Merk
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å logge på eller endre kataloger.
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å endre kataloger.
Denne siden beskriver hvordan du oppretter et program for å få programmatisk tilgang til Defender for Cloud Apps uten en bruker. Hvis du trenger programmatisk tilgang til Defender for Cloud Apps på vegne av en bruker, kan du se Få tilgang med brukerkontekst. Hvis du ikke er sikker på hvilken tilgang du trenger, kan du se siden Administrere API-tokener .
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps viser mye av dataene og handlingene gjennom et sett med programmatiske API-er. Disse API-ene hjelper deg med å automatisere arbeidsflyter og innovere basert på Defender for Cloud Apps funksjoner. API-tilgang krever OAuth2.0-godkjenning. Hvis du vil ha mer informasjon, kan du se OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code Flow.
Generelt sett må du utføre følgende trinn for å bruke API-ene:
- Opprett et Microsoft Entra program.
- Få et tilgangstoken ved hjelp av dette programmet.
- Bruk tokenet til å få tilgang Defender for Cloud Apps API.
Denne artikkelen forklarer hvordan du oppretter et Microsoft Entra program, får et tilgangstoken til Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps og validerer tokenet.
Opprett en app for Defender for Cloud Apps
Registrer et nytt program i Microsoft Entra administrasjonssenter. Hvis du vil ha mer informasjon, kan du se Hurtigstart: Registrere et program med Microsoft Entra administrasjonssenter.
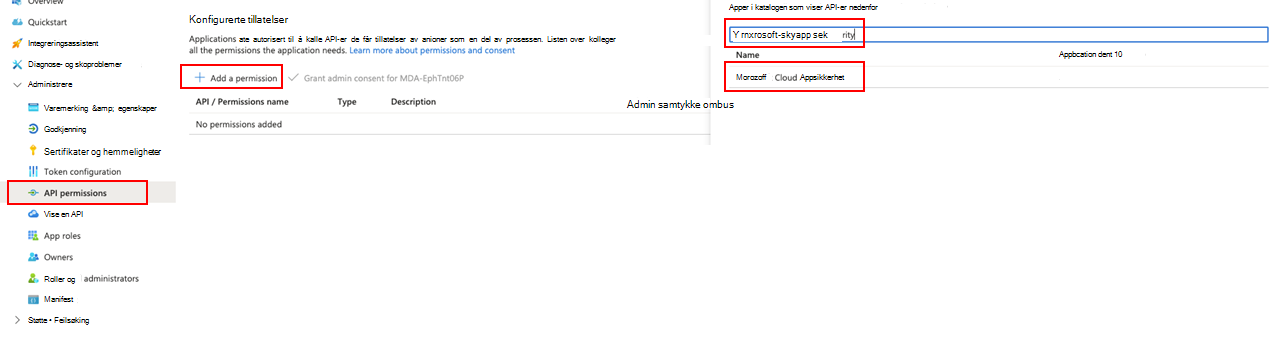
Hvis du vil gi appen tilgang til Defender for Cloud Apps og tilordne tillatelsen Les alle varsler, velger du API-tillatelser Legg til tillatelses-API-er>>organisasjonen bruker>, skriver inn Microsoft Cloud App Security og velger deretter Microsoft Cloud App SecurityI 199
Obs!
Microsoft Cloud App Security vises ikke i den opprinnelige listen. Begynn å skrive navnet i tekstboksen for å se det vises. Pass på å skrive inn dette navnet, selv om produktet nå kalles Defender for Cloud Apps.
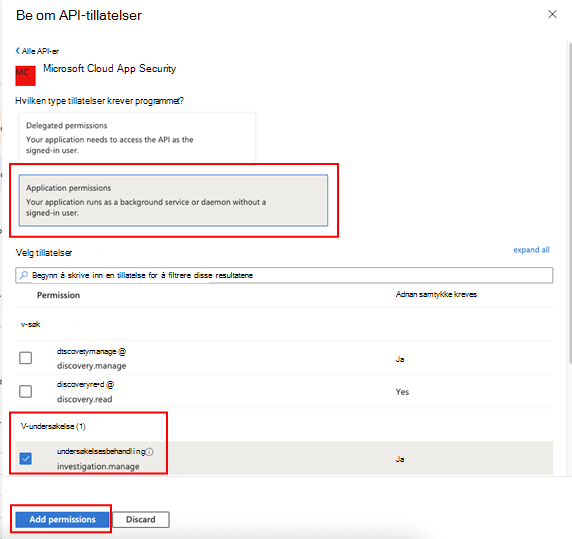
Velg Undersøkelse av programtillatelser.Les>, og velg deretter Legg til tillatelser.
Du må velge de relevante tillatelsene. Investigation.Read er bare et eksempel. Hvis du vil se andre tillatelsesomfang, kan du se Tillatelsesomfang som støttes
Hvis du vil finne ut hvilken tillatelse du trenger, kan du se på Tillatelser-delen i API-en du er interessert i å ringe.
Velg Gi administratorsamtykke.
Obs!
Hver gang du legger til en tillatelse, må du velge Gi administratorsamtykke for at den nye tillatelsen skal tre i kraft.
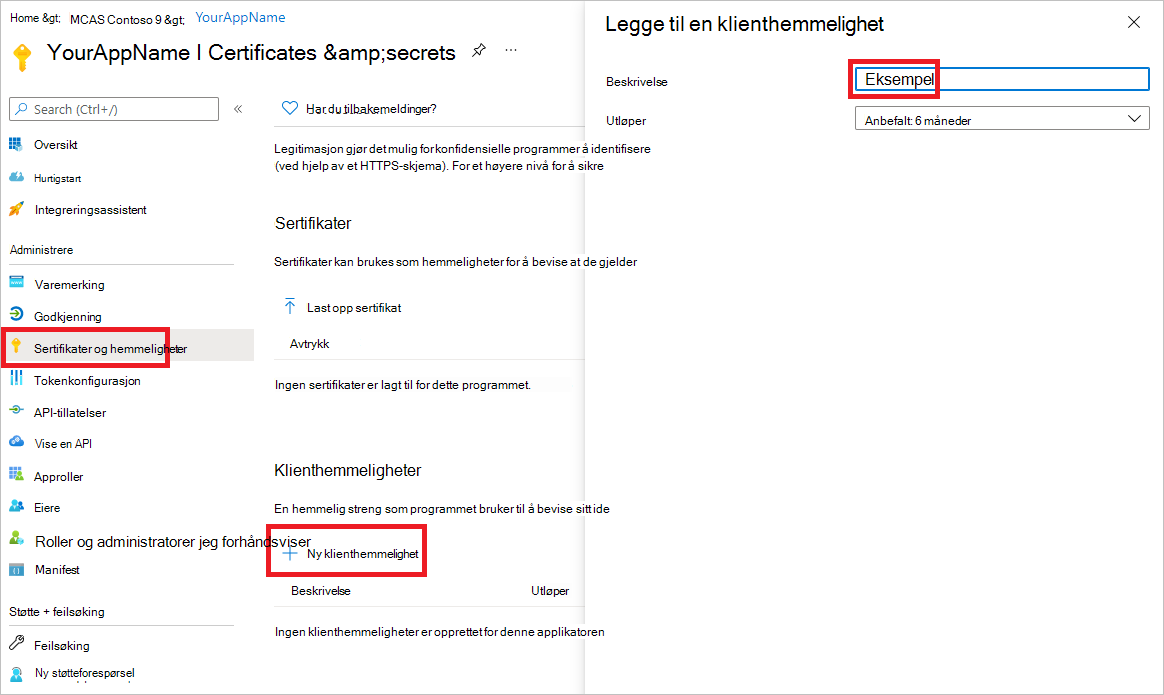
Hvis du vil legge til en hemmelighet i programmet, velger du Sertifikater & hemmeligheter, og velger Ny klienthemmelighet. Legg til en beskrivelse i hemmeligheten, og velg deretter Legg til.
Obs!
Når du har valgt Legg til, velger du kopier den genererte hemmelige verdien. Du kan ikke hente denne verdien etter at du har forlatt den.
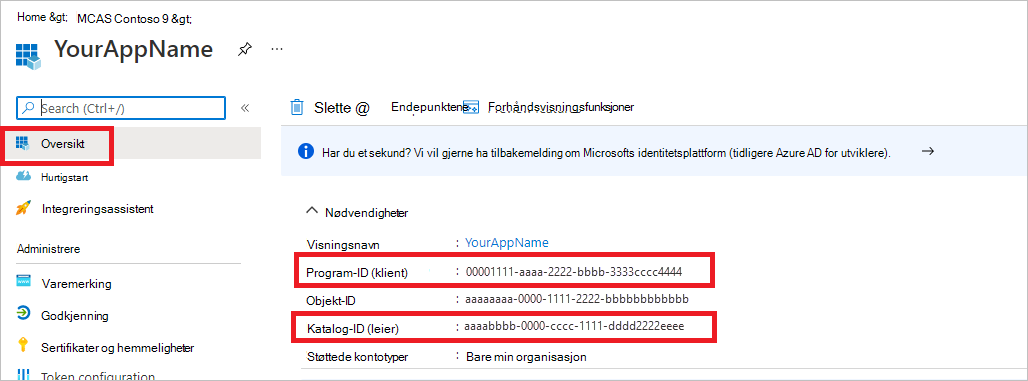
Skriv ned program-ID-en og leier-ID-en. Gå til Oversikt på programsiden, og kopier program-ID-en (klient)-ID-en og katalog-ID-en (leier).
Bare for Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps partnere. Angi at appen skal være flertenant (tilgjengelig i alle leiere etter samtykke). Dette er nødvendig for tredjepartsapper (for eksempel hvis du oppretter en app som er ment å kjøre i flere kunders leier). Dette er ikke nødvendig hvis du oppretter en tjeneste som du bare vil kjøre i leieren (hvis du for eksempel oppretter et program for din egen bruk som bare samhandler med dine egne data). Slik angir du at appen skal være flertenant:
Gå til godkjenning, og legg til
https://portal.azure.comsom URI for omadressering.Velg forretningsforbindelsene i et hvilket som helst samtykke i organisasjonskatalogprogrammet under Støttede kontotyper for å få tilgang til appen for flere enheter.
Du trenger at programmet godkjennes i hver leier der du har tenkt å bruke den. Dette er fordi programmet samhandler Defender for Cloud Apps på vegne av kunden.
Du (eller kunden din hvis du skriver en tredjepartsapp) må velge samtykkekoblingen og godkjenne appen. Samtykket bør gjøres med en bruker som har administrative rettigheter i Active Directory.
Samtykkekoblingen dannes på følgende måte:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/authorize?prompt=consent&client_id=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000&response_type=code&sso_reload=trueDer 00000000-0000-0000-0000-00000000000 er erstattet med program-ID-en.
Ferdig! Du har registrert et program! Se eksempler nedenfor for tokeninnhenting og validering.
Tillatelsesomfang som støttes
| Navn på tillatelse | Beskrivelse | Støttede handlinger |
|---|---|---|
| Undersøkelse.lest | Utfør alle støttede handlinger på aktiviteter og varsler, bortsett fra å lukke varsler. Vis IP-områder, men ikke legge til, oppdatere eller slette. Utfør alle enhetshandlinger. |
Aktivitetsliste, henting, tilbakemelding Varslingsliste, henting, som lest/ulest Enhetsliste, hente, hente tre Delnettliste |
| Investigation.manage | Utfør alle investigation.read-handlinger i tillegg til å administrere varsler og IP-områder. | Aktivitetsliste, henting, tilbakemelding Varslingsliste, henting, som lest/ulest, lukk Enhetsliste, hente, hente tre Delnettliste, opprett/oppdater/slett |
| Discovery.read | Utfør alle støttede handlinger på aktiviteter og varsler, bortsett fra å lukke varsler. Vis oppdagelsesrapporter og kategorier. |
Varslingsliste, henting, som lest/ulest Rapporter for oppdagingsliste, listerapportkategorier |
| Discovery.manage | Discovery.read-tillatelser Lukk varsler, last opp opp oppdagingsfiler og generer blokkskript |
Varslingsliste, henting, som lest/ulest, lukk Rapporter for oppdagingsliste, listerapportkategorier Opplasting av søkefil, generer blokkskript |
| Settings.read | List opp IP-områder. | Delnettliste |
| Settings.manage | List opp og administrer IP-områder. | Delnettliste, opprett/oppdater/slett |
Få et tilgangstoken
Hvis du vil ha mer informasjon om Microsoft Entra tokener, kan du se Microsoft Entra opplæringen.
Bruk PowerShell
# This script acquires the App Context Token and stores it in the variable $token for later use in the script.
# Paste your Tenant ID, App ID, and App Secret (App key) into the indicated quotes below.
$tenantId = '' ### Paste your tenant ID here
$appId = '' ### Paste your Application ID here
$appSecret = '' ### Paste your Application key here
$resourceAppIdUri = '05a65629-4c1b-48c1-a78b-804c4abdd4af'
$oAuthUri = "https://login.microsoftonline.com/$TenantId/oauth2/token"
$authBody = [Ordered] @{
resource = "$resourceAppIdUri"
client_id = "$appId"
client_secret = "$appSecret"
grant_type = 'client_credentials'
}
$authResponse = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Uri $oAuthUri -Body $authBody -ErrorAction Stop
$token = $authResponse.access_token
Bruk C#
Følgende kode ble testet med NuGet Microsoft.Identity.Client 4.47.2.
Opprett et nytt konsollprogram.
Installer NuGet Microsoft.Identity.Client.
Legg til følgende:
using Microsoft.Identity.Client;Kopier og lim inn følgende kode i appen (ikke glem å oppdatere de tre variablene:
tenantId, appId, appSecret):string tenantId = "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"; // Paste your own tenant ID here string appId = "00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444"; // Paste your own app ID here string appSecret = "22222222-2222-2222-2222-222222222222"; // Paste your own app secret here for a test, and then store it in a safe place! const string authority = "https://login.microsoftonline.com"; const string audience = "05a65629-4c1b-48c1-a78b-804c4abdd4af"; IConfidentialClientApplication myApp = ConfidentialClientApplicationBuilder.Create(appId).WithClientSecret(appSecret).WithAuthority($"{authority}/{tenantId}").Build(); List scopes = new List() { $"{audience}/.default" }; AuthenticationResult authResult = myApp.AcquireTokenForClient(scopes).ExecuteAsync().GetAwaiter().GetResult(); string token = authResult.AccessToken;
Bruk Python
Se Microsofts godkjenningsbibliotek (MSAL) for Python.
Bruk krøll
Obs!
Følgende fremgangsmåte forutsetter at Curl for Windows allerede er installert på datamaskinen.
Åpne en ledetekst, og angi CLIENT_ID til Azure-program-ID-en.
Angi CLIENT_SECRET til Azure-programhemmeligheten.
Angi TENANT_ID til Azure-leier-ID-en til kunden som ønsker å bruke appen til å få tilgang til Defender for Cloud Apps.
Utfør denne kommandoen:
curl -i -X POST -H "Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded" -d "grant_type=client_credentials" -d "client_id=%CLIENT_ID%" -d "scope=05a65629-4c1b-48c1-a78b-804c4abdd4af/.default" -d "client_secret=%CLIENT_SECRET%" "https://login.microsoftonline.com/%TENANT_ID%/oauth2/v2.0/token" -kDu får et svar i følgende skjema:
{"token_type":"Bearer","expires_in":3599,"ext_expires_in":0,"access_token":"eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIn <truncated> aWReH7P0s0tjTBX8wGWqJUdDA"}
Validere tokenet
Kontroller at du har riktig token:
Kopier og lim inn tokenet du fikk i forrige trinn i JWT for å dekode det.
Valider at du får et «roller»-krav med de ønskede tillatelsene.
I illustrasjonen nedenfor kan du se et dekodet token hentet fra en app med tillatelser til alle Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps roller:
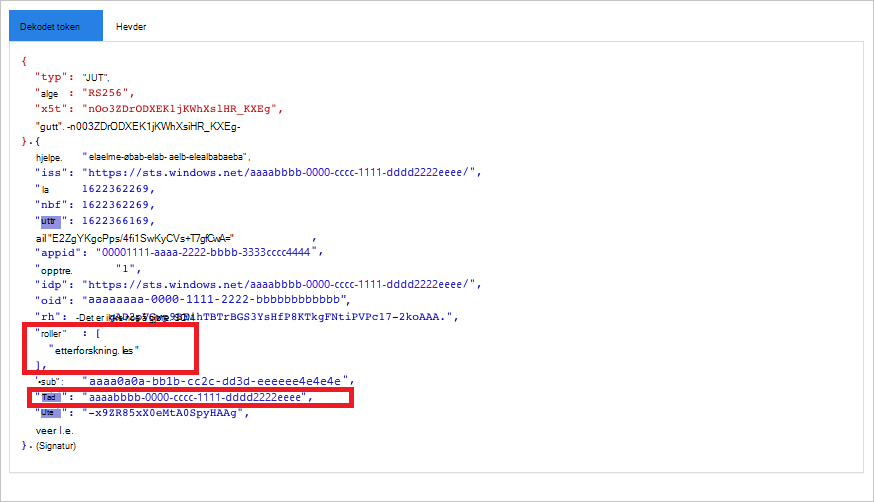
Bruke tokenet til å få tilgang Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps API
Velg API-en du vil bruke. Hvis du vil ha mer informasjon, kan du se Defender for Cloud Apps API-er.
Angi autorisasjonshodet i http-forespørselen du sender til "Bærer {token}" (Bærer er godkjenningsskjemaet).
Utløpstiden for tokenet er én time. Du kan sende mer enn én forespørsel med samme token.
Følgende er et eksempel på hvordan du sender en forespørsel for å få en liste over varsler ved hjelp av C#:
var httpClient = new HttpClient(); var request = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Get, "https://portal.cloudappsecurity.com/cas/api/v1/alerts/"); request.Headers.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Bearer", token); var response = httpClient.SendAsync(request).GetAwaiter().GetResult(); // Do something useful with the response