Cluster an SAP ASCS/SCS instance on a Windows failover cluster by using a file share in Azure
Windows
Windows Server failover clustering is the foundation of a high-availability SAP ASCS/SCS installation and DBMS in Windows.
A failover cluster is a group of 1+n independent servers (nodes) that work together to increase the availability of applications and services. If a node failure occurs, Windows Server failover clustering calculates the number of failures that can occur and still maintain a healthy cluster to provide applications and services. You can choose from different quorum modes to achieve failover clustering.
Prerequisites
Before you begin the tasks that are described in this article, review the following articles and SAP notes:
- Azure Virtual Machines high-availability architecture and scenarios for SAP NetWeaver
- SAP Note 1928533, which contains:
- A list of Azure VM sizes that are supported for the deployment of SAP software
- Important capacity information for Azure VM sizes
- Supported SAP software, and operating system (OS) and database combinations
- Required SAP kernel version for Windows on Microsoft Azure
- SAP Note 2015553 lists prerequisites for SAP-supported SAP software deployments in Azure.
- SAP Note 2178632 has detailed information about all monitoring metrics reported for SAP in Azure.
- SAP Note 1999351 has additional troubleshooting information for the Azure Enhanced Monitoring Extension for SAP.
- SAP Note 2287140 lists prerequisites for SAP-supported CA feature of SMB 3.x protocol.
- SAP Note 2802770 has troubleshooting information for the slow running SAP transaction AL11 on Windows 2012 and 2016.
- SAP Note 1911507 has information about transparent failover feature for a file share on Windows Server with the SMB 3.0 protocol.
- SAP Note 662452 has recommendation(deactivating 8.3 name generation) to address Poor file system performance/errors during data accesses.
- Install SAP NetWeaver high availability on a Windows failover cluster and file share for SAP ASCS/SCS instances on Azure
Note
Clustering SAP ASCS/SCS instances by using a file share is supported for SAP systems with SAP Kernel 7.22 (and later). For details see SAP note 2698948
Windows Server failover clustering in Azure
Compared to bare-metal or private cloud deployments, Azure Virtual Machines requires additional steps to configure Windows Server failover clustering. When you build a cluster, you need to set several IP addresses and virtual host names for the SAP ASCS/SCS instance.
Name resolution in Azure and the cluster virtual host name
The Azure cloud platform doesn't offer the option to configure virtual IP addresses, such as floating IP addresses. You need an alternative solution to set up a virtual IP address to reach the cluster resource in the cloud.
The Azure Load Balancer service provides an internal load balancer for Azure. With the internal load balancer, clients reach the cluster over the cluster virtual IP address.
Deploy the internal load balancer in the resource group that contains the cluster nodes. Then, configure all necessary port forwarding rules by using the probe ports of the internal load balancer. The clients can connect via the virtual host name. The DNS server resolves the cluster IP address. The internal load balancer handles port forwarding to the active node of the cluster.
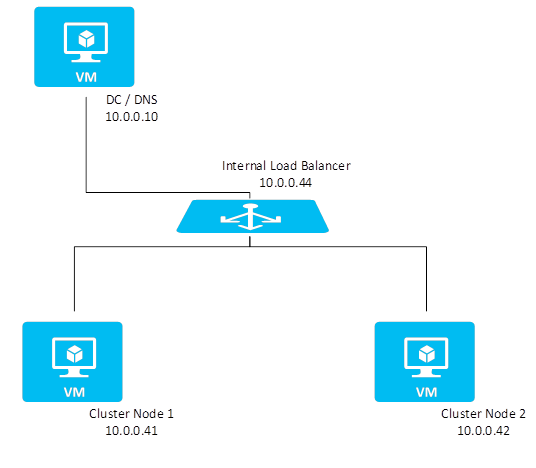
Figure 1: Windows Server failover clustering configuration in Azure without a shared disk
SAP ASCS/SCS HA with file share
SAP developed a new approach, and an alternative to cluster shared disks, for clustering an SAP ASCS/SCS instance on a Windows failover cluster. Instead of using cluster shared disks, you can use an SMB file share to deploy SAP global host files.
Note
An SMB file share is an alternative to using cluster shared disks for clustering SAP ASCS/SCS instances.
This architecture is specific in the following ways:
- SAP central services (with its own file structure and message and enqueue processes) are separate from the SAP global host files.
- SAP central services run under an SAP ASCS/SCS instance.
- SAP ASCS/SCS instance is clustered and is accessible by using the <ASCS/SCS virtual host name> virtual host name.
- SAP global files are placed on the SMB file share and are accessed by using the <SAP global host> host name: \\<SAP global host>\sapmnt\<SID>\SYS...
- The SAP ASCS/SCS instance is installed on a local disk on both cluster nodes.
- The <ASCS/SCS virtual host name> network name is different from <SAP global host>.
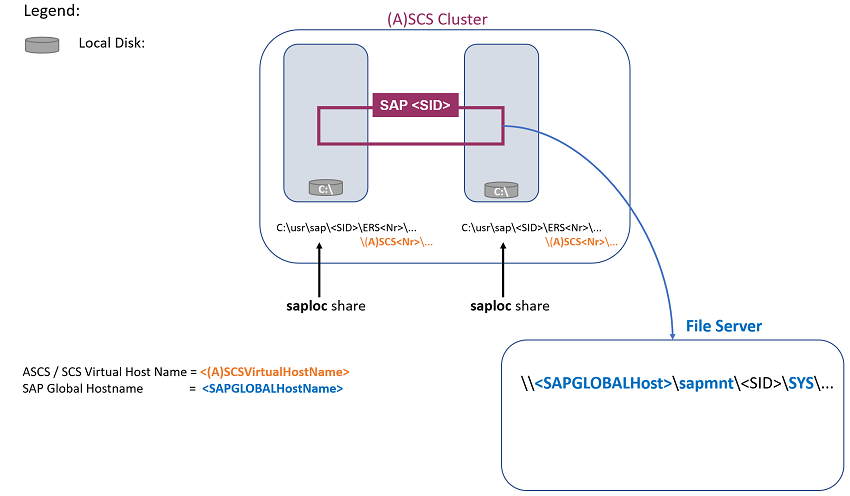
Figure 2: New SAP ASCS/SCS HA architecture with an SMB file share
Prerequisites for an SMB file share:
- SMB 3.0 (or later) protocol.
- Ability to set Active Directory access control lists (ACLs) for Active Directory user groups and the
computer$computer object. - The file share must be HA-enabled:
- Disks used to store files must not be a single point of failure.
- Server or VM downtime does not cause downtime on the file share.
The SAP <SID> cluster role does not contain cluster shared disks or a generic file share cluster resource.
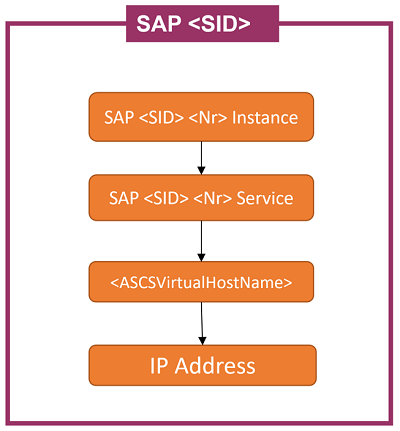
Figure 3: SAP <SID> cluster role resources for using a file share
Scale-out file shares with Storage Spaces Direct in Azure as an SAPMNT file share
You can use a scale-out file share to host and protect SAP global host files. A scale-out file share also offers a highly available SAPMNT file share service.
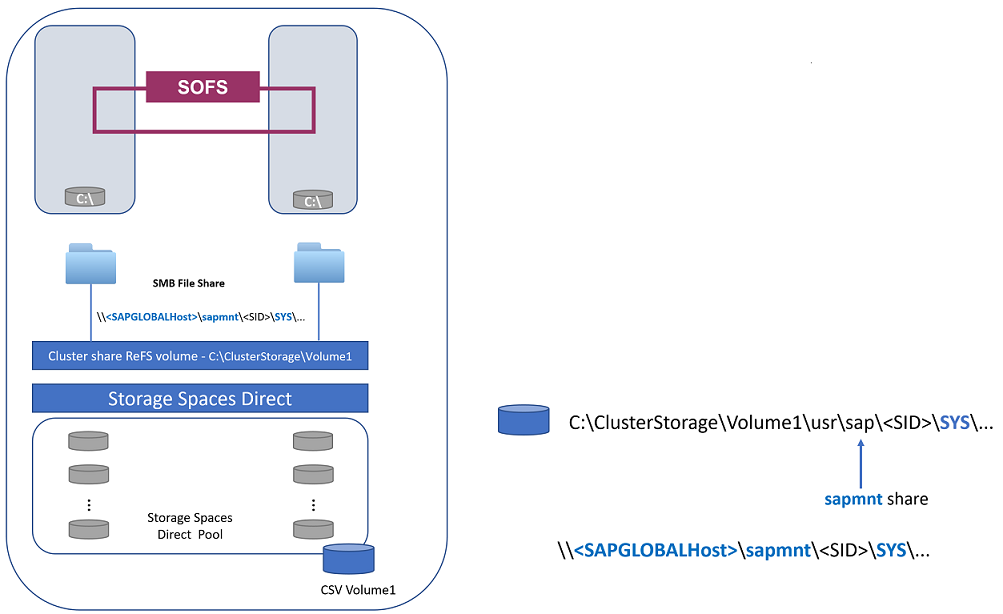
Figure 4: A scale-out file share used to protect SAP global host files
Important
Scale-out file shares are fully supported in the Microsoft Azure cloud, and in on-premises environments.
A scale-out file share offers a highly available and horizontally scalable SAPMNT file share.
Storage Spaces Direct is used as a shared disk for a scale-out file share. You can use Storage Spaces Direct to build highly available and scalable storage using servers with local storage. Shared storage that is used for a scale-out file share, like for SAP global host files, is not a single point of failure.
When choosing Storage Spaces Direct, consider these use cases:
- The virtual machines used to build the Storage Spaces Direct cluster need to be deployed in an Azure availability set.
- For disaster recovery of a Storage Spaces Direct Cluster, you can use Azure Site Recovery Services.
- It is not supported to stretch the Storage Space Direct Cluster across different Azure Availability Zones.
SAP prerequisites for scale-out file shares in Azure
To use a scale-out file share, your system must meet the following requirements:
- At least two cluster nodes for a scale-out file share.
- Each node must have at least two local disks.
- For performance reason, you must use mirroring resiliency:
- Two-way mirroring for a scale-out file share with two cluster nodes.
- Three-way mirroring for a scale-out file share with three (or more) cluster nodes.
- We recommend three (or more) cluster nodes for a scale-out file share, with three-way mirroring. This setup offers more scalability and more storage resiliency than the scale-out file share setup with two cluster nodes and two-way mirroring.
- You must use Azure Premium disks.
- We recommend that you use Azure Managed Disks.
- We recommend that you format volumes by using Resilient File System (ReFS).
- For more information, see SAP Note 1869038 - SAP support for ReFS filesystem and the Choosing the file system chapter of the article Planning volumes in Storage Spaces Direct.
- Be sure that you install Microsoft KB4025334 cumulative update.
- You can use DS-Series or DSv2-Series Azure VM sizes.
- For good network performance between VMs, which is needed for Storage Spaces Direct disk sync, use a VM type that has at least a “high” network bandwidth. For more information, see the DSv2-Series and DS-Series specifications.
- We recommend that you reserve some unallocated capacity in the storage pool. Leaving some unallocated capacity in the storage pool gives volumes space to repair "in place" if a drive fails. This improves data safety and performance. For more information, see Choosing volume size.
- You don't need to configure the Azure internal load balancer for the scale-out file share network name, such as for <SAP global host>. This is done for the <ASCS/SCS virtual host name> of the SAP ASCS/SCS instance or for the DBMS. A scale-out file share scales out the load across all cluster nodes. <SAP global host> uses the local IP address for all cluster nodes.
Important
You cannot rename the SAPMNT file share, which points to <SAP global host>. SAP supports only the share name "sapmnt."
For more information, see SAP Note 2492395 - Can the share name sapmnt be changed?
Configure SAP ASCS/SCS instances and a scale-out file share in two clusters
You must deploy the SAP ASCS/SCS instances in a separate cluster, with their own SAP <SID> cluster role. In this case, you configure the scale-out file share on another cluster, with another cluster role.
Important
The setup must meet the following requirement: the SAP ASCS/SCS instances and the SOFS share must be deployed in separate clusters.
Important
In this scenario, the SAP ASCS/SCS instance is configured to access the SAP global host by using UNC path \\<SAP global host>\sapmnt\<SID>\SYS.
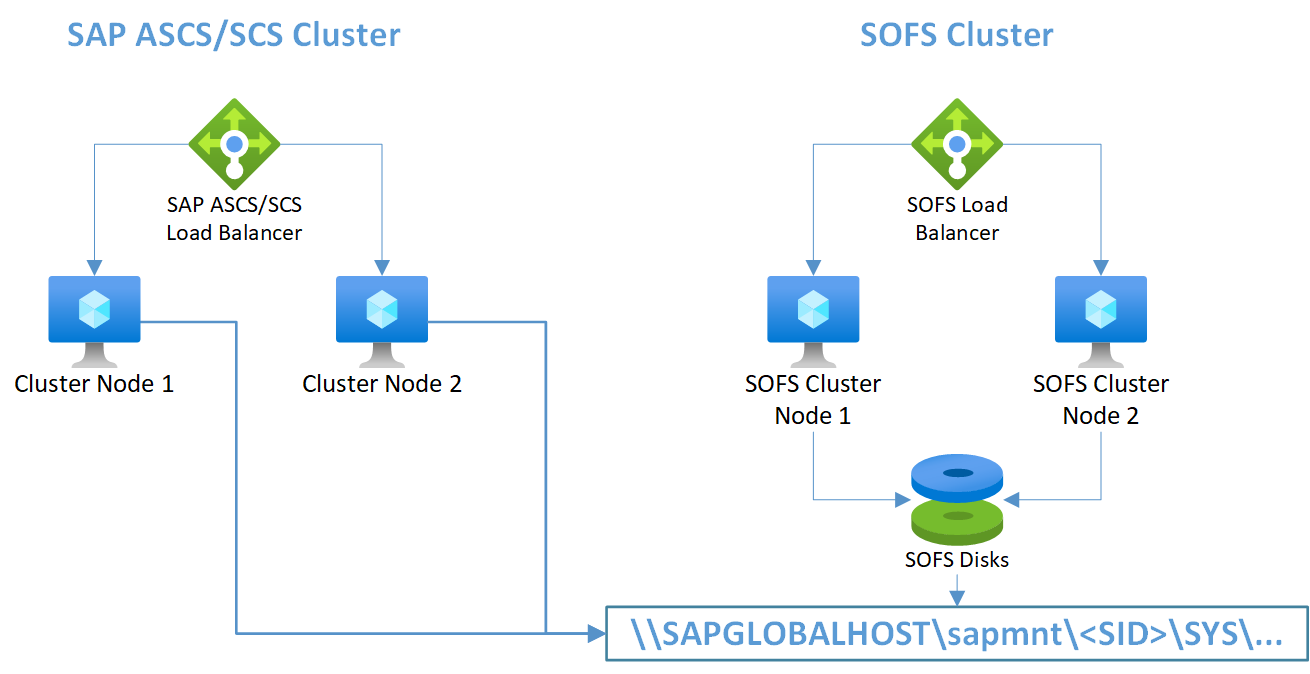
Figure 5: An SAP ASCS/SCS instance and a scale-out file share deployed in two clusters
Optional configurations
The following diagrams show multiple SAP instances on Azure VMs running Microsoft Windows Failover Cluster to reduce the total number of VMs.
This can either be local SAP Application Servers on a SAP ASCS/SCS cluster or a SAP ASCS/SCS Cluster Role on Microsoft SQL Server Always On nodes.
Important
Installing a local SAP Application Server on a SQL Server Always On node is not supported.
Both, SAP ASCS/SCS and the Microsoft SQL Server database, are single points of failure (SPOF). To protect these SPOFs in a Windows environment WSFC is used.
While the resource consumption of the SAP ASCS/SCS is fairly small, a reduction of the memory configuration for either SQL Server or the SAP Application Server by 2 GB is recommended.
SAP Application Servers on WSFC nodes using Windows SOFS
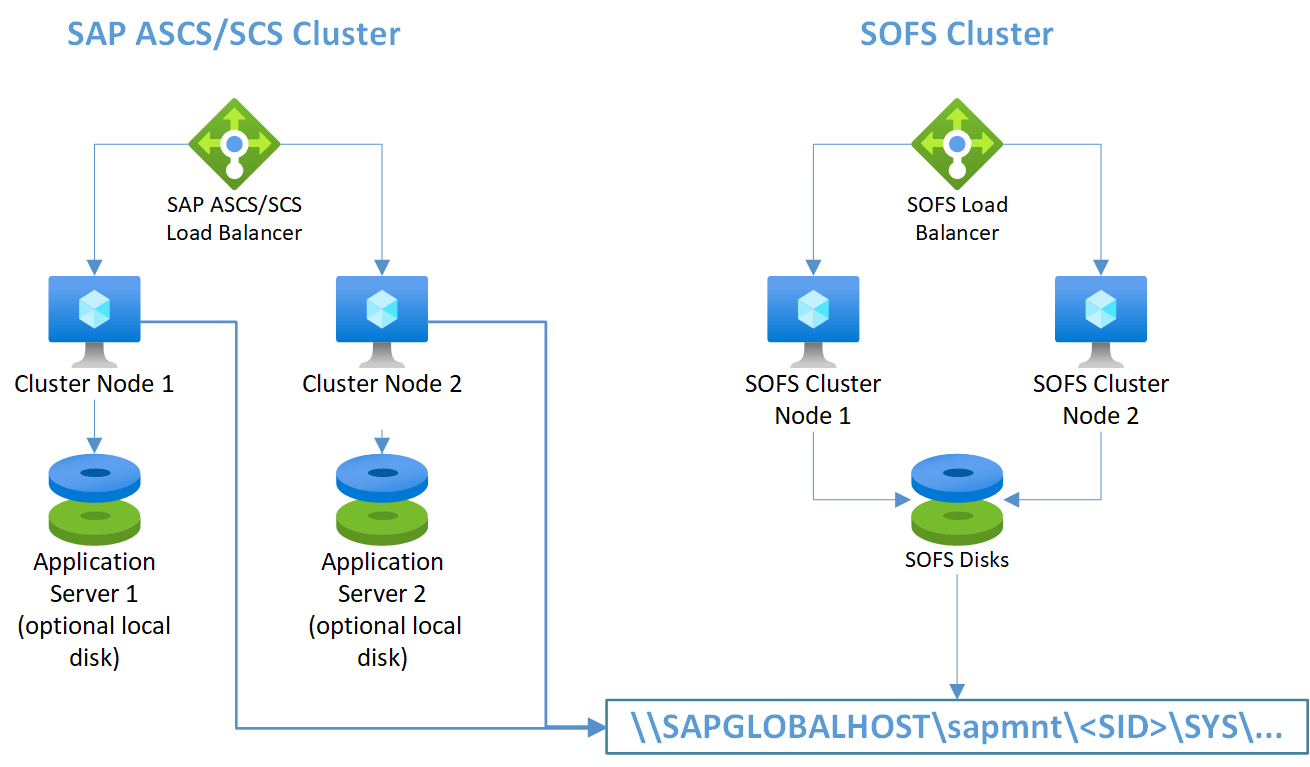
Note
The picture shows the use of additional local disks. This is optional for customers who will not install application software on the OS drive (C:)
SAP ASCS/SCS on SQL Server Always On nodes using Windows SOFS
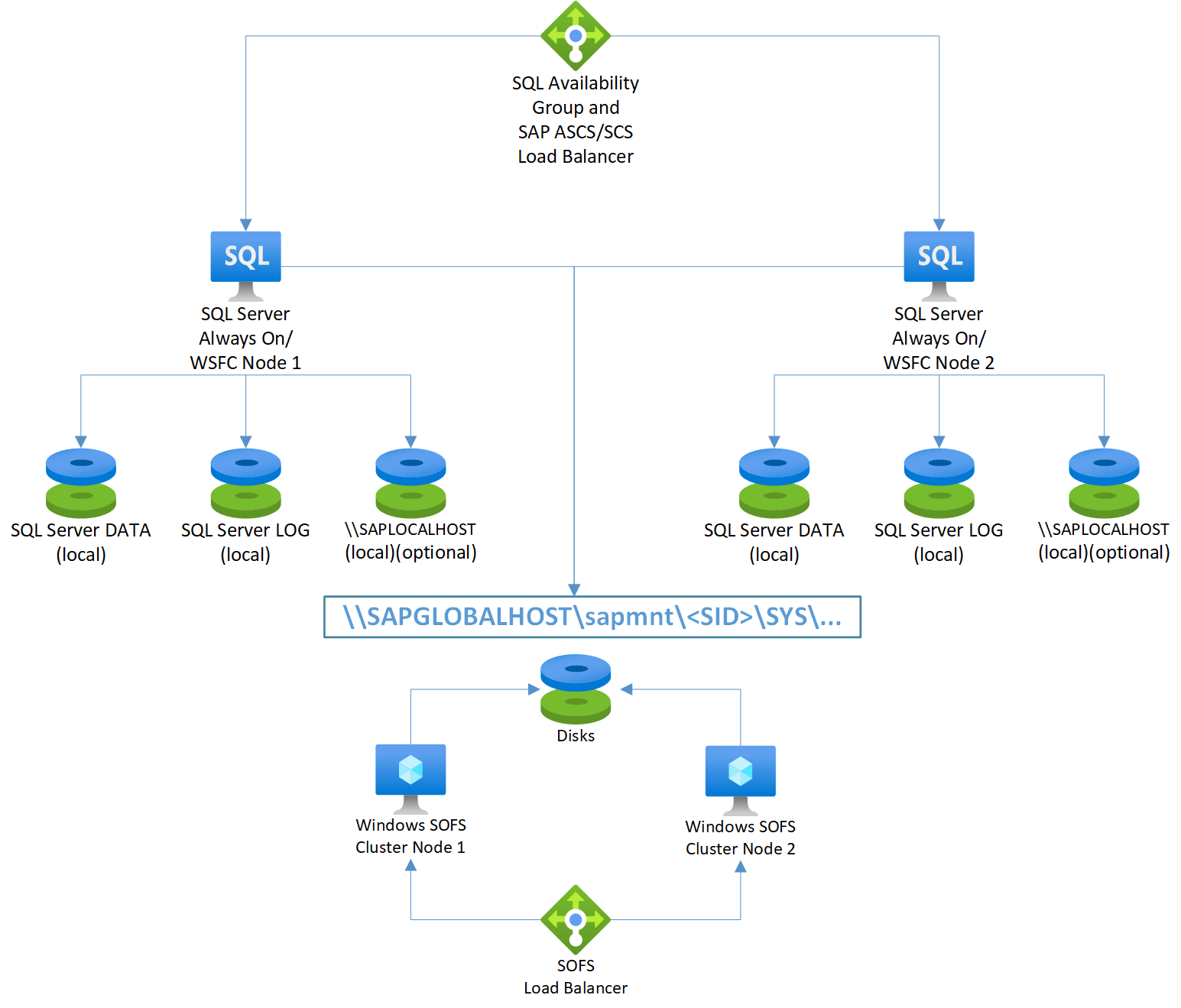
Note
The picture shows the use of additional local disks. This is optional for customers who will not install application software on the OS drive (C:)
Important
In the Azure cloud, each cluster that is used for SAP and scale-out file shares must be deployed in its own Azure availability set or across Azure Availability Zones. This ensures distributed placement of the cluster VMs across the underlying Azure infrastructure. Availability Zone deployments are supported with this technology.
Generic file share with SIOS DataKeeper as cluster shared disks
A generic file share is another option for achieving a highly available file share.
In this case, you can use a third-party SIOS solution as a cluster shared disk.
Next steps
- Prepare the Azure infrastructure for SAP HA by using a Windows failover cluster and file share for an SAP ASCS/SCS instance
- Install SAP NetWeaver HA on a Windows failover cluster and file share for an SAP ASCS/SCS instance
- Deploy a two-node Storage Spaces Direct scale-out file server for UPD storage in Azure
- Storage Spaces Direct in Windows Server 2016
- Deep dive: Volumes in Storage Spaces Direct