Introduction to Microsoft Spark Utilities
Microsoft Spark Utilities (MSSparkUtils) is a builtin package to help you easily perform common tasks. You can use MSSparkUtils to work with file systems, to get environment variables, to chain notebooks together, and to work with secrets. MSSparkUtils are available in PySpark (Python), Scala, .NET Spark (C#), and R (Preview) notebooks and Synapse pipelines.
Pre-requisites
Configure access to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
Synapse notebooks use Microsoft Entra pass-through to access the ADLS Gen2 accounts. You need to be a Storage Blob Data Contributor to access the ADLS Gen2 account (or folder).
Synapse pipelines use workspace's Managed Service Identity (MSI) to access the storage accounts. To use MSSparkUtils in your pipeline activities, your workspace identity needs to be Storage Blob Data Contributor to access the ADLS Gen2 account (or folder).
Follow these steps to make sure your Microsoft Entra ID and workspace MSI have access to the ADLS Gen2 account:
Open the Azure portal and the storage account you want to access. You can navigate to the specific container you want to access.
Select the Access control (IAM) from the left panel.
Select Add > Add role assignment to open the Add role assignment page.
Assign the following role. For detailed steps, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal.
Setting Value Role Storage Blob Data Contributor Assign access to USER and MANAGEDIDENTITY Members your Microsoft Entra account and your workspace identity Note
The managed identity name is also the workspace name.

Select Save.
You can access data on ADLS Gen2 with Synapse Spark via the following URL:
abfss://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.windows.net/<path>
Configure access to Azure Blob Storage
Synapse uses Shared access signature (SAS) to access Azure Blob Storage. To avoid exposing SAS keys in the code, we recommend creating a new linked service in Synapse workspace to the Azure Blob Storage account you want to access.
Follow these steps to add a new linked service for an Azure Blob Storage account:
- Open the Azure Synapse Studio.
- Select Manage from the left panel and select Linked services under the External connections.
- Search Azure Blob Storage in the New linked Service panel on the right.
- Select Continue.
- Select the Azure Blob Storage Account to access and configure the linked service name. Suggest using Account key for the Authentication method.
- Select Test connection to validate the settings are correct.
- Select Create first and click Publish all to save your changes.
You can access data on Azure Blob Storage with Synapse Spark via following URL:
wasb[s]://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.blob.core.windows.net/<path>
Here is a code example:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Azure storage access info
blob_account_name = 'Your account name' # replace with your blob name
blob_container_name = 'Your container name' # replace with your container name
blob_relative_path = 'Your path' # replace with your relative folder path
linked_service_name = 'Your linked service name' # replace with your linked service name
blob_sas_token = mssparkutils.credentials.getConnectionStringOrCreds(linked_service_name)
# Allow SPARK to access from Blob remotely
wasb_path = 'wasbs://%s@%s.blob.core.windows.net/%s' % (blob_container_name, blob_account_name, blob_relative_path)
spark.conf.set('fs.azure.sas.%s.%s.blob.core.windows.net' % (blob_container_name, blob_account_name), blob_sas_token)
print('Remote blob path: ' + wasb_path)
val blob_account_name = "" // replace with your blob name
val blob_container_name = "" //replace with your container name
val blob_relative_path = "/" //replace with your relative folder path
val linked_service_name = "" //replace with your linked service name
val blob_sas_token = mssparkutils.credentials.getConnectionStringOrCreds(linked_service_name)
val wasbs_path = f"wasbs://$blob_container_name@$blob_account_name.blob.core.windows.net/$blob_relative_path"
spark.conf.set(f"fs.azure.sas.$blob_container_name.$blob_account_name.blob.core.windows.net",blob_sas_token)
var blob_account_name = ""; // replace with your blob name
var blob_container_name = ""; // replace with your container name
var blob_relative_path = ""; // replace with your relative folder path
var linked_service_name = ""; // replace with your linked service name
var blob_sas_token = Credentials.GetConnectionStringOrCreds(linked_service_name);
spark.Conf().Set($"fs.azure.sas.{blob_container_name}.{blob_account_name}.blob.core.windows.net", blob_sas_token);
var wasbs_path = $"wasbs://{blob_container_name}@{blob_account_name}.blob.core.windows.net/{blob_relative_path}";
Console.WriteLine(wasbs_path);
# Azure storage access info
blob_account_name <- 'Your account name' # replace with your blob name
blob_container_name <- 'Your container name' # replace with your container name
blob_relative_path <- 'Your path' # replace with your relative folder path
linked_service_name <- 'Your linked service name' # replace with your linked service name
blob_sas_token <- mssparkutils.credentials.getConnectionStringOrCreds(linked_service_name)
# Allow SPARK to access from Blob remotely
sparkR.session()
wasb_path <- sprintf('wasbs://%s@%s.blob.core.windows.net/%s',blob_container_name, blob_account_name, blob_relative_path)
sparkR.session(sprintf('fs.azure.sas.%s.%s.blob.core.windows.net',blob_container_name, blob_account_name), blob_sas_token)
print( paste('Remote blob path: ',wasb_path))
Configure access to Azure Key Vault
You can add an Azure Key Vault as a linked service to manage your credentials in Synapse. Follow these steps to add an Azure Key Vault as a Synapse linked service:
Open the Azure Synapse Studio.
Select Manage from the left panel and select Linked services under the External connections.
Search Azure Key Vault in the New linked Service panel on the right.
Select the Azure Key Vault Account to access and configure the linked service name.
Select Test connection to validate the settings are correct.
Select Create first and click Publish all to save your change.
Synapse notebooks use Microsoft Entra pass-through to access Azure Key Vault. Synapse pipelines use workspace identity(MSI) to access Azure Key Vault. To make sure your code work both in notebook and in Synapse pipeline, we recommend granting secret access permission for both your Microsoft Entra account and workspace identity.
Follow these steps to grant secret access to your workspace identity:
- Open the Azure portal and the Azure Key Vault you want to access.
- Select the Access policies from the left panel.
- Select Add Access Policy:
- Choose Key, Secret, & Certificate Management as config template.
- Select your Microsoft Entra account and your workspace identity (same as your workspace name) in the select principal or make sure it is already assigned.
- Select Select and Add.
- Select the Save button to commit changes.
File system utilities
mssparkutils.fs provides utilities for working with various file systems, including Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (ADLS Gen2) and Azure Blob Storage. Make sure you configure access to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 and Azure Blob Storage appropriately.
Run the following commands for an overview of the available methods:
from notebookutils import mssparkutils
mssparkutils.fs.help()
mssparkutils.fs.help()
using Microsoft.Spark.Extensions.Azure.Synapse.Analytics.Notebook.MSSparkUtils;
FS.Help()
library(notebookutils)
mssparkutils.fs.help()
Results in:
mssparkutils.fs provides utilities for working with various FileSystems.
Below is overview about the available methods:
cp(from: String, to: String, recurse: Boolean = false): Boolean -> Copies a file or directory, possibly across FileSystems
mv(src: String, dest: String, create_path: Boolean = False, overwrite: Boolean = False): Boolean -> Moves a file or directory, possibly across FileSystems
ls(dir: String): Array -> Lists the contents of a directory
mkdirs(dir: String): Boolean -> Creates the given directory if it does not exist, also creating any necessary parent directories
put(file: String, contents: String, overwrite: Boolean = false): Boolean -> Writes the given String out to a file, encoded in UTF-8
head(file: String, maxBytes: int = 1024 * 100): String -> Returns up to the first 'maxBytes' bytes of the given file as a String encoded in UTF-8
append(file: String, content: String, createFileIfNotExists: Boolean): Boolean -> Append the content to a file
rm(dir: String, recurse: Boolean = false): Boolean -> Removes a file or directory
Use mssparkutils.fs.help("methodName") for more info about a method.
List files
List the content of a directory.
mssparkutils.fs.ls('Your directory path')
mssparkutils.fs.ls("Your directory path")
FS.Ls("Your directory path")
mssparkutils.fs.ls("Your directory path")
View file properties
Returns file properties including file name, file path, file size, file modification time, and whether it is a directory and a file.
files = mssparkutils.fs.ls('Your directory path')
for file in files:
print(file.name, file.isDir, file.isFile, file.path, file.size, file.modifyTime)
val files = mssparkutils.fs.ls("/")
files.foreach{
file => println(file.name,file.isDir,file.isFile,file.size,file.modifyTime)
}
var Files = FS.Ls("/");
foreach(var File in Files) {
Console.WriteLine(File.Name+" "+File.IsDir+" "+File.IsFile+" "+File.Size);
}
files <- mssparkutils.fs.ls("/")
for (file in files) {
writeLines(paste(file$name, file$isDir, file$isFile, file$size, file$modifyTime))
}
Create new directory
Creates the given directory if it does not exist and any necessary parent directories.
mssparkutils.fs.mkdirs('new directory name')
mssparkutils.fs.mkdirs("new directory name")
FS.Mkdirs("new directory name")
mssparkutils.fs.mkdirs("new directory name")
Copy file
Copies a file or directory. Supports copy across file systems.
mssparkutils.fs.cp('source file or directory', 'destination file or directory', True)# Set the third parameter as True to copy all files and directories recursively
mssparkutils.fs.cp("source file or directory", "destination file or directory", true) // Set the third parameter as True to copy all files and directories recursively
FS.Cp("source file or directory", "destination file or directory", true) // Set the third parameter as True to copy all files and directories recursively
mssparkutils.fs.cp('source file or directory', 'destination file or directory', True)
Performant copy file
This method provides a faster way of copying or moving files, especially large volumes of data.
mssparkutils.fs.fastcp('source file or directory', 'destination file or directory', True) # Set the third parameter as True to copy all files and directories recursively
Note
The method only supports in Azure Synapse Runtime for Apache Spark 3.3 and Azure Synapse Runtime for Apache Spark 3.4.
Preview file content
Returns up to the first 'maxBytes' bytes of the given file as a String encoded in UTF-8.
mssparkutils.fs.head('file path', maxBytes to read)
mssparkutils.fs.head("file path", maxBytes to read)
FS.Head("file path", maxBytes to read)
mssparkutils.fs.head('file path', maxBytes to read)
Move file
Moves a file or directory. Supports move across file systems.
mssparkutils.fs.mv('source file or directory', 'destination directory', True) # Set the last parameter as True to firstly create the parent directory if it does not exist
mssparkutils.fs.mv("source file or directory", "destination directory", true) // Set the last parameter as True to firstly create the parent directory if it does not exist
FS.Mv("source file or directory", "destination directory", true)
mssparkutils.fs.mv('source file or directory', 'destination directory', True) # Set the last parameter as True to firstly create the parent directory if it does not exist
Write file
Writes the given string out to a file, encoded in UTF-8.
mssparkutils.fs.put("file path", "content to write", True) # Set the last parameter as True to overwrite the file if it existed already
mssparkutils.fs.put("file path", "content to write", true) // Set the last parameter as True to overwrite the file if it existed already
FS.Put("file path", "content to write", true) // Set the last parameter as True to overwrite the file if it existed already
mssparkutils.fs.put("file path", "content to write", True) # Set the last parameter as True to overwrite the file if it existed already
Append content to a file
Appends the given string to a file, encoded in UTF-8.
mssparkutils.fs.append("file path", "content to append", True) # Set the last parameter as True to create the file if it does not exist
mssparkutils.fs.append("file path","content to append",true) // Set the last parameter as True to create the file if it does not exist
FS.Append("file path", "content to append", true) // Set the last parameter as True to create the file if it does not exist
mssparkutils.fs.append("file path", "content to append", True) # Set the last parameter as True to create the file if it does not exist
Note
mssparkutils.fs.append() and mssparkutils.fs.put() do not support concurrent writing to the same file due to lack of atomicity guarantees.
Delete file or directory
Removes a file or a directory.
mssparkutils.fs.rm('file path', True) # Set the last parameter as True to remove all files and directories recursively
mssparkutils.fs.rm("file path", true) // Set the last parameter as True to remove all files and directories recursively
FS.Rm("file path", true) // Set the last parameter as True to remove all files and directories recursively
mssparkutils.fs.rm('file path', True) # Set the last parameter as True to remove all files and directories recursively
Notebook utilities
Not supported.
You can use the MSSparkUtils Notebook Utilities to run a notebook or exit a notebook with a value. Run the following command to get an overview of the available methods:
mssparkutils.notebook.help()
Get results:
The notebook module.
exit(value: String): void -> This method lets you exit a notebook with a value.
run(path: String, timeoutSeconds: int, arguments: Map): String -> This method runs a notebook and returns its exit value.
Note
Notebook utilities aren't applicable for Apache Spark job definitions (SJD).
Reference a notebook
Reference a notebook and returns its exit value. You can run nesting function calls in a notebook interactively or in a pipeline. The notebook being referenced will run on the Spark pool of which notebook calls this function.
mssparkutils.notebook.run("notebook path", <timeoutSeconds>, <parameterMap>)
For example:
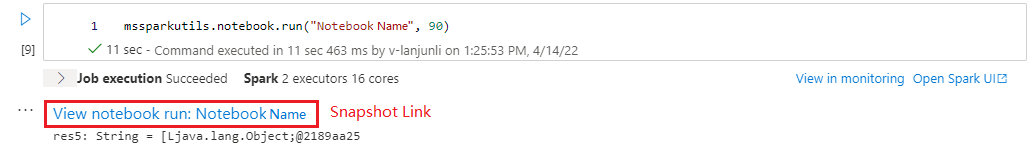
mssparkutils.notebook.run("folder/Sample1", 90, {"input": 20 })
After the run finished, you will see a snapshot link named 'View notebook run: Notebook Name' shown in the cell output, you can click the link to see the snapshot for this specific run.
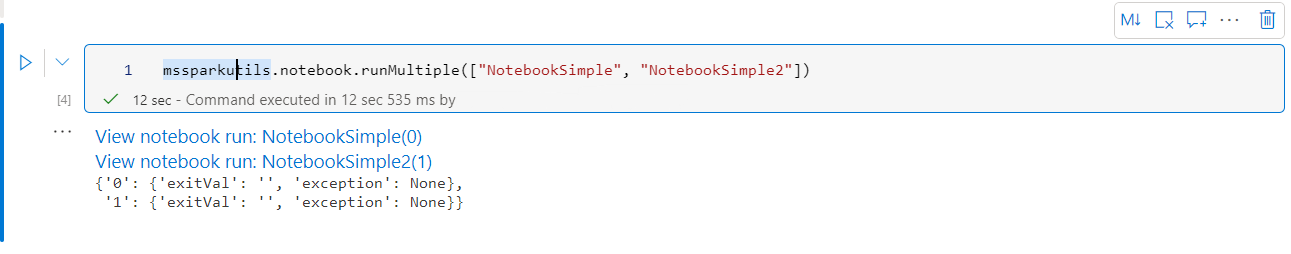
Reference run multiple notebooks in parallel
The method mssparkutils.notebook.runMultiple() allows you to run multiple notebooks in parallel or with a predefined topological structure. The API is using a multi-thread implementation mechanism within a spark session, which means the compute resources are shared by the reference notebook runs.
With mssparkutils.notebook.runMultiple(), you can:
Execute multiple notebooks simultaneously, without waiting for each one to finish.
Specify the dependencies and order of execution for your notebooks, using a simple JSON format.
Optimize the use of Spark compute resources and reduce the cost of your Synapse projects.
View the Snapshots of each notebook run record in the output, and debug/monitor your notebook tasks conveniently.
Get the exit value of each executive activity and use them in downstream tasks.
You can also try to run the mssparkutils.notebook.help("runMultiple") to find the example and detailed usage.
Here's a simple example of running a list of notebooks in parallel using this method:
mssparkutils.notebook.runMultiple(["NotebookSimple", "NotebookSimple2"])
The execution result from the root notebook is as follows:
The following is an example of running notebooks with topological structure using mssparkutils.notebook.runMultiple(). Use this method to easily orchestrate notebooks through a code experience.
# run multiple notebooks with parameters
DAG = {
"activities": [
{
"name": "NotebookSimple", # activity name, must be unique
"path": "NotebookSimple", # notebook path
"timeoutPerCellInSeconds": 90, # max timeout for each cell, default to 90 seconds
"args": {"p1": "changed value", "p2": 100}, # notebook parameters
},
{
"name": "NotebookSimple2",
"path": "NotebookSimple2",
"timeoutPerCellInSeconds": 120,
"args": {"p1": "changed value 2", "p2": 200}
},
{
"name": "NotebookSimple2.2",
"path": "NotebookSimple2",
"timeoutPerCellInSeconds": 120,
"args": {"p1": "changed value 3", "p2": 300},
"retry": 1,
"retryIntervalInSeconds": 10,
"dependencies": ["NotebookSimple"] # list of activity names that this activity depends on
}
]
}
mssparkutils.notebook.runMultiple(DAG)
Note
- The method only supports in Azure Synapse Runtime for Apache Spark 3.3 and Azure Synapse Runtime for Apache Spark 3.4.
- The parallelism degree of the multiple notebook run is restricted to the total available compute resource of a Spark session.
Exit a notebook
Exits a notebook with a value. You can run nesting function calls in a notebook interactively or in a pipeline.
When you call an exit() function from a notebook interactively, Azure Synapse will throw an exception, skip running subsequence cells, and keep the Spark session alive.
When you orchestrate a notebook that calls an
exit()function in a Synapse pipeline, Azure Synapse will return an exit value, complete the pipeline run, and stop the Spark session.When you call an
exit()function in a notebook being referenced, Azure Synapse will stop the further execution in the notebook being referenced, and continue to run next cells in the notebook that call therun()function. For example: Notebook1 has three cells and calls anexit()function in the second cell. Notebook2 has five cells and callsrun(notebook1)in the third cell. When you run Notebook2, Notebook1 will be stopped at the second cell when hitting theexit()function. Notebook2 will continue to run its fourth cell and fifth cell.
mssparkutils.notebook.exit("value string")
For example:
Sample1 notebook locates under folder/ with following two cells:
- cell 1 defines an input parameter with default value set to 10.
- cell 2 exits the notebook with input as exit value.
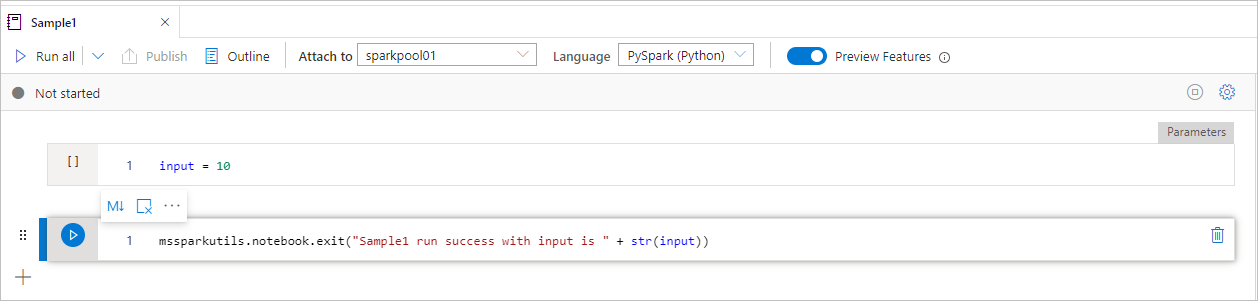
You can run the Sample1 in another notebook with default values:
exitVal = mssparkutils.notebook.run("folder/Sample1")
print (exitVal)
Results in:
Sample1 run success with input is 10
You can run the Sample1 in another notebook and set the input value as 20:
exitVal = mssparkutils.notebook.run("mssparkutils/folder/Sample1", 90, {"input": 20 })
print (exitVal)
Results in:
Sample1 run success with input is 20
You can use the MSSparkUtils Notebook Utilities to run a notebook or exit a notebook with a value. Run the following command to get an overview of the available methods:
mssparkutils.notebook.help()
Get results:
The notebook module.
exit(value: String): void -> This method lets you exit a notebook with a value.
run(path: String, timeoutSeconds: int, arguments: Map): String -> This method runs a notebook and returns its exit value.
Reference a notebook
Reference a notebook and returns its exit value. You can run nesting function calls in a notebook interactively or in a pipeline. The notebook being referenced will run on the Spark pool of which notebook calls this function.
mssparkutils.notebook.run("notebook path", <timeoutSeconds>, <parameterMap>)
For example:
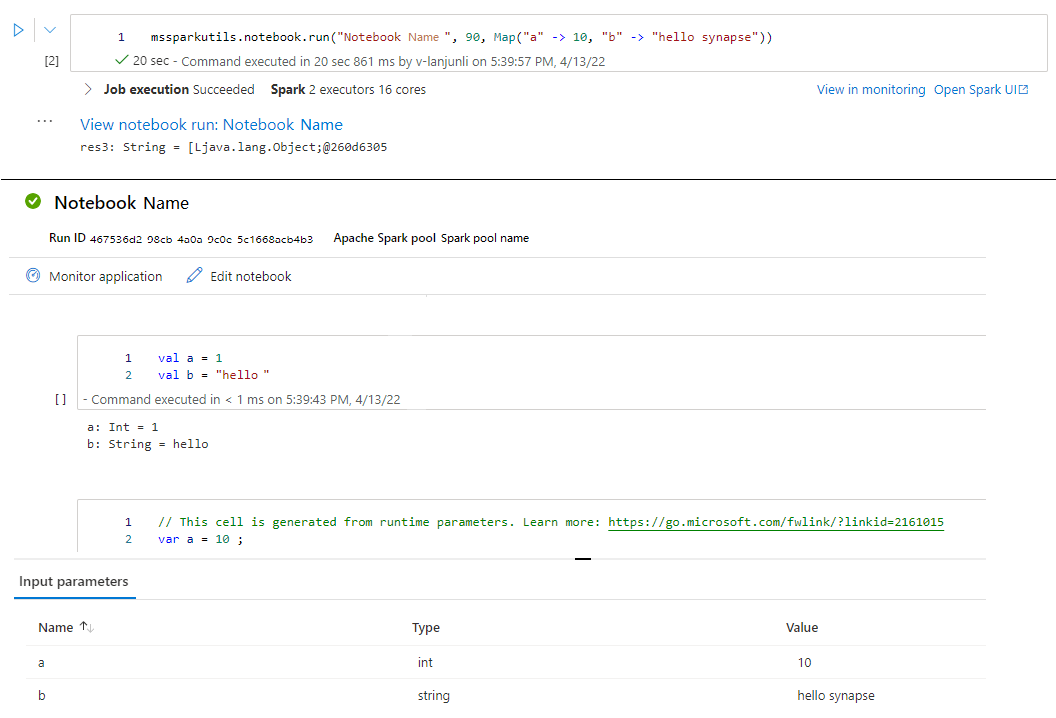
mssparkutils.notebook.run("folder/Sample1", 90, Map("input" -> 20))
After the run finished, you will see a snapshot link named 'View notebook run: Notebook Name' shown in the cell output, you can click the link to see the snapshot for this specific run.
Exit a notebook
Exits a notebook with a value. You can run nesting function calls in a notebook interactively or in a pipeline.
When you call an
exit()function a notebook interactively, Azure Synapse will throw an exception, skip running subsequence cells, and keep Spark session alive.When you orchestrate a notebook that calls an
exit()function in a Synapse pipeline, Azure Synapse will return an exit value, complete the pipeline run, and stop the Spark session.When you call an
exit()function in a notebook being referenced, Azure Synapse will stop the further execution in the notebook being referenced, and continue to run next cells in the notebook that call therun()function. For example: Notebook1 has three cells and calls anexit()function in the second cell. Notebook2 has five cells and callsrun(notebook1)in the third cell. When you run Notebook2, Notebook1 will be stopped at the second cell when hitting theexit()function. Notebook2 will continue to run its fourth cell and fifth cell.
mssparkutils.notebook.exit("value string")
For example:
Sample1 notebook locates under mssparkutils/folder/ with following two cells:
- cell 1 defines an input parameter with default value set to 10.
- cell 2 exits the notebook with input as exit value.

You can run the Sample1 in another notebook with default values:
val exitVal = mssparkutils.notebook.run("mssparkutils/folder/Sample1")
print(exitVal)
Results in:
exitVal: String = Sample1 run success with input is 10
Sample1 run success with input is 10
You can run the Sample1 in another notebook and set the input value as 20:
val exitVal = mssparkutils.notebook.run("mssparkutils/folder/Sample1", 90, {"input": 20 })
print(exitVal)
Results in:
exitVal: String = Sample1 run success with input is 20
Sample1 run success with input is 20
You can use the MSSparkUtils Notebook Utilities to run a notebook or exit a notebook with a value. Run the following command to get an overview of the available methods:
mssparkutils.notebook.help()
Get results:
The notebook module.
exit(value: String): void -> This method lets you exit a notebook with a value.
run(path: String, timeoutSeconds: int, arguments: Map): String -> This method runs a notebook and returns its exit value.
Reference a notebook
Reference a notebook and returns its exit value. You can run nesting function calls in a notebook interactively or in a pipeline. The notebook being referenced will run on the Spark pool of which notebook calls this function.
mssparkutils.notebook.run("notebook path", <timeoutSeconds>, <parameterMap>)
For example:
mssparkutils.notebook.run("folder/Sample1", 90, list("input": 20))
After the run finished, you will see a snapshot link named 'View notebook run: Notebook Name' shown in the cell output, you can click the link to see the snapshot for this specific run.
Exit a notebook
Exits a notebook with a value. You can run nesting function calls in a notebook interactively or in a pipeline.
When you call an
exit()function a notebook interactively, Azure Synapse will throw an exception, skip running subsequence cells, and keep Spark session alive.When you orchestrate a notebook that calls an
exit()function in a Synapse pipeline, Azure Synapse will return an exit value, complete the pipeline run, and stop the Spark session.When you call an
exit()function in a notebook being referenced, Azure Synapse will stop the further execution in the notebook being referenced, and continue to run next cells in the notebook that call therun()function. For example: Notebook1 has three cells and calls anexit()function in the second cell. Notebook2 has five cells and callsrun(notebook1)in the third cell. When you run Notebook2, Notebook1 will be stopped at the second cell when hitting theexit()function. Notebook2 will continue to run its fourth cell and fifth cell.
mssparkutils.notebook.exit("value string")
For example:
Sample1 notebook locates under folder/ with following two cells:
- cell 1 defines an input parameter with default value set to 10.
- cell 2 exits the notebook with input as exit value.

You can run the Sample1 in another notebook with default values:
exitVal <- mssparkutils.notebook.run("folder/Sample1")
print (exitVal)
Results in:
Sample1 run success with input is 10
You can run the Sample1 in another notebook and set the input value as 20:
exitVal <- mssparkutils.notebook.run("mssparkutils/folder/Sample1", 90, list("input": 20))
print (exitVal)
Results in:
Sample1 run success with input is 20
Credentials utilities
You can use the MSSparkUtils Credentials Utilities to get the access tokens of linked services and manage secrets in Azure Key Vault.
Run the following command to get an overview of the available methods:
mssparkutils.credentials.help()
mssparkutils.credentials.help()
Not supported.
mssparkutils.credentials.help()
Get result:
getToken(audience, name): returns AAD token for a given audience, name (optional)
isValidToken(token): returns true if token hasn't expired
getConnectionStringOrCreds(linkedService): returns connection string or credentials for linked service
getFullConnectionString(linkedService): returns full connection string with credentials
getPropertiesAll(linkedService): returns all the properties of a linked servicegetSecret(akvName, secret, linkedService): returns AKV secret for a given AKV linked service, akvName, secret key
getSecret(akvName, secret): returns AKV secret for a given akvName, secret key
getSecretWithLS(linkedService, secret): returns AKV secret for a given linked service, secret key
putSecret(akvName, secretName, secretValue, linkedService): puts AKV secret for a given akvName, secretName
putSecret(akvName, secretName, secretValue): puts AKV secret for a given akvName, secretName
putSecretWithLS(linkedService, secretName, secretValue): puts AKV secret for a given linked service, secretName
getToken(audience, name): returns AAD token for a given audience, name (optional)
isValidToken(token): returns true if token hasn't expired
getConnectionStringOrCreds(linkedService): returns connection string or credentials for linked service
getFullConnectionString(linkedService): returns full connection string with credentials
getPropertiesAll(linkedService): returns all the properties of a linked servicegetSecret(akvName, secret, linkedService): returns AKV secret for a given AKV linked service, akvName, secret key
getSecret(akvName, secret): returns AKV secret for a given akvName, secret key
getSecretWithLS(linkedService, secret): returns AKV secret for a given linked service, secret key
putSecret(akvName, secretName, secretValue, linkedService): puts AKV secret for a given akvName, secretName
putSecret(akvName, secretName, secretValue): puts AKV secret for a given akvName, secretName
putSecretWithLS(linkedService, secretName, secretValue): puts AKV secret for a given linked service, secretName
getToken(audience, name): returns AAD token for a given audience, name (optional)
isValidToken(token): returns true if token hasn't expired
getConnectionStringOrCreds(linkedService): returns connection string or credentials for linked service
getFullConnectionString(linkedService): returns full connection string with credentials
getPropertiesAll(linkedService): returns all the properties of a linked servicegetSecret(akvName, secret, linkedService): returns AKV secret for a given AKV linked service, akvName, secret key
getSecret(akvName, secret): returns AKV secret for a given akvName, secret key
putSecret(akvName, secretName, secretValue, linkedService): puts AKV secret for a given akvName, secretName
putSecret(akvName, secretName, secretValue): puts AKV secret for a given akvName, secretName
putSecretWithLS(linkedService, secretName, secretValue): puts AKV secret for a given linked service, secretName
Note
Currently getSecretWithLS(linkedService, secret) is not supported in C#.
getToken(audience, name): returns AAD token for a given audience, name (optional)
isValidToken(token): returns true if token hasn't expired
getConnectionStringOrCreds(linkedService): returns connection string or credentials for linked service
getFullConnectionString(linkedService): returns full connection string with credentials
getPropertiesAll(linkedService): returns all the properties of a linked servicegetSecret(akvName, secret, linkedService): returns AKV secret for a given AKV linked service, akvName, secret key
getSecret(akvName, secret): returns AKV secret for a given akvName, secret key
getSecretWithLS(linkedService, secret): returns AKV secret for a given linked service, secret key
putSecret(akvName, secretName, secretValue, linkedService): puts AKV secret for a given akvName, secretName
putSecret(akvName, secretName, secretValue): puts AKV secret for a given akvName, secretName
putSecretWithLS(linkedService, secretName, secretValue): puts AKV secret for a given linked service, secretName
Get token
Returns Microsoft Entra token for a given audience, name (optional). The table below list all the available audience types:
| Audience Type | String literal to be used in API call |
|---|---|
| Azure Storage | Storage |
| Azure Key Vault | Vault |
| Azure Management | AzureManagement |
| Azure SQL Data Warehouse (Dedicated and Serverless) | DW |
| Azure Synapse | Synapse |
| Azure Data Lake Store | DataLakeStore |
| Azure Data Factory | ADF |
| Azure Data Explorer | AzureDataExplorer |
| Azure Database for MySQL | AzureOSSDB |
| Azure Database for MariaDB | AzureOSSDB |
| Azure Database for PostgreSQL | AzureOSSDB |
mssparkutils.credentials.getToken('audience Key')
mssparkutils.credentials.getToken("audience Key")
Credentials.GetToken("audience Key")
mssparkutils.credentials.getToken('audience Key')
Validate token
Returns true if token hasn't expired.
mssparkutils.credentials.isValidToken('your token')
mssparkutils.credentials.isValidToken("your token")
Credentials.IsValidToken("your token")
mssparkutils.credentials.isValidToken('your token')
Get connection string or credentials for linked service
Returns connection string or credentials for linked service.
mssparkutils.credentials.getConnectionStringOrCreds('linked service name')
mssparkutils.credentials.getConnectionStringOrCreds("linked service name")
Credentials.GetConnectionStringOrCreds("linked service name")
mssparkutils.credentials.getConnectionStringOrCreds('linked service name')
Get secret using workspace identity
Returns Azure Key Vault secret for a given Azure Key Vault name, secret name, and linked service name using workspace identity. Make sure you configure access to Azure Key Vault appropriately.
mssparkutils.credentials.getSecret('azure key vault name','secret name','linked service name')
mssparkutils.credentials.getSecret("azure key vault name","secret name","linked service name")
Credentials.GetSecret("azure key vault name","secret name","linked service name")
mssparkutils.credentials.getSecret('azure key vault name','secret name','linked service name')
Get secret using user credentials
Returns Azure Key Vault secret for a given Azure Key Vault name, secret name, and linked service name using user credentials.
mssparkutils.credentials.getSecret('azure key vault name','secret name')
mssparkutils.credentials.getSecret("azure key vault name","secret name")
Credentials.GetSecret("azure key vault name","secret name")
mssparkutils.credentials.getSecret('azure key vault name','secret name')
Put secret using workspace identity
Puts Azure Key Vault secret for a given Azure Key Vault name, secret name, and linked service name using workspace identity. Make sure you configure the access to Azure Key Vault appropriately.
mssparkutils.credentials.putSecret('azure key vault name','secret name','secret value','linked service name')
Put secret using workspace identity
Puts Azure Key Vault secret for a given Azure Key Vault name, secret name, and linked service name using workspace identity. Make sure you configure the access to Azure Key Vault appropriately.
mssparkutils.credentials.putSecret("azure key vault name","secret name","secret value","linked service name")
Put secret using workspace identity
Puts Azure Key Vault secret for a given Azure Key Vault name, secret name, and linked service name using workspace identity. Make sure you configure the access to Azure Key Vault appropriately.
mssparkutils.credentials.putSecret('azure key vault name','secret name','secret value','linked service name')
Put secret using user credentials
Puts Azure Key Vault secret for a given Azure Key Vault name, secret name, and linked service name using user credentials.
mssparkutils.credentials.putSecret('azure key vault name','secret name','secret value')
Put secret using user credentials
Puts Azure Key Vault secret for a given Azure Key Vault name, secret name, and linked service name using user credentials.
mssparkutils.credentials.putSecret('azure key vault name','secret name','secret value')
Put secret using user credentials
Puts Azure Key Vault secret for a given Azure Key Vault name, secret name, and linked service name using user credentials.
mssparkutils.credentials.putSecret("azure key vault name","secret name","secret value")
Environment utilities
Run following commands to get an overview of the available methods:
mssparkutils.env.help()
mssparkutils.env.help()
mssparkutils.env.help()
Env.Help()
Get result:
getUserName(): returns user name
getUserId(): returns unique user id
getJobId(): returns job id
getWorkspaceName(): returns workspace name
getPoolName(): returns Spark pool name
getClusterId(): returns cluster id
Get user name
Returns current user name.
mssparkutils.env.getUserName()
mssparkutils.env.getUserName()
mssparkutils.env.getUserName()
Env.GetUserName()
Get user ID
Returns current user ID.
mssparkutils.env.getUserId()
mssparkutils.env.getUserId()
mssparkutils.env.getUserId()
Env.GetUserId()
Get job ID
Returns job ID.
mssparkutils.env.getJobId()
mssparkutils.env.getJobId()
mssparkutils.env.getJobId()
Env.GetJobId()
Get workspace name
Returns workspace name.
mssparkutils.env.getWorkspaceName()
mssparkutils.env.getWorkspaceName()
mssparkutils.env.getWorkspaceName()
Env.GetWorkspaceName()
Get pool name
Returns Spark pool name.
mssparkutils.env.getPoolName()
mssparkutils.env.getPoolName()
mssparkutils.env.getPoolName()
Env.GetPoolName()
Get cluster ID
Returns current cluster ID.
mssparkutils.env.getClusterId()
mssparkutils.env.getClusterId()
mssparkutils.env.getClusterId()
Env.GetClusterId()
Runtime Context
Mssparkutils runtime utils exposed 3 runtime properties, you can use the mssparkutils runtime context to get the properties listed as below:
- Notebookname - The name of current notebook, will always return value for both interactive mode and pipeline mode.
- Pipelinejobid - The pipeline run ID, will return value in pipeline mode and return empty string in interactive mode.
- Activityrunid - The notebook activity run ID, will return value in pipeline mode and return empty string in interactive mode.
Currently runtime context support both Python and Scala.
mssparkutils.runtime.context
ctx <- mssparkutils.runtime.context()
for (key in ls(ctx)) {
writeLines(paste(key, ctx[[key]], sep = "\t"))
}
%%spark
mssparkutils.runtime.context
Session management
Stop an interactive session
Instead of manually click stop button, sometimes it's more convenient to stop an interactive session by calling an API in the code. For such cases, we provide an API mssparkutils.session.stop() to support stopping the interactive session via code, it's available for Scala and Python.
mssparkutils.session.stop()
mssparkutils.session.stop()
mssparkutils.session.stop()
mssparkutils.session.stop() API will stop the current interactive session asynchronously in the background, it stops the Spark session and release resources occupied by the session so they are available to other sessions in the same pool.
Note
We don't recommend call language built-in APIs like sys.exit in Scala or sys.exit() in Python in your code, because such APIs just
kill the interpreter process, leaving Spark session alive and resources not released.
Package Dependencies
If you want to develop notebooks or jobs locally and need to reference the relevant packages for compilation/IDE hints, you can use the following packages.