Заметка
Доступ к этой странице требует авторизации. Вы можете попробовать войти в систему или изменить каталог.
Доступ к этой странице требует авторизации. Вы можете попробовать сменить директорию.
В этом примере показано, как использовать интерфейсы IXMLHTTPRequest2 и IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback вместе с задачами для отправки HTTP-запросов GET и POST в веб-службу в приложении универсальная платформа Windows (UWP). Путем объединения IXMLHTTPRequest2 с задачами, можно написать код, который объединяется с другими задачами. Например, можно использовать задачу загрузки в цепочке этих задач. Задача загрузки может также реагировать на отмену работы.
Совет
Пакет SDK REST для C++ можно также использовать для выполнения HTTP-запросов из приложения UWP с помощью приложения C++ или классического приложения C++. Дополнительные сведения см. в пакете SDK REST для C++ (Codename "Casablanca").
Дополнительные сведения о задачах см. в разделе "Параллелизм задач". Дополнительные сведения об использовании задач в приложении UWP см. в статье асинхронное программирование в C++ и создании асинхронных операций в C++ для приложений UWP.
В этом документе сначала показаны способы создания HttpRequest и его вспомогательных классов. Затем показано, как использовать этот класс из приложения UWP, использующего C++ и XAML.
Пример использования, но не использующий IXMLHTTPRequest2 задачи, см . в кратком руководстве по подключению с помощью HTTP-запроса XML (IXMLHTTPRequest2).
Совет
IXMLHTTPRequest2 и IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback являются интерфейсами, которые мы рекомендуем использовать в приложении UWP. Можно также адаптировать этот пример для использования в приложении для настольных систем.
Необходимые компоненты
Поддержка UWP является необязательной в Visual Studio 2017 и более поздних версиях. Чтобы установить его, откройте visual Studio Installer из Windows меню и выберите используемую версию Visual Studio. Нажмите кнопку "Изменить" и убедитесь, что установлен флажок "Разработка UWP". В разделе "Необязательные компоненты" убедитесь, что средства UWP C++ проверяются. Используйте версию 141 для Visual Studio 2017 или версии 142 для Visual Studio 2019.
Определение классов HttpRequest, HttpRequestBuffersCallback и HttpRequestStringCallback
В случае использования интерфейса IXMLHTTPRequest2 для создания веб-запросов по протоколу HTTP необходимо реализовать интерфейс IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback для получения ответа сервера и реагирования на другие события. В этом примере определяется класс HttpRequest для создания веб-запросов и классы HttpRequestBuffersCallback и HttpRequestStringCallback для обработки ответов. Классы HttpRequestBuffersCallback и HttpRequestStringCallback поддерживают класс HttpRequest; пользователь работает только с классом HttpRequest из кода приложения.
Методы GetAsync, PostAsync класса HttpRequest позволяют запустить операции HTTP GET и POST, соответственно. Эти методы используют класс HttpRequestStringCallback для чтения ответа сервера в виде строки. Методы SendAsync и ReadAsync позволяют выполнять потоковую передачу большого содержимого в виде блоков. Эти методы возвращают параллелизм::task для представления операции. Методы GetAsync создают PostAsync значение, где task<std::wstring> часть wstring представляет ответ сервера. Методы SendAsync и ReadAsync генерируют значения task<void>; эти задачи завершаются по завершению операций отправки и чтения.
IXMLHTTPRequest2 Так как интерфейсы действуют асинхронно, в этом примере используется параллелизм::task_completion_event для создания задачи, которая завершается после завершения или отмены операции скачивания. Класс HttpRequest создает основанное на задаче продолжение из этой задачи, чтобы установить конечный результат. Класс HttpRequest использует основанное на задаче продолжение, чтобы убедиться, что задача продолжения выполняется, даже если предыдущая задача выдает ошибку или отменяется. Дополнительные сведения о продолжениях на основе задач см. в разделе "Параллелизм задач"
Чтобы поддерживать отмену, классы HttpRequest, HttpRequestBuffersCallback и HttpRequestStringCallback используют токены отмены. Метод HttpRequestBuffersCallback параллелизмаHttpRequestStringCallback::cancellation_token:::register_callback позволяет событию завершения задачи реагировать на отмену. Этот обратный вызов отмены прерывает загрузку. Дополнительные сведения об отмене см. в разделе "Отмена".
Определение класса HttpRequest
В главном меню выберите "Файл>нового>проекта".
Используйте шаблон пустого приложения C++ (универсального приложения Windows) для создания пустого проекта приложения XAML. В этом примере проект называется
UsingIXMLHTTPRequest2.Добавьте в проект файл заголовка с именем HttpRequest.h и файл исходного кода с именем HttpRequest.cpp.
В pch.h добавьте следующий код:
#include <ppltasks.h> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <wrl.h> #include <msxml6.h>В HttpRequest.h добавьте следующий код:
#pragma once #include "pch.h" inline void CheckHResult(HRESULT hResult) { if (hResult == E_ABORT) { concurrency::cancel_current_task(); } else if (FAILED(hResult)) { throw Platform::Exception::CreateException(hResult); } } namespace Web { namespace Details { // Implementation of IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback used when partial buffers are needed from the response. // When only the complete response is needed, use HttpRequestStringCallback instead. class HttpRequestBuffersCallback : public Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClass< Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClassFlags<Microsoft::WRL::ClassicCom>, IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback, Microsoft::WRL::FtmBase> { public: HttpRequestBuffersCallback(IXMLHTTPRequest2* httpRequest, concurrency::cancellation_token ct = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) : request(httpRequest), cancellationToken(ct), responseReceived(false), dataHResult(S_OK), statusCode(200) { // Register a callback function that aborts the HTTP operation when // the cancellation token is canceled. if (cancellationToken != concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) { registrationToken = cancellationToken.register_callback([this]() { if (request != nullptr) { request->Abort(); } }); } dataEvent = concurrency::task_completion_event<void>(); } // Called when the HTTP request is being redirected to a new URL. IFACEMETHODIMP OnRedirect(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, PCWSTR) { return S_OK; } // Called when HTTP headers have been received and processed. IFACEMETHODIMP OnHeadersAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, DWORD statusCode, PCWSTR reasonPhrase) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { this->statusCode = statusCode; this->reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase; concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when a portion of the entity body has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnDataAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream* stream) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { // Store a reference on the stream so it can be accessed by the task. dataStream = stream; // The work must be done as fast as possible, and must not block this thread, // for example, waiting on another event object. Here we simply set an event // that can be processed by another thread. concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when the entire entity response has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnResponseReceived(IXMLHTTPRequest2* xhr, ISequentialStream* responseStream) { responseReceived = true; return OnDataAvailable(xhr, responseStream); } // Called when an error occurs during the HTTP request. IFACEMETHODIMP OnError(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, HRESULT hrError) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataHResult = hrError; dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Create a task that completes when data is available, in an exception-safe way. concurrency::task<void> CreateDataTask(); HRESULT GetError() const { return dataHResult; } int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } std::wstring const& GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } bool IsResponseReceived() const { return responseReceived; } // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. unsigned int ReadData( _Out_writes_(outputBufferSize) byte* outputBuffer, unsigned int outputBufferSize); private: ~HttpRequestBuffersCallback() { // Unregister the callback. if (cancellationToken != concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) { cancellationToken.deregister_callback(registrationToken); } } // Signals that the download operation was canceled. concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken; // Used to unregister the cancellation token callback. concurrency::cancellation_token_registration registrationToken; // The IXMLHTTPRequest2 that processes the HTTP request. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> request; // Task completion event that is set when data is available or error is triggered. concurrency::task_completion_event<void> dataEvent; concurrency::critical_section dataEventLock; // We cannot store the error obtained from IXHR2 in the dataEvent since any value there is first-writer-wins, // whereas we want a subsequent error to override an initial success. HRESULT dataHResult; // Referenced pointer to the data stream. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<ISequentialStream> dataStream; // HTTP status code and reason returned by the server. int statusCode; std::wstring reasonPhrase; // Whether the response has been completely received. bool responseReceived; }; }; // Utility class for performing asynchronous HTTP requests. // This class only supports one outstanding request at a time. class HttpRequest { public: HttpRequest(); int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } std::wstring const& GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } // Whether the response has been completely received, if using ReadAsync(). bool IsResponseComplete() const { return responseComplete; } // Start an HTTP GET on the specified URI. The returned task completes once the entire response // has been received, and the task produces the HTTP response text. The status code and reason // can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> GetAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a string body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> PostAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a stream body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> PostAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, const std::wstring& str, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Send a request but don't return the response. Instead, let the caller read it with ReadAsync(). concurrency::task<void> SendAsync( const std::wstring& httpMethod, Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Read a chunk of data from the HTTP response, up to a specified length or until we reach the end // of the response, and store the value in the provided buffer. This is useful for large content, // enabling the streaming of the result. concurrency::task<void> ReadAsync( Windows::Storage::Streams::IBuffer^ readBuffer, unsigned int offsetInBuffer, unsigned int requestedBytesToRead); static void CreateMemoryStream(IStream **stream); private: // Start a download of the specified URI using the specified method. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> DownloadAsync( PCWSTR httpMethod, PCWSTR uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamBytesToSend); // Referenced pointer to the callback, if using SendAsync/ReadAsync. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback> buffersCallback; int statusCode; std::wstring reasonPhrase; // Whether the response has been completely received, if using ReadAsync(). bool responseComplete; }; };В HttpRequest.cpp добавьте следующий код:
#include "pch.h" #include "HttpRequest.h" #include <robuffer.h> #include <shcore.h> using namespace concurrency; using namespace Microsoft::WRL; using namespace Platform; using namespace std; using namespace Web; using namespace Windows::Foundation; using namespace Windows::Storage::Streams; // Implementation of IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback used when only the complete response is needed. // When processing chunks of response data as they are received, use HttpRequestBuffersCallback instead. class HttpRequestStringCallback : public RuntimeClass<RuntimeClassFlags<ClassicCom>, IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback, FtmBase> { public: HttpRequestStringCallback(IXMLHTTPRequest2* httpRequest, cancellation_token ct = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) : request(httpRequest), cancellationToken(ct) { // Register a callback function that aborts the HTTP operation when // the cancellation token is canceled. if (cancellationToken != cancellation_token::none()) { registrationToken = cancellationToken.register_callback([this]() { if (request != nullptr) { request->Abort(); } }); } } // Called when the HTTP request is being redirected to a new URL. IFACEMETHODIMP OnRedirect(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, PCWSTR) { return S_OK; } // Called when HTTP headers have been received and processed. IFACEMETHODIMP OnHeadersAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, DWORD statusCode, PCWSTR reasonPhrase) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { this->statusCode = statusCode; this->reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase; } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when a portion of the entity body has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnDataAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream*) { return S_OK; } // Called when the entire entity response has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnResponseReceived(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream* responseStream) { wstring wstr; HRESULT hr = ReadUtf8StringFromSequentialStream(responseStream, wstr); // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { completionEvent.set(make_tuple<HRESULT, wstring>(move(hr), move(wstr))); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Simulate the functionality of DataReader.ReadString(). // This is needed because DataReader requires IRandomAccessStream and this // code has an ISequentialStream that does not have a conversion to IRandomAccessStream like IStream does. HRESULT ReadUtf8StringFromSequentialStream(ISequentialStream* readStream, wstring& str) { // Convert the response to Unicode wstring. HRESULT hr; // Holds the response as a Unicode string. wstringstream ss; while (true) { ULONG cb; char buffer[4096]; // Read the response as a UTF-8 string. Since UTF-8 characters are 1-4 bytes long, // we need to make sure we only read an integral number of characters. So we'll // start with 4093 bytes. hr = readStream->Read(buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 3, &cb); if (FAILED(hr) || (cb == 0)) { break; // Error or no more data to process, exit loop. } if (cb == sizeof(buffer) - 3) { ULONG subsequentBytesRead; unsigned int i, cl; // Find the first byte of the last UTF-8 character in the buffer. for (i = cb - 1; (i >= 0) && ((buffer[i] & 0xC0) == 0x80); i--); // Calculate the number of subsequent bytes in the UTF-8 character. if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0x80) { cl = 1; } else if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0xE0) { cl = 2; } else if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0xF0) { cl = 3; } else { cl = 4; } // Read any remaining bytes. if (cb < i + cl) { hr = readStream->Read(buffer + cb, i + cl - cb, &subsequentBytesRead); if (FAILED(hr)) { break; // Error, exit loop. } cb += subsequentBytesRead; } } // First determine the size required to store the Unicode string. int const sizeRequired = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, buffer, cb, nullptr, 0); if (sizeRequired == 0) { // Invalid UTF-8. hr = HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError()); break; } unique_ptr<char16[]> wstr(new(std::nothrow) char16[sizeRequired + 1]); if (wstr.get() == nullptr) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; break; } // Convert the string from UTF-8 to UTF-16LE. This can never fail, since // the previous call above succeeded. MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, buffer, cb, wstr.get(), sizeRequired); wstr[sizeRequired] = L'\0'; // Terminate the string. ss << wstr.get(); // Write the string to the stream. } str = SUCCEEDED(hr) ? ss.str() : wstring(); return (SUCCEEDED(hr)) ? S_OK : hr; // Don't return S_FALSE. } // Called when an error occurs during the HTTP request. IFACEMETHODIMP OnError(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, HRESULT hrError) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { completionEvent.set(make_tuple<HRESULT, wstring>(move(hrError), wstring())); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Retrieves the completion event for the HTTP operation. task_completion_event<tuple<HRESULT, wstring>> const& GetCompletionEvent() const { return completionEvent; } int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } wstring GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } private: ~HttpRequestStringCallback() { // Unregister the callback. if (cancellationToken != cancellation_token::none()) { cancellationToken.deregister_callback(registrationToken); } } // Signals that the download operation was canceled. cancellation_token cancellationToken; // Used to unregister the cancellation token callback. cancellation_token_registration registrationToken; // The IXMLHTTPRequest2 that processes the HTTP request. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> request; // Task completion event that is set when the // download operation completes. task_completion_event<tuple<HRESULT, wstring>> completionEvent; int statusCode; wstring reasonPhrase; }; // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. unsigned int Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback::ReadData( _Out_writes_(outputBufferSize) byte* outputBuffer, unsigned int outputBufferSize) { // Lock the data event while doing the read, to ensure that any bytes we don't read will // result in the correct event getting triggered. concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); ULONG bytesRead; CheckHResult(dataStream.Get()->Read(outputBuffer, outputBufferSize, &bytesRead)); if (bytesRead < outputBufferSize) { // We need to reset the data event, which we can only do by creating a new one. dataEvent = task_completion_event<void>(); } return bytesRead; } // Create a task that completes when data is available, in an exception-safe way. task<void> Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback::CreateDataTask() { concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); return create_task(dataEvent, cancellationToken); } HttpRequest::HttpRequest() : responseComplete(true), statusCode(200) { } // Start a download of the specified URI using the specified method. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::DownloadAsync(PCWSTR httpMethod, PCWSTR uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend) { // Create an IXMLHTTPRequest2 object. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> xhr; CheckHResult(CoCreateInstance(CLSID_XmlHttpRequest, nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_PPV_ARGS(&xhr))); // Create callback. auto stringCallback = Make<HttpRequestStringCallback>(xhr.Get(), cancellationToken); CheckHResult(stringCallback ? S_OK : E_OUTOFMEMORY); auto completionTask = create_task(stringCallback->GetCompletionEvent()); // Create a request. CheckHResult(xhr->Open(httpMethod, uri, stringCallback.Get(), nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)); if (postStream != nullptr && contentType != nullptr) { CheckHResult(xhr->SetRequestHeader(L"Content-Type", contentType)); } // Send the request. CheckHResult(xhr->Send(postStream, postStreamSizeToSend)); // Return a task that completes when the HTTP operation completes. // We pass the callback to the continuation because the lifetime of the // callback must exceed the operation to ensure that cancellation // works correctly. return completionTask.then([this, stringCallback](tuple<HRESULT, wstring> resultTuple) { // If the GET operation failed, throw an Exception. CheckHResult(std::get<0>(resultTuple)); statusCode = stringCallback->GetStatusCode(); reasonPhrase = stringCallback->GetReasonPhrase(); return std::get<1>(resultTuple); }); } // Start an HTTP GET on the specified URI. The returned task completes once the entire response // has been received, and the task produces the HTTP response text. The status code and reason // can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::GetAsync(Uri^ uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { return DownloadAsync(L"GET", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, nullptr, nullptr, 0); } void HttpRequest::CreateMemoryStream(IStream **stream) { auto randomAccessStream = ref new Windows::Storage::Streams::InMemoryRandomAccessStream(); CheckHResult(CreateStreamOverRandomAccessStream(randomAccessStream, IID_PPV_ARGS(stream))); } // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a string body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::PostAsync(Uri^ uri, const wstring& body, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { int length = 0; ComPtr<IStream> postStream; CreateMemoryStream(&postStream); if (body.length() > 0) { // Get the required buffer size. int size = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, // UTF-8 0, // Conversion type body.c_str(), // Unicode string to convert static_cast<int>(body.length()), // Size nullptr, // Output buffer 0, // Output buffer size nullptr, nullptr); CheckHResult((size != 0) ? S_OK : HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError())); std::unique_ptr<char[]> tempData(new char[size]); length = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, // UTF-8 0, // Conversion type body.c_str(), // Unicode string to convert static_cast<int>(body.length()), // Size tempData.get(), // Output buffer size, // Output buffer size nullptr, nullptr); CheckHResult((length != 0) ? S_OK : HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError())); CheckHResult(postStream->Write(tempData.get(), length, nullptr)); } return DownloadAsync(L"POST", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, L"text/plain;charset=utf-8", postStream.Get(), length); } // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a stream body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::PostAsync(Uri^ uri, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { return DownloadAsync(L"POST", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, contentType, postStream, postStreamSizeToSend); } // Send a request but don't return the response. Instead, let the caller read it with ReadAsync(). task<void> HttpRequest::SendAsync(const wstring& httpMethod, Uri^ uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { // Create an IXMLHTTPRequest2 object. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> xhr; CheckHResult(CoCreateInstance(CLSID_XmlHttpRequest, nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_PPV_ARGS(&xhr))); // Create callback. buffersCallback = Make<Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback>(xhr.Get(), cancellationToken); CheckHResult(buffersCallback ? S_OK : E_OUTOFMEMORY); ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback> xhrCallback; CheckHResult(buffersCallback.As(&xhrCallback)); // Open and send the request. CheckHResult(xhr->Open(httpMethod.c_str(), uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), xhrCallback.Get(), nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)); responseComplete = false; CheckHResult(xhr->Send(nullptr, 0)); // Return a task that completes when the HTTP operation completes. // Since buffersCallback holds a reference on the callback, the lifetime of the callback will exceed // the operation and ensure that cancellation works correctly. return buffersCallback->CreateDataTask().then([this]() { CheckHResult(buffersCallback->GetError()); statusCode = buffersCallback->GetStatusCode(); reasonPhrase = buffersCallback->GetReasonPhrase(); }); } // Read a chunk of data from the HTTP response, up to a specified length or until we reach the end // of the response, and store the value in the provided buffer. This is useful for large content, // enabling the streaming of the result. task<void> HttpRequest::ReadAsync(Windows::Storage::Streams::IBuffer^ readBuffer, unsigned int offsetInBuffer, unsigned int requestedBytesToRead) { if (offsetInBuffer + requestedBytesToRead > readBuffer->Capacity) { throw ref new InvalidArgumentException(); } // Return a task that completes when a read completes. // We pass the callback to the continuation because the lifetime of the // callback must exceed the operation to ensure that cancellation // works correctly. return buffersCallback->CreateDataTask().then([this, readBuffer, offsetInBuffer, requestedBytesToRead]() { CheckHResult(buffersCallback->GetError()); // Get a pointer to the location to copy data into. ComPtr<IBufferByteAccess> bufferByteAccess; CheckHResult(reinterpret_cast<IUnknown*>(readBuffer)->QueryInterface(IID_PPV_ARGS(&bufferByteAccess))); byte* outputBuffer; // Returned internal pointer, do not free this value. CheckHResult(bufferByteAccess->Buffer(&outputBuffer)); // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. readBuffer->Length = buffersCallback->ReadData(outputBuffer + offsetInBuffer, requestedBytesToRead); if (buffersCallback->IsResponseReceived() && (readBuffer->Length < requestedBytesToRead)) { responseComplete = true; } }); }
Использование класса HttpRequest в приложении UWP
В этом разделе показано, как использовать HttpRequest класс в приложении UWP. Приложение предоставляет окно ввода, определяющее ресурс URL-адреса, и кнопки команд, которые выполняют операции GET и POST, и команду кнопки, которая отменяет текущую операцию.
Использование класса HttpRequest
В MainPage.xaml определите элемент StackPanel следующим образом.
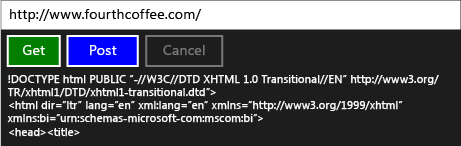
<StackPanel HorizontalAlignment="Left" Width="440" Background="{StaticResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}"> <TextBox x:Name="InputTextBox" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="http://www.fourthcoffee.com/"/> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <Button x:Name="GetButton" Content="Get" Background="Green" Click="GetButton_Click"/> <Button x:Name="PostButton" Content="Post" Background="Blue" Click="PostButton_Click"/> <Button x:Name="CancelButton" Content="Cancel" Background="Red" IsEnabled="False" Click="CancelButton_Click"/> <ProgressRing x:Name="ResponseProgressRing" /> </StackPanel> <TextBlock x:Name="ResponseTextBlock" TextWrapping="Wrap"/> </StackPanel>В MainPage.xaml.h добавьте эту директиву
#include:#include "HttpRequest.h"В MainPage.xaml.h добавьте следующие переменные-члены
privateв классMainPage:// Produces HTTP requets. Web::HttpRequest m_httpRequest; // Enables us to cancel the active HTTP request. concurrency::cancellation_token_source m_cancelHttpRequestSource;В MainPage.xaml.h объявите
privateметодProcessHttpRequest:// Displays the result of the provided HTTP request on the UI. void ProcessHttpRequest(concurrency::task<std::wstring> httpRequest);В MainPage.xaml.cpp добавьте эти операторы
using:using namespace concurrency; using namespace std; using namespace Web;В MainPage.xaml.cpp реализуйте методы
GetButton_Click,PostButton_ClickиCancelButton_ClickклассаMainPage.void MainPage::GetButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Create a new cancellation token source for the web request. m_cancelHttpRequestSource = cancellation_token_source(); // Set up the GET request parameters. auto uri = ref new Uri(InputTextBox->Text); auto token = m_cancelHttpRequestSource.get_token(); // Send the request and then update the UI. ProcessHttpRequest(m_httpRequest.GetAsync(uri, token)); } void MainPage::PostButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Create a new cancellation token source for the web request. m_cancelHttpRequestSource = cancellation_token_source(); // Set up the POST request parameters. auto uri = ref new Uri(InputTextBox->Text); wstring postData(L"This is sample POST data."); auto token = m_cancelHttpRequestSource.get_token(); // Send the request and then update the UI. ProcessHttpRequest(m_httpRequest.PostAsync(uri, postData, token)); } void MainPage::CancelButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Disable the Cancel button. // It will be re-enabled during the next web request. CancelButton->IsEnabled = false; // Initiate cancellation. m_cancelHttpRequestSource.cancel(); }Совет
Если приложению не требуется поддержка отмены, передайте параллелизм::cancellation_token::none в
HttpRequest::GetAsyncметоды иHttpRequest::PostAsyncметоды.В MainPage.xaml.cpp реализуйте метод
MainPage::ProcessHttpRequest.// Displays the result of the provided HTTP request on the UI. void MainPage::ProcessHttpRequest(task<wstring> httpRequest) { // Enable only the Cancel button. GetButton->IsEnabled = false; PostButton->IsEnabled = false; CancelButton->IsEnabled = true; // Clear the previous response and start the progress ring. ResponseTextBlock->Text = ""; ResponseProgressRing->IsActive = true; // Create a continuation that shows the results on the UI. // The UI must be updated on the ASTA thread. // Therefore, schedule the continuation to run on the current context. httpRequest.then([this](task<wstring> previousTask) { try { // // Show the result on the UI. wstring response = previousTask.get(); if (m_httpRequest.GetStatusCode() == 200) { // The request succeeded. Show the response. ResponseTextBlock->Text = ref new String(response.c_str()); } else { // The request failed. Show the status code and reason. wstringstream ss; ss << L"The server returned " << m_httpRequest.GetStatusCode() << L" (" << m_httpRequest.GetReasonPhrase() << L')'; ResponseTextBlock->Text = ref new String(ss.str().c_str()); } } catch (const task_canceled&) { // Indicate that the operation was canceled. ResponseTextBlock->Text = "The operation was canceled"; } catch (Exception^ e) { // Indicate that the operation failed. ResponseTextBlock->Text = "The operation failed"; // TODO: Handle the error further. (void)e; } // Enable the Get and Post buttons. GetButton->IsEnabled = true; PostButton->IsEnabled = true; CancelButton->IsEnabled = false; // Stop the progress ring. ResponseProgressRing->IsActive = false; }, task_continuation_context::use_current()); }В свойствах проекта в разделе Компоновщик, Входные данные, укажите
shcore.libиmsxml6.lib.
Здесь приводится работающее приложение:
Дальнейшие шаги
Пошаговые руководства по среде выполнения с параллелизмом
См. также
Параллелизм задач
Отмена в библиотеке параллельных шаблонов
Асинхронное программирование на языке C++
Создание асинхронных операций на C++ для приложений UWP
Краткое руководство. Подключение с помощью HTTP-запроса XML (IXMLHTTPRequest2)класса задач (среда выполнения параллелизма)
Класс task_completion_event