Azure AI services on Azure Government
This article provides developer guidance for using Computer Vision, Face API, Text Analytics, and Translator Azure AI services. For feature variations and limitations, see Compare Azure Government and global Azure.
Prerequisites
Note
We recommend that you use the Azure Az PowerShell module to interact with Azure. To get started, see Install Azure PowerShell. To learn how to migrate to the Az PowerShell module, see Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Az.
- Install and Configure Azure PowerShell
- Connect PowerShell with Azure Government
Provision Azure AI services accounts
In order to access any of the Azure AI services APIs, you must first provision an Azure AI services account for each of the APIs you want to access. You can create Azure AI services in the Azure Government portal, or you can use Azure PowerShell to access the APIs and services as described in this article.
Note
You must go through the process of creating an account and retrieving account key (explained below) for each of the APIs you want to access.
Make sure that you have the Cognitive Services resource provider registered on your account.
You can do this by running the following PowerShell command:
Get-AzResourceProviderIf you do not see
Microsoft.CognitiveServices, you have to register the resource provider by running the following command:Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.CognitiveServicesIn the PowerShell command below, replace
<rg-name>,<name-of-your-api>, and<location-of-resourcegroup>with your relevant account information.Replace the
type of APItag with any of the following APIs you want to access:- ComputerVision
- Face
- Language
- TextTranslation
- OpenAI
New-AzCognitiveServicesAccount -ResourceGroupName '<rg-name>' -name '<name-of-your-api>' -Type <type of API> -SkuName S0 -Location '<location-of-resourcegroup>'Example:
New-AzCognitiveServicesAccount -ResourceGroupName 'resourcegrouptest' -name 'myFaceAPI' -Type Face -SkuName S0 -Location 'usgovvirginia'After you run the command, you should see something like this:
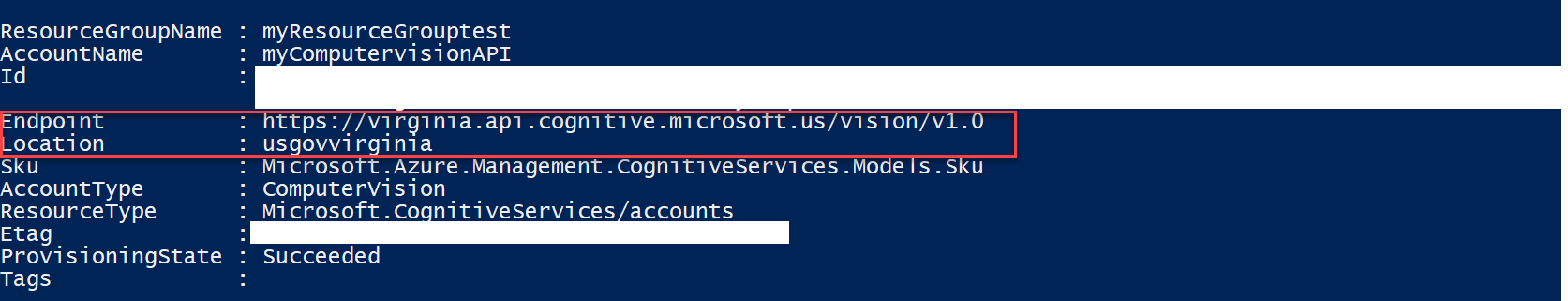
Copy and save the "Endpoint" attribute somewhere as you will need it when making calls to the API.
Retrieve account key
You must retrieve an account key to access the specific API.
In the PowerShell command below, replace the <youraccountname> tag with the name that you gave the Account that you created above. Replace the rg-name tag with the name of your resource group.
Get-AzCognitiveServicesAccountKey -Name <youraccountname> -ResourceGroupName 'rg-name'
Example:
Get-AzCognitiveServicesAccountKey -Name myFaceAPI -ResourceGroupName 'resourcegrouptest'
Copy and save the first key somewhere as you will need it to make calls to the API.

Now you are ready to make calls to the APIs.
Follow API quickstarts
The quickstarts below will help you to get started with the APIs available through Azure AI services in Azure Government.
Note
The URI for accessing Azure AI Services resources in Azure Government is different than in Azure. For a list of Azure Government endpoints, see Compare Azure Government and global Azure.
- Azure AI Vision | quickstart
- Azure Face | quickstart
- Azure AI Language | quickstart
- Azure AI Translator | quickstart
Note
Virtual Network support for Translator service is limited to only
US Gov Virginiaregion. The URI for accessing the API is:https://<your-custom-domain>.cognitiveservices.azure.us/translator/text/v3.0- You can find your custom domain endpoint in the overview blade on the Azure Government portal once the resource is created.
There are two regions:
US Gov VirginiaandUS Gov Arizona.
- Azure OpenAI | quickstart
Next Steps
- Subscribe to the Azure Government blog
- Get help on Stack Overflow by using the "azure-gov" tag