Use Change Analysis (classic)
Important
Azure Monitor Change Analysis (classic) will be retired October 31, 2025. The experience will be replaced by the Change Analysis API powered by Azure Resource Graph. Learn more about the future of Change Analysis and how to migrate to Azure Resource Graph.
While standard monitoring solutions might alert you to a live site issue, outage, or component failure, they often don't explain the cause. Let's say your site worked five minutes ago, and now it's broken. What changed in the last five minutes?
Change Analysis (classic) is designed to answer that question in Azure Monitor.
Building on the power of Azure Resource Graph, Change Analysis (classic):
- Provides insights into your Azure application changes.
- Increases observability.
- Reduces mean time to repair (MTTR).
Note
Change Analysis (classic) is currently only available in Public Azure Cloud.
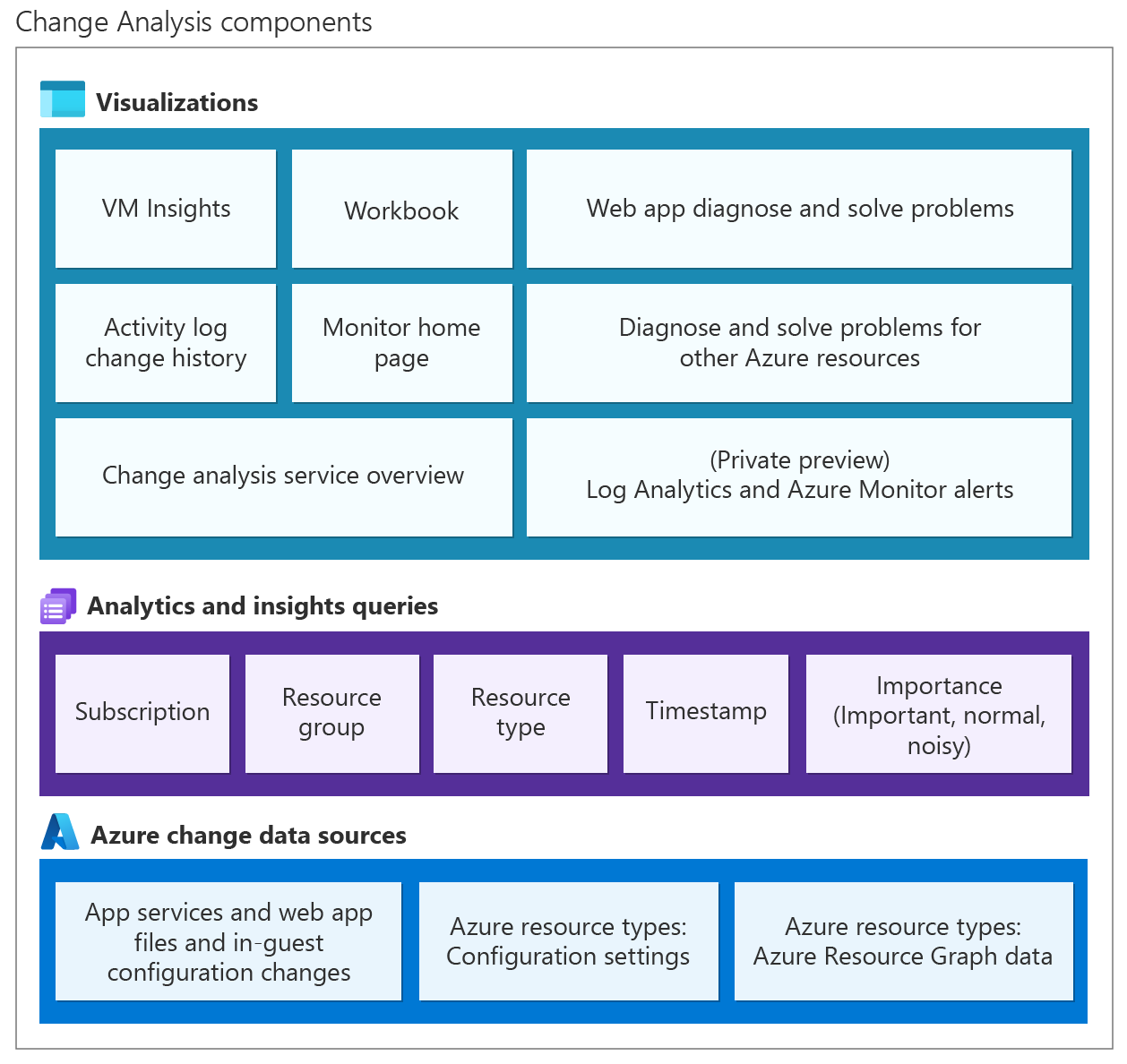
Change Analysis (classic) architecture
Change Analysis (classic) detects various types of changes, from the infrastructure layer through application deployment. A subscription-level Azure resource provider, it:
- Checks resource changes in the subscription.
- Provides data for various diagnostic tools to help users understand what changes caused issues.
The following diagram illustrates the architecture of Change Analysis (classic):
Supported resource types
Change Analysis (classic) service supports resource property level changes in all Azure resource types, including common resources like:
- Virtual Machine
- Virtual machine scale set
- App Service
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Azure Function
- Networking resources:
- Network Security Group
- Virtual Network
- Application Gateway, etc.
- Data services:
- Storage
- SQL
- Redis Cache
- Azure Cosmos DB, etc.
Data sources
Change Analysis (classic) queries for:
- Azure Resource Manager resource properties.
- Resource configuration changes.
- App Service Function and Web App in-guest changes.
Change Analysis (classic) also tracks resource dependency changes to diagnose and monitor an application end-to-end.
Azure Resource Manager resource properties changes
Using Azure Resource Graph, Change Analysis (classic) provides a historical record of how the Azure resources that host your application changed over time. The following basic configuration settings are set using Azure Resource Manager and tracked by Azure Resource Graph:
- Managed identities
- Platform OS upgrade
- Hostnames
Resource configuration changes
In addition to the settings set via Azure Resource Manager, you can set configuration settings using the CLI, Bicep, etc., such as:
- IP Configuration rules
- TLS settings
- Extension versions
Azure Resource Graph doesn't capture these setting changes. Change Analysis (classic) fills this gap by capturing snapshots of changes in those main configuration properties, like changes to the connection string, etc. Snapshots are taken of configuration changes and change details every up to 6 hours.
See known limitations regarding resource configuration change analysis.
Changes in Azure Function and Web Apps (in-guest changes)
Every 30 minutes, Change Analysis captures the configuration state of a web application. For example, it can detect changes in the application environment variables, configuration files, and WebJobs. The tool computes the differences and presents the changes.
Refer to our troubleshooting guide if you don't see:
- File changes within 30 minutes
- Configuration changes within 6 hours
See known limitations regarding in-guest change analysis.
Currently, all text-based files under site root wwwroot with the following extensions are supported:
- *.json
- *.xml
- *.ini
- *.yml
- *.config
- *.properties
- *.html
- *.cshtml
- *.js
- requirements.txt
- Gemfile
- Gemfile.lock
- config.gemspec
Dependency changes
Changes to resource dependencies can also cause issues in a resource. For example, if a web app calls into a Redis cache, the Redis cache SKU could affect the web app performance.
As another example, if port 22 was closed in a virtual machine's Network Security Group, it causes connectivity errors.
Web App diagnose and solve problems navigator (preview)
Change Analysis (classic) checks the web app's DNS record, to detect changes in dependencies and app components that could cause issues.
Currently, the following dependencies are supported in Web App Diagnose and solve problems | Navigator:
- Web Apps
- Azure Storage
- Azure SQL
Limitations
- OS environment: For Azure Function and Web App in-guest changes, Change Analysis (classic) currently only works with Windows environments, not Linux.
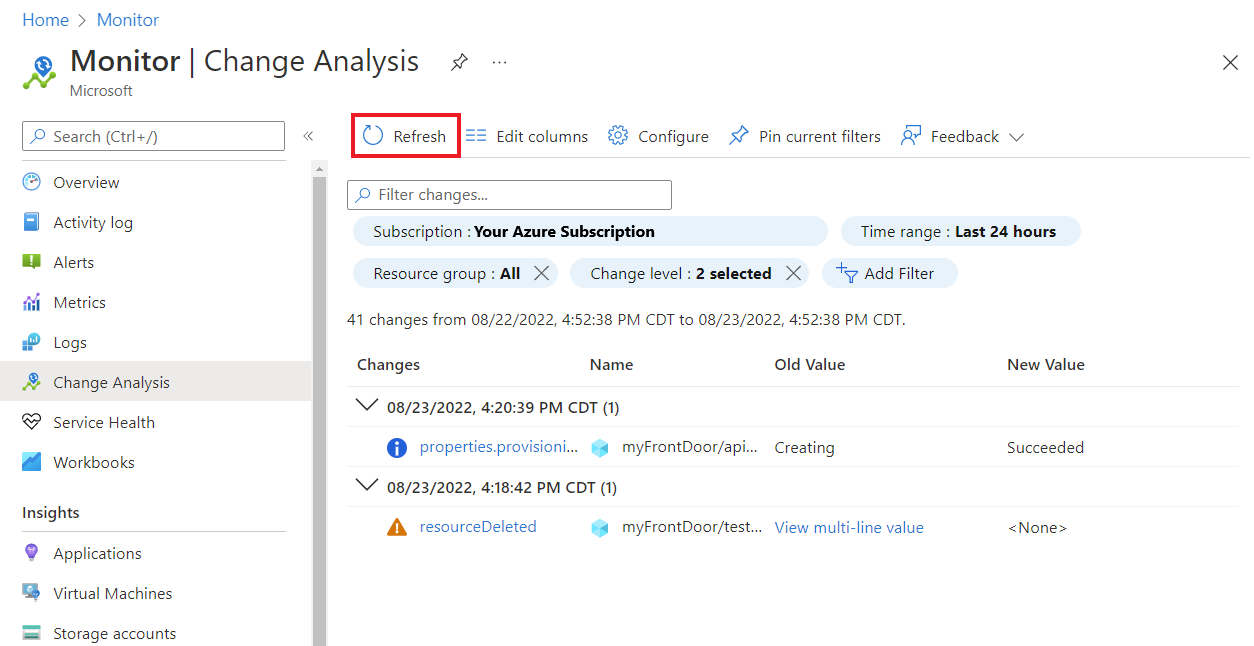
- Web app deployment changes: Code deployment change information might not be available immediately in the Change Analysis (classic) tool. To view the latest changes in Change Analysis (classic), select Refresh.
- Function and Web App file changes: File changes take up to 30 minutes to display.
- Function and Web App configuration changes: Due to the snapshot approach to configuration changes, timestamps of configuration changes could take up to 6 hours to display from when the change actually happened.
- Web app deployment and configuration changes: A site extension collects these changes and stores them on disk space owned by your application. Thus, data collection and storage is subject to your application's behavior. Check to see if a misbehaving application is affecting the results.
- Snapshot retention for all changes: Azure Resource Graphs (ARG) tracks the Change Analysis data for resources. ARG only keeps snapshot history of tracked resources for 14 days.
Frequently asked questions
This section provides answers to common questions.
Does using Change Analysis (classic) incur cost?
You can use Change Analysis (classic) at no extra cost. Enable the Microsoft.ChangeAnalysis resource provider, and anything supported by Change Analysis (classic) is open to you.
Next steps
- Learn about enabling Change Analysis (classic)
- Learn about visualizations in Change Analysis (classic)
- Learn how to troubleshoot problems in Change Analysis (classic)
- Enable Application Insights for Azure web apps.
- Enable Application Insights for Azure VM and Azure virtual machine scale set IIS-hosted apps.