Step 3 - Deploy the search-enabled .NET website
Deploy the search-enabled website as an Azure Static Web Apps site. This deployment includes both the React app for the web pages, and the Function app for search operations.
The static web app pulls the information and files for deployment from GitHub using your fork of the azure-search-static-web-app repository.
Create a Static Web App in Visual Studio Code
In Visual Studio Code, make sure you're at the repository root, and not the bulk-insert folder (for example,
azure-search-static-web-app).Select Azure from the Activity Bar, then open Resources from the side bar.
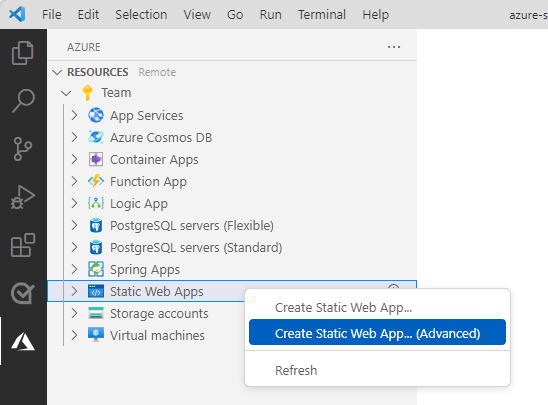
Right-click Static Web Apps and then select Create Static Web App (Advanced). If you don't see this option, verify that you have the Azure Functions extension for Visual Studio Code.
If you see a pop-up window asking you to commit your changes, don't do this. The secrets from the bulk import step shouldn't be committed to the repository.
To roll back the changes, in Visual Studio Code select the Source Control icon in the Activity bar, then select each changed file in the Changes list and select the Discard changes icon.
Follow the prompts to create the static web app:
Prompt Enter Select a resource group for new resources. Create a new resource group for the static app. Enter the name for the new Static Web App. Give your static app a name, such as my-demo-static-web-app.Select a SKU Select the free SKU for this tutorial. Select a location for new resources. Choose a region near you. Choose build preset to configure default project structure. Select Custom. Select the location of your client application code client
This is the path, from the root of the repository, to your static web app.Enter the path of your build output... build
This is the path, from your static web app, to your generated files.If you get an error about an incorrect region, make sure the resource group and static web app resource are in one of the supported regions listed in the error response.
When the static web app is created, a GitHub workflow YML file is also created locally and on GitHub in your fork. This workflow executes in your fork, building and deploying the static web app and functions.
Check the status of static web app deployment using any of these approaches:
Select Open Actions in GitHub from the Notifications. This opens a browser window pointed to your forked repo.
Select the Actions tab in your forked repository. You should see a list of all workflows on your fork.
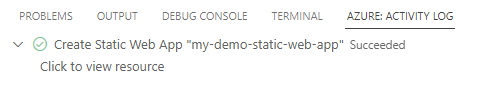
Select the Azure: Activity Log in Visual Code. You should see a message similar to the following screenshot.
Get the Azure AI Search query key in Visual Studio Code
While you might be tempted to reuse your search admin key for query purposes that isn't following the principle of least privilege. The Azure Function should use the query key to conform to least privilege.
In Visual Studio Code, open a new terminal window.
Get the query API key with this Azure CLI command:
az search query-key list --resource-group YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-RESOURCE-GROUP --service-name YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-NAMEKeep this query key to use in the next section. The query key authorizes read access to a search index.
Add environment variables in Azure portal
The Azure Function app won't return search data until the search secrets are in settings.
Select Azure from the Activity Bar.
Right-click on your Static Web Apps resource then select Open in Portal.
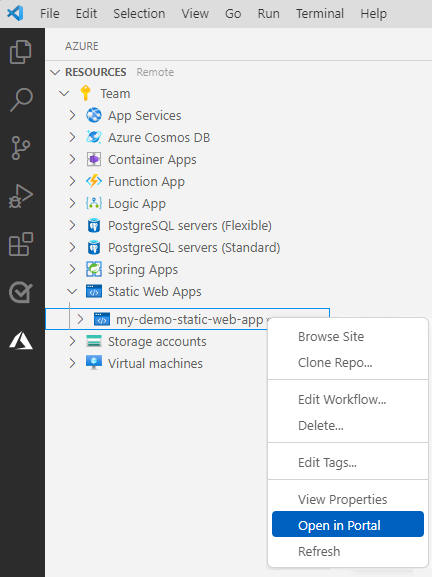
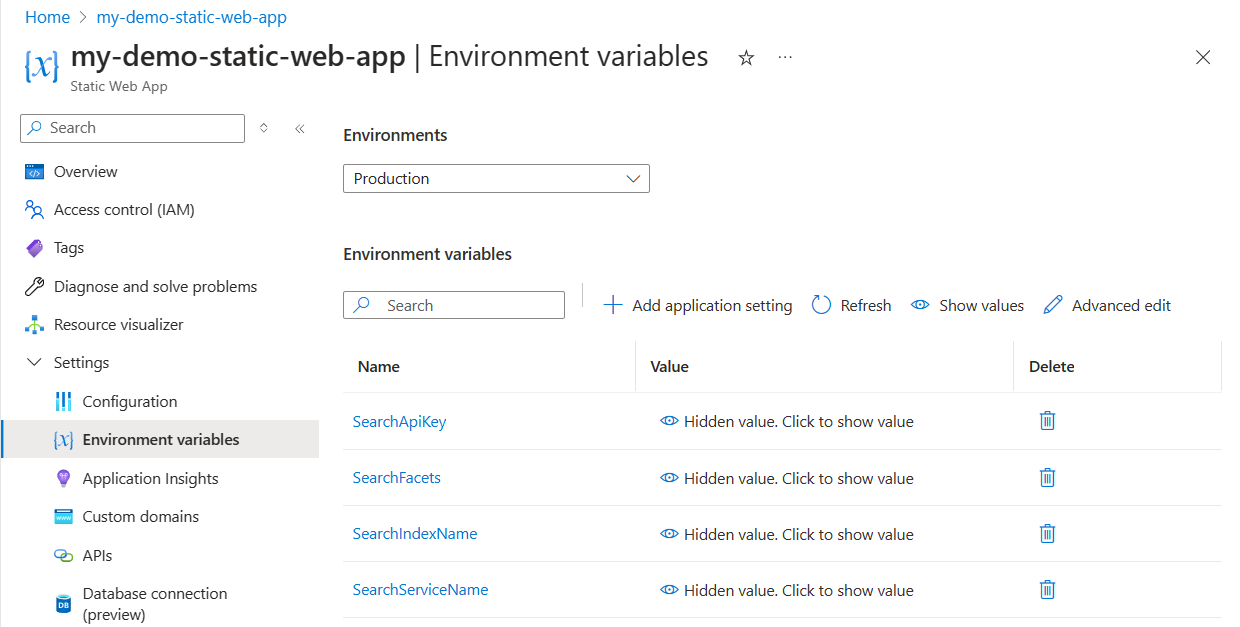
Select Environment variables then select + Add application setting.
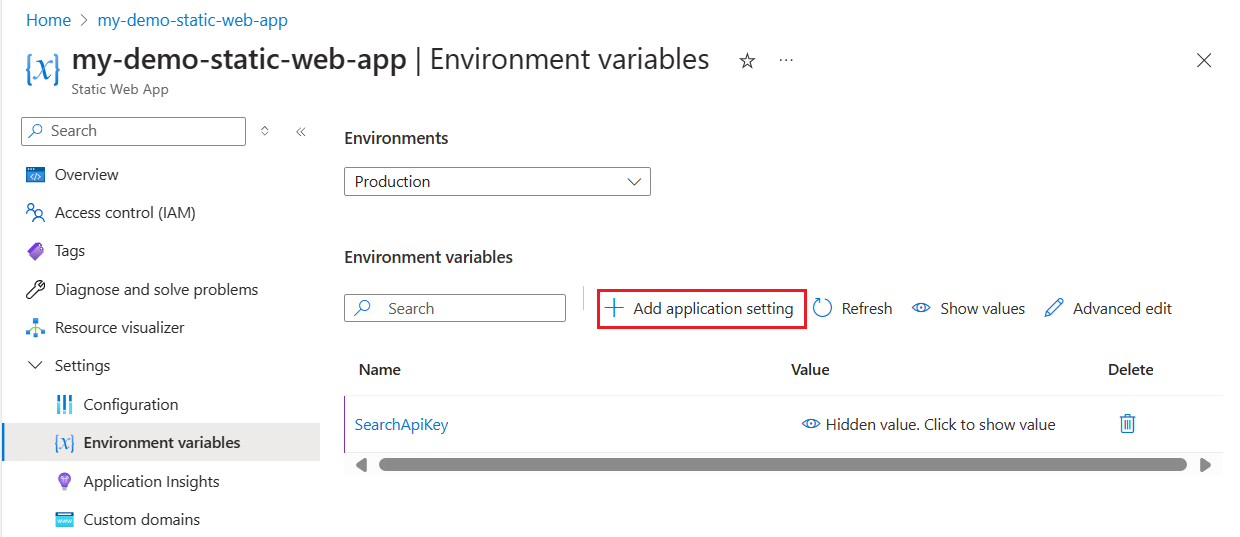
Add each of the following settings:
Setting Your Search resource value SearchApiKey Your search query key SearchServiceName Your search resource name SearchIndexName good-booksSearchFacets authors*,language_codeAzure AI Search requires different syntax for filtering collections than it does for strings. Add a
*after a field name to denote that the field is of typeCollection(Edm.String). This allows the Azure Function to add filters correctly to queries.Check your settings to make sure they look like the following screenshot.
Return to Visual Studio Code.
Refresh your static web app to see the application settings and functions.
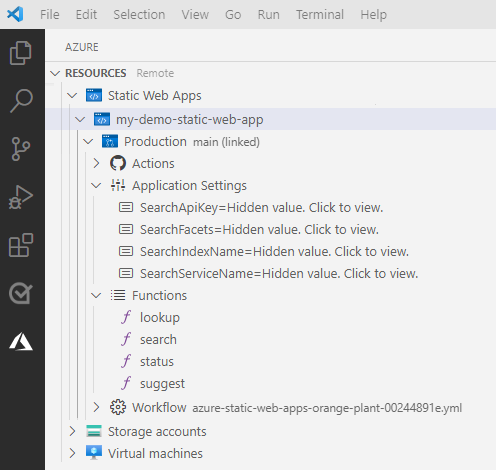
If you don't see the application settings, revisit the steps for updating and relaunching the GitHub workflow.
Use search in your static web app
In Visual Studio Code, open the Activity bar, and select the Azure icon.
In the Side bar, right-click on your Azure subscription under the
Static Web Appsarea and find the static web app you created for this tutorial.Right-click the static web app name and select Browse site.
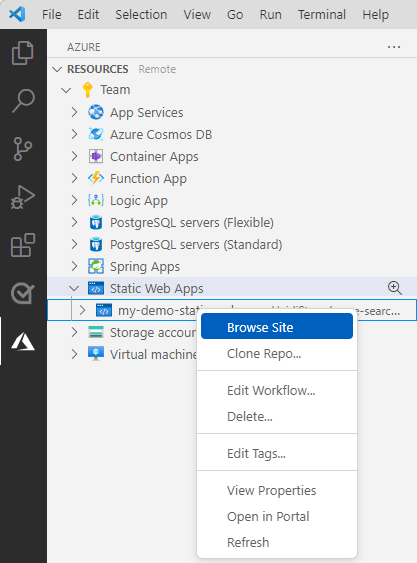
Select Open in the pop-up dialog.
In the website search bar, enter a search query such as
code, so the suggest feature suggests book titles. Select a suggestion or continue entering your own query. Press enter when you've completed your search query.Review the results then select one of the books to see more details.
Troubleshooting
If the web app didn't deploy or work, use the following list to determine and fix the issue:
Did the deployment succeed?
In order to determine if your deployment succeeded, you need to go to your fork of the sample repo and review the success or failure of the GitHub action. There should be only one action and it should have static web app settings for the
app_location,api_location, andoutput_location. If the action didn't deploy successfully, dive into the action logs and look for the last failure.Does the client (front-end) application work?
You should be able to get to your web app and it should successfully display. If the deployment succeeded but the website doesn't display, this might be an issue with how the static web app is configured for rebuilding the app, once it is on Azure.
Does the API (serverless back-end) application work?
You should be able to interact with the client app, searching for books and filtering. If the form doesn't return any values, open the browser's developer tools, and determine if the HTTP calls to the API were successful. If the calls weren't successful, the most likely reason if the static web app configurations for the API endpoint name and search query key are incorrect.
If the path to the Azure function code (
api_location) isn't correct in the YML file, the application loads but won't call any of the functions that provide integration with Azure AI Search. Revisit the deployment section to make sure paths are correct.
Clean up resources
To clean up the resources created in this tutorial, delete the resource group or individual resources.
In Visual Studio Code, open the Activity bar, and select the Azure icon.
In the Side bar, right-click on your Azure subscription under the
Static Web Appsarea and find the app you created for this tutorial.Right-click the app name then select Delete.
If you no longer want the GitHub fork of the sample, remember to delete that on GitHub. Go to your fork's Settings then delete the repository.
To delete Azure AI Search, find your search service and select Delete at the top of the page.
Next steps
Tilbakemeldinger
Kommer snart: Gjennom 2024 faser vi ut GitHub Issues som tilbakemeldingsmekanisme for innhold, og erstatter det med et nytt system for tilbakemeldinger. Hvis du vil ha mer informasjon, kan du se: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Send inn og vis tilbakemelding for