Hendelser
29. apr., 14 - 30. apr., 19
Bli med i den ultimate virtuelle Windows Server-hendelsen 29.–30. april for omfattende tekniske økter og direkte Q&A med Microsoft-teknikere.
Registrer deg nåDenne nettleseren støttes ikke lenger.
Oppgrader til Microsoft Edge for å dra nytte av de nyeste funksjonene, sikkerhetsoppdateringene og den nyeste tekniske støtten.
Applies To: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008
Distributed File System Replication, or DFS Replication, is a role service in Windows Server that enables you to efficiently replicate folders across multiple servers and sites. You can replicate all types of folders, including folders referred to by a DFS namespace path.
DFS Replication is an efficient, multiple-master replication engine that you can use to keep folders synchronized between servers across limited bandwidth network connections. The service replaces the File Replication Service (FRS) as the replication engine for DFS namespaces.
Tips
Consider using Azure File Sync to reduce your on-premises storage footprint. Azure File Sync can keep multiple Windows file servers in sync. Each server needs to only keep a cache on-premises while the full copy of the data is in the cloud. Azure File Sync also provides the benefit of cloud backups with integrated snapshots. For more information, see Planning for an Azure File Sync deployment.
DFS Replication uses a compression algorithm known as remote differential compression, or RDC. RDC detects changes to the data in a file and enables DFS Replication to replicate only the changed file blocks instead of the entire file.
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) uses DFS Replication to replicate the sysvol folder in domains that use the Windows Server 2008 or later domain functional level. For more information about replicating the sysvol folder by using DFS Replication, see Migrate the sysvol folder replication to DFS Replication.
To use DFS Replication, you create replication groups and add replicated folders to the groups. Replicated folders are stored on servers in the group, which are referred to as members. DFS Replication establishes connections between the members of a group.
The following figure illustrates the relationship between a replication group, the members in the group, and the replicated folders.
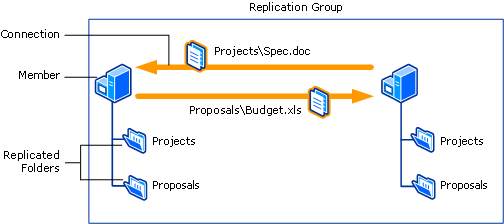
A replicated folder stays synchronized on each member in a group. In the figure, there are two replicated folders: Projects and Proposals. As the data changes in each replicated folder, the changes are replicated across connections between the members of the replication group. The connections between all members form the replication topology.
Creating multiple replicated folders in a single replication group simplifies the process of deploying replicated folders. The topology, schedule, and bandwidth throttling for the replication group are applied to each replicated folder. To deploy more replicated folders, you can run the Dfsradmin.exe tool or use a wizard to define the local path and permissions for the new replicated folder.
Each replicated folder has unique settings, such as file and subfolder filters. The settings let you filter out different files and subfolders for each replicated folder.
The replicated folders stored on each member can be located on different volumes in the member, and the replicated folders don't need to be shared folders or part of a namespace. However, the DFS Management snap-in simplifies sharing replicated folders and optionally publishing them in an existing namespace.
DFS Replication is a part of the File and Storage Services role for Windows Server. The management tools for DFS (DFS Management, the DFS Replication module for Windows PowerShell, and command-line tools) are installed separately as part of the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
You can install DFS Replication by using Server Manager, Windows PowerShell, or Windows Admin Center.
You can administer DFS Replication by using DFS Management, the dfsradmin and dfsrdiag commands, or scripts that call WMI.
Before you can deploy DFS Replication, you must configure your servers as follows:
Confirm file system and volume format. Determine the folders that you want to replicate, and identify any folders located on volumes that are formatted with the NTFS file system. DFS Replication doesn't support the Resilient File System (ReFS) or the FAT file system. DFS Replication also doesn't support replicating content stored on Cluster Shared Volumes.
Verify antivirus compatibility. Contact your antivirus software vendor to confirm your antivirus software is compatible with DFS Replication.
Update AD DS schema. Update the AD DS schema to include Windows Server 2003 R2 or later schema additions. You can't use read-only replicated folders with the Windows Server 2003 R2 or later schema additions.
Prepare replication group servers. Install DFS Replication on all servers that you plan to use as members of a replication group.
Check forest location. Ensure all servers in a replication group are located in the same forest. You can't enable replication across servers in different forests.
DFS Replication on an Azure virtual machine is a verified scenario for Windows Server. However, there are some limitations and requirements for this implementation.
Snapshots and saved states. To restore a server that's running DFS Replication, don't use snapshots or saved states to replicate anything other than the sysvol folder. If you attempt this type of restore, DFS Replication fails. This restoration requires special database recovery steps. Also, don't export, clone, or copy the virtual machines. For more information, see DFSR no longer replicates files after restoring a virtualized server's snapshot and Safely virtualizing DFSR.
DFS Replication backups. To back up data in a replicated folder that's stored in a virtual machine, use backup software that's located on the guest virtual machine. Don't back up or restore a virtualized DFS Replication server from the host virtual machine.
Domain controller access. DFS Replication requires access to physical or virtualized domain controllers. The DFS Replication service can't communicate directly with Microsoft Entra ID.
VPN connection. DFS Replication requires a VPN connection between your on-premises replication group members and any members hosted in Azure virtual machines. You also need to configure the on-premises router (such as Forefront Threat Management Gateway) to allow the RPC Endpoint Mapper (port 135) and a randomly assigned port between 49152 and 65535 to pass over the VPN connection. You can use the Set-DfsrMachineConfiguration cmdlet or the dfsrdiag command-line tool to specify a static port instead of the random port. For more information about how to specify a static port for DFS Replication, see Set-DfsrServiceConfiguration. For information about related ports to open for managing Windows Server, see Service overview and network port requirements for Windows.
To learn how to get started with Azure virtual machines, visit the Microsoft Azure website.
To install DFS Replication by using Server Manager, follow these steps:
Open Server Manager.
Select Manage, and then select Add Roles and Features. The Add Roles and Features wizard opens.
Under Server Selection, select the server or virtual hard disk (VHD) where you want to install DFS Replication. The server or VHD should be an offline virtual machine.
To install the DFS Replication service, go to Server Roles.
Expand File and Storage Services > File and iSCSI Services, and then select DFS Replication.
To install the DFS Management Tools, go to Features.
Expand Remote Server Administration Tools, Role Administration Tools, and then expand File Services Tools.
Select DFS Management Tools.
The DFS Management Tools option installs the DFS Management snap-in, the DFS Replication and DFS Namespaces modules for Windows PowerShell, and command-line tools. The option doesn't install any DFS services on the server.
To install the DFS Replication by using Windows PowerShell, follow these steps:
Open a Windows PowerShell session with elevated user rights.
Enter the following command to install the desired RSAT role services or features to support DFS replication.
For the <name\> parameter, enter of the names of the RSAT role services or features that you want to install. You can install one or multiple services and features in a single command. The table lists the names of the relevant RSAT role services and features.
Install-WindowsFeature <name>
| RSAT role service/feature | Value for <name> parameter |
|---|---|
| DFS Replication | FS-DFS-Replication |
| DFS Management Tools | RSAT-DFS-Mgmt-Con |
To install the DFS Replication service only, enter the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature "RSAT-DFS-Mgmt-Con"
To install both the DFS Replication service and the DFS Management Tools, enter the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature "FS-DFS-Replication", "RSAT-DFS-Mgmt-Con"
Hendelser
29. apr., 14 - 30. apr., 19
Bli med i den ultimate virtuelle Windows Server-hendelsen 29.–30. april for omfattende tekniske økter og direkte Q&A med Microsoft-teknikere.
Registrer deg nåOpplæring
Modul
Implement a hybrid file server infrastructure - Training
Implement a hybrid file server infrastructure using Azure Files and Azure File Sync, and migrate SMB file servers to Azure.
Sertifisering
Microsoft Certified: Windows Server Hybrid Administrator Associate - Certifications
As a Windows Server hybrid administrator, you integrate Windows Server environments with Azure services and manage Windows Server in on-premises networks.