Cluster an SAP ASCS/SCS instance on a Windows failover cluster by using a shared disk in Azure
Windows
Windows Server Failover Clustering (WSFC) is the foundation of a high-availability (HA) SAP ASCS/SCS installation and database management systems (DBMSs) in Windows.
A failover cluster is a group of 1+n independent servers (nodes) that work together to increase the availability of applications and services. If a node failure occurs, WSFC calculates the number of failures that can occur and still maintain a healthy cluster to provide applications and services. You can choose from various quorum modes to achieve failover clustering.
Prerequisites
Before you begin the tasks in this article, review the article High-availability architecture and scenarios for SAP NetWeaver.
Windows Server Failover Clustering in Azure
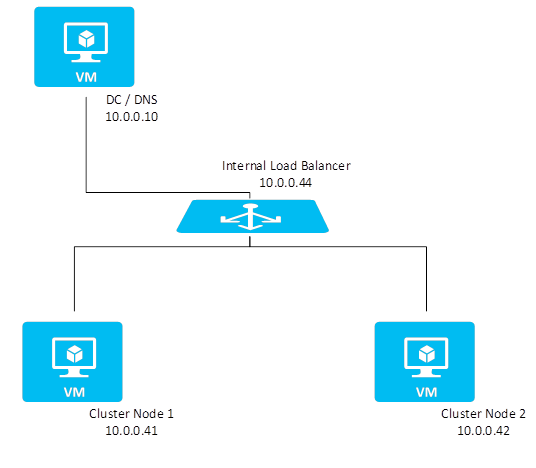
WSFC with Azure virtual machines (VMs) requires additional configuration steps. When you build a cluster, you need to set several IP addresses and virtual host names for the SAP ASCS/SCS instance.
Name resolution in Azure and the cluster virtual host name
The Azure cloud platform doesn't offer the option to configure virtual IP addresses, such as floating IP addresses. You need an alternative solution to set up a virtual IP address to reach the cluster resource in the cloud.
The Azure Load Balancer service provides an internal load balancer for Azure. With the internal load balancer, clients reach the cluster over the cluster's virtual IP address.
Deploy the internal load balancer in the resource group that contains the cluster nodes. Then, configure all necessary port-forwarding rules by using the probe ports of the internal load balancer. Clients can connect via the virtual host name. The DNS server resolves the cluster IP address, and the internal load balancer handles port forwarding to the active node of the cluster.
SAP ASCS/SCS HA with cluster shared disks
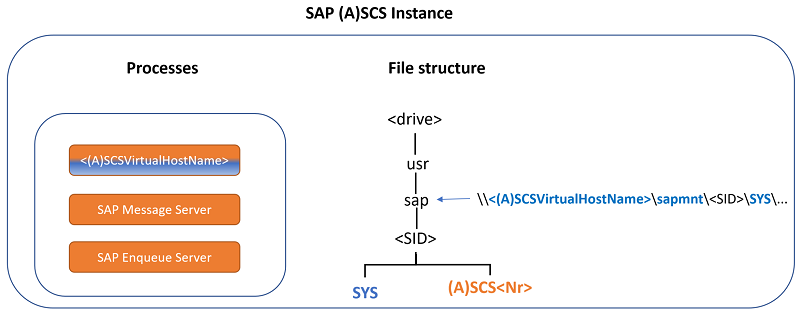
In Windows, an SAP ASCS/SCS instance contains SAP central services, the SAP message server, enqueue server processes, and SAP global host files. SAP global host files store central files for the entire SAP system.
An SAP ASCS/SCS instance has the following components:
SAP central services:
- Two processes (for a message server and an enqueue server) and an ASCS/SCS virtual host name that's used to access the two processes
- File structure: S:\usr\sap\<SID>\ASCS/SCS<instance number>
SAP global host files:
File structure: S:\usr\sap\<SID>\SYS...
The sapmnt file share, which enables access to these global S:\usr\sap\<SID>\SYS... files by using the following UNC path:
\\<ASCS/SCS virtual host name>\sapmnt\<SID>\SYS...
In a high-availability setting, you cluster SAP ASCS/SCS instances. You use cluster shared disks (drive S in this article's example) to place the SAP ASCS/SCS and SAP global host files.
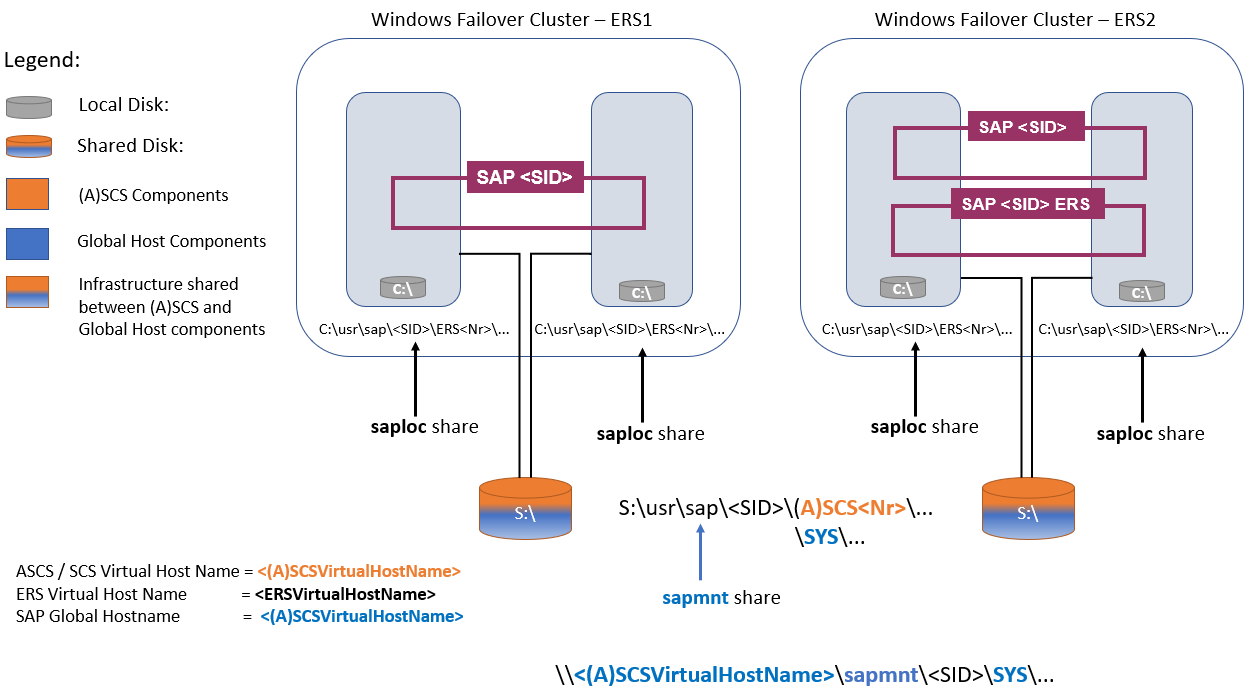
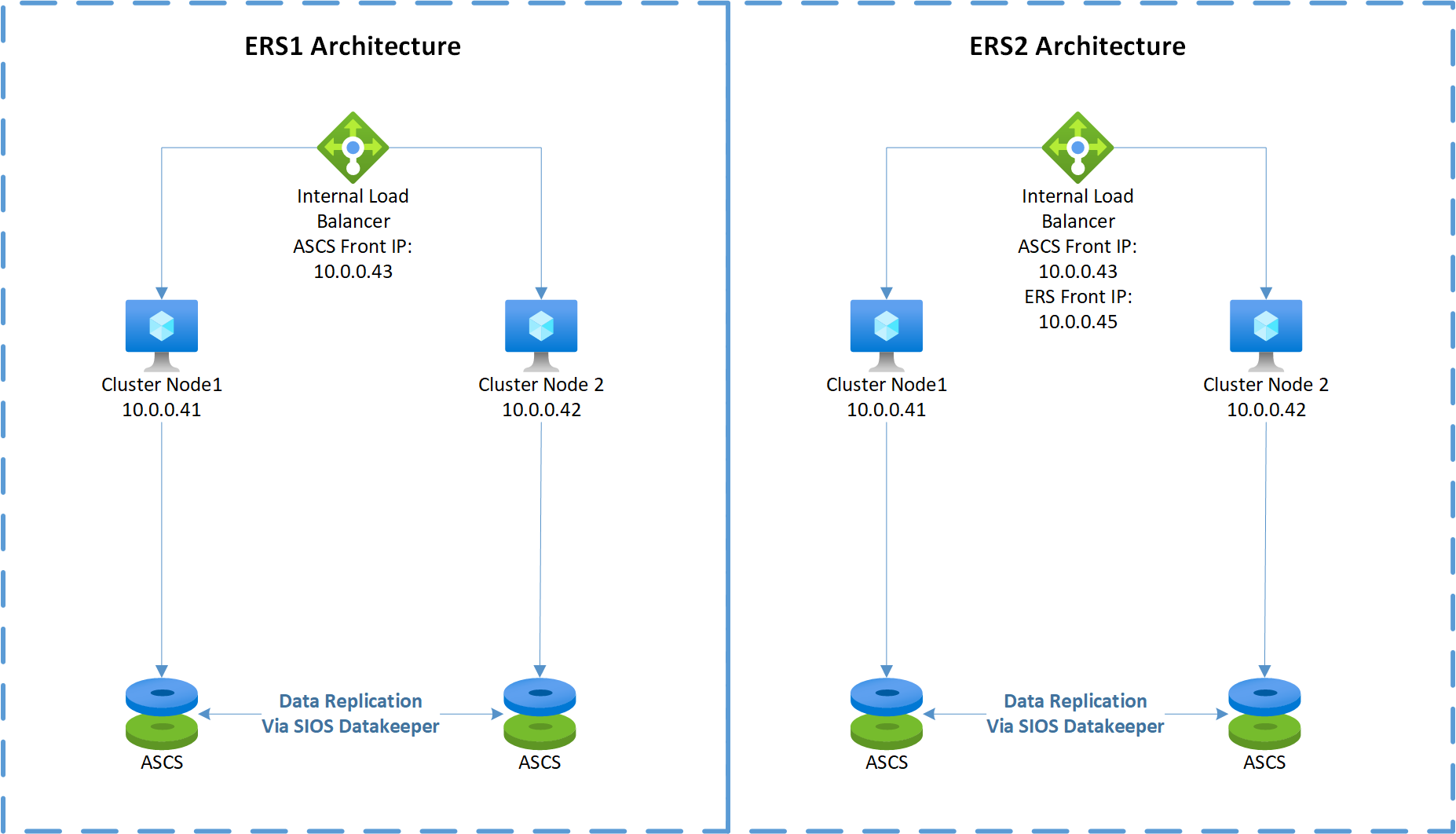
With an Enqueue Replication Server 1 (ERS1) architecture:
- The same ASCS/SCS virtual host name is used to access the SAP message server and enqueue server processes, in addition to the SAP global host files via the sapmnt file share.
- The same cluster shared disk (drive S) is shared between them.
With Enqueue Replication Server 2 (ERS2) architecture:
- The same ASCS/SCS virtual host name is used to access the SAP message server process, in addition to the SAP global host files via the sapmnt file share.
- The same cluster shared disk (drive S) is shared between them.
- There's a separate ERS virtual host name to access the enqueue server process.
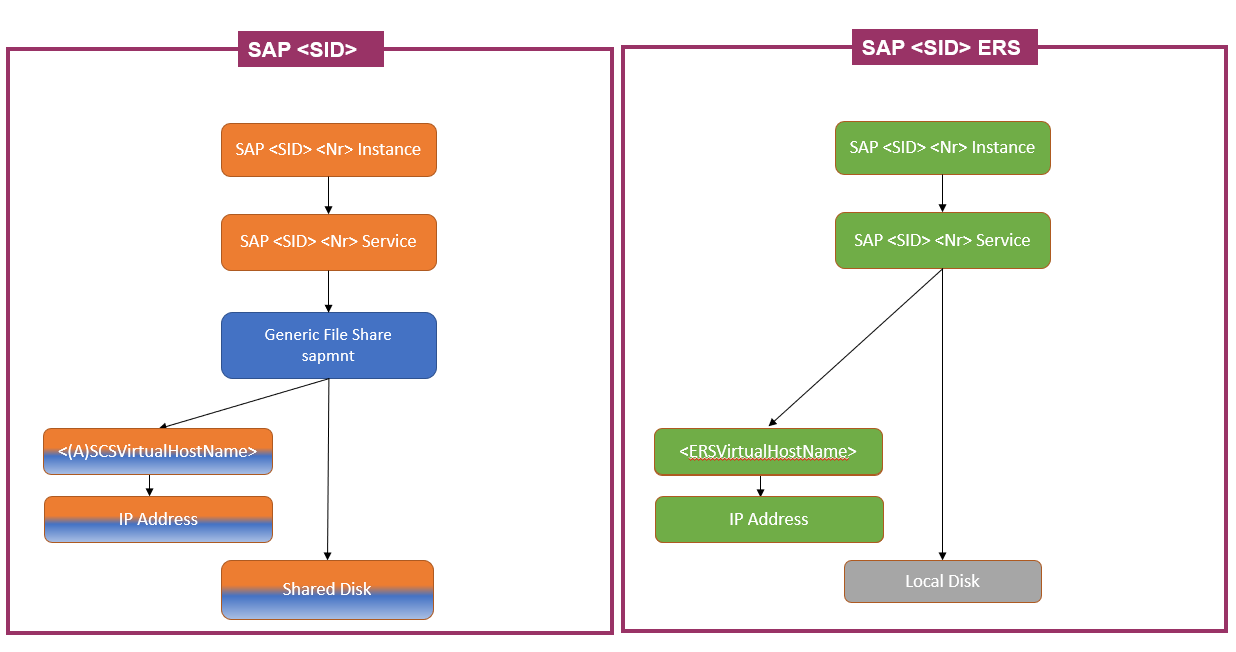
Shared disks and Enqueue Replication Server
Shared disks are supported with an ERS1 architecture, where the ERS1 instance:
- Is not clustered.
- Uses a
localhostname. - Is deployed on local disks on each of the cluster nodes.
Shared disks are also supported with an ERS2 architecture, where the ERS2 instance:
- Is clustered.
- Uses a dedicated virtual or network host name.
- Needs the IP address of ERS virtual host name to be configured on an Azure internal load balancer, in addition to the (A)SCS IP address.
- Is deployed on local disks on each of the clustered nodes, so there's no need for a shared disk.
For more information about ERS1 and ERS2, see Enqueue Replication Server in a Microsoft Failover Cluster and New Enqueue Replicator in Failover Cluster environments on the SAP website.
Options for shared disks in Azure for SAP workloads
There are two options for shared disks in a Windows failover cluster in Azure:
- Use Azure shared disks to attach Azure managed disks to multiple VMs simultaneously.
- Use SIOS DataKeeper Cluster Edition to create a mirrored storage that simulates cluster shared storage.
When you're selecting the technology for shared disks, keep in mind the following considerations about Azure shared disks for SAP workloads:
- Use of Azure shared disks with Azure Premium SSD disks is supported for SAP deployment in availability sets and availability zones.
- Azure Ultra Disk Storage disks and Azure Standard SSD disks are not supported as Azure shared disks for SAP workloads.
- Be sure to provision Azure Premium SSD disks with a minimum disk size, as specified in Premium SSD ranges, to be able to attach to the required number of VMs simultaneously. You typically need two VMs for SAP ASCS Windows failover clusters.
Keep in mind the following considerations about SIOS:
- The SIOS solution provides real-time synchronous data replication between two disks.
- With the SIOS solution, you operate with two managed disks. If you're using either availability sets or availability zones, the managed disks are on different storage clusters.
- Deployment in availability zones is supported.
- The SIOS solution requires installing and operating third-party software, which you need to purchase separately.
Azure shared disks
You can implement SAP ASCS/SCS HA with Azure shared disks.
Prerequisites and limitations
Currently, you can use Azure Premium SSD disks as Azure shared disks for the SAP ASCS/SCS instance. The following limitations are currently in place:
- Azure Ultra Disk Storage disks and Standard SSD disks are not supported as Azure shared disks for SAP workloads.
- Azure Shared disks with Premium SSD disks are supported for SAP deployment in availability sets and availability zones.
- Azure shared disks with Premium SSD disks come with two storage options:
- Locally redundant storage (LRS) for Premium SSD shared disks (
skuNamevalue ofPremium_LRS) is supported with deployment in availability sets. - Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) for Premium SSD shared disks (
skuNamevalue ofPremium_ZRS) is supported with deployment in availability zones.
- Locally redundant storage (LRS) for Premium SSD shared disks (
- The Azure shared disk value maxShares determines how many cluster nodes can use the shared disk. For an SAP ASCS/SCS instance, you typically configure two nodes in WSFC. You then set the value for
maxSharesto2. - An Azure proximity placement group (PPG) is not required for Azure shared disks. But for SAP deployment with PPGs, follow these guidelines:
- If you're using PPGs for an SAP system deployed in a region, all virtual machines that share a disk must be part of the same PPG.
- If you're using PPGs for an SAP system deployed across zones, as described in Proximity placement groups with zonal deployments, you can attach
Premium_ZRSstorage to virtual machines that share a disk.
For more information, review the Limitations section of the documentation for Azure shared disks.
Important considerations for Premium SSD shared disks
Consider these important points about Azure Premium SSD shared disks:
LRS for Premium SSD shared disks:
- SAP deployment with LRS for Premium SSD shared disks operates with a single Azure shared disk on one storage cluster. If there's a problem with the storage cluster where the Azure shared disk is deployed, it affects your SAP ASCS/SCS instance.
ZRS for Premium SSD shared disks:
- Write latency for ZRS is higher than that of LRS because of cross-zonal copying of data.
- The distance between availability zones in different regions varies, and so does ZRS disk latency across availability zones. Benchmark your disks to identify the latency of ZRS disks in your region.
- ZRS for Premium SSD shared disks synchronously replicates data across three availability zones in the region. If there's a problem in one of the storage clusters, your SAP ASCS/SCS instance continues to run because storage failover is transparent to the application layer.
- For more information, review the Limitations section of the documentation about ZRS for managed disks.
For other important considerations about planning your SAP deployment, review Plan and implement an SAP deployment on Azure and Azure Storage types for SAP workloads.
Supported OS versions
Windows Server 2016, 2019, and later are supported. Use the latest datacenter images.
We strongly recommend using at least Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, for these reasons:
- WSFC in Windows Server 2019 is Azure aware.
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter includes integration and awareness of Azure host maintenance and improved experience by monitoring for Azure scheduled events.
- You can use distributed network names. (It's the default option.) There's no need to have a dedicated IP address for the cluster network name. Also, you don't need to configure an IP address on an Azure internal load balancer.
Shared disks in Azure with SIOS DataKeeper
Another option for shared disks is to use SIOS DataKeeper Cluster Edition to create a mirrored storage that simulates cluster shared storage. The SIOS solution provides real-time synchronous data replication.
To create a shared disk resource for a cluster:
- Attach an additional disk to each of the virtual machines in a Windows cluster configuration.
- Run SIOS DataKeeper Cluster Edition on both virtual machine nodes.
- Configure SIOS DataKeeper Cluster Edition so that it mirrors the content of the additional disk-attached volume from the source virtual machine to the additional disk-attached volume of the target virtual machine. SIOS DataKeeper abstracts the source and target local volumes, and then presents them to WSFC as one shared disk.
Note
You don't need shared disks for high availability with some DBMS products, like SQL Server. SQL Server Always On replicates DBMS data and log files from the local disk of one cluster node to the local disk of another cluster node. In this case, the Windows cluster configuration doesn't need a shared disk.
Optional configurations
The following diagrams show multiple SAP instances on Azure VMs running Windows Server Failover Clustering to reduce the total number of VMs.
This configuration can be either local SAP application servers on an SAP ASCS/SCS cluster or an SAP ASCS/SCS cluster role on Microsoft SQL Server Always On nodes.
Important
Installing a local SAP application server on a SQL Server Always On node is not supported.
Both SAP ASCS/SCS and the Microsoft SQL Server database are single points of failure (SPOFs). WSFC helps protect these SPOFs in a Windows environment.
Although the resource consumption of the SAP ASCS/SCS is fairly small, we recommend a reduction of the memory configuration for either SQL Server or the SAP application server by 2 GB.
This diagram illustrates SAP application servers on WSFC nodes with the use of SIOS DataKeeper:
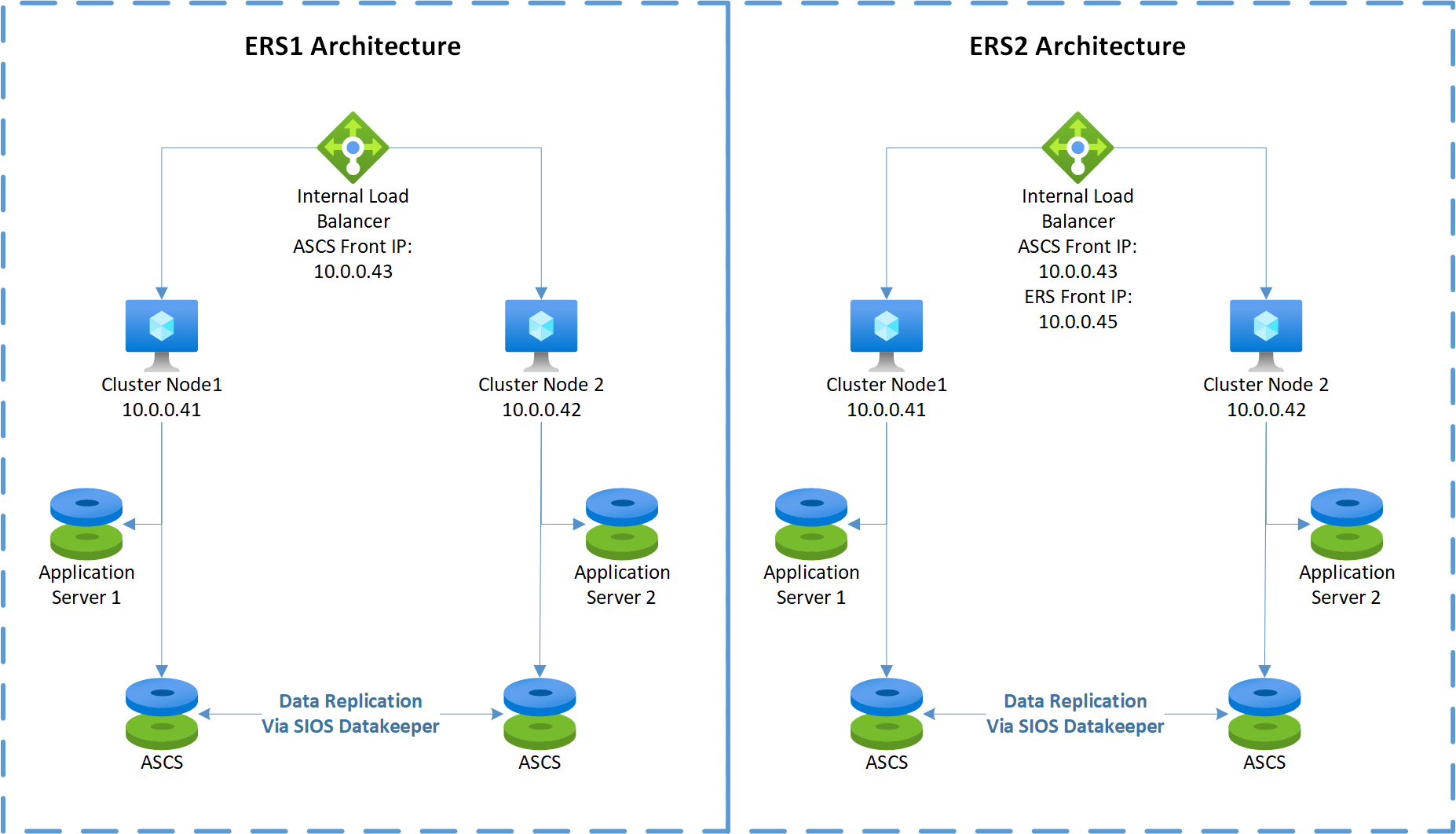
Because the SAP application servers are installed locally, there's no need to set up any synchronization.
This diagram illustrates SAP ASCS/SCS on SQL Server Always On nodes with the use of SIOS DataKeeper:
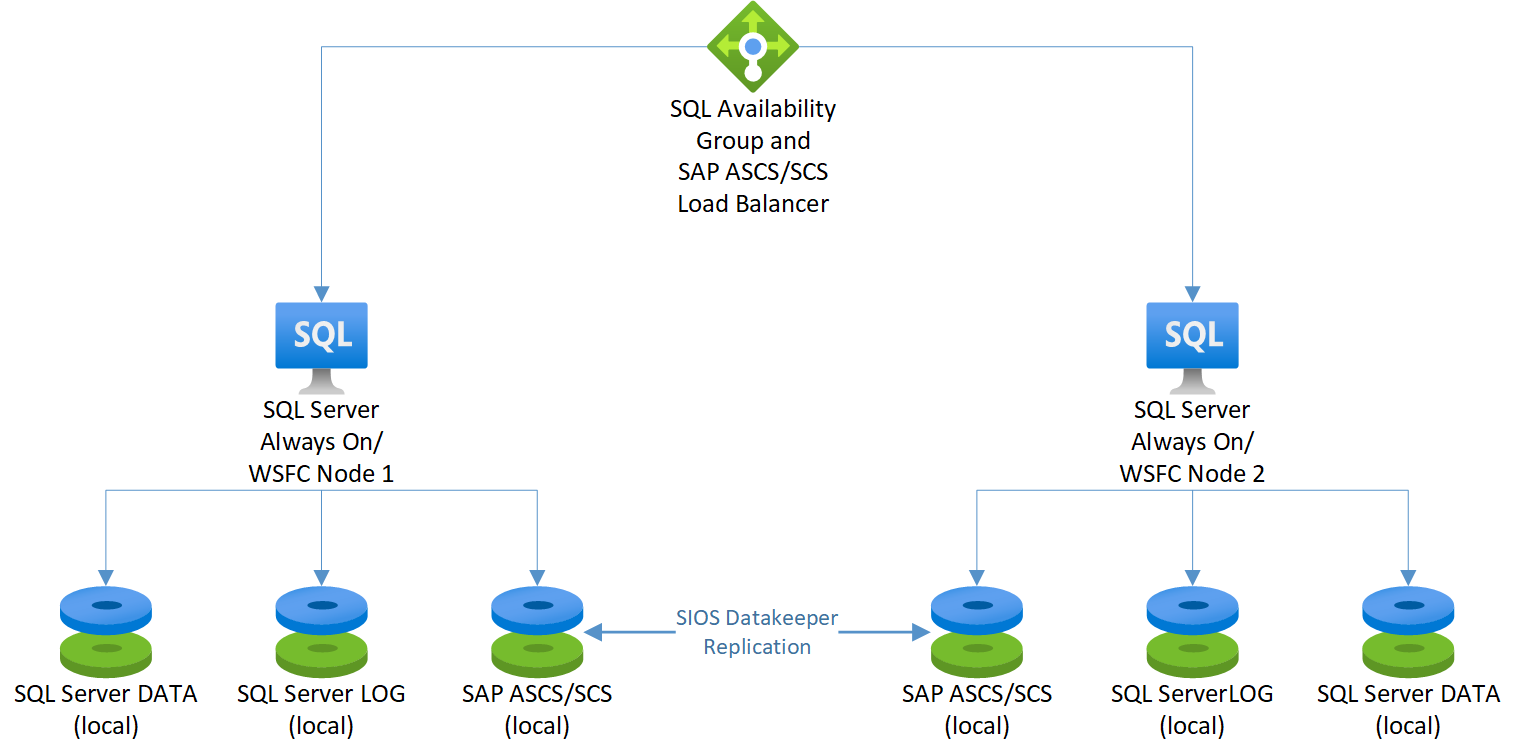
For information about other configurations, see the following resources:
Optional configuration for SAP application servers on WSFC nodes using Windows Scale-Out File Server