How to configure APM integration and CA certificates
Note
The Basic, Standard, and Enterprise plans will be deprecated starting from mid-March, 2025, with a 3 year retirement period. We recommend transitioning to Azure Container Apps. For more information, see the Azure Spring Apps retirement announcement.
The Standard consumption and dedicated plan will be deprecated starting September 30, 2024, with a complete shutdown after six months. We recommend transitioning to Azure Container Apps. For more information, see Migrate Azure Spring Apps Standard consumption and dedicated plan to Azure Container Apps.
This article applies to: ❌ Basic/Standard ✔️ Enterprise
This article shows you how to configure application performance monitor (APM) integration and certificate authority (CA) certificates in the Azure Spring Apps Enterprise plan.
You can enable or disable Tanzu Build Service on an Azure Springs Apps Enterprise plan instance. For more information, see the Build service on demand section of Use Tanzu Build Service.
Prerequisites
- An already provisioned Azure Spring Apps Enterprise plan instance. For more information, see Quickstart: Build and deploy apps to Azure Spring Apps using the Enterprise plan.
- Azure CLI version 2.49.0 or higher. Use the following command to install the Azure Spring Apps extension:
az extension add --name spring
Supported scenarios - APM and CA certificates integration
Tanzu Build Service uses buildpack binding to integrate with Tanzu Partner Buildpacks and other cloud native buildpacks such as the ca-certificates buildpack on GitHub.
Currently, Azure Spring Apps supports the following APM types:
- ApplicationInsights
- Dynatrace
- AppDynamics
- New Relic
- ElasticAPM
Azure Spring Apps supports CA certificates for all language family buildpacks, but not all supported APMs. The following table shows the binding types supported by Tanzu language family buildpacks.
| Buildpack | ApplicationInsights | New Relic | AppDynamics | Dynatrace | ElasticAPM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Java | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| .NET | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| Go | ✔ | ||||
| Python | |||||
| NodeJS | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Web servers | ✔ | ||||
| Java Native Image | |||||
| PHP | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
For information about using Web servers, see Deploy web static files.
Tanzu Build Service is enabled by default in Azure Spring Apps Enterprise. If you choose to disable the build service, you can deploy applications but only by using a custom container image. This section provides guidance for both build service enabled and disabled scenarios.
Supported APM types
This section lists the supported languages and required environment variables for the APMs that you can use for your integrations.
Application Insights
Supported languages:
- Java
Environment variables required for buildpack binding:
connection-string
For other supported environment variables, see Application Insights Overview.
DynaTrace
Supported languages:
- Java
- .NET
- Go
- Node.js
- WebServers
- PHP
Environment variables required for buildpack binding:
api-urlorenvironment-id(used in build step)api-token(used in build step)TENANTTENANTTOKENCONNECTION_POINT
For other supported environment variables, see Dynatrace
New Relic
Supported languages:
- Java
- .NET
- Node.js
- PHP
Environment variables required for buildpack binding:
license_keyapp_name
For other supported environment variables, see New Relic
Elastic
Supported languages:
- Java
- Node.js
- PHP
Environment variables required for buildpack binding:
service_nameapplication_packagesserver_url
For other supported environment variables, see Elastic
AppDynamics
Supported languages:
- Java
- Node.js
Environment variables required for buildpack binding:
agent_application_nameagent_tier_nameagent_node_nameagent_account_nameagent_account_access_keycontroller_host_namecontroller_ssl_enabledcontroller_port
For other supported environment variables, see AppDynamics
Bindings in builder is deprecated
Note
Previously, you would manage APM integration and CA certificates via bindings in the builder. The bindings in builder feature is deprecated and is being removed in the future. We recommend that you migrate the APM configured in bindings. For more information, see the Migrate the APM configured in bindings section.
When you use your own container registry for the build service or disable the build service, the bindings feature in builder is not available.
When you use a managed Azure Container Registry for the build service, the registry is still available for backward compatibility, but is being removed in the future.
When you use the Azure CLI to create a service instance, you might get the error message Buildpack bindings feature is deprecated, it's not available when your own container registry is used for build service or build service is disabled. This message indicates that you're using an old version of the Azure CLI. To fix this issue, upgrade the Azure CLI. For more information, see How to update the Azure CLI.
Configure APM integration for app builds and deployments
You can configure APM in Azure Spring Apps in the following two ways:
Manage APM configurations on the service instance level and bind to app builds and deployments by referring to them. This approach is the recommended way to configure APM.
Manage APM configurations via bindings in the builder and bind to app builds and deployments by referring to the builder.
Note
This approach is the old way to configure APM, and it's now deprecated. We recommend that you migrate the APM configured in bindings. For more information, see the Migrate the APM configured in bindings section.
You can now configure APM in Azure Spring Apps by managing APM configurations on the service instance level and bind to app builds and deployments by referring to them. This approach is the recommended way to configure APM.
The following sections provide guidance for both of these approaches.
Manage APMs on the service instance level (recommended)
You can create an APM configuration and bind to app builds and deployments, as explained in the following sections.
Manage APM configuration in Azure Spring Apps
You can manage APM integration by configuring properties or secrets in the APM configuration using the Azure portal or the Azure CLI.
Note
When configuring properties or secrets via APM configurations, use key names without the APM name as prefix. For example, don't use a DT_ prefix for Dynatrace or APPLICATIONINSIGHTS_ for Application Insights. Tanzu APM buildpacks transform the key name to the original environment variable name with a prefix.
If you intend to override or configure some properties or secrets, such as app name or app level, you need to set environment variables when deploying an app with the original environment variables with the APM name as prefix.
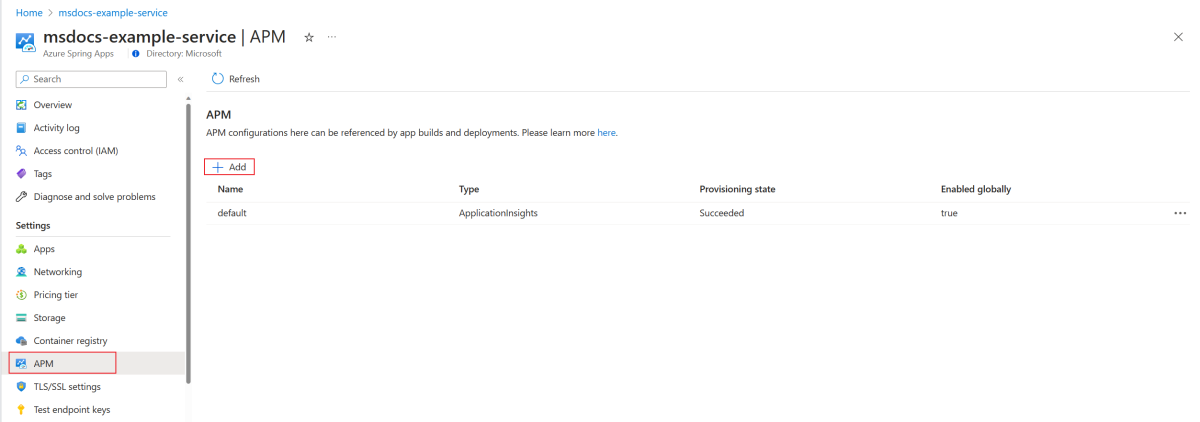
Use the following steps to show, add, edit, or delete an APM configuration:
Open the Azure portal.
In the navigation pane, select APM.
To create an APM configuration, select Add. If you want to enable the APM configuration globally, select Enable globally. All the subsequent builds and deployments use the APM configuration automatically.
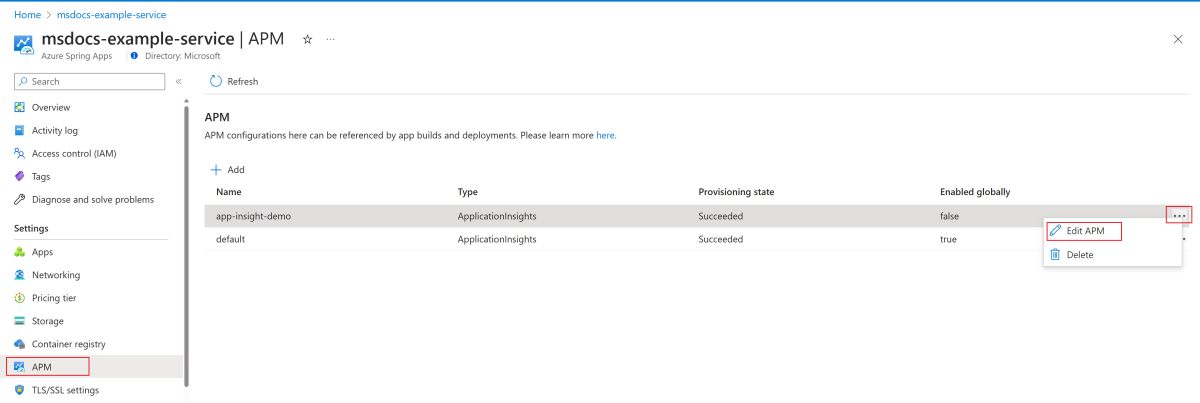
To view or edit an APM configuration, select the ellipsis (...) button for the configuration, then select Edit APM.
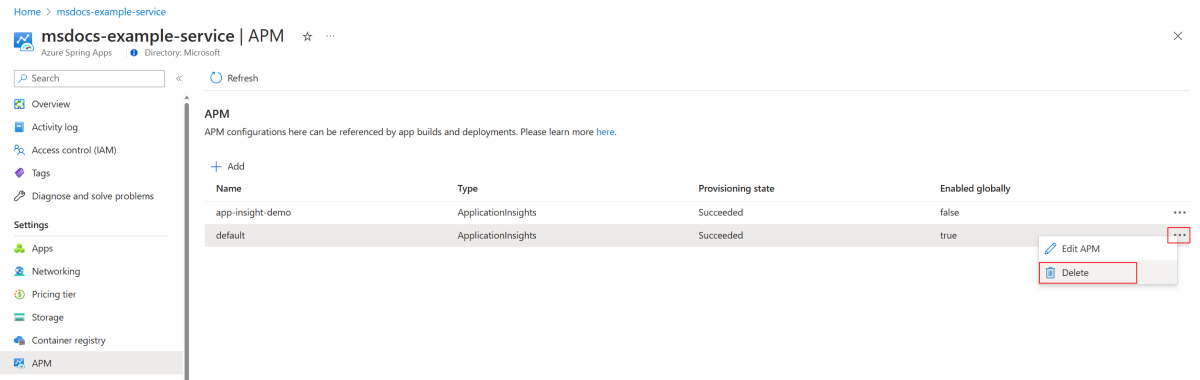
To delete an APM configuration, select the ellipsis (...) button for the configuration and then select Delete. If the APM configuration is used by any build or deployment, you aren't able to delete it.
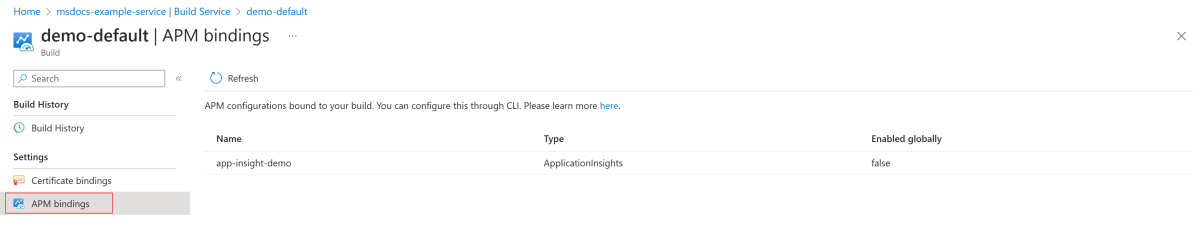
Use the following steps to view the APM configurations bound to the build:
Navigate to the Build Service page for your Azure Spring Apps instance.
On the navigation pane, in the Settings section, select APM bindings.
On the APM bindings page, view the APM configurations bound to the build.
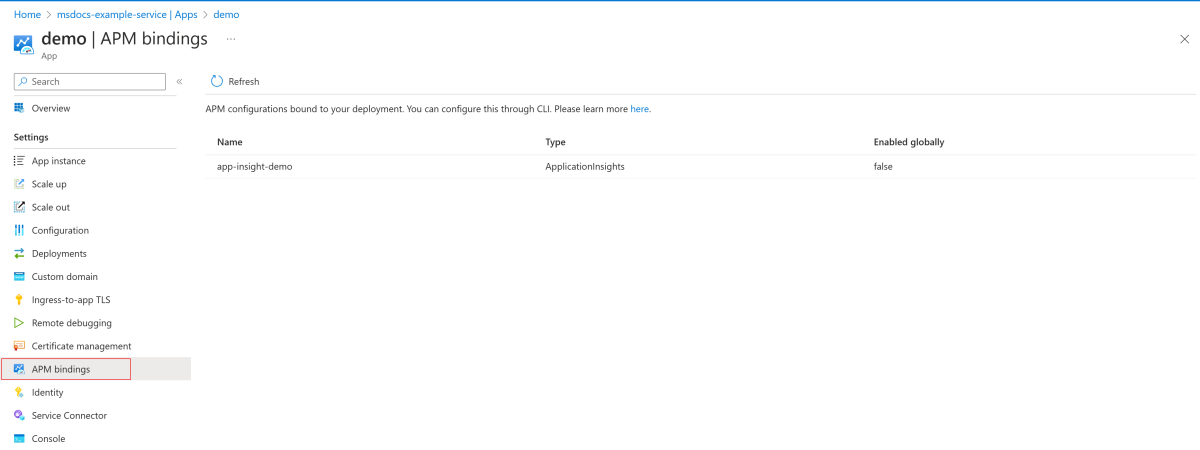
Use the following steps to view the APM configurations bound to the deployment:
For more information on the properties and secrets parameters for your buildpack, see the Supported Scenarios - APM and CA Certificates Integration section.
Bind to app builds and deployments
For a build service that uses a managed Azure Container Registry, use the following command to integrate APM into your deployments:
az spring app deploy \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \
--name <app-name> \
--builder <builder-name> \
--apms <APM-name> \
--artifact-path <path-to-your-JAR-file>
When you enable an APM configuration globally, all the subsequent builds and deployments use it automatically, and it's unnecessary to specify the --apms parameter. If you want to override the APM configuration enabled globally for a deployment, specify the APM configurations via --apms parameter.
For a build service that uses your own container registry, you can build an application into a container image and deploy the image to the current or other Azure Spring Apps Enterprise service instances.
Providing your own container registry separates building from deployment. You can use the build command to create or update a build with a builder, then use the deploy command to deploy the container image to the service.
Use the following command to build an image and configure APM:
az spring build-service build <create|update> \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \
--name <app-name> \
--builder <builder-name> \
--apms <APM-name> \
--artifact-path <path-to-your-JAR-file>
When you enable an APM configuration globally, all the subsequent builds and deployments use it automatically, and it's unnecessary to specify the --apms parameter. If you want to override the APM configuration enabled globally for a build, specify the APM configurations via the --apms parameter.
Use the following command to deploy the application with the container image built previously and configure APM. You can use the APM configuration enabled globally or use the --apms parameter to specify APM configuration.
az spring app deploy \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \
--name <app-name> \
--container-image <your-container-image> \
--container-registry <your-container-registry> \
--registry-password <your-password> \
--registry-username <your-username> \
--apms <your-APM>
When you disable the build service, you can only deploy an application with a container image. For more information, see Deploy an application with a custom container image.
You can use multiple instances of Azure Spring Apps Enterprise, where some instances build and deploy images and others only deploy images. Consider the following scenario:
For one instance, you enable the build service with a user container registry. Then, you build from an artifact file or source code with APM or a CA certificate into a container image. You can then deploy to the current Azure Spring Apps instance or other service instances. For more information, see the Build and deploy polyglot applications section of How to deploy polyglot apps in Azure Spring Apps Enterprise.
In another instance with the build service disabled, you deploy an application with the container image in your registry and also make use of APM.
In this scenario, you can use the APM configuration enabled globally or use the --apms parameter to specify the APM configuration, as shown in the following example:
az spring app deploy \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \
--name <app-name> \
--container-image <your-container-image> \
--container-registry <your-container-registry> \
--registry-password <your-password> \
--registry-username <your-username> \
--apms <your-APM>
Manage APMs via bindings in builder (deprecated)
When the build service uses the Azure Spring Apps managed container registry, you can build an application to an image and then deploy it, but only within the current Azure Spring Apps service instance.
Manage APM configurations via bindings in builder
You can manage APM configurations via bindings in builder. For more information, see the Manage bindings in builder in Azure Spring Apps (deprecated) section.
Bind to app builds and deployments
Use the following command to integrate APM into your deployments. The APM is configured via bindings in the builder:
az spring app deploy \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \
--name <app-name> \
--builder <builder-name> \
--artifact-path <path-to-your-JAR-file>
Enable Application Insights when creating the service instance
If you enable Application Insights when creating a service instance, the following conditions apply:
- If you use a managed Azure Container Registry for the build service, Application Insights is bound to bindings in the default builder.
- If you use your own container registry for the build service or you disable the build service, a default APM configuration is created for Application Insights. The default APM is enabled globally and all the subsequent builds and deployments use it automatically.
Configure CA certificates for app builds and deployments
You can configure CA certificates in Azure Spring Apps in the following two ways:
- You can manage public certificates in the TLS/SSL settings and bind to app builds and deployments by referring to them. This approach is the recommended way to configure CA certificates.
- You can manage public certificates in the TLS/SSL settings and bind CA certificates via bindings in the builder. For more information, see the Manage bindings in builder in Azure Spring Apps (deprecated) section.
Note
This approach is the old way to configure CA certificates and it has been deprecated. We recommend that you migrate the CA certificate configured in bindings. For more information, see the Migrate CA certificate configured in bindings section.
You can now manage public certificates in the TLS/SSL settings and bind to app builds and deployments by referring to them. This approach is the recommended way to configure CA certificates.
To manage public certificates on the service instance level, see the Import a certificate section of Use TLS/SSL certificates in your application in Azure Spring Apps. then, follow one of the approaches described in the following sections to bind CA certificates to app builds and deployments.
Bind CA certificates to app builds and deployments
For information on how to bind CA certificates to deployments, see the Load a certificate section of Use TLS/SSL certificates in your application in Azure Spring Apps. Then, use the following instructions to bind to app builds.
When you enable the build service and use a managed Azure Container Registry, use the following command to integrate CA certificates into your deployment:
az spring app deploy \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \
--name <app-name> \
--builder <builder-name> \
--build-certificates <CA certificate-name> \
--artifact-path <path-to-your-JAR-file>
When you use your own container registry for the build service or disable the build service, use the following command to integrate CA certificates into your build:
az spring build-service build <create|update> \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \
--name <app-name> \
--builder <builder-name> \
--certificates <CA certificate-name> \
--artifact-path <path-to-your-JAR-file>
View CA certificates bound to app builds
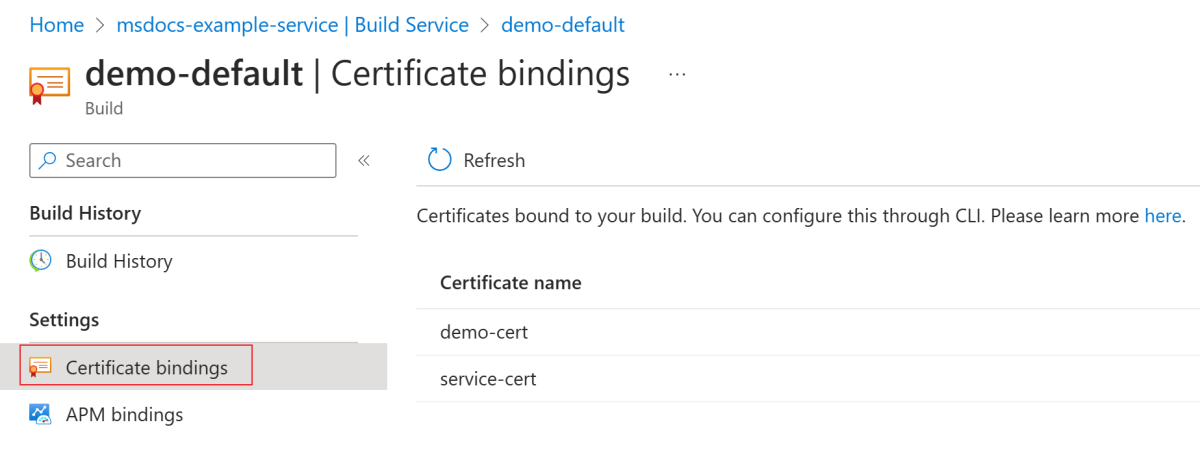
Use the following steps to view the CA certificates bound to the build:
Navigate to your build page.
On the navigation pane, in the Settings section, select Certificate bindings.
On the Certificate bindings page, view the CA certificates bound to the build.
Bind CA certificates via bindings in builder (deprecated)
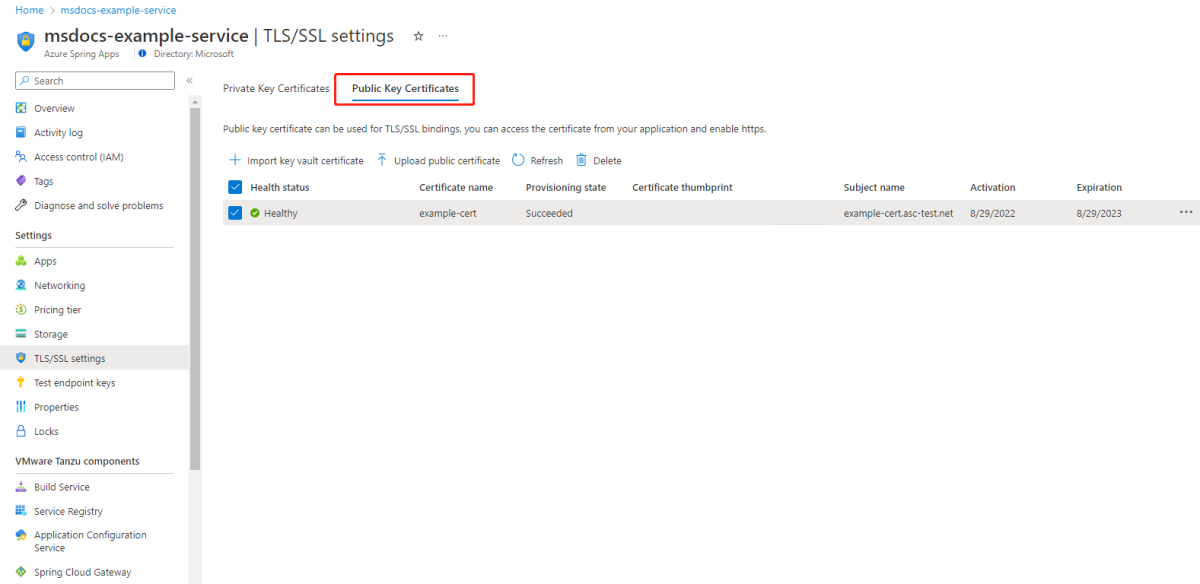
CA certificates use the ca-certificates buildpack to support providing CA certificates to the system trust store at build and runtime.
In the Azure Spring Apps Enterprise plan, the CA certificates use the Public Key Certificates tab on the TLS/SSL settings page in the Azure portal, as shown in the following screenshot:
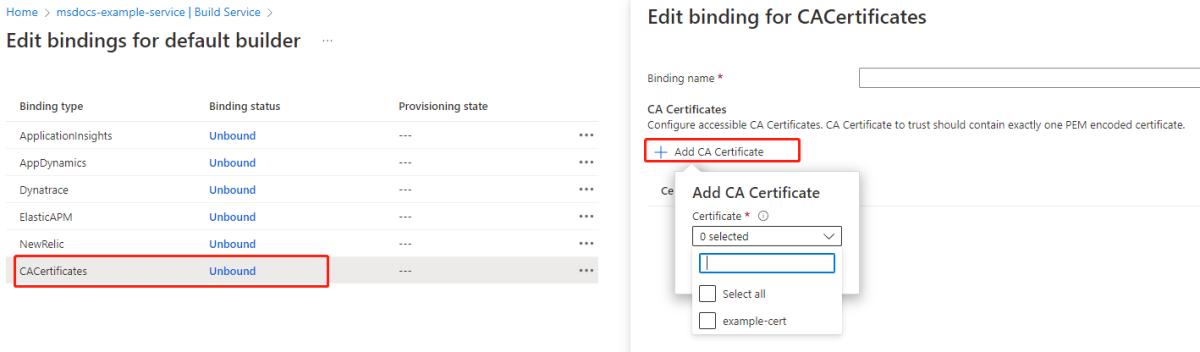
You can configure the CA certificates on the Edit binding page. The succeeded certificates are shown in the CA Certificates list.
Manage bindings in builder in Azure Spring Apps (deprecated)
This section applies only to an Azure Spring Apps Enterprise service instance with the build service enabled. With the build service enabled, one buildpack binding means either credential configuration against one APM type, or CA certificates configuration against the CA certificates type. For APM integration, follow the earlier instructions to configure the necessary environment variables or secrets for your APM.
Note
When configuring environment variables for APM bindings, use key names without a prefix. For example, do not use a DT_ prefix for a Dynatrace binding or APPLICATIONINSIGHTS_ for Application Insights. Tanzu APM buildpacks transform the key name to the original environment variable name with a prefix.
You can manage buildpack bindings with the Azure portal or the Azure CLI.
Use the following steps to view the buildpack bindings:
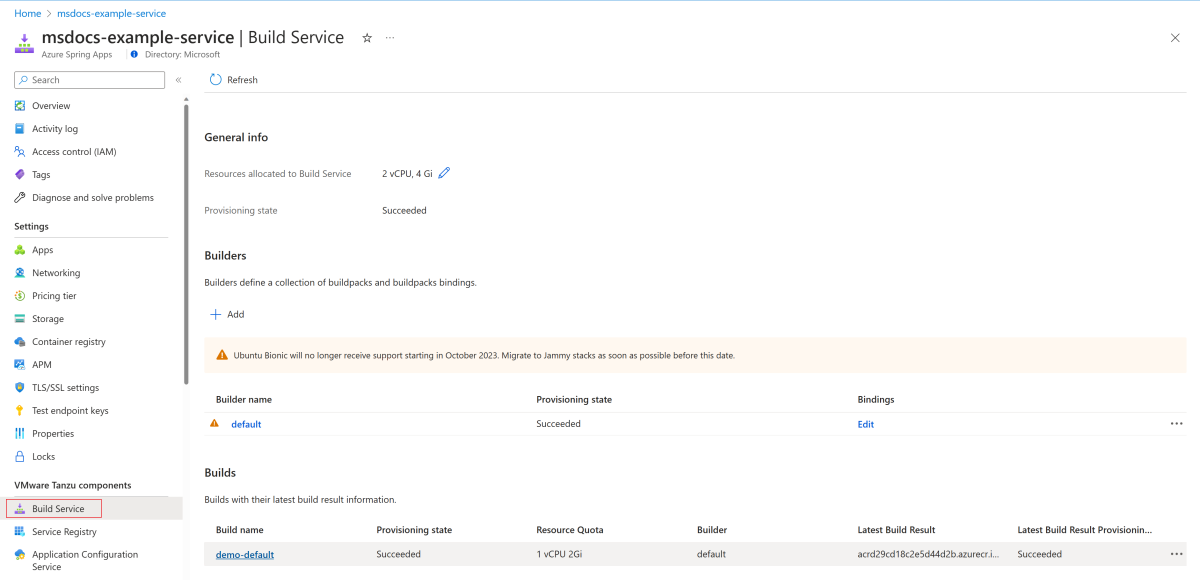
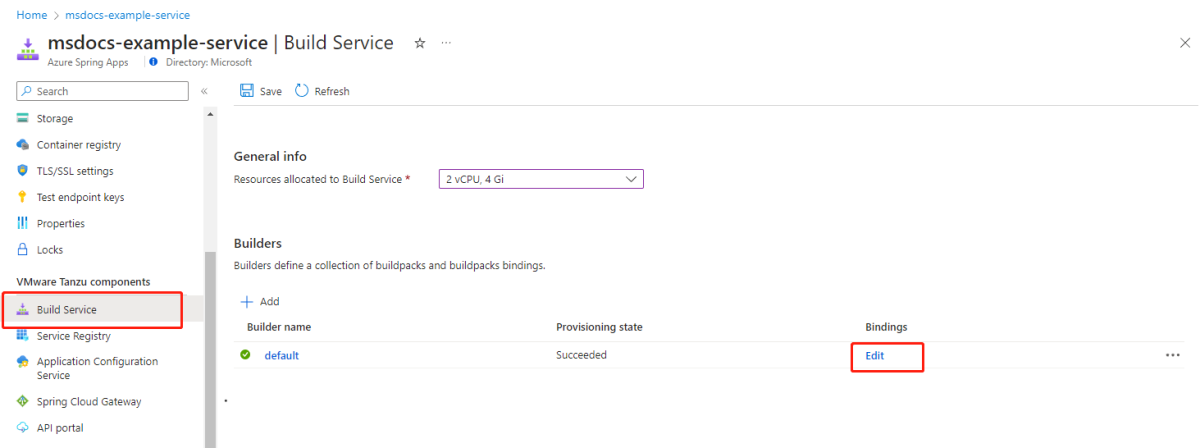
In the Azure portal, go to your Azure Spring Apps Enterprise service instance.
In the navigation pane, select Build Service.
Select Edit under the Bindings column to view the bindings configured for a builder.
Review the bindings on the Edit binding for default builder page.
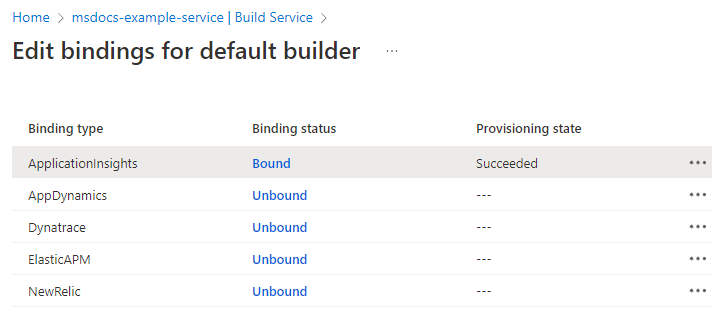
Create a buildpack binding
To create a buildpack binding, select Unbound on the Edit Bindings page, specify the binding properties, and then select Save.
Unbind a buildpack binding
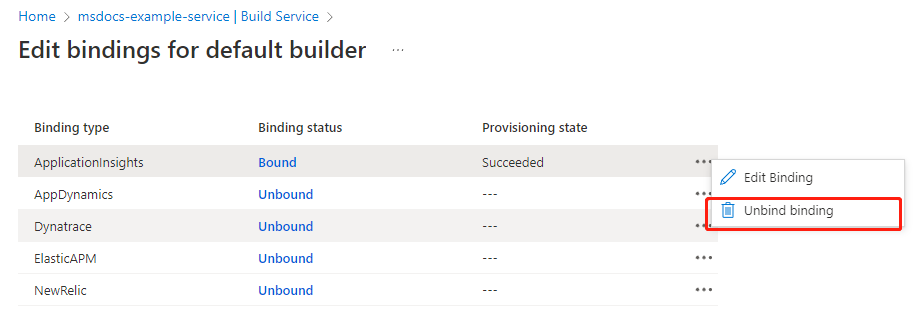
You can unbind a buildpack binding by using the Unbind binding command, or by editing the binding properties.
To use the Unbind binding command, select the Bound hyperlink, and then select Unbind binding.
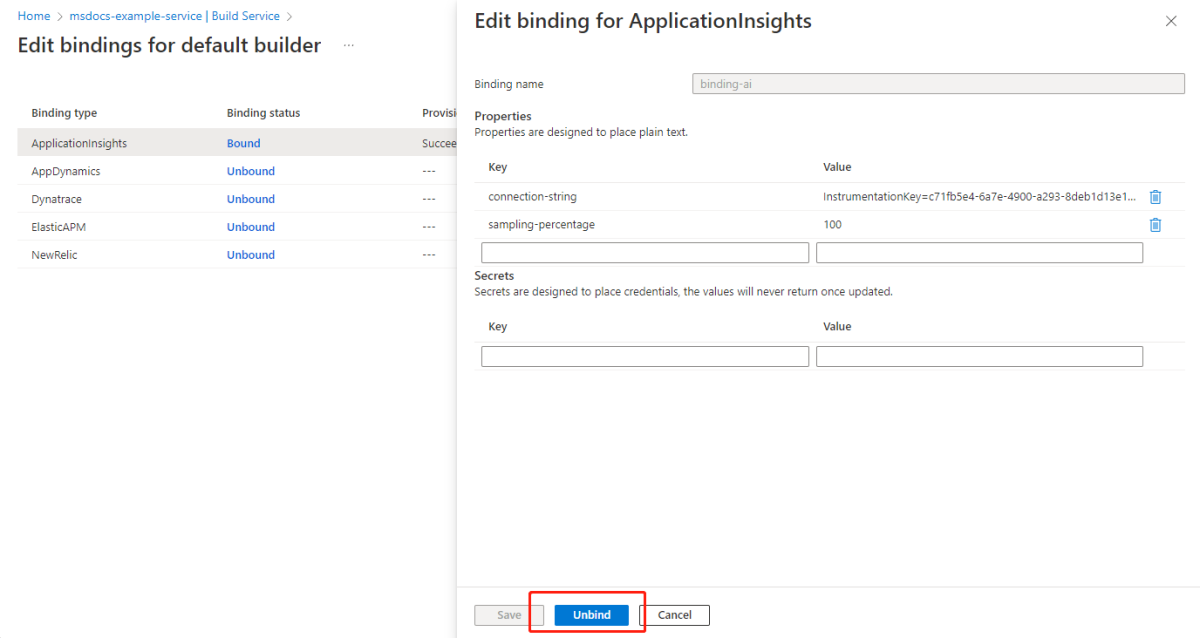
To unbind a buildpack binding by editing binding properties, select Edit Binding, and then select Unbind.
When you unbind a binding, the bind status changes from Bound to Unbound.
Migrate APM and CA certificates from bindings in builder
The bindings feature in builder is deprecated and is being removed in the future. We recommend that you migrate bindings in builder.
You can configure APM and CA certificates in bindings and you can migrate them by using the following sections.
Migrate the APM configured in bindings
In most use cases, there's only one APM configured in bindings in the default builder. You can create a new APM configuration with the same configuration in bindings and enable this APM configuration globally. All the subsequent builds and deployments use this configuration automatically. Use the following steps to migrate:
Use the following command to create an APM configuration:
az spring apm create \ --resource-group <resource-group-name> \ --service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \ --name <your-APM-name> \ --type <your-APM-type> \ --properties a=b c=d \ --secrets e=f g=hUse the following command to enable the APM configuration globally:
az spring apm enable-globally \ --resource-group <resource-group-name> \ --service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \ --name <your-APM-name> \Use the following command to redeploy all the applications to use the new APM configuration enabled globally:
az spring app deploy \ --resource-group <resource-group-name> \ --service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \ --name <app-name> \ --builder <builder-name> \ --artifact-path <path-to-your-JAR-file>Verify that the new APM configuration works for all the applications. If everything works fine, use the following command to remove the APM bindings in builder:
az spring build-service builder buildpack-binding delete \ --resource-group <resource-group-name> \ --service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \ --name <your-APM-buildpack-binding-name> \ --builder-name <your-builder-name>
If there are several APMs configured in bindings, you can create several APM configurations with the same configuration in bindings and enable the APM configuration globally if it's applicable. Use the --apms parameter to specify an APM configuration for a deployment if you want to override the APM enabled globally, as shown in the following command:
az spring app deploy \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \
--name <app-name> \
--builder <builder-name> \
--apms <APM-name> \
--artifact-path <path-to-your-JAR-file>
During the migration process, APM is configured in both bindings and APM configuration. In this case, the APM configuration takes effect and the binding is ignored.
Migrate CA certificate configured in bindings
Use the following steps to migrate a CA certificate:
For a CA certificate configured in binding, if it's used in runtime, you can load the certificate into your application. For more information, see Load a certificate section of Use TLS/SSL certificates in your application in Azure Spring Apps.
Use the following command to redeploy all the applications using the CA certificate. If you use the certificate at build time, use the
--build-certificatesparameter to specify the CA certificate to use at build time for a deployment:az spring app deploy \ --resource-group <resource-group-name> \ --service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \ --name <app-name> \ --builder <builder-name> \ --build-certificates <CA certificate-name> \ --artifact-path <path-to-your-JAR-file>Verify if the CA certificate works for all the applications using it. If everything works fine, use the following command to remove the CA certificate bindings in the builder:
az spring build-service builder buildpack-binding delete \ --resource-group <resource-group-name> \ --service <Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name> \ --name <your-CA-certificate-buildpack-binding-name> \ --builder-name <your-builder-name>