Tutorial: Use a system-assigned managed identity on a VM to access Azure Resource Manager
This quickstart shows you how to use a system-assigned managed identity as a virtual machine (VM)'s identity to access the Azure Resource Manager API. Managed identities for Azure resources are automatically managed by Azure and enable you to authenticate to services that support Microsoft Entra authentication without needing to insert credentials into your code.
Managed identities for Azure resources is a feature of Microsoft Entra ID. Each of the Azure services that support managed identities for Azure resources are subject to their own timeline. Make sure you review the availability status of managed identities for your resource and known issues before you begin.
You'll learn how to:
- Grant your virtual machine (VM) access to a resource group in Azure Resource Manager
- Get an access token using a virtual machine (VM) identity and use it to call Azure Resource Manager
Use a Windows VM system-assigned managed identity to access resource manager
Tip
Steps in this article might vary slightly based on the portal you start from.
This tutorial explains how to create a system-assigned identity, assign it to a Windows Virtual Machine (VM), and then use that identity to access the Azure Resource Manager API. Managed Service Identities are automatically managed by Azure. They enable authentication to services that support Microsoft Entra authentication, without needing to embed credentials into your code.
You'll learn how to:
- Grant your VM access to Azure Resource Manager.
- Get an access token by using the VM's system-assigned managed identity to access Resource Manager.
Sign in to the Azure portal with your administrator account.
Navigate to the Resource Groups tab.
Select the Resource Group that you want to grant the VM's managed identity access.
In the left panel, select Access control (IAM).
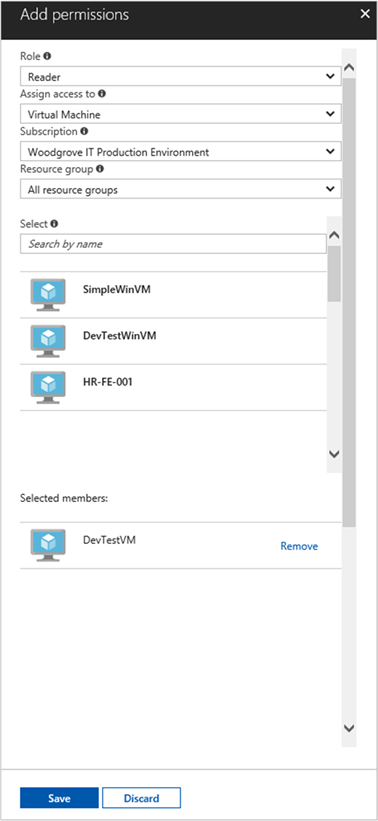
Select Add, then select Add role assignment.
In the Role tab, select Reader. This role allows view all resources, but doesn't allow you to make any changes.
In the Members tab, for the Assign access to option, select Managed identity, then select + Select members.
Ensure the proper subscription is listed in the Subscription dropdown. For Resource Group, select All resource groups.
For the Manage identity dropdown, select Virtual Machine.
For Select, choose your VM in the dropdown, then select Save.
Get an access token
Use the VM's system-assigned managed identity and call the Resource Manager to get an access token.
To complete these steps, you need an SSH client. If you're using Windows, you can use the SSH client in the Windows Subsystem for Linux. If you need assistance configuring your SSH client's keys, see How to Use SSH keys with Windows on Azure, or How to create and use an SSH public and private key pair for Linux VMs in Azure.
- In the portal, navigate to your Linux VM and in the Overview, select Connect.
- Connect to the VM with the SSH client of your choice.
- In the terminal window, using
curl, make a request to the local managed identities for Azure resources endpoint to get an access token for Azure Resource Manager. Thecurlrequest for the access token is below.
curl 'http://169.254.169.254/metadata/identity/oauth2/token?api-version=2018-02-01&resource=https://management.azure.com/' -H Metadata:true
Note
The value of the resource parameter must be an exact match for what is expected by Microsoft Entra ID. In the case of the Resource Manager's resource ID, you must include the trailing slash on the URI.
The response includes the access token you need to access Azure Resource Manager.
Response:
{
"access_token":"eyJ0eXAiOi...",
"refresh_token":"",
"expires_in":"3599",
"expires_on":"1504130527",
"not_before":"1504126627",
"resource":"https://management.azure.com",
"token_type":"Bearer"
}
Use this access token to access Azure Resource Manager; for example, to read the details of the resource group to which you previously granted this VM access. Replace the values of <SUBSCRIPTION-ID>, <RESOURCE-GROUP>, and <ACCESS-TOKEN> with the ones you created earlier.
Note
The URL is case-sensitive, so ensure if you are using the exact case as you used earlier when you named the resource group, and the uppercase “G” in “resourceGroup”.
curl https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION-ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE-GROUP>?api-version=2016-09-01 -H "Authorization: Bearer <ACCESS-TOKEN>"
The response back with the specific resource group information:
{
"id":"/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/DevTest",
"name":"DevTest",
"location":"westus",
"properties":
{
"provisioningState":"Succeeded"
}
}
Use a Linux VM system-assigned managed identity to access a resource group in resource manager
Tip
Steps in this article might vary slightly based on the portal you start from.
This tutorial explains how to create a system-assigned identity, assign it to a Linux Virtual Machine (VM), and then use that identity to access the Azure Resource Manager API. Managed Service Identities are automatically managed by Azure. They enable authentication to services that support Microsoft Entra authentication, without needing to embed credentials into your code.
You learn how to:
- Grant your VM access to Azure resource manager.
- Get an access token by using the VM's system-assigned managed identity to access resource manager.
Sign in to the Azure portal with your administrator account.
Navigate to the Resource Groups tab.
Select the Resource Group that you want to grant the VM's managed identity access.
In the left panel, select Access control (IAM).
Select Add, then select Add role assignment.
In the Role tab, select Reader. This role allows view all resources, but doesn't allow you to make any changes.
In the Members tab, in the Assign access to option, select Managed identity, then select + Select members.
Ensure the proper subscription is listed in the Subscription dropdown. For Resource Group, select All resource groups.
In the Manage identity dropdown, select Virtual Machine.
In the Select option, choose your VM in the dropdown, then select Save.

Get an access token
Use the VM's system-assigned managed identity and call the resource manager to get an access token.
To complete these steps, you need an SSH client. If you're using Windows, you can use the SSH client in the Windows Subsystem for Linux. If you need assistance configuring your SSH client's keys, see How to Use SSH keys with Windows on Azure, or How to create and use an SSH public and private key pair for Linux VMs in Azure.
- In the Azure portal, navigate to your Linux VM.
- In the Overview, select Connect.
- Connect to the VM with the SSH client of your choice.
- In the terminal window, using
curl, make a request to the local managed identities for Azure resources endpoint to get an access token for Azure resource manager. Thecurlrequest for the access token is below.
curl 'http://169.254.169.254/metadata/identity/oauth2/token?api-version=2018-02-01&resource=https://management.azure.com/' -H Metadata:true
Note
The value of the resource parameter must be an exact match for what is expected by Microsoft Entra ID. In the case of the resource manager resource ID, you must include the trailing slash on the URI.
The response includes the access token you need to access Azure resource manager.
Response:
{
"access_token":"eyJ0eXAiOi...",
"refresh_token":"",
"expires_in":"3599",
"expires_on":"1504130527",
"not_before":"1504126627",
"resource":"https://management.azure.com",
"token_type":"Bearer"
}
Use this access token to access Azure resource manager. For example, to read the details of the resource group to which you previously granted this VM access. Replace the values of <SUBSCRIPTION-ID>, <RESOURCE-GROUP>, and <ACCESS-TOKEN> with the ones you created earlier.
Note
The URL is case-sensitive, so ensure if you are using the exact case as you used earlier when you named the resource group, and the uppercase “G” in resourceGroup.
curl https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION-ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE-GROUP>?api-version=2016-09-01 -H "Authorization: Bearer <ACCESS-TOKEN>"
The response back with the specific resource group information:
{
"id":"/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/DevTest",
"name":"DevTest",
"location":"westus",
"properties":
{
"provisioningState":"Succeeded"
}
}
Next steps
In this quickstart, you learned how to use a system-assigned managed identity on a VM to access the Azure Resource Manager API. To learn more about Azure Resource Manager, see:
Tilbakemeldinger
Kommer snart: Gjennom 2024 faser vi ut GitHub Issues som tilbakemeldingsmekanisme for innhold, og erstatter det med et nytt system for tilbakemeldinger. Hvis du vil ha mer informasjon, kan du se: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Send inn og vis tilbakemelding for