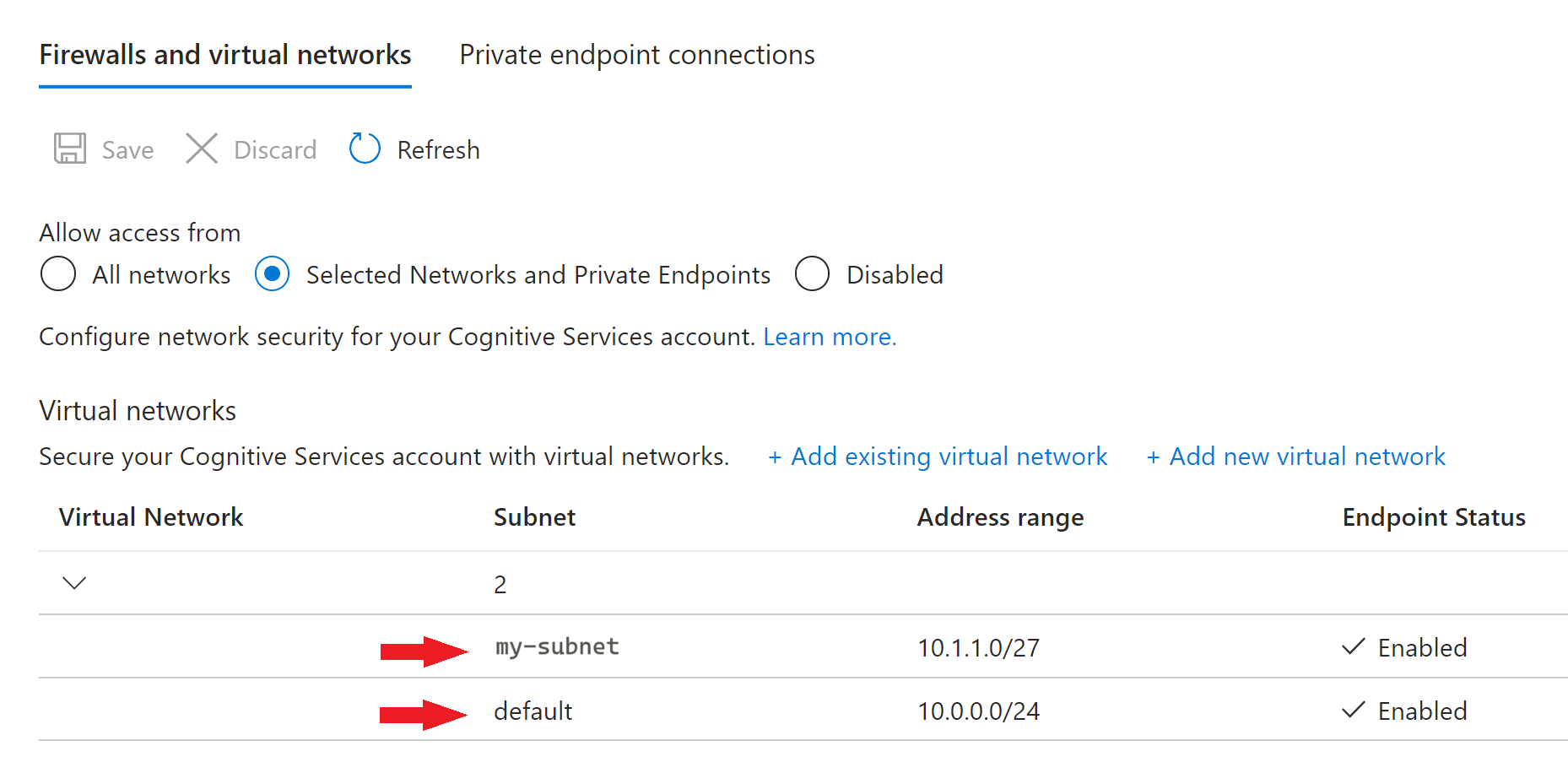
Microsoft.CognitiveServicesservice endpoint is automatically enabled. If you later disable it, you need to re-enable it manually to restore the service endpoint access to the Translator resource (and to a subset of other Azure AI services resources).Now, when you choose the Selected Networks and Private Endpoints tab, you can see your enabled virtual network and subnets under the Virtual networks section.
How to check the service endpoint
From the Resource Management group in the left side panel, select Networking.
Select your virtual network and then select the desired subnet.
A new Subnets window appears.
Select Service endpoints from the Settings menu located on the left side panel.
From the Settings menu in the left side panel, choose Service Endpoints and, in the main window, check that your virtual network subnet is included in the
Microsoft.CognitiveServiceslist.
Use the Custom Translator portal
The following table describes Custom Translator project accessibility per Translator resource Networking → Firewalls and virtual networks security setting:
Important
If you configure Selected Networks and Private Endpoints via the Networking → Firewalls and virtual networks tab, you can't use the Custom Translator portal to create workspaces to train and publish models. However, you can still use the Translator resource with Custom Translator non-interactive REST API to build and publish custom models.
| Translator resource network security setting | Custom Translator portal accessibility |
|---|---|
| All networks | • No restrictions |
| Selected Networks and Private Endpoints | • Not accessible. Use Custom Translator non-interactive REST API to build and publish custom models. |
| Disabled | • Not accessible |
To use Custom Translator without relaxing network access restrictions on your production Translator resource, consider this workaround:
Create another Translator resource for development that can be used on a public network.
Prepare your custom model in the Custom Translator portal on the development resource.
Copy the model on your development resource to your production resource using Custom Translator non-interactive REST API
workspaces→copy authorization and models→copy functions.
Billing region codes
Use a billing region code, listed in the following table, with the 'Create a workspace' API for each supported billing region:
Create a workspace POST request
curl -X POST "https://<resource-name>.cognitiveservices.azure.com/translator/customtranslator/api/texttranslator/v1.0/workspaces" --header "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key:<resource-key>" --data "{'Name': '<workspace-name>', 'Subscription': {'SubscriptionKey': '<resource-key>', 'BillingRegionCode': '<billing-region-code>' }}"
Supported billing code regions and codes
| Billing Region Name | Billing Region Code |
|---|---|
| East Asia | AE |
| Southeast Asia | ASE |
| Australia East | AUE |
| Brazil South | BRS |
| Canada Central | CAC |
| France Central | FC |
| Global | GBL |
| Central India | INC |
| Japan East | JPE |
| Japan West | JPW |
| Korea Central | KC |
| North Europe | NEU |
| South Africa North | SAN |
| Sweden Central | SWC |
| UAE North | UAEN |
| UK South | UKS |
| Central US | USC |
| East US | USE |
| East US 2 | USE2 |
| North Central US | USNC |
| South Central US | USSC |
| West US | USW |
| West US 2 | USW2 |
| West Central US | USWC |
| West Europe | WEU |
Congratulations! You learned how to use Azure VNet service endpoints with Custom Translator.
Learn more
Visit the Custom Translator API page to view our non-interactive REST APIs.