Data in Azure Machine Learning v1
APPLIES TO:  Azure CLI ml extension v1
Azure CLI ml extension v1
APPLIES TO:  Python SDK azureml v1
Python SDK azureml v1
Azure Machine Learning makes it easy to connect to your data in the cloud. It provides an abstraction layer over the underlying storage service, so that you can securely access and work with your data without the need to write code specific to your storage type. Azure Machine Learning also provides these data capabilities:
- Interoperability with Pandas and Spark DataFrames
- Versioning and tracking of data lineage
- Data labeling
- Data drift monitoring
Data workflow
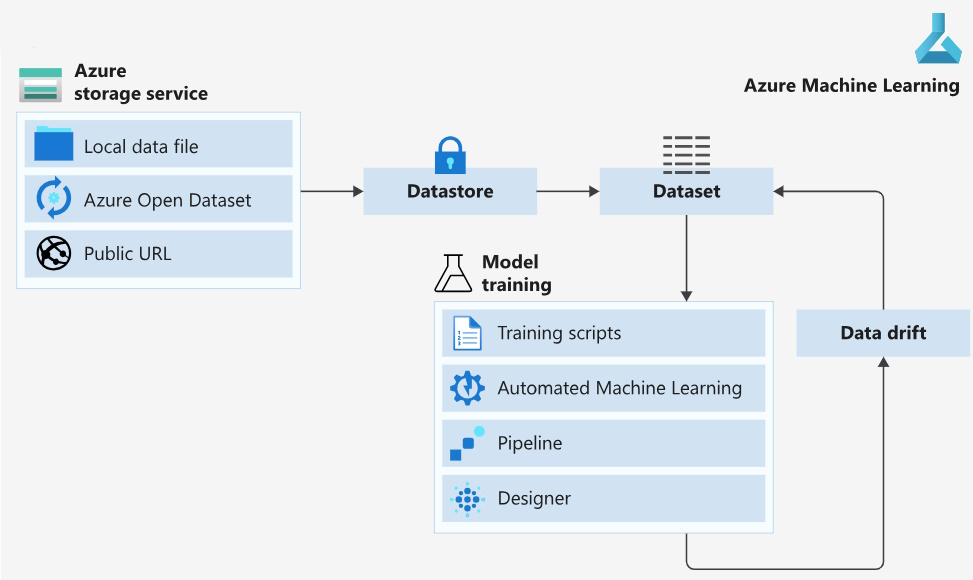
To use the data in your cloud-based storage solution, we recommend this data delivery workflow. The workflow assumes that you have an Azure storage account, and data in an Azure cloud-based storage service.
Create an Azure Machine Learning datastore to store connection information to your Azure storage
From that datastore, create an Azure Machine Learning dataset to point to a specific file or files in your underlying storage
To use that dataset in your machine learning experiment, you can either
Mount the dataset to the compute target of your experiment, for model training
OR
Consume the dataset directly in Azure Machine Learning solutions - for example, automated machine learning (automated ML) experiment runs, machine learning pipelines, or the Azure Machine Learning designer.
Create dataset monitors for your model output dataset to detect data drift
For detected data drift, update your input dataset and retrain your model accordingly
This screenshot shows the recommended workflow:
Connect to storage with datastores
Azure Machine Learning datastores securely host your data storage connection information on Azure, so you don't have to place that information in your scripts. For more information about connecting to a storage account and data access in your underlying storage service, visit Register and create a datastore.
These supported Azure cloud-based storage services can register as datastores:
- Azure Blob Container
- Azure File Share
- Azure Data Lake
- Azure Data Lake Gen2
- Azure SQL Database
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL
- Databricks File System
- Azure Database for MySQL
Tip
You can create datastores with credential-based authentication to access storage services, for example a service principal or a shared access signature (SAS) token. Users with Reader access to the workspace can access these credentials.
If this is a concern, visit create a datastore that uses identity-based data access for more information about connections to storage services.
Reference data in storage with datasets
Azure Machine Learning datasets aren't copies of your data. Dataset creation itself creates a reference to the data in its storage service, along with a copy of its metadata.
Because datasets are lazily evaluated, and the data remains in its existing location, you
- Incur no extra storage cost
- Don't risk unintentional changes to your original data sources
- Improve ML workflow performance speeds
To interact with your data in storage, create a dataset to package your data into a consumable object for machine learning tasks. Register the dataset to your workspace, to share and reuse it across different experiments without data ingestion complexities.
You can create datasets from local files, public urls, Azure Open Datasets, or Azure storage services via datastores.
There are two types of datasets:
A FileDataset references single or multiple files in your datastores or public URLs. If your data is already cleansed and ready for training experiments, you can download or mount files referenced by FileDatasets to your compute target
A TabularDataset represents data in a tabular format, by parsing the provided file or list of files. You can load a TabularDataset into a pandas or Spark DataFrame for further manipulation and cleansing. For a complete list of data formats from which you can create TabularDatasets, visit the TabularDatasetFactory class
These resources offer more information about dataset capabilities:
- Version and track dataset lineage
- Monitor your dataset to help with data drift detection
Work with your data
With datasets, you can accomplish machine learning tasks through seamless integration with Azure Machine Learning features.
- Create a data labeling project
- Train machine learning models:
- Access datasets for scoring with batch inference in machine learning pipelines
- Set up a dataset monitor for data drift detection
Label data with data labeling projects
Labeling large volumes of data in machine learning projects can become a headache. Projects that involve a computer vision component, such as image classification or object detection, often require thousands of images and corresponding labels.
Azure Machine Learning provides a central location to create, manage, and monitor labeling projects. Labeling projects help coordinate the data, labels, and team members, so that you can more efficiently manage the labeling tasks. Currently supported tasks involve image classification, either multi-label or multi-class, and object identification using bounded boxes.
Create an image labeling project or text labeling project, and output a dataset for use in machine learning experiments.
Monitor model performance with data drift
In the context of machine learning, data drift involves the change in model input data that leads to model performance degradation. It's a major reason that model accuracy degrades over time, and data drift monitoring helps detect model performance issues.
For more information, visit Create a dataset monitor to learn how to detect and alert to data drift on new data in a dataset.
Next steps
- Create a dataset in Azure Machine Learning studio or with the Python SDK
- Try out dataset training examples with our sample notebooks