Replicate Azure VMs to another Azure region
This article describes how to enable replication of Azure VMs, from one Azure region to another.
Before you start
This article assumes that you've prepared for Site Recovery deployment, as described in the Azure to Azure disaster recovery tutorial.
Prerequisites should be in place, and you should have created a Recovery Services vault.
Enable replication
Use the following procedure to replicate Azure VMs to another Azure region. As an example, primary Azure region is East Asia, and the secondary is Southeast Asia.
In the vault > Site Recovery page, under Azure virtual machines, select Enable replication.
In the Enable replication page, under Source, do the following:
Region: Select the Azure region from where you want to protect your VMs. For example, the source location is East Asia.
Note
For cross-regional disaster recovery, the source location should be different from the Recovery Services Vault and its Resource Group's location. However, it can be the same as any of them for zonal disaster recovery.
Subscription: Select the subscription to which your source VMs belong. This can be any subscription within the same Microsoft Entra tenant where your recovery services vault exists.
Resource group: Select the resource group to which your source virtual machines belong. All the VMs in the selected resource group are listed for protection in the next step.
Virtual machine deployment model: Select Azure deployment model of the source machines.
Disaster recovery between availability zones: Select Yes if you want to perform zonal disaster recovery on virtual machines.

Select Next.
In Virtual machines, select each VM that you want to replicate. You can only select machines for which replication can be enabled. You can select up to 10 VMs. Then select Next.

In Replication settings, you can configure the following settings:
Under Location and Resource group,
Target location: Select the location where your source virtual machine data must be replicated. Depending on the location of selected machines, Site Recovery provides you with the list of suitable target regions. We recommend that you keep the target location the same as the Recovery Services vault location.
Target subscription: Select the target subscription used for disaster recovery. By default, the target subscription will be same as the source subscription.
Target resource group: Select the resource group to which all your replicated virtual machines belong.
- By default, Site Recovery creates a new resource group in the target region with an asr suffix in the name.
- If the resource group created by Site Recovery already exists, it's reused.
- You can customize the resource group settings.
- The location of the target resource group can be any Azure region, except the region in which the source VMs are hosted.
Note
You can also create a new target resource group by selecting Create new.

Under Network,
Failover virtual network: Select the failover virtual network.
Note
You can also create a new failover virtual network by selecting Create new.
Failover subnet: Select the failover subnet.

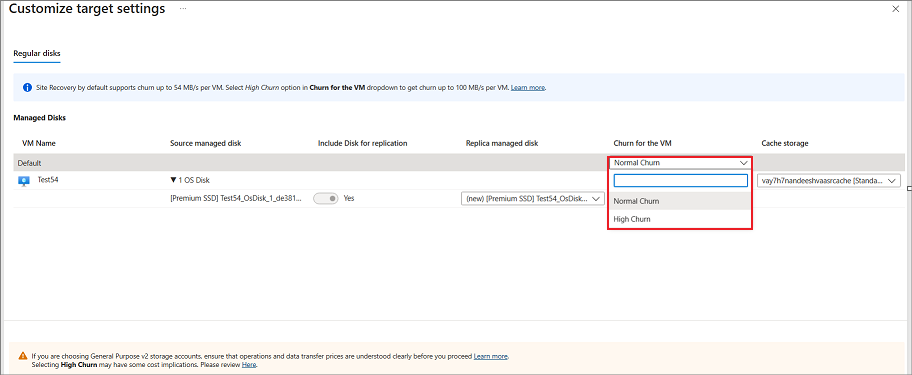
Storage: Select View/edit storage configuration. Customize target settings page opens.

- Replica-managed disk: Site Recovery creates new replica-managed disks in the target region to mirror the source VM's managed disks with the same storage type (Standard or premium) as the source VM's managed disk.
- Cache storage: Site Recovery needs extra storage account called cache storage in the source region. All the changes happening on the source VMs are tracked and sent to cache storage account before replicating them to the target location.
Note
Azure Site Recovery has a High Churn option that you can choose to protect VMs with high data change rate. With this, you can use a Premium Block Blob type of storage account. By default, the Normal Churn option is selected. For more information, see Azure VM Disaster Recovery - High Churn Support.
Availability options: Select appropriate availability option for your VM in the target region. If an availability set that was created by Site Recovery already exists, it's reused. Select View/edit availability options to view or edit the availability options.
Note
- While configuring the target availability sets, configure different availability sets for differently sized VMs.
- You cannot change the availability type - single instance, availability set or availability zone, after you enable replication. You must disable and enable replication to change the availability type.
Capacity reservation: Capacity Reservation lets you purchase capacity in the recovery region, and then failover to that capacity. You can either create a new Capacity Reservation Group or use an existing one. For more information, see how capacity reservation works. Select View or Edit Capacity Reservation group assignment to modify the capacity reservation settings. On triggering Failover, the new VM is created in the assigned Capacity Reservation Group.

Select Next.
In Manage, do the following:
- Under Replication policy,
- Replication policy: Select the replication policy. Defines the settings for recovery point retention history and app-consistent snapshot frequency. By default, Site Recovery creates a new replication policy with default settings of 24 hours for recovery point retention.
- Replication group: Create replication group to replicate VMs together to generate Multi-VM consistent recovery points. Note that enabling multi-VM consistency can impact workload performance and should only be used if machines are running the same workload and you need consistency across multiple machines.
- Under Extension settings,
- Select Update settings and Automation account.

- Under Replication policy,
Select Next
In Review, review the VM settings and select Enable replication.

After the VMs are enabled for replication, you can check the status of VM health under Replicated items. The time taken for initial replication depends on various factors such as the disk size, used storage on the disks, etc. Data transfer happens at ~23% of the disk throughput. Initial replication creates a snapshot of the disk and transfers that snapshot.
Enable replication for added disks
If you add disks to an Azure VM for which replication is enabled, the following occurs:
Replication health for the VM shows a warning, and a note informs telling you that one or more disks are available for protection.
If you enable protection for the added disks, the warning will disappear after the initial replication of the disk.
If you choose not to enable replication for the disk, you can select to dismiss the warning.

To enable replication for an added disk, do the following:
In the vault > Replicated Items, click the VM to which you added the disk.
Click Disks, and then select the data disk for which you want to enable replication (these disks have a Not protected status).
In Disk Details, click Enable replication.

After the enable replication job runs, and the initial replication finishes, the replication health warning for the disk issue is removed.
Note
- During initial replication the status might take some time to refresh, without progress. Click the Refresh button, to get the latest status.
- If a recovery point has not been generated in last 60 minutes, the replication health of the virtual machine will become critical.
Next steps
- Learn more about running a test failover.