Merk
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å logge på eller endre kataloger.
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å endre kataloger.
This article demonstrates how to create a network of dataflow blocks that perform image processing in a Windows Forms application.
This example loads image files from the specified folder, creates a composite image, and displays the result. The example uses the dataflow model to route images through the network. In the dataflow model, independent components of a program communicate with one another by sending messages. When a component receives a message, it performs some action and then passes the result to another component. Compare this with the control flow model, in which an application uses control structures, for example, conditional statements, loops, and so on, to control the order of operations in a program.
Prerequisites
Read Dataflow before you start this walkthrough.
Note
The TPL Dataflow Library (the System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow namespace) is not distributed with .NET. To install the System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow namespace in Visual Studio, open your project, choose Manage NuGet Packages from the Project menu, and search online for the System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow package. Alternatively, to install it using the .NET Core CLI, run dotnet add package System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow.
Sections
This walkthrough contains the following sections:
Creating the Windows Forms Application
This section describes how to create the basic Windows Forms application and add controls to the main form.
To Create the Windows Forms Application
In Visual Studio, create a Visual C# or Visual Basic Windows Forms Application project. In this document, the project is named
CompositeImages.On the form designer for the main form, Form1.cs (Form1.vb for Visual Basic), add a ToolStrip control.
Add a ToolStripButton control to the ToolStrip control. Set the DisplayStyle property to Text and the Text property to Choose Folder.
Add a second ToolStripButton control to the ToolStrip control. Set the DisplayStyle property to Text, the Text property to Cancel, and the Enabled property to
False.Add a PictureBox object to the main form. Set the Dock property to Fill.
Creating the Dataflow Network
This section describes how to create the dataflow network that performs image processing.
To Create the Dataflow Network
Add a reference to System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow.dll to your project.
Ensure that Form1.cs (Form1.vb for Visual Basic) contains the following
using(Usingin Visual Basic) statements:using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Drawing; using System.Drawing.Imaging; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow; using System.Windows.Forms;Add the following data members to the
Form1class:// The head of the dataflow network. ITargetBlock<string> headBlock = null; // Enables the user interface to signal cancellation to the network. CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource;Add the following method,
CreateImageProcessingNetwork, to theForm1class. This method creates the image processing network.// Creates the image processing dataflow network and returns the // head node of the network. ITargetBlock<string> CreateImageProcessingNetwork() { // // Create the dataflow blocks that form the network. // // Create a dataflow block that takes a folder path as input // and returns a collection of Bitmap objects. var loadBitmaps = new TransformBlock<string, IEnumerable<Bitmap>>(path => { try { return LoadBitmaps(path); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // Handle cancellation by passing the empty collection // to the next stage of the network. return Enumerable.Empty<Bitmap>(); } }); // Create a dataflow block that takes a collection of Bitmap objects // and returns a single composite bitmap. var createCompositeBitmap = new TransformBlock<IEnumerable<Bitmap>, Bitmap>(bitmaps => { try { return CreateCompositeBitmap(bitmaps); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // Handle cancellation by passing null to the next stage // of the network. return null; } }); // Create a dataflow block that displays the provided bitmap on the form. var displayCompositeBitmap = new ActionBlock<Bitmap>(bitmap => { // Display the bitmap. pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage; pictureBox1.Image = bitmap; // Enable the user to select another folder. toolStripButton1.Enabled = true; toolStripButton2.Enabled = false; Cursor = DefaultCursor; }, // Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context // so that the action runs on the UI thread. new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions { TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext() }); // Create a dataflow block that responds to a cancellation request by // displaying an image to indicate that the operation is cancelled and // enables the user to select another folder. var operationCancelled = new ActionBlock<object>(delegate { // Display the error image to indicate that the operation // was cancelled. pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.CenterImage; pictureBox1.Image = pictureBox1.ErrorImage; // Enable the user to select another folder. toolStripButton1.Enabled = true; toolStripButton2.Enabled = false; Cursor = DefaultCursor; }, // Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context // so that the action runs on the UI thread. new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions { TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext() }); // // Connect the network. // // Link loadBitmaps to createCompositeBitmap. // The provided predicate ensures that createCompositeBitmap accepts the // collection of bitmaps only if that collection has at least one member. loadBitmaps.LinkTo(createCompositeBitmap, bitmaps => bitmaps.Count() > 0); // Also link loadBitmaps to operationCancelled. // When createCompositeBitmap rejects the message, loadBitmaps // offers the message to operationCancelled. // operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a // predicate. loadBitmaps.LinkTo(operationCancelled); // Link createCompositeBitmap to displayCompositeBitmap. // The provided predicate ensures that displayCompositeBitmap accepts the // bitmap only if it is non-null. createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(displayCompositeBitmap, bitmap => bitmap != null); // Also link createCompositeBitmap to operationCancelled. // When displayCompositeBitmap rejects the message, createCompositeBitmap // offers the message to operationCancelled. // operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a // predicate. createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(operationCancelled); // Return the head of the network. return loadBitmaps; }Implement the
LoadBitmapsmethod.// Loads all bitmap files that exist at the provided path. IEnumerable<Bitmap> LoadBitmaps(string path) { List<Bitmap> bitmaps = new List<Bitmap>(); // Load a variety of image types. foreach (string bitmapType in new string[] { "*.bmp", "*.gif", "*.jpg", "*.png", "*.tif" }) { // Load each bitmap for the current extension. foreach (string fileName in Directory.GetFiles(path, bitmapType)) { // Throw OperationCanceledException if cancellation is requested. cancellationTokenSource.Token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); try { // Add the Bitmap object to the collection. bitmaps.Add(new Bitmap(fileName)); } catch (Exception) { // TODO: A complete application might handle the error. } } } return bitmaps; }Implement the
CreateCompositeBitmapmethod.// Creates a composite bitmap from the provided collection of Bitmap objects. // This method computes the average color of each pixel among all bitmaps // to create the composite image. Bitmap CreateCompositeBitmap(IEnumerable<Bitmap> bitmaps) { Bitmap[] bitmapArray = bitmaps.ToArray(); // Compute the maximum width and height components of all // bitmaps in the collection. Rectangle largest = new Rectangle(); foreach (var bitmap in bitmapArray) { if (bitmap.Width > largest.Width) largest.Width = bitmap.Width; if (bitmap.Height > largest.Height) largest.Height = bitmap.Height; } // Create a 32-bit Bitmap object with the greatest dimensions. Bitmap result = new Bitmap(largest.Width, largest.Height, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb); // Lock the result Bitmap. var resultBitmapData = result.LockBits( new Rectangle(new Point(), result.Size), ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, result.PixelFormat); // Lock each source bitmap to create a parallel list of BitmapData objects. var bitmapDataList = (from bitmap in bitmapArray select bitmap.LockBits( new Rectangle(new Point(), bitmap.Size), ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb)) .ToList(); // Compute each column in parallel. Parallel.For(0, largest.Width, new ParallelOptions { CancellationToken = cancellationTokenSource.Token }, i => { // Compute each row. for (int j = 0; j < largest.Height; j++) { // Counts the number of bitmaps whose dimensions // contain the current location. int count = 0; // The sum of all alpha, red, green, and blue components. int a = 0, r = 0, g = 0, b = 0; // For each bitmap, compute the sum of all color components. foreach (var bitmapData in bitmapDataList) { // Ensure that we stay within the bounds of the image. if (bitmapData.Width > i && bitmapData.Height > j) { unsafe { byte* row = (byte*)(bitmapData.Scan0 + (j * bitmapData.Stride)); byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i)); a += *pix; pix++; r += *pix; pix++; g += *pix; pix++; b += *pix; } count++; } } //prevent divide by zero in bottom right pixelless corner if (count == 0) break; unsafe { // Compute the average of each color component. a /= count; r /= count; g /= count; b /= count; // Set the result pixel. byte* row = (byte*)(resultBitmapData.Scan0 + (j * resultBitmapData.Stride)); byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i)); *pix = (byte)a; pix++; *pix = (byte)r; pix++; *pix = (byte)g; pix++; *pix = (byte)b; } } }); // Unlock the source bitmaps. for (int i = 0; i < bitmapArray.Length; i++) { bitmapArray[i].UnlockBits(bitmapDataList[i]); } // Unlock the result bitmap. result.UnlockBits(resultBitmapData); // Return the result. return result; }Note
The C# version of the
CreateCompositeBitmapmethod uses pointers to enable efficient processing of the System.Drawing.Bitmap objects. Therefore, you must enable the Allow unsafe code option in your project in order to use the unsafe keyword. For more information about how to enable unsafe code in a Visual C# project, see Build Page, Project Designer (C#).
The following table describes the members of the network.
| Member | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
loadBitmaps |
TransformBlock<TInput,TOutput> | Takes a folder path as input and produces a collection of Bitmap objects as output. |
createCompositeBitmap |
TransformBlock<TInput,TOutput> | Takes a collection of Bitmap objects as input and produces a composite bitmap as output. |
displayCompositeBitmap |
ActionBlock<TInput> | Displays the composite bitmap on the form. |
operationCancelled |
ActionBlock<TInput> | Displays an image to indicate that the operation is canceled and enables the user to select another folder. |
To connect the dataflow blocks to form a network, this example uses the LinkTo method. The LinkTo method contains an overloaded version that takes a Predicate<T> object that determines whether the target block accepts or rejects a message. This filtering mechanism enables message blocks to receive only certain values. In this example, the network can branch in one of two ways. The main branch loads the images from disk, creates the composite image, and displays that image on the form. The alternate branch cancels the current operation. The Predicate<T> objects enable the dataflow blocks along the main branch to switch to the alternative branch by rejecting certain messages. For example, if the user cancels the operation, the dataflow block createCompositeBitmap produces null (Nothing in Visual Basic) as its output. The dataflow block displayCompositeBitmap rejects null input values, and therefore, the message is offered to operationCancelled. The dataflow block operationCancelled accepts all messages and therefore, displays an image to indicate that the operation is canceled.
The following illustration shows the image processing network:
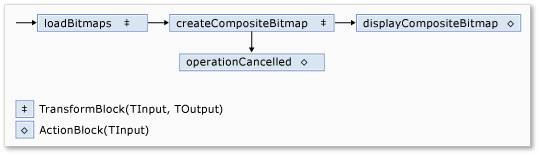
Because the displayCompositeBitmap and operationCancelled dataflow blocks act on the user interface, it is important that these actions occur on the user-interface thread. To accomplish this, during construction, these objects each provide an ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions object that has the TaskScheduler property set to TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext. The TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext method creates a TaskScheduler object that performs work on the current synchronization context. Because the CreateImageProcessingNetwork method is called from the handler of the Choose Folder button, which runs on the user-interface thread, the actions for the displayCompositeBitmap and operationCancelled dataflow blocks also run on the user-interface thread.
This example uses a shared cancellation token instead of setting the CancellationToken property because the CancellationToken property permanently cancels dataflow block execution. A cancellation token enables this example to reuse the same dataflow network multiple times, even when the user cancels one or more operations. For an example that uses CancellationToken to permanently cancel the execution of a dataflow block, see How to: Cancel a Dataflow Block.
Connecting the Dataflow Network to the User Interface
This section describes how to connect the dataflow network to the user interface. The creation of the composite image and cancellation of the operation are initiated from the Choose Folder and Cancel buttons. When the user chooses either of these buttons, the appropriate action is initiated in an asynchronous manner.
To Connect the Dataflow Network to the User Interface
On the form designer for the main form, create an event handler for the Click event for the Choose Folder button.
Implement the Click event for the Choose Folder button.
// Event handler for the Choose Folder button. private void toolStripButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Create a FolderBrowserDialog object to enable the user to // select a folder. FolderBrowserDialog dlg = new FolderBrowserDialog { ShowNewFolderButton = false }; // Set the selected path to the common Sample Pictures folder // if it exists. string initialDirectory = Path.Combine( Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonPictures), "Sample Pictures"); if (Directory.Exists(initialDirectory)) { dlg.SelectedPath = initialDirectory; } // Show the dialog and process the dataflow network. if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { // Create a new CancellationTokenSource object to enable // cancellation. cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource(); // Create the image processing network if needed. headBlock ??= CreateImageProcessingNetwork(); // Post the selected path to the network. headBlock.Post(dlg.SelectedPath); // Enable the Cancel button and disable the Choose Folder button. toolStripButton1.Enabled = false; toolStripButton2.Enabled = true; // Show a wait cursor. Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor; } }On the form designer for the main form, create an event handler for the Click event for the Cancel button.
Implement the Click event for the Cancel button.
// Event handler for the Cancel button. private void toolStripButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Signal the request for cancellation. The current component of // the dataflow network will respond to the cancellation request. cancellationTokenSource.Cancel(); }
The Complete Example
The following example shows the complete code for this walkthrough.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CompositeImages
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
// The head of the dataflow network.
ITargetBlock<string> headBlock = null;
// Enables the user interface to signal cancellation to the network.
CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// Creates the image processing dataflow network and returns the
// head node of the network.
ITargetBlock<string> CreateImageProcessingNetwork()
{
//
// Create the dataflow blocks that form the network.
//
// Create a dataflow block that takes a folder path as input
// and returns a collection of Bitmap objects.
var loadBitmaps = new TransformBlock<string, IEnumerable<Bitmap>>(path =>
{
try
{
return LoadBitmaps(path);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Handle cancellation by passing the empty collection
// to the next stage of the network.
return Enumerable.Empty<Bitmap>();
}
});
// Create a dataflow block that takes a collection of Bitmap objects
// and returns a single composite bitmap.
var createCompositeBitmap = new TransformBlock<IEnumerable<Bitmap>, Bitmap>(bitmaps =>
{
try
{
return CreateCompositeBitmap(bitmaps);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Handle cancellation by passing null to the next stage
// of the network.
return null;
}
});
// Create a dataflow block that displays the provided bitmap on the form.
var displayCompositeBitmap = new ActionBlock<Bitmap>(bitmap =>
{
// Display the bitmap.
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage;
pictureBox1.Image = bitmap;
// Enable the user to select another folder.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = true;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = false;
Cursor = DefaultCursor;
},
// Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context
// so that the action runs on the UI thread.
new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions
{
TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()
});
// Create a dataflow block that responds to a cancellation request by
// displaying an image to indicate that the operation is cancelled and
// enables the user to select another folder.
var operationCancelled = new ActionBlock<object>(delegate
{
// Display the error image to indicate that the operation
// was cancelled.
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.CenterImage;
pictureBox1.Image = pictureBox1.ErrorImage;
// Enable the user to select another folder.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = true;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = false;
Cursor = DefaultCursor;
},
// Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context
// so that the action runs on the UI thread.
new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions
{
TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()
});
//
// Connect the network.
//
// Link loadBitmaps to createCompositeBitmap.
// The provided predicate ensures that createCompositeBitmap accepts the
// collection of bitmaps only if that collection has at least one member.
loadBitmaps.LinkTo(createCompositeBitmap, bitmaps => bitmaps.Count() > 0);
// Also link loadBitmaps to operationCancelled.
// When createCompositeBitmap rejects the message, loadBitmaps
// offers the message to operationCancelled.
// operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a
// predicate.
loadBitmaps.LinkTo(operationCancelled);
// Link createCompositeBitmap to displayCompositeBitmap.
// The provided predicate ensures that displayCompositeBitmap accepts the
// bitmap only if it is non-null.
createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(displayCompositeBitmap, bitmap => bitmap != null);
// Also link createCompositeBitmap to operationCancelled.
// When displayCompositeBitmap rejects the message, createCompositeBitmap
// offers the message to operationCancelled.
// operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a
// predicate.
createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(operationCancelled);
// Return the head of the network.
return loadBitmaps;
}
// Loads all bitmap files that exist at the provided path.
IEnumerable<Bitmap> LoadBitmaps(string path)
{
List<Bitmap> bitmaps = new List<Bitmap>();
// Load a variety of image types.
foreach (string bitmapType in
new string[] { "*.bmp", "*.gif", "*.jpg", "*.png", "*.tif" })
{
// Load each bitmap for the current extension.
foreach (string fileName in Directory.GetFiles(path, bitmapType))
{
// Throw OperationCanceledException if cancellation is requested.
cancellationTokenSource.Token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
try
{
// Add the Bitmap object to the collection.
bitmaps.Add(new Bitmap(fileName));
}
catch (Exception)
{
// TODO: A complete application might handle the error.
}
}
}
return bitmaps;
}
// Creates a composite bitmap from the provided collection of Bitmap objects.
// This method computes the average color of each pixel among all bitmaps
// to create the composite image.
Bitmap CreateCompositeBitmap(IEnumerable<Bitmap> bitmaps)
{
Bitmap[] bitmapArray = bitmaps.ToArray();
// Compute the maximum width and height components of all
// bitmaps in the collection.
Rectangle largest = new Rectangle();
foreach (var bitmap in bitmapArray)
{
if (bitmap.Width > largest.Width)
largest.Width = bitmap.Width;
if (bitmap.Height > largest.Height)
largest.Height = bitmap.Height;
}
// Create a 32-bit Bitmap object with the greatest dimensions.
Bitmap result = new Bitmap(largest.Width, largest.Height,
PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
// Lock the result Bitmap.
var resultBitmapData = result.LockBits(
new Rectangle(new Point(), result.Size), ImageLockMode.WriteOnly,
result.PixelFormat);
// Lock each source bitmap to create a parallel list of BitmapData objects.
var bitmapDataList = (from bitmap in bitmapArray
select bitmap.LockBits(
new Rectangle(new Point(), bitmap.Size),
ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb))
.ToList();
// Compute each column in parallel.
Parallel.For(0, largest.Width, new ParallelOptions
{
CancellationToken = cancellationTokenSource.Token
},
i =>
{
// Compute each row.
for (int j = 0; j < largest.Height; j++)
{
// Counts the number of bitmaps whose dimensions
// contain the current location.
int count = 0;
// The sum of all alpha, red, green, and blue components.
int a = 0, r = 0, g = 0, b = 0;
// For each bitmap, compute the sum of all color components.
foreach (var bitmapData in bitmapDataList)
{
// Ensure that we stay within the bounds of the image.
if (bitmapData.Width > i && bitmapData.Height > j)
{
unsafe
{
byte* row = (byte*)(bitmapData.Scan0 + (j * bitmapData.Stride));
byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i));
a += *pix; pix++;
r += *pix; pix++;
g += *pix; pix++;
b += *pix;
}
count++;
}
}
//prevent divide by zero in bottom right pixelless corner
if (count == 0)
break;
unsafe
{
// Compute the average of each color component.
a /= count;
r /= count;
g /= count;
b /= count;
// Set the result pixel.
byte* row = (byte*)(resultBitmapData.Scan0 + (j * resultBitmapData.Stride));
byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i));
*pix = (byte)a; pix++;
*pix = (byte)r; pix++;
*pix = (byte)g; pix++;
*pix = (byte)b;
}
}
});
// Unlock the source bitmaps.
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapArray.Length; i++)
{
bitmapArray[i].UnlockBits(bitmapDataList[i]);
}
// Unlock the result bitmap.
result.UnlockBits(resultBitmapData);
// Return the result.
return result;
}
// Event handler for the Choose Folder button.
private void toolStripButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a FolderBrowserDialog object to enable the user to
// select a folder.
FolderBrowserDialog dlg = new FolderBrowserDialog
{
ShowNewFolderButton = false
};
// Set the selected path to the common Sample Pictures folder
// if it exists.
string initialDirectory = Path.Combine(
Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonPictures),
"Sample Pictures");
if (Directory.Exists(initialDirectory))
{
dlg.SelectedPath = initialDirectory;
}
// Show the dialog and process the dataflow network.
if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
// Create a new CancellationTokenSource object to enable
// cancellation.
cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
// Create the image processing network if needed.
headBlock ??= CreateImageProcessingNetwork();
// Post the selected path to the network.
headBlock.Post(dlg.SelectedPath);
// Enable the Cancel button and disable the Choose Folder button.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = false;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = true;
// Show a wait cursor.
Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor;
}
}
// Event handler for the Cancel button.
private void toolStripButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Signal the request for cancellation. The current component of
// the dataflow network will respond to the cancellation request.
cancellationTokenSource.Cancel();
}
~Form1()
{
cancellationTokenSource.Dispose();
}
}
}
The following illustration shows typical output for the common \Sample Pictures\ folder.

