take_while_view class (C++ Standard Library)
A view that contains the leading elements of a range that match a predicate.
Syntax
template<view V, class Pred> requires
input_range<V> && is_object_v<Pred> &&
indirect_unary_predicate<const Pred, iterator_t<V>>
class take_while_view : public view_interface<take_while_view<V, Pred>>;
Template parameters
Pred
The type of the predicate that determines the leading elements to put in the view.
V
The type of the underlying view.
View characteristics
For a description of the following entries, see View class characteristics
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Range adaptor | views::take_while |
| Underlying range | Must satisfy input_range or higher |
| Element type | Same as the underlying range |
| View iterator category | Same as the underlying range |
| Sized | No |
Is const-iterable |
Only if the underlying range is const iterable and the predicate can work with const references. |
| Common range | No |
| Borrowed range | No |
Members
| Member functions | Description |
|---|---|
| ConstructorsC++20 | Construct the view. |
baseC++20 |
Get the underlying range. |
beginC++20 |
Get an iterator to the first element. |
endC++20 |
Get the sentinel at the end of the view. |
predC++20 |
Get a reference to the predicate that determines which elements to take. |
Inherited from view_interface |
Description |
backC++20 |
Get the last element. |
dataC++20 |
Get a pointer to the first element. |
emptyC++20 |
Test whether the view is empty. |
frontC++20 |
Get the first element. |
operator[]C++20 |
Get the element at the specified position. |
operator boolC++20 |
Test whether the view isn't empty. |
size |
Get the number of elements in the view. |
Requirements
Header: <ranges> (since C++20)
Namespace: std::ranges
Compiler Option: /std:c++20 or later is required.
Constructors
Construct an instance of a take_while_view
1) take_while_view() requires
default_initializable<V> &&
default_initializable<Pred> = default;
2) constexpr take_while_view(V base, Pred pred);
Parameters
base
The underlying view.
pred
The predicate that determines the leading elements to put in the view.
For information about template parameter types, see Template parameters.
Return value
A take_while_view object.
Remarks
The best way to create a take_while_view is by using the views::take_while range adaptor. Range adaptors are the intended way to create view classes. The view types are exposed in case you want to create your own custom view type.
1) Move constructs the take_while_view from a base view and a pred predicate. Both base and pred are moved via std::move().
2) Constructs an empty take_while_view. The underlying view and predicate are default constructed.
Example: take_while_view
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <ranges>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{0, 1, 2, 3, -4, 5, 6};
auto twv = std::views::take_while(v, [](int i) {return i >= 0; });
for (auto& e : twv)
{
std::cout << e << ' '; // 0 1 2 3
}
std::cout << '\n';
// Using the '|' operator to create a take_view
for (auto i : v | std::views::take_while([](int i) {return i < 5; }))
{
std::cout << i << ' '; // 0 1 2 3 -4
}
}
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3 -4
base
Gets a copy of the underlying view.
// Uses a copy constructor to return the underlying view
1) constexpr V base() const& requires std::copy_constructible<V>;
// Uses a move constructor to return the underlying view
2) constexpr V base() &&;
Parameters
None.
Returns
A copy of the underlying view.
begin
Get an iterator to the first element in the view.
1) constexpr auto begin() requires (!Simple_view<V>);
2) constexpr auto begin() const requires
range<const V> &&
indirect_unary_predicate<const Pred, iterator_t<const V>>
Parameters
None.
Return value
An iterator pointing at the first element in the view. The behavior is undefined if the view doesn't have a predicate.
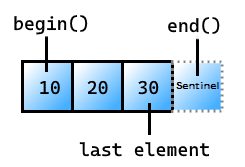
Remarks
For 1, the Simple_view requirement means that a view V and const V have the same iterator and sentinel types.
end
Get the sentinel at the end of the view.
1) constexpr auto end() requires (!Simple_view<V>);
2) constexpr auto end() const requires
range<const V> &&
indirect_unary_predicate<const Pred, iterator_t<const V>
Parameters
None.
Return value
The sentinel that follows the last element in the view.

Remarks
For 1, the Simple_view requirement means that a view V and const V have the same iterator and sentinel types.
pred
Get a reference to the predicate used to select which leading elements will go in the view.
constexpr const Pred& pred() const;
Return value
A reference to the predicate used to select the leading elements to put in the view.
Example pred
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <ranges>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{ 0, 1, 2, 3, -4, 5, 6 };
auto mv = v | std::views::take_while(
[](int i) {return i < 5; });
std::cout << std::boolalpha << mv.pred()(v[6]); // outputs false because v[6] = 6 and 6 is not less than 5 (the predicate)
}