Virtual network peering
Virtual network peering enables you to seamlessly connect two or more Virtual Networks in Azure. The virtual networks appear as one for connectivity purposes. The traffic between virtual machines in peered virtual networks uses the Microsoft backbone infrastructure. Like traffic between virtual machines in the same network, traffic is routed through Microsoft's private network only.
Azure supports the following types of peering:
Virtual network peering: Connecting virtual networks within the same Azure region.
Global virtual network peering: Connecting virtual networks across Azure regions.
The benefits of using virtual network peering, whether local or global, include:
A low-latency, high-bandwidth connection between resources in different virtual networks.
The ability for resources in one virtual network to communicate with resources in a different virtual network.
The ability to transfer data between virtual networks across Azure subscriptions, Microsoft Entra tenants, deployment models, and Azure regions.
The ability to peer virtual networks created through the Azure Resource Manager.
The ability to peer a virtual network created through Resource Manager to one created through the classic deployment model. To learn more about Azure deployment models, see Understand Azure deployment models.
No downtime to resources in either virtual network when creating the peering, or after the peering is created.
Network traffic between peered virtual networks is private. Traffic between the virtual networks is kept on the Microsoft backbone network. No public Internet, gateways, or encryption is required in the communication between the virtual networks.
Connectivity
For peered virtual networks, resources in either virtual network can directly connect with resources in the peered virtual network.
The network latency between virtual machines in peered virtual networks in the same region is the same as the latency within a single virtual network. The network throughput is based on the bandwidth that's allowed for the virtual machine, proportionate to its size. There isn't any extra restriction on bandwidth within the peering.
The traffic between virtual machines in peered virtual networks is routed directly through the Microsoft backbone infrastructure, not through a gateway or over the public Internet.
You can apply network security groups in either virtual network to block access to other virtual networks or subnets. When you configure virtual network peering, either open or close the network security group rules between the virtual networks. If you open full connectivity between peered virtual networks, you can apply network security groups to block or deny specific access. Full connectivity is the default option. To learn more about network security groups, see Security groups.
Resize the address space of Azure virtual networks that are peered
You can resize the address space of Azure virtual networks that are peered without incurring any downtime on the currently peered address space. This feature is useful when you need to resize the virtual network's address space after scaling your workloads. Once the address space is resized, peers must sync with the new address space changes. Resizing works for both IPv4 and IPv6 address spaces.
Addresses can be resized in the following ways:
Modifying the address range prefix of an existing address range (For example changing 10.1.0.0/16 to 10.1.0.0/18)
Adding address ranges to a virtual network
Deleting address ranges from a virtual network
Resizing of address space is supported cross-tenant
Syncing of virtual network peers can be performed through the Azure portal or with Azure PowerShell. We recommend that you run sync after every resize address space operation instead of performing multiple resizing operations and then running the sync operation. To learn how to update the address space for a peered virtual network, see Updating the address space for a peered virtual network.
Important
This feature doesn't support scenarios where the virtual network to be updated is peered with:
- A classic virtual network
Service chaining
Service chaining enables you to direct traffic from one virtual network to a virtual appliance or gateway in a peered network through user-defined routes.
To enable service chaining, configure user-defined routes that point to virtual machines in peered virtual networks as the next hop IP address. User-defined routes could also point to virtual network gateways to enable service chaining.
You can deploy hub-and-spoke networks, where the hub virtual network hosts infrastructure components such as a network virtual appliance or VPN gateway. All the spoke virtual networks can then peer with the hub virtual network. Traffic flows through network virtual appliances or VPN gateways in the hub virtual network.
Virtual network peering enables the next hop in a user-defined route to be the IP address of a virtual machine in the peered virtual network, or a VPN gateway. You can't route between virtual networks with a user-defined route that specifies an Azure ExpressRoute gateway as the next hop type. To learn more about user-defined routes, see User-defined routes overview. To learn how to create a hub and spoke network topology, see Hub-spoke network topology in Azure.
Gateways and on-premises connectivity
Each virtual network, including a peered virtual network, can have its own gateway. A virtual network can use its gateway to connect to an on-premises network. You can also configure virtual network-to-virtual network connections by using gateways, even for peered virtual networks.
When you configure both options for virtual network interconnectivity, the traffic between the virtual networks flows through the peering configuration. The traffic uses the Azure backbone.
You can also configure the gateway in the peered virtual network as a transit point to an on-premises network. In this case, the virtual network that is using a remote gateway can't have its own gateway. A virtual network could have only one gateway, the gateway should be either local or remote gateway in the peered virtual network as shown in the following diagram:
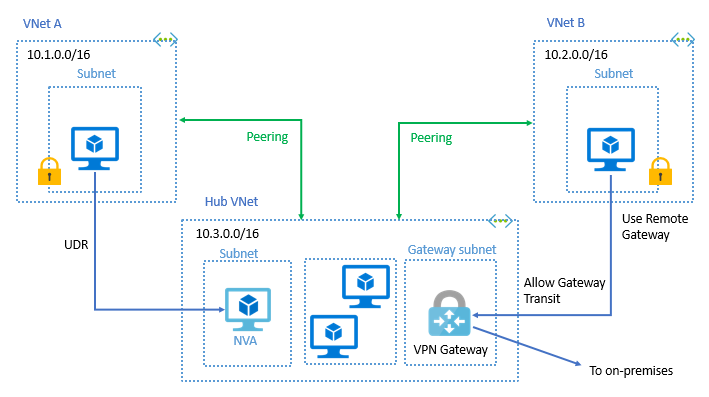
Both virtual network peering and global virtual network peering support gateway transit.
Gateway transit between virtual networks created through different deployment models is supported. The gateway must be in the virtual network in the Resource Manager model. To learn more about using a gateway for transit, see Configure a VPN gateway for transit in a virtual network peering.
When you peer virtual networks that share a single Azure ExpressRoute connection, the traffic between them goes through the peering relationship. That traffic uses the Azure backbone network. You can still use local gateways in each virtual network to connect to the on-premises circuit. Otherwise, you can use a shared gateway and configure transit for on-premises connectivity.
Troubleshoot
To confirm that virtual networks are peered, you can check effective routes. Check routes for a network interface in any subnet in a virtual network. If a virtual network peering exists, all subnets within the virtual network have routes with next hop type VNet peering, for each address space in each peered virtual network. For more information, see Diagnose a virtual machine routing problem.
You can also troubleshoot connectivity to a virtual machine in a peered virtual network using Azure Network Watcher. A connectivity check lets you see how traffic is routed from a source virtual machine's network interface to a destination virtual machine's network interface. For more information, see Troubleshoot connections with Azure Network Watcher using the Azure portal.
You can also try the Troubleshoot virtual network peering issues.
Constraints for peered virtual networks
The following constraints apply only when virtual networks are globally peered:
Resources in one virtual network can't communicate with the front-end IP address of a basic load balancer (internal or public) in a globally peered virtual network.
Some services that use a basic load balancer don't work over global virtual network peering. For more information, see What are the constraints related to Global VNet Peering and Load Balancers?.
You can't perform virtual network peerings as part of the PUT virtual network operation.
For more information, see Requirements and constraints. To learn more about the supported number of peerings, see Networking limits.
Permissions
To learn about permissions required to create a virtual network peering, see Permissions.
Pricing
There's a nominal charge for ingress and egress traffic that uses a virtual network peering connection. For more information, see Virtual Network pricing.
Gateway Transit is a peering property that enables a virtual network to utilize a VPN/ExpressRoute gateway in a peered virtual network. Gateway transit works for both cross premises and network-to-network connectivity. Traffic to the gateway (ingress or egress) in the peered virtual network incurs virtual network peering charges on the spoke virtual network (or virtual network without a VPN gateway). For more information, see VPN Gateway pricing for VPN gateway charges and ExpressRoute Gateway pricing for ExpressRoute gateway charges.
Note
A previous version of this document stated that virtual network peering charges would not apply on the spoke VNet (or non-gateway VNet) with Gateway Transit. It now reflects accurate pricing per the pricing page.
Next steps
You can create a peering between two virtual networks. The networks can belong to the same subscription, different deployment models in the same subscription, or different subscriptions. Complete a tutorial for one of the following scenarios:
Azure deployment model Subscription Both Resource Manager Same Different One Resource Manager, one classic Same Different To learn how to create a hub and spoke network topology, see Hub-spoke network topology in Azure.
To learn about all virtual network peering settings, see Create, change, or delete a virtual network peering.
For answers to common virtual network peering and global virtual network peering questions, see VNet Peering.