Encrypt disks using customer-managed keys in Azure DevTest Labs
Server-side encryption (SSE) protects your data and helps you meet your organizational security and compliance commitments. SSE automatically encrypts your data stored on managed disks in Azure (OS and data disks) at rest by default when persisting it to the cloud. Learn more about Disk Encryption on Azure.
Within DevTest Labs, all OS disks and data disks created as part of a lab are encrypted using platform-managed keys. However, as a lab owner you can choose to encrypt lab virtual machine disks using your own keys. If you choose to manage encryption with your own keys, you can specify a customer-managed key to use for encrypting data in lab disks. To learn more on Server-side encryption (SSE) with customer-managed keys, and other managed disk encryption types, see Customer-managed keys. Also, see restrictions with using customer-managed keys.
Note
- The setting applies to newly created disks in the lab. If you choose to change the disk encryption set at some point, older disks in the lab will continue to remain encrypted using the previous disk encryption set.
The following section shows how a lab owner can set up encryption using a customer-managed key.
Pre-requisites
If you don’t have a disk encryption set, follow this article to set up a Key Vault and a Disk Encryption Set. Note the following requirements for the disk encryption set:
- The disk encryption set needs to be in same region and subscription as your lab.
- Ensure you (lab owner) have at least a reader-level access to the disk encryption set that will be used to encrypt lab disks.
For labs created prior to 8/1/2020, lab owner will need to ensure lab system assigned identity is enabled. To do so, lab owner can go to their lab, click on Configuration and policies, click on Identity (Preview) blade, change System Assigned identity Status to On and click on Save. For new labs created after 8/1/2020 lab's system assigned identity will be enabled by default.

For the lab to handle encryption for all the lab disks, lab owner needs to explicitly grant the lab’s system-assigned identity reader role on the disk encryption set as well as virtual machine contributor role on the underlying Azure subscription. The lab owner can do so by completing the following steps:
Ensure you are a member of User Access Administrator role at the Azure subscription level so that you can manage user access to Azure resources.
On the Disk Encryption Set page, assign at least the Reader role to the lab name for which the disk encryption set will be used.
For detailed steps, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal.
Navigate to the Subscription page in the Azure portal.
Assign the Virtual Machine Contributor role to the lab name (system-assigned identity for the lab).
Encrypt lab OS disks with a customer-managed key
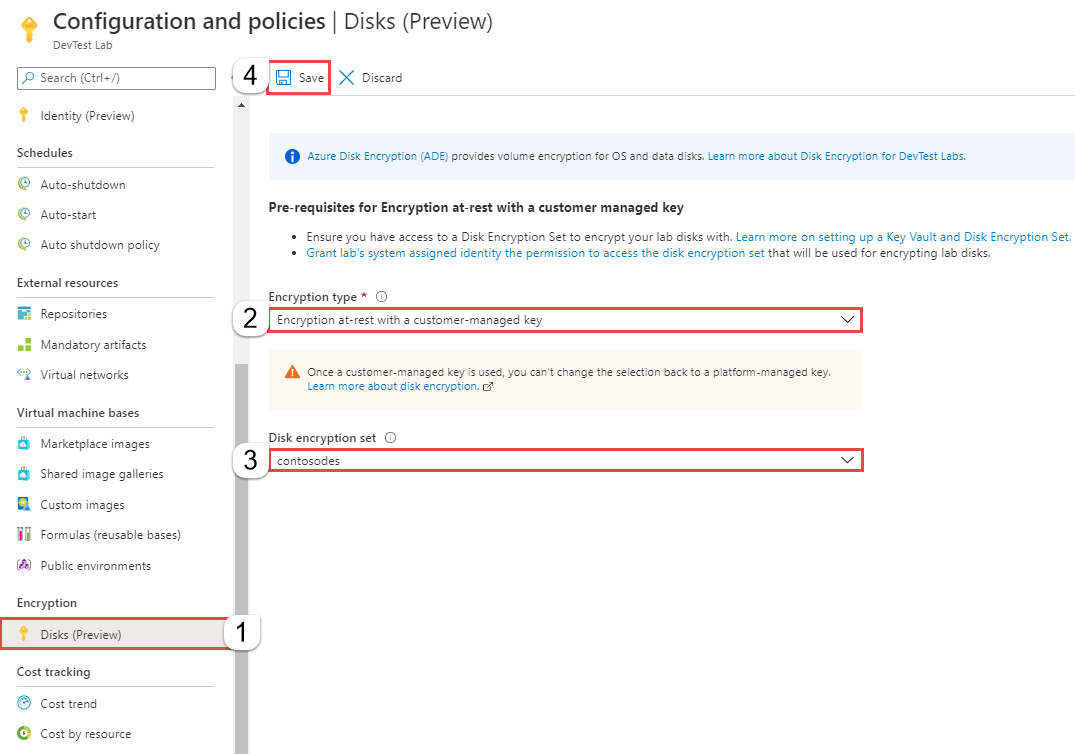
On the home page for your lab in the Azure portal, select Configuration and policies on the left menu.
On the Configuration and policies page, select Disks (Preview) in the Encryption section. By default, Encryption type is set to Encryption at-rest with a platform managed key.

For Encryption type, select Encryption at-rest with a customer managed key from drop-down list.
For Disk encryption set, select the disk encryption set you created earlier. It's the same disk encryption set that the system-assigned identity of the lab can access.
Select Save on the toolbar.
On the message box with the following text: This setting will apply to newly created machines in the lab. Old OS disk will remain encrypted with the old disk encryption set, select OK.
Once configured, lab disks will be encrypted with the customer-managed key provided using the disk encryption set.
How to validate if disks are being encrypted
Go to a lab virtual machine created after enabling disk encryption with a customer managed key on the lab.

Click on the resource group of the VM and click on the OS Disk.

Go to Encryption and validate if encryption is set to customer managed key with the Disk Encryption Set you selected.

Related content
See the following articles: