Merk
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å logge på eller endre kataloger.
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å endre kataloger.
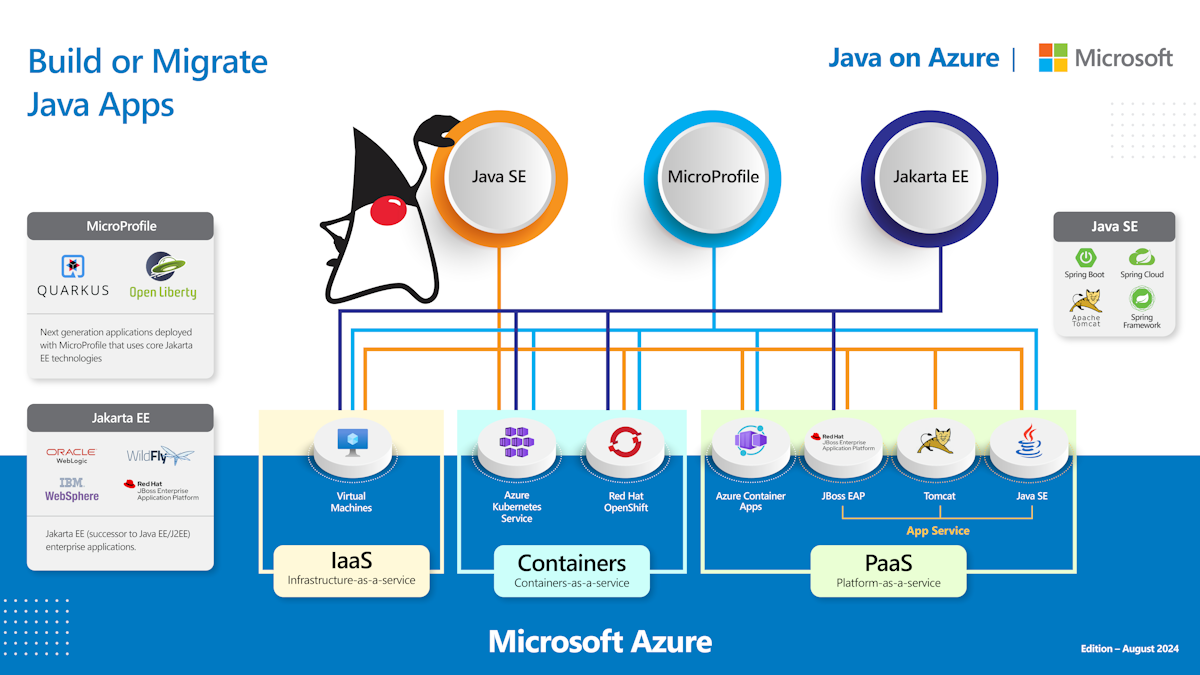
The Java ecosystem includes diverse technologies such as Java SE, Jakarta EE (successor to Java EE and J2EE), Spring, numerous application servers, and other frameworks. Whatever you're doing with Java - building an app, using a framework, and running an application server - Azure supports your workload with an abundance of choice. Similarly, Azure supports any application architecture - from monolithic applications running on VMs or in containers to cloud-native, microservices-based applications running on fully managed services.
Typically, to run your Java application, you deploy it to an application server - an instance of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that runs your applications. Or you can build a standalone application with an embedded application server. Either way, the application server provides common application infrastructure and functional capabilities, collaborating with Web containers to return a dynamic, customized response to a client request. The client request can be processed using software components that might include servlets, dynamic pages, enterprise beans, supporting classes, dependent libraries, and data drivers.
Tomcat, JBoss EAP, WildFly, WebLogic, and WebSphere are popular application servers. Similarly, Spring Boot, Quarkus, and Open Liberty are popular frameworks for building standalone applications with embedded application servers. Azure supports them all, enabling you to use any Java application server and deploy your Java application with confidence and ease.
Deploy Spring Boot or Java app to any application server - Tomcat and Jakarta EE
With Azure, you can run any version and any distribution of Java and any application server, without restrictions, and without having to manage your own physical infrastructure. You decide how much control you want, or how much day-to-day management you want Azure to handle for you with options like virtual machines, containers, and fully managed services. If you're using commercially supported Java app servers or frameworks - such as VMware Spring Runtime, Red Hat JBoss EAP, Oracle WebLogic Server, or IBM WebSphere, Liberty, or OpenLiberty - Azure offers jointly developed and supported offerings for all of them.
Deployment options
Azure provides an abundance of deployment options for Java applications, including infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), containers-as-a-service (CaaS), and platform-as-a-service (PaaS) hosting services. You can lift-and-shift existing Java applications to virtual machines (VMs), containerize them in multiple ways, or deploy them onto fully managed PaaS services to optimize ease of management, developer and operational productivity, and total cost of ownership.
VMs and containers
You're free to use any distribution and version of Java - and any application server - when you deploy to virtual machines or containers on Azure. The choice is entirely up to you. Just remember, you need to manually configure the infrastructure and its components. Deployment options that fall into this category include:
Azure Virtual Machines, which give you the flexibility of virtualization without having to purchase and maintain the physical hardware that runs it. However, you still need to maintain the VM by installing, configuring, and patching the software that runs on it.
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets, which lets you create and manage a group of load-balanced VMs. The number of VM instances can automatically increase or decrease in response to demand or a defined schedule.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), which simplifies deploying a managed Kubernetes cluster by handling all of the operational overhead for you - including critical tasks like maintenance and health monitoring. AKS supports elastic provisioning of capacity, including event-driven autoscaling and KEDA triggers.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift, which provides highly available, fully managed OpenShift clusters on-demand. OpenShift delivers added-value features to complement Kubernetes, making it a turnkey container platform that delivers improved developer and operator experience.
While you can deploy any Java runtime on all these IaaS and CaaS services, we recommend that you use one of the following runtimes:
Microsoft Build of OpenJDK for Java 11 or 17 - the base container images for which Microsoft supplies and maintains.
Eclipse Adoptium Temurin for Java 8 - the Java runtime for which is provided by the Eclipse Adoptium project (formerly the OpenJDK project).
Both of these builds are available free-of-charge for local development and testing, and for building production-ready binaries using any platform or DevOps tools - without having to pay any licensing fees. We recommend them as a matter of convenience. When you use one of these builds, if you have any issues and have a qualifying support plan for Azure, you can open an Azure support ticket - without any more costs. That said, it's worth pointing out that these recommendations are just that - the options that we recommend among various other freely available builds of OpenJDK for ease-of-support. For more information, see Java support on Azure and Azure Stack.
Beyond selecting an LTS runtime, teams running on Azure infrastructure can optionally use the Azure Command Launcher for Java to apply battle-tested defaults without hand-tuning JVM flags for cloud and container environments.
Azure Command Launcher for Java (Public Preview)
The Azure Command Launcher for Java is an optional JVM launcher optimized for Azure that automatically applies cloud-tailored JVM parameters for Java workloads. This launcher is designed for Java applications running on Azure VMs, VM Scale Sets, AKS, Azure Red Hat OpenShift, and Azure Container Instances. By using the Azure Command Launcher for Java, you can improve resource utilization, enhance first-deploy performance, and reduce wasted memory and CPU without manual JVM tuning. For more information, see Public Preview: Azure Command Launcher for Java.
All of these IaaS and CaaS deployment options let you easily deploy the Apache Tomcat application server. If you're using a commercial offering - such as Spring Runtime from VMware, JBoss EAP from Red Hat, WebLogic Server from Oracle, or WebSphere from IBM - Azure offers jointly developed and supported hosting options from those vendors as well. They're covered later, under Jointly built and supported solutions with Java ecosystem partners.
Fully managed (PaaS) services
Fully managed PaaS services for running Java applications on Azure include the following options:
- Azure Container Apps, which lets you run microservices and containerized applications on a serverless platform. Common uses include deploying API endpoints, hosting background processing applications, handling event-driven processing, and running microservices. Applications built on Azure Container Apps can dynamically scale based on HTTP traffic, event-driven processing, CPU, or memory load, or any KEDA-supported scaler.
- Azure App Service, an HTTP-based service for hosting web applications, REST APIs, and mobile back ends - with built-in security, load balancing, autoscaling, and automated management. App Service also supports comprehensive DevOps capabilities, such as continuous deployment, package management, staging environments, custom domains, and TLS/SSL certificates.
Java runtimes for Azure App Service and for Azure Container Apps deployed as code or binaries (JAR/WAR) are supplied and maintained by Microsoft. They only support LTS distributions of OpenJDK, using Eclipse Adoptium Temurin for Java 8 and the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK for Java 11 and 17. That said, there are some caveats - for example, our jointly developed and supported partner offerings (discussed later) use their own runtimes.
The Azure Command Launcher for Java targets customer-managed runtimes and isn't used by the Microsoft-managed Java runtimes provided by Azure App Service or Azure Container Apps. However, developers who deploy their own custom container images to Azure Container Apps can choose to use the launcher inside those images, as those containers use customer-managed runtimes.
For Azure Container Apps built from your own container images, since you need to build and manage your own container images from source code, you're free to use the distribution and version of Java - and application server - of your choice.
Serverless functions
Sometimes you don't need an entire Java application. For example, for real-time data processing, you might just need a small piece of code that can be triggered at scale - perhaps by millions and millions of events. Such events can be ingested via Azure Event Hubs, processed by event-driven serverless Java code running at scale in Azure Functions, and saved into a data store such as Azure Cosmos DB.
Jointly built and supported solutions with Java ecosystem partners
Microsoft has partnered with leading vendors in the Java ecosystem to deliver best-in-class solutions for running Java on Azure - ranging from jointly developed and supported managed services to Azure Marketplace offerings for popular Java application servers. We also integrated popular application monitoring tools, which are covered later in this documentation.
JBoss EAP (Red Hat)
Red Hat provides open-source solutions for the enterprise. One such solution is JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (EAP), a popular application server platform that's Java EE Certified and Jakarta EE Compliant in both Web Profile and Full Platform. Red Hat is also a contributor for the Java standards, OpenJDK, MicroProfile, Jakarta EE, and Quarkus.
We partnered with Red Hat to deliver Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (EAP) on Azure App Service - enabling Java developers to deploy their Jakarta EE applications into App Service without requiring a separate Red Hat subscription or license with integrated support from both companies. We also launched similar joint offerings for JBoss EAP on Azure VMs, on Azure VM Scale Sets, and on Azure RedHat OpenShift (ARO) - the latter also jointly operated by Microsoft and Red Hat.
WebLogic Server (Oracle)
We partnered with Oracle to deliver Oracle WebLogic Server (WLS) on Azure VMs and Oracle WebLogic Server on Azure Kubernetes Service. These solutions facilitate easy migrations to Azure by automating boilerplate operations such as provisioning virtual networks/storage, installing Linux/Java resources, setting up WebLogic Server, and configuring security with a network security group.
WebSphere/Liberty/Open Liberty (IBM)
We partnered with IBM, jointly developing solutions for WebSphere Application Server (WAS) on Azure VMs, WebSphere Liberty and Open Liberty on Azure Kubernetes Service, and WebSphere Liberty and Open Liberty on Azure Red Hat OpenShift. For more information, see What are solutions to run the IBM WebSphere family of products on Azure? These solutions enable easy migration of WebSphere workloads to Azure, automating most of the resource provisioning tasks needed to set up a highly available WebSphere cluster. The partnership covers a range of use cases - from existing mission-critical workloads to cloud-native applications.
Apache Kafka on Confluent Cloud (Confluent)
In the past, Azure customers who wanted to use Confluent's Kafka service had to create and manage resources and users separately in Azure and Confluent Cloud. To ease this pain, Confluent and Microsoft partnered to deliver Apache Kafka for Confluent Cloud, an Azure Marketplace offering that provides Apache Kafka as a fully managed service - including the ability to create and manage Confluent Cloud resources through the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure Management SDKs.
Today, the customer experience is simpler, safer, and more seamless. Customers can provision and manage Confluent Cloud resources along with their Azure resources, as part of a unified workflow - and take advantage of fully managed connectors built for Azure Functions, Azure Blob Storage, Azure Event Hubs, Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, and Microsoft SQL Server. Developers can continue to code using Apache Kafka client libraries.
Summary
Joint development with partners for many of these offerings is a continual, ongoing effort. As our partners continue to innovate on their offerings, we're working closely with them to quickly bring those same innovations to Azure - so that customers can deploy and scale their Java applications with confidence and ease.
In summary, Azure supports your workload with an abundance of choice regardless of what you're doing with Java. You can build any Java app, use any framework, run any application server, and support any application architecture - from monolithic applications running on VMs or in containers to cloud-native, microservices-based applications running on fully managed services. Azure provides tooling to optimize Java runtime configuration for cloud-native deployments, including the Azure Command Launcher for Java (Public Preview) for VM and container scenarios. For more information, see Public Preview: Azure Command Launcher for Java.