Примітка
Доступ до цієї сторінки вимагає авторизації. Ви можете спробувати увійти в систему або змінити каталоги.
Доступ до цієї сторінки вимагає авторизації. Ви можете спробувати змінити каталоги.
Azure Blob Storage supports optional anonymous read access to containers and blobs. However, anonymous access may present a security risk. We recommend that you disable anonymous access for optimal security. Disallowing anonymous access helps to prevent data breaches caused by undesired anonymous access.
By default, anonymous access to your blob data is always prohibited. The default configuration for an Azure Resource Manager storage account prohibits users from configuring anonymous access to containers and blobs in a storage account. This default configuration disallows all anonymous access to an Azure Resource Manager storage account, regardless of the access setting for an individual container.
When anonymous access for the storage account is disallowed, Azure Storage rejects all anonymous read requests against blob data. Users can't later configure anonymous access for containers in that account. Any containers that have already been configured for anonymous access will no longer accept anonymous requests.
Warning
When a container is configured for anonymous access, any client can read data in that container. Anonymous access presents a potential security risk, so if your scenario does not require it, we recommend that you disallow it for the storage account.
Remediation for Azure Resource Manager versus classic storage accounts
This article describes how to use a DRAG (Detection-Remediation-Audit-Governance) framework to continuously manage anonymous access for storage accounts that are using the Azure Resource Manager deployment model. All general-purpose v2 storage accounts, premium block blob storage accounts, premium file share accounts, and Blob Storage accounts use the Azure Resource Manager deployment model.
If your storage account is using the classic deployment model, we recommend that you migrate to the Azure Resource Manager deployment model. Azure Storage accounts that use the classic deployment model were retired on August 31, 2024. For more information, see Update on classic storage account retirement.
About anonymous read access
Anonymous access to your data is always prohibited by default. There are two separate settings that affect anonymous access:
Anonymous access setting for the storage account. An Azure Resource Manager storage account offers a setting to allow or disallow anonymous access for the account. Microsoft recommends disallowing anonymous access for your storage accounts for optimal security.
When anonymous access is permitted at the account level, blob data isn't available for anonymous read access unless the user takes the additional step to explicitly configure the container's anonymous access setting.
Configure the container's anonymous access setting. By default, a container's anonymous access setting is disabled, meaning that authorization is required for every request to the container or its data. A user with the appropriate permissions can modify a container's anonymous access setting to enable anonymous access only if anonymous access is allowed for the storage account.
The following table summarizes how the two settings together affect anonymous access for a container.
| Anonymous access level for the container is set to Private (default setting) | Anonymous access level for the container is set to Container | Anonymous access level for the container is set to Blob | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anonymous access is disallowed for the storage account | No anonymous access to any container in the storage account. | No anonymous access to any container in the storage account. The storage account setting overrides the container setting. | No anonymous access to any container in the storage account. The storage account setting overrides the container setting. |
| Anonymous access is allowed for the storage account | No anonymous access to this container (default configuration). | Anonymous access is permitted to this container and its blobs. | Anonymous access is permitted to blobs in this container, but not to the container itself. |
When anonymous access is permitted for a storage account and configured for a specific container, then a request to read a blob in that container that is passed without an Authorization header is accepted by the service, and the blob's data is returned in the response. However, if the request is passed with an Authorization header, then anonymous access on the storage account is ignored, and the request is authorized based on the provided credentials.
Detect anonymous requests from client applications
When you disallow anonymous read access for a storage account, you risk rejecting requests to containers and blobs that are currently configured for anonymous access. Disallowing anonymous access for a storage account overrides the access settings for individual containers in that storage account. When anonymous access is disallowed for the storage account, any future anonymous requests to that account will fail.
To understand how disallowing anonymous access may affect client applications, we recommend that you enable logging and metrics for that account and analyze patterns of anonymous requests over an interval of time. Use metrics to determine the number of anonymous requests to the storage account, and use logs to determine which containers are being accessed anonymously.
Monitor anonymous requests with Metrics Explorer
To track anonymous requests to a storage account, use Azure Metrics Explorer in the Azure portal. For more information about Metrics Explorer, see Analyze metrics with Azure Monitor metrics explorer.
Follow these steps to create a metric that tracks anonymous requests:
Navigate to your storage account in the Azure portal. Under the Monitoring section, select Metrics.
Select Add metric. In the Metric dialog, specify the following values:
- Leave the Scope field set to the name of the storage account.
- Set the Metric Namespace to Blob. This metric reports requests against Blob storage only.
- Set the Metric field to Transactions.
- Set the Aggregation field to Sum.
The new metric displays the sum of the number of transactions against Blob storage over a given interval of time. The resulting metric appears as shown in the following image:

Next, select the Add filter button to create a filter on the metric for anonymous requests.
In the Filter dialog, specify the following values:
- Set the Property value to Authentication.
- Set the Operator field to the equal sign (=).
- Set the Values field to Anonymous by selecting it from the dropdown or typing it in.
In the upper-right corner, select the time interval over which you want to view the metric. You can also indicate how granular the aggregation of requests should be, by specifying intervals anywhere from 1 minute to 1 month.
After you have configured the metric, anonymous requests will begin to appear on the graph. The following image shows anonymous requests aggregated over the past 30 minutes.
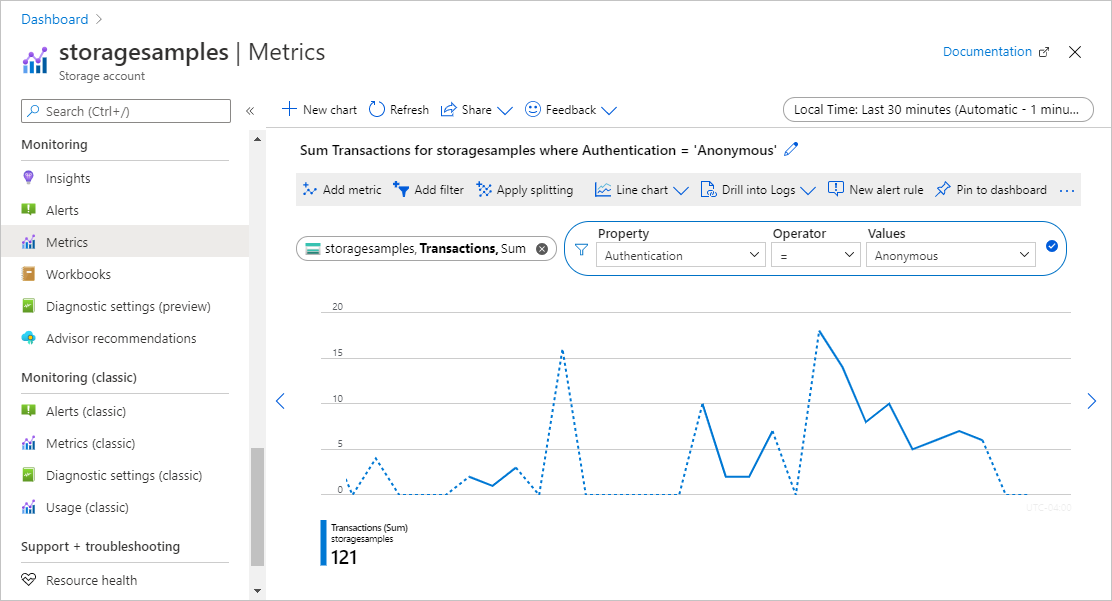
You can also configure an alert rule to notify you when a certain number of anonymous requests are made against your storage account. For more information, see Create, view, and manage metric alerts using Azure Monitor.
Analyze logs to identify containers receiving anonymous requests
Azure Storage logs capture details about requests made against the storage account, including how a request was authorized. You can analyze the logs to determine which containers are receiving anonymous requests.
To log requests to your Azure Storage account in order to evaluate anonymous requests, you can use Azure Storage logging in Azure Monitor. For more information, see Monitor Azure Storage.
Azure Storage logging in Azure Monitor supports using log queries to analyze log data. To query logs, you can use an Azure Log Analytics workspace. To learn more about log queries, see Tutorial: Get started with Log Analytics queries.
Create a diagnostic setting in the Azure portal
To log Azure Storage data with Azure Monitor and analyze it with Azure Log Analytics, you must first create a diagnostic setting that indicates what types of requests and for which storage services you want to log data. After you configure logging for your storage account, the logs are available in the Log Analytics workspace. To create a workspace, see Create a Log Analytics workspace in the Azure portal.
To learn how to create a diagnostic setting in the Azure portal, see Create diagnostic settings in Azure Monitor.
For a reference of fields available in Azure Storage logs in Azure Monitor, see Resource logs.
Query logs for anonymous requests
Azure Storage logs in Azure Monitor include the type of authorization that was used to make a request to a storage account. In your log query, filter on the AuthenticationType property to view anonymous requests.
To retrieve logs for the last seven days for anonymous requests against Blob storage, open your Log Analytics workspace. Next, paste the following query into a new log query and run it:
StorageBlobLogs
| where TimeGenerated > ago(7d) and AuthenticationType == "Anonymous"
| project TimeGenerated, AccountName, AuthenticationType, Uri
You can also configure an alert rule based on this query to notify you about anonymous requests. For more information, see Create, view, and manage log alerts using Azure Monitor.
Responses to anonymous requests
When Blob Storage receives an anonymous request, that request will succeed if all of the following conditions are true:
- Anonymous access is allowed for the storage account.
- The targeted container is configured to allow anonymous access.
- The request is for read access.
If any of those conditions aren't true, the request fails. The response code on failure depends on whether the anonymous request was made with a version of the service that supports the bearer challenge. The bearer challenge is supported with service versions 2019-12-12 and newer:
- If the anonymous request was made with a service version that supports the bearer challenge, then the service returns error code 401 (Unauthorized).
- If the anonymous request was made with a service version that doesn't support the bearer challenge and anonymous access is disallowed for the storage account, then the service returns error code 409 (Conflict).
- If the anonymous request was made with a service version that does not support the bearer challenge and anonymous access is allowed for the storage account, then the service returns error code 404 (Not Found).
For more information about the bearer challenge, see Bearer challenge.
Remediate anonymous access for the storage account
After you evaluate anonymous requests to containers and blobs in your storage account, you can take action to remediate anonymous access for the whole account by setting the account's AllowBlobPublicAccess property to False.
The anonymous access setting for a storage account overrides the individual settings for containers in that account. When you disallow anonymous access for a storage account, any containers that are configured to permit anonymous access are no longer accessible anonymously. If you disallow anonymous access for the account, you don't also need to disable anonymous access for individual containers.
If your scenario requires that certain containers need to be available for anonymous access, then you should move those containers and their blobs into separate storage accounts that are reserved for anonymous access. You can then disallow anonymous access for any other storage accounts.
Remediating anonymous access requires version 2019-04-01 or later of the Azure Storage resource provider. For more information, see Azure Storage Resource Provider REST API.
Permissions for disallowing anonymous access
To set the AllowBlobPublicAccess property for the storage account, a user must have permissions to create and manage storage accounts. Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) roles that provide these permissions include the Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/write action. Built-in roles with this action include:
- The Azure Resource Manager Owner role
- The Azure Resource Manager Contributor role
- The Storage Account Contributor role
Role assignments must be scoped to the level of the storage account or higher to permit a user to disallow anonymous access for the storage account. For more information about role scope, see Understand scope for Azure RBAC.
Be careful to restrict assignment of these roles only to those administrative users who require the ability to create a storage account or update its properties. Use the principle of least privilege to ensure that users have the fewest permissions that they need to accomplish their tasks. For more information about managing access with Azure RBAC, see Best practices for Azure RBAC.
These roles don't provide access to data in a storage account via Microsoft Entra ID. However, they include the Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listkeys/action, which grants access to the account access keys. With this permission, a user can use the account access keys to access all data in a storage account.
The Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listkeys/action itself grants data access via the account keys, but doesn't grant a user the ability to change the AllowBlobPublicAccess property for a storage account. For users who need to access data in your storage account but shouldn't have the ability to change the storage account's configuration, consider assigning roles such as Storage Blob Data Contributor, Storage Blob Data Reader, or Reader and Data Access.
Note
The classic subscription administrator roles Service Administrator and Co-Administrator include the equivalent of the Azure Resource Manager Owner role. The Owner role includes all actions, so a user with one of these administrative roles can also create storage accounts and manage account configuration. For more information, see Azure roles, Microsoft Entra roles, and classic subscription administrator roles.
Set the storage account's AllowBlobPublicAccess property to False
To disallow anonymous access for a storage account, set the account's AllowBlobPublicAccess property to False.
Important
Disallowing anonymous access for a storage account overrides the access settings for all containers in that storage account. When anonymous access is disallowed for the storage account, any future anonymous requests to that account will fail. Before changing this setting, be sure to understand the impact on client applications that may be accessing data in your storage account anonymously by following the steps outlined in Detect anonymous requests from client applications.
To disallow anonymous access for a storage account in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Navigate to your storage account in the Azure portal.
Locate the Configuration setting under Settings.
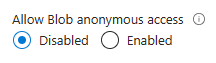
Set Allow Blob anonymous access to Disabled.
Note
Disallowing anonymous access for a storage account does not affect any static websites hosted in that storage account. The $web container is always publicly accessible.
After you update the anonymous access setting for the storage account, it may take up to 30 seconds before the change is fully propagated.
Sample script for bulk remediation
The following sample PowerShell script runs against all Azure Resource Manager storage accounts in a subscription and sets the AllowBlobPublicAccess setting for those accounts to False.
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Finds storage accounts in a subscription where AllowBlobPublicAccess is True or null.
.DESCRIPTION
This script runs against all Azure Resource Manager storage accounts in a subscription
and sets the "AllowBlobPublicAccess" property to False.
Standard operation will enumerate all accounts where the setting is enabled and allow the
user to decide whether or not to disable the setting.
Classic storage accounts will require individual adjustment of containers to remove public
access, and will not be affected by this script.
Run with BypassConfirmation=$true if you wish to disallow public access on all Azure Resource Manager
storage accounts without individual confirmation.
You will need access to the subscription to run the script.
.PARAMETER BypassConformation
Set this to $true to skip confirmation of changes. Not recommended.
.PARAMETER SubscriptionId
The subscription ID of the subscription to check.
.PARAMETER ReadOnly
Set this parameter so that the script makes no changes to any subscriptions and only reports affect accounts.
.PARAMETER NoSignin
Set this parameter so that no sign-in occurs -- you must sign in first. Use this if you're invoking this script repeatedly for multiple subscriptions and want to avoid being prompted to sign-in for each subscription.
.OUTPUTS
This command produces only STDOUT output (not standard PowerShell) with information about affect accounts.
#>
param(
[boolean]$BypassConfirmation = $false,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName = 'SubscriptionId')]
[String] $SubscriptionId,
[switch] $ReadOnly, # Use this if you don't want to make changes, but want to get information about affected accounts
[switch] $NoSignin # Use this if you are already signed in and don't want to be prompted again
)
begin {
if ( ! $NoSignin.IsPresent ) {
Login-AzAccount | Out-Null
}
}
process {
try {
Select-AzSubscription -SubscriptionId $SubscriptionId -ErrorAction Stop | Out-Null
}
catch {
Write-Error "Unable to access select subscription '$SubscriptionId' as the signed in user -- ensure that you have access to this subscription." -ErrorAction Stop
}
foreach ($account in Get-AzStorageAccount) {
if ($null -eq $account.AllowBlobPublicAccess -or $account.AllowBlobPublicAccess -eq $true) {
Write-host "Account:" $account.StorageAccountName " isn't disallowing public access."
if ( ! $ReadOnly.IsPresent ) {
if (!$BypassConfirmation) {
$confirmation = Read-Host "Do you wish to disallow public access? [y/n]"
}
if ($BypassConfirmation -or $confirmation -eq 'y') {
try {
Set-AzStorageAccount -Name $account.StorageAccountName -ResourceGroupName $account.ResourceGroupName -AllowBlobPublicAccess $false
Write-Host "Success!"
}
catch {
Write-Output $_
}
}
}
}
elseif ($account.AllowBlobPublicAccess -eq $false) {
Write-Host "Account:" $account.StorageAccountName "has public access disabled, no action required."
}
else {
Write-Host "Account:" $account.StorageAccountName ". Error, please manually investigate."
}
}
}
end {
Write-Host "Script complete"
}
Check the anonymous access setting for multiple accounts
To check the anonymous access setting across a set of storage accounts with optimal performance, you can use the Azure Resource Graph Explorer in the Azure portal. To learn more about using the Resource Graph Explorer, see Quickstart: Run your first Resource Graph query using Azure Resource Graph Explorer.
Running the following query in the Resource Graph Explorer returns a list of storage accounts and displays anonymous access setting for each account:
resources
| where type =~ 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts'
| extend allowBlobPublicAccess = parse_json(properties).allowBlobPublicAccess
| project subscriptionId, resourceGroup, name, allowBlobPublicAccess
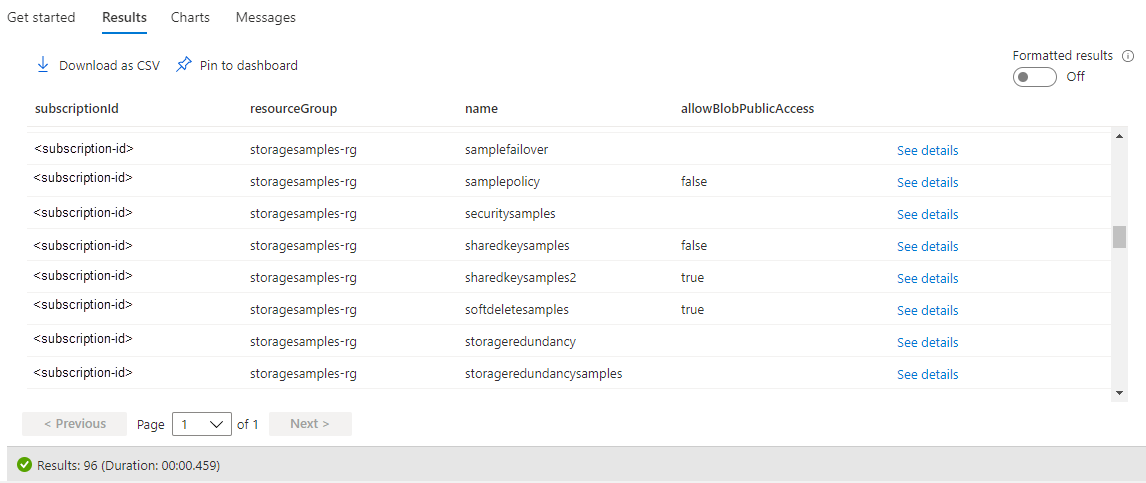
The following image shows the results of a query across a subscription. For storage accounts where the AllowBlobPublicAccess property is explicitly set, it appears in the results as true or false. If the AllowBlobPublicAccess property isn't set for a storage account, it appears as blank (or null) in the query results.
Use Azure Policy to audit for compliance
If you have a large number of storage accounts, you might want to perform an audit to make sure that those accounts are configured to prevent anonymous access. To audit a set of storage accounts for their compliance, use Azure Policy. Azure Policy is a service that you can use to create, assign, and manage policies that apply rules to Azure resources. Azure Policy helps you to keep those resources compliant with your corporate standards and service level agreements. For more information, see Overview of Azure Policy.
Create a policy with an Audit effect
Azure Policy supports effects that determine what happens when a policy rule is evaluated against a resource. The Audit effect creates a warning when a resource isn't in compliance, but doesn't stop the request. For more information about effects, see Understand Azure Policy effects.
To create a policy with an Audit effect for the anonymous access setting for a storage account with the Azure portal, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, navigate to the Azure Policy service.
Under the Authoring section, select Definitions.
Select Add policy definition to create a new policy definition.
For the Definition location field, select the More button to specify where the audit policy resource is located.
Specify a name for the policy. You can optionally specify a description and category.
Under Policy rule, add the following policy definition to the policyRule section.
{ "if": { "allOf": [ { "field": "type", "equals": "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts" }, { "not": { "field":"Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/allowBlobPublicAccess", "equals": "false" } } ] }, "then": { "effect": "audit" } }Save the policy.
Assign the policy
Next, assign the policy to a resource. The scope of the policy corresponds to that resource and any resources beneath it. For more information on policy assignment, see Azure Policy assignment structure.
To assign the policy with the Azure portal, follow these steps:
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the Azure Policy service.
- Under the Authoring section, select Assignments.
- Select Assign policy to create a new policy assignment.
- For the Scope field, select the scope of the policy assignment.
- For the Policy definition field, select the More button, then select the policy you defined in the previous section from the list.
- Provide a name for the policy assignment. The description is optional.
- Leave Policy enforcement set to Enabled. This setting has no effect on the audit policy.
- Select Review + create to create the assignment.
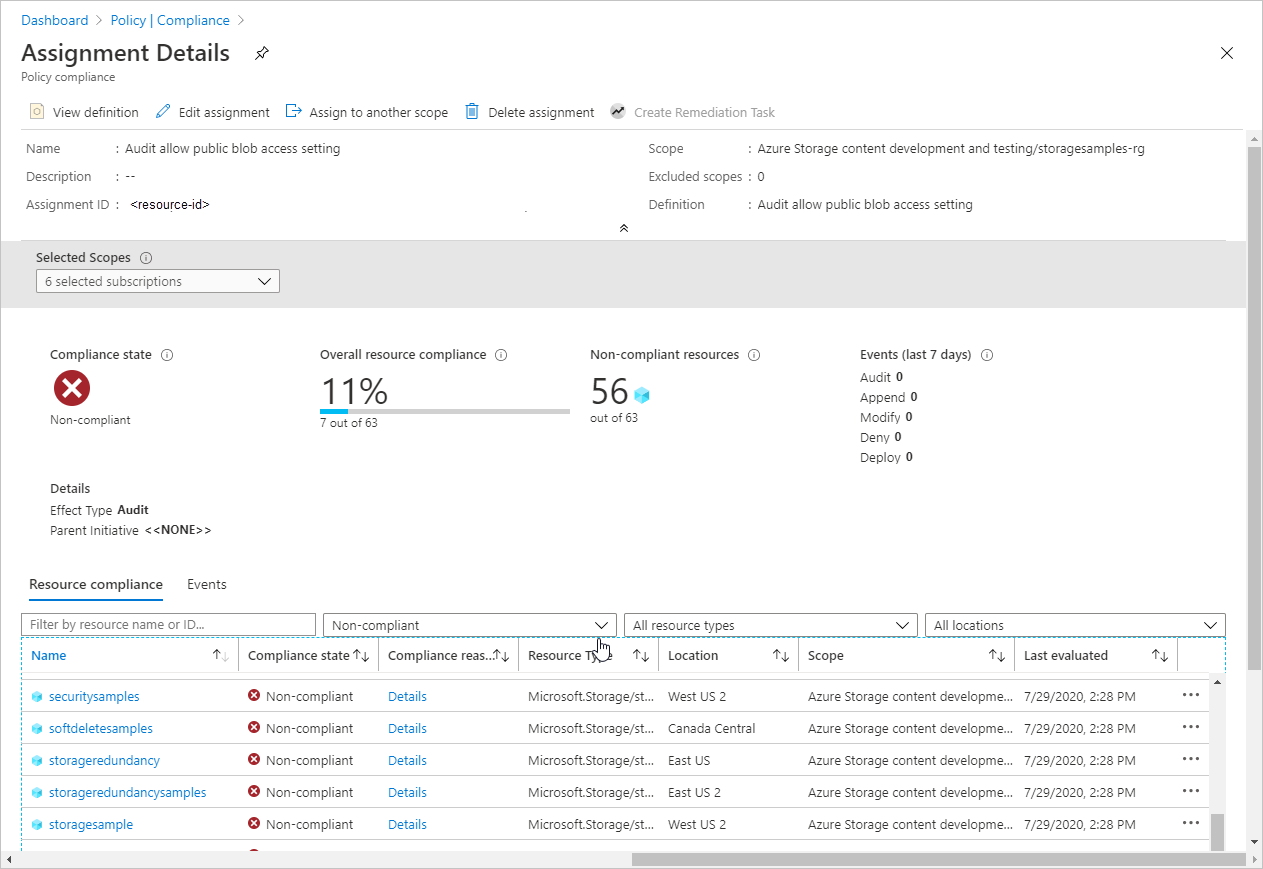
View compliance report
After you've assigned the policy, you can view the compliance report. The compliance report for an audit policy provides information on which storage accounts aren't in compliance with the policy. For more information, see Get policy compliance data.
It may take several minutes for the compliance report to become available after the policy assignment is created.
To view the compliance report in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, navigate to the Azure Policy service.
Select Compliance.
Filter the results for the name of the policy assignment that you created in the previous step. The report shows how many resources aren't in compliance with the policy.
You can drill down into the report for additional details, including a list of storage accounts that aren't in compliance.
Use Azure Policy to enforce authorized access
Azure Policy supports cloud governance by ensuring that Azure resources adhere to requirements and standards. To ensure that storage accounts in your organization permit only authorized requests, you can create a policy that prevents the creation of a new storage account with an anonymous access setting that allows anonymous requests. This policy will also prevent all configuration changes to an existing account if the anonymous access setting for that account isn't compliant with the policy.
The enforcement policy uses the Deny effect to prevent a request that would create or modify a storage account to allow anonymous access. For more information about effects, see Understand Azure Policy effects.
To create a policy with a Deny effect for an anonymous access setting that allows anonymous requests, follow the same steps described in Use Azure Policy to audit for compliance, but provide the following JSON in the policyRule section of the policy definition:
{
"if": {
"allOf": [
{
"field": "type",
"equals": "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts"
},
{
"not": {
"field":"Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/allowBlobPublicAccess",
"equals": "false"
}
}
]
},
"then": {
"effect": "deny"
}
}
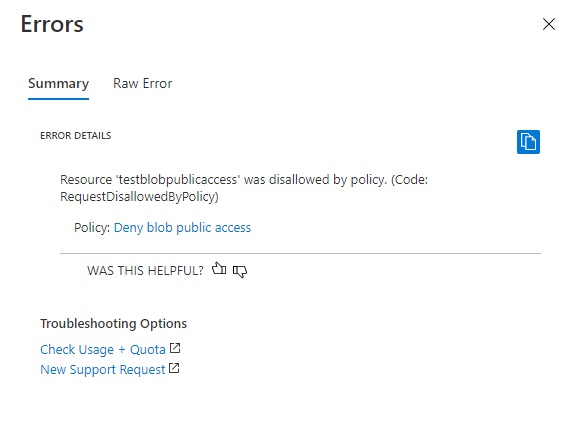
After you create the policy with the Deny effect and assign it to a scope, a user can't create a storage account that allows anonymous access. Nor can a user make any configuration changes to an existing storage account that currently allows anonymous access. Attempting to do so results in an error. The anonymous access setting for the storage account must be set to false to proceed with account creation or configuration.
The following image shows the error that occurs if you try to create a storage account that allows anonymous access when a policy with a Deny effect requires that anonymous access is disallowed.