Windows Admin Center known issues
Applies to: Windows Admin Center, Windows Admin Center Preview
If you encounter an issue not described on this page, let us know at the Windows Admin Center feedback page.
Installer
When you install Windows Admin Center using your own certificate, if you copy the thumbprint from the certificate manager Microsoft Management Center (MMC) tool, when you paste it, it contains an invalid character at the beginning. As a workaround, enter the first character of the thumbprint, then copy and paste the characters that come after the first.
Windows Admin Center doesn't support ports lower than 1024. In service mode, you can optionally configure port 80 to redirect to your specified port.
General
Self-signed certificates accessed on
https://localhost:[port]can cause the Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome browsers to block Windows Admin Center. When you're blocked, you should see an error message that says your connection isn't private. To resolve this issue, update Windows Admin Center to the latest version.Using certain versions of extensions with earlier versions of Windows Admin Center can result in icons not displaying properly. To resolve this issue, update to the latest version of Windows Admin Center
Manually modifying URLs to include the names of different machines while using Windows Admin Center without going through the connection experience in the UI can cause extensions to not load properly, especially extensions compatible with specific hardware. We don't recommend manually modifying URLs for navigation in Windows Admin Center.
If you have Windows Admin Center installed as a heavily used gateway on Windows Server 2016, the service can crash and display an error in the event log that contains
Faulting application name: sme.exeandFaulting module name: WsmSvc.dll. This error happens because of a bug that we've fixed as of Windows Server 2019. However, we've also released a patch for Windows Server 2016 to address this issue in the February 2019 cumulative update, KB4480977.If you have Windows Admin Center installed as a gateway and your connection list appears to be corrupted, follow these steps:
Warning
The procedure in these instructions deletes the connection list and settings for all Windows Admin Center users on the gateway.
Uninstall Windows Admin Center.
Go to C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\NetworkService\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft and delete the Server Management Experience folder.
Reinstall Windows Admin Center.
If you leave the tool open and idle for a long period of time, several error messages appear that say "The runspace state is not valid for this operation." If this issue occurs, refresh your browser. If you encounter this error, send us feedback.
There can be minor differences between version numbers of open-source software (OSS) running in Windows Admin Center modules versus what's listed in the third Party Software Notice.
You can access and use Windows Admin Center tool application programming interfaces (APIs) through other methods during an active session of Windows Admin Center if you have access to that session. The actions you take using these APIs only affect the machine you installed Windows Admin Center on, also known as the gateway machine. They don't affect machines managed remotely without authentication through the Windows Admin Center gateway.
Some APIs used by Windows Admin Center, including the DeploymentShare API, require the user to be a local administrator. Network share creation operations cannot be performed by a standard Windows user by default. Windows Admin Center cannot elevate a standard user account to administrator. Adding the user to the "Gateway administrators" group in Settings only changes the permissions the user has within the gateway, not on the system.
- You may not run into this issue on modernized gateway builds of Windows Admin Center. By default, modernized gateway builds utilize a form login to access the gateway, which does not have the local administrator restriction. Existing versions of Windows Admin Center utilize NTLM/Kerberos, which obtains a token limited to the localhost environment. NTLM/Kerberos login is also available on modernized gateway builds.
Extension Manager
When you update Windows Admin Center, you must reinstall your extensions.
If you add an extension feed that is inaccessible, no warning or error message appears.
Partner extension issues
Dell's EMC OpenManage Integration extension utilizes APIs provided by Windows Admin Center to push files onto target nodes. APIs such as NodeExtensionInstall only work when the user is a gateway administrator; it doesn't support non-admin use.
Browser-specific issues
This section describes issues that can happen when you use Windows Admin Center in an internet browser.
Microsoft Edge
If you have Windows Admin Center deployed as a service and you're using Microsoft Edge as your browser, you might not be able to connect your gateway to Azure after opening a new browser window. There isn't currently a solution for this issue, but you can work around it by adding https://login.microsoftonline.com, https://login.live.com, and the URL of your gateway as trusted sites and allowed sites for pop-up blocker settings on your client-side browser.
For more information, see the troubleshooting guide.
Google Chrome
Before version 70, Chrome had a bug that affected the WebSockets protocol and Windows New Technology Local Area Network Manager (NTLM) authentication. This bug also affects the following programs:
Windows Events
PowerShell
Remote Desktop
Many credential prompts might appear while you're using Chrome, especially when you're adding connections in a workgroup environment.
If you have Windows Admin Center deployed as a service, you must enable popups from the gateway URL to use Azure integration.
Mozilla Firefox
Windows Admin Center isn't tested with Mozilla Firefox, but most functionality should work.
If you're using Windows 10, you need to import the Windows Admin Center Client certificate into Firefox to use Windows Admin Center.
WebSocket compatibility when using a proxy service
Scenarios involving using Windows Admin Center with a proxy service often don't support the WebSocket protocol, which can affect the following programs:
Remote Desktop
PowerShell
Packet Monitoring
Windows Events
Events
When you export large log files, you can sometimes receive an error message about packet size.
To resolve this issue:
Open an elevated command prompt on the gateway machine.
Run the following command:
winrm set winrm/config @{MaxEnvelopeSizekb="8192"}
Remote Desktop
When you deploy Windows Admin Center as a service, the Remote Desktop tool sometimes doesn't load after the Windows Admin Center service updates to a new version. To work around this issue, clear your browser cache.
The Remote Desktop tool sometimes doesn't connect when managing Windows Server 2012.
When using the Remote Desktop to connect to a machine that isn't Domain joined, you must enter your account in the
MACHINENAME\USERNAMEsyntax.Some configurations can block Windows Admin Center's remote desktop client with group policy. If you're blocked by this issue, open the Local Group Policy Editor and reconfigure the Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections Group Policy Object (GPO).
The Remote Desktop tool doesn't currently support any text, image, or file copy and paste between the local desktop and the remote session.
You can copy text the same way you would during a local session by either right-clicking and selecting Copy or pressing the Ctrl+C keys, but you can only paste by right-clicking and selecting Paste.
Remote sessions don't support the following keys and keyboard shortcuts:
Alt+Tab
Function keys
Windows Key
PrtScn
When using Remote Desktop to connect to a machine, keyboard language mapping may not work properly.
Support for Windows Server 2012 R2, 2012, and 2008 R2
Windows Admin Center requires PowerShell features that aren't included in Windows Server 2012 R2, 2012, or 2008 R2. If you plan to manage Windows Server with Windows Admin Center, you must install Windows Management Framework (WMF) version 5.1 or later on those servers.
To install WMF:
Open an elevated PowerShell window.
Enter
$PSVersiontableto verify if you have WMF installed and check the version number.Download and install WMF if you haven't already.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC can't deploy on machines configured to use Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC).
To use RBAC in a cluster, you must deploy the configuration to each member node individually.
When you deploy RBAC, you may get unauthorized errors incorrectly attributed to the RBAC configuration.
Server Manager solution
This section describes common issues you can run into in Server Manager on Windows Admin Center.
Certificates
Server Manager on Windows Admin Center doesn't currently support importing the .PFX Encrypted Certificate into the current user store.
Files
Windows Admin Center doesn't currently support uploading or downloading files over 100 MB in size.
PowerShell
The issue described in WebSocket compatibility when using a proxy service affects PowerShell.
PowerShell in Server Manager doesn't support pasting into the window by right-clicking. To paste into the window, you need to right-click and select Paste from the drop-down context menu or use the Ctrl+V shortcut.
PowerShell in Server Manager doesn't support the Ctrl+C shortcut to copy content to the clipboard. To copy content, highlight the text, right-click it, then select Copy.
When you make the Windows Admin Center window smaller, the terminal content adjusts to fit the new window size. When you return the window to its original size, the content might not return to its original state. You can restore the text by using the
Clear-Hostcommand, or disconnect and reconnect using the button above the terminal.
Registry Editor
Registry Editor for Windows Admin Center for Windows Server hasn't implemented search functionality.
Roles and Features
When you select roles or features that don't have available installation sources, the system skips them.
If you choose to not automatically restart after you install a role, you won't see any more notification messages asking you to restart.
If you do choose to automatically reboot, the reboot occurs before the status bar reaches 100%.
Storage
DVD, CD, and Floppy drives don't appear as volumes on down-level.
Some properties in Volumes and Disks appear as unknown or blank in the Details panel because they aren't available in down-level storage.
If you're creating a new Resilient File System (ReFS) volume, ReFS only supports an allocation unit size of 64K on Windows 2012 and 2012 R2 machines. If you create a ReFS volume with a smaller allocation unit size on down-level targets, file system formatting doesn't work, making the new volume unusable. To resolve this issue, delete the unusable volume, then create a new one with 64K allocation unit size.
Updates
After the system installs updates, it sometimes caches the install status and requires a browser refresh. If you see an error message that says "Keyset does not exist" when attempting to set up Azure Update management, follow these directions on the managed node:
Stop the Cryptographic Services service.
Change the folder options to show hidden files, if necessary.
Go to the %allusersprofile%\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\S-1-5-18 folder and delete all its contents.
Restart the Cryptographic Services service.
Reinstall Update Management with Windows Admin Center.
Virtual machines
If you're managing your virtual machines (VMs) on a Windows Server 2012 session host, the in-browser VMConnect tool can't connect to the VM. You can resolve this issue by downloading the .rdp file to connect to the VM.
If you've set up Azure Site Recovery on a host outside of Windows Admin Center, it can't protect VMs from inside Windows Admin Center.
Windows Admin Center doesn't currently support advanced features available in Hyper-V Manager, such as Virtual SAN Manager, Move VM, Export VM, and VM Replication.
Virtual switches
When you add network interface controllers (NICs) to a team for switch-embedded teaming (SET), you must make sure they're on the same subnet.
Computer Management solution
The Computer Management solution contains some Server Manager tools, so the same known issues that apply to Server Manager apply here. We're aware of the following Computer Management solution-specific issues:
If you sign in to your Windows 10 device with a Microsoft Account (MSA) or Microsoft Entra ID, you must use manage-as to provide credentials for a local administrator account.
When you try to manage the local host, a message appears telling you to elevate the gateway process. If you select No in the User Account Control window that appears, you must cancel the connection attempt and start over.
Windows 10 has WinRM and PowerShell remoting disabled by default.
To enable management of the Windows 10 Client, open an elevated PowerShell prompt and run the
Enable-PSRemotingcmdlet.You should also update your firewall to allow connections from outside the local subnet by running
Set-NetFirewallRule -Name WINRM-HTTP-In-TCP -RemoteAddress Any. For more information about how to update your firewall in more restrictive network scenarios, see Enable PSRemoting.
Cluster deployment
This section describes known issues that affect cluster deployment.
Adding servers to cluster groups
Windows Admin Center doesn't currently support scenarios with mixed work group machines when adding servers. All machines you add to cluster groups must be part of the same work group. If they aren't, an error message appears that says "Cannot create a cluster with servers in different Active Directory domains. Verify the server names are correct. Move all the servers into the same domain and try again." You can't proceed with setting up the cluster unless you use machines from the same work group.
Enabling Hyper-V on VMs
You can only install and enable Hyper-V on VMs running Azure Stack HCI. Trying to enable Hyper-V on VMs without Azure Stack HCI generates an error message that says "A prerequisite check for the Hyper-V feature failed," as shown in the following screenshot.

To install Hyper-V on VMs running Azure Stack HCI, open an elevated PowerShell prompt and run the following command:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName 'Microsoft-Hyper-V'
Server restart time after updates
At times, servers may take longer than anticipated to restart after installing updates. To determine if the server has restarted successfully, the Windows Admin Center cluster deployment wizard periodically checks the server's restart state. However, if the user manually restarts the server outside of the wizard, the wizard is unable to capture the server state in a suitable manner.
To work around this issue, close the cluster deployment wizard before manually restarting the server. Once you've restarted the server, you can open the cluster deployment wizard again.
Storage error after deleting a cluster
If you delete a cluster, you can encounter an error if you haven't cleared the storage pools from the deleted cluster. The deleted cluster object locks the storage pools, so you must manually clear the pools.
If you've already encountered this error message, here's how to clear the deleted cluster object from the storage pools:
Open an elevated PowerShell window.
On all nodes, run the following command:
Clear-ClusterNodeNext, remove all previous storage pools by running the following command:
Get-StoragePool -IsPrimordial 0 | Remove-StoragePoolIf you've configured the storage pools to be read-only, then you must change the storage pools to write mode before removing them by running the following command:
Get-StoragePool <PoolName> | Set-StoragePool -IsReadOnly $false
If you haven't encountered this error but want to avoid it, follow these instructions.
Open an elevated PowerShell window.
Run this command to remove the virtual disk:
Get-VirtualDisk | Remove-VirtualDiskNext, Run this command to remove the storage pools:
Get-StoragePool -IsPrimordial 0 | Remove-StoragePoolAfter that, run this command to remove resources associated with the cluster:
Get-ClusterResource | ? ResourceType -eq "virtual machine" | Remove-ClusterResource Get-ClusterResource | ? ResourceType -like "*virtual machine*" | Remove-ClusterResourceNow, run this command to clean up:
Remove-Cluster -CleanupADFinally, run this command on all nodes:
Clear-ClusterNode
Stretch cluster creation
We recommend you use domain-joined servers when you create a stretch cluster. Due to WinRM limitations, you can encounter a network segmentation issue when you try to use work group machines while deploying a stretch cluster.
Undo and start over
When you use the same machines repeatedly while deploying clusters, you need to regularly clean up that set of machines. For more information about how to run cleanup processes on your cluster, see Deploy hyperconverged infrastructure.
CredSSP in cluster creation
The Windows Admin Center cluster deployment wizard uses CredSSP. Sometimes, CredSSP can cause an error message that says "There was an error during the validation. Review error and try again" appear when you're validating a cluster, as shown in the following screenshot.
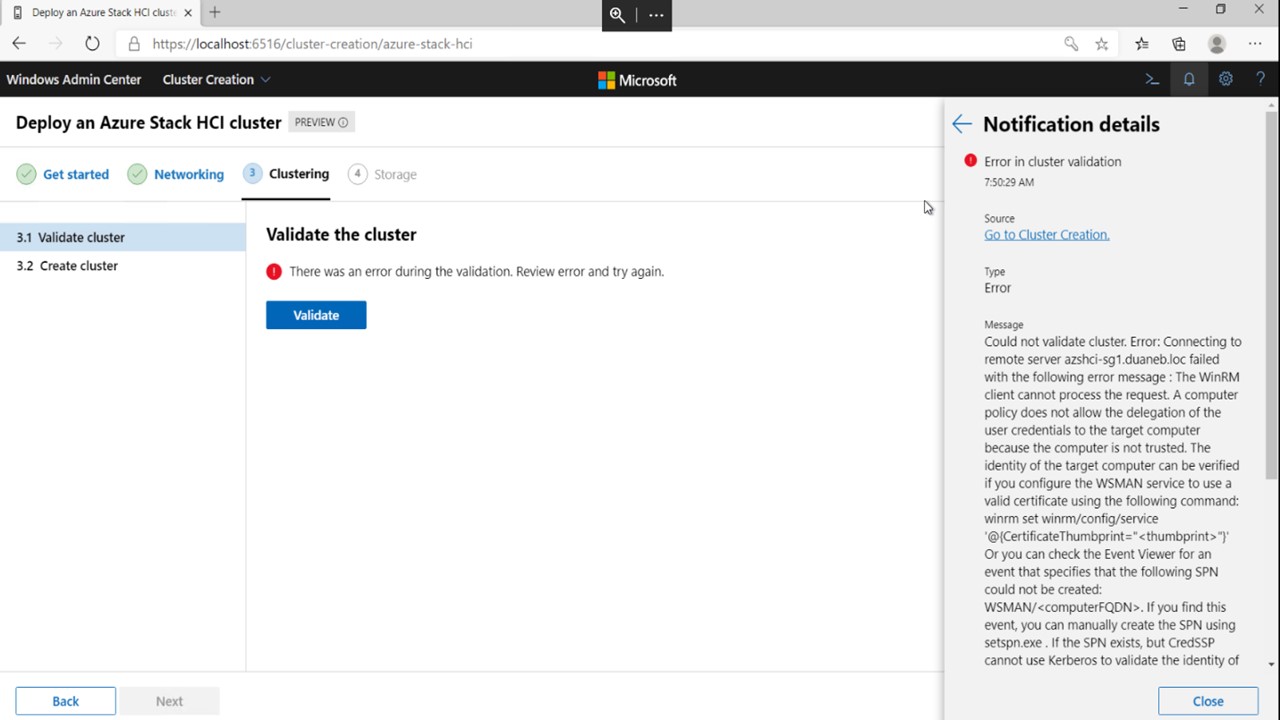
To resolve this issue:
Open an elevated PowerShell window.
Disable CredSSP settings on all nodes and the Windows Admin Center gateway machine.
Run this command on your gateway machine:
Disable-WSManCredSSP -Role ClientRun this command on all nodes in your cluster:
Disable-WSManCredSSP -Role Server
Run the following command on all nodes to repair their trusts.
Test-ComputerSecureChannel -Verbose -Repair -Credential <account name>Next, open a command prompt and run the following command on all nodes to reset group policy propagated data:
gpupdate /forceReboot each node.
After rebooting the nodes, open PowerShell again and run the following command to test the connectivity between your gateway machine and target nodes.
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <node fqdn>
CredSSP
When you use the Updates tool, you sometimes see an error message that says "You can't use Cluster-Aware updating tool without enabling CredSSP and providing explicit credentials" when you try to update new clusters, as shown in the following screenshot.

To resolve this issue, update Windows Admin Center to version 2110 or later.
The CredSSP session endpoint permission issue is a common CredSSP error that appears when Windows Admin Center is running on Windows client machines. To resolve this issue, you should add affected users to the Windows Admin Center CredSSP administrators group, then ask the user to sign back in to the desktop computer running Windows Admin Center.
Nested virtualization
When you're validating Azure Stack HCI cluster deployments on VMs, you must enable nested virtualization before you enable roles or features by running the following command in PowerShell:
Set-VMProcessor -VMName <VMName> -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions $true
If you're using virtual switch teaming in a VM environment, you also need to run this command on the session host after creating a VM:
Get-VM | %{ Set-VMNetworkAdapter -VMName $_.Name -MacAddressSpoofing On -AllowTeaming On }
If you're deploying a cluster using the Azure Stack HCI OS, there's an extra requirement. The VM boot virtual hard drive must be preinstalled with Hyper-V features. To preinstall these features, run the following command before creating the VMs:
Install-WindowsFeature –VHD <Path to the VHD> -Name Hyper-V, RSAT-Hyper-V-Tools, Hyper-V-PowerShell
Remote direct memory access support
The cluster deployment feature in Windows Admin Center 2007 doesn't support remote direct memory access (RDMA) configurations. To resolve this issue, update to a later version of Windows Admin Center.
Failover Cluster Manager solution
When managing a hyper-converged or traditional cluster, you can sometimes see an error message that says "Shell not found." You can do one of the following to resolve this issue:
- Reload your browser
- Go to another tool, then return to Failover Cluster Manager
You can sometimes encounter an issue when managing a down-level cluster with an incomplete configuration. To resolve this issue, make sure the cluster has the RSAT-Clustering-PowerShell feature installed and enabled on each member node. If not, open PowerShell and enter the following command on each cluster node:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name RSAT-Clustering-PowerShellIf Windows Admin Center can't discover the cluster, try adding it with the entire fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
When connecting to a cluster using Windows Admin Center installed as a gateway while using a username and password to authenticate, you must select Use these credentials for all connections so to make the credentials available to query the member nodes.
Hyper-Converged Cluster Manager solution
Windows Admin Center has disabled certain commands, such as Drives - Update firmware, Servers - Remove and Volumes - Open, because it doesn't currently support them.
Azure services
The following sections describe issues you can encounter when using Azure services while in Windows Admin Center.
Azure login and gateway registration
When attempting to register your Windows Admin Center gateway in the Azure China 21Vianet or Azure US Gov cloud domains in version 2211, the gateway can sometimes redirect you to the Azure Global sign-in experience. To work around this issue, use an earlier version of Windows Admin Center.
In the 2009 release, you can run into issues signing in to Azure or registering your Windows Admin Center gateway with Azure. Try doing the following to troubleshoot the issue:
Before using any Azure features in Windows Admin Center, including gateway registration, make sure you've signed in to your Azure account in a different tab or window. We recommend you sign in through the Azure portal.
If you successfully sign in to Azure during gateway registration but don't see visual confirmation on the Azure page of your Windows Admin Center settings, refresh the page by going to another page, then returning.
If you've already given admin approval for Windows Admin Center in the portal but still see an error message that says "Need admin approval", try signing in to Azure using the banners around Windows Admin Center instead of going to the Settings page.
If your proxy is misconfigured, you can see an error message that says "Error: Value cannot be null. Parameter name: httpClientFactory." To resolve this issue, go to the Settings page and adjust your settings to the correct configuration.
Azure File Sync permissions
Azure File Sync requires permissions in Azure that Windows Admin Center didn't provide before version 1910. If you registered your Windows Admin Center gateway with Azure using a version earlier than 1910, you must update your Microsoft Entra application in order to use Azure File Sync in the latest version of Windows Admin Center. The extra permissions let Azure File Sync automatically configure storage account access as described in Ensure Azure File Sync has access to the storage account.
There are two ways you can update Microsoft Entra ID.
To update using the registration method:
Go to Settings > Azure > Unregister
Register Windows Admin Center with Azure again, making sure you choose to create a new Microsoft Entra application.
To update using Azure:
Open Microsoft Entra ID.
Go to App Registrations, select the name of application you want to update to open its overview page.
Once you're in the application overview page, go to API permissions.
Select Add a permission.
Select Microsoft Graph > Delegated permissions > Directory and select the Directory.AccessAsUser.All checkbox.
Finally, select Add permissions to save the changes you made to the app.
Options for setting up Azure management services
Azure management services, including Azure Monitor, Azure Update Management, and Azure Security Center, all use the Microsoft Monitoring Agent for on-premises servers. Azure Update Management supports limited regions and needs its Log Analytics workspace linked to an Azure Automation account. If you want to set up multiple services in Windows Admin Center, you need to set up Azure Update Management first, then either Azure Security Center or Azure Monitor.
If you've already configured Azure management services that use the Microsoft Monitoring Agent before trying to use Azure Update Management in Windows Admin Center, the service only lets you configure Azure Update Management if existing resources linked to the Microsoft Monitoring Agent support it.
If the linked resources don't support Azure Update Management, there are two ways you can work around it.
To resolve the issue using the Control Panel:
On the Start menu, go to Control Panel > Microsoft Monitoring Agent.
Follow the directions in How do I stop an agent from communicating with Log Analytics to disconnect your server from Azure Monitor, Azure Security Center, or other Azure management solutions you're currently using.
Configure Azure Update Management in Windows Admin Center.
Reconnect to the Azure management solutions you disconnected in step 2.
To resolve the issue using Azure Update Management:
Follow the instructions in Update Management overview to manually set up the Azure resources you need for Azure Update Management.
Follow the directions in Adding or removing a workspace to manually update the Microsoft Monitoring Agent outside of Windows Admin Center and add the new workspace for the Update Management solution you want to use.
Windows Remote Management errors
You may encounter the following error messages when using Windows Remote Management.
General connection error
When you encounter this error, the following error message appears:
Cluster wasn't created Connecting to remote server tk5-3wp13r1131.cfdev.nttest.microsoft.com failed
with the following error message:
WinRM cannot complete the operation. Verify that the specified computer name is valid, that the
computer is accessible over the network, and that a firewall exception for the WinRM service is
enabled and allows access from this computer. By default, the WinRM firewall exception for public
profiles limits access to remote computers within the same local subnet. For more information, see
the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
This error usually appears when you're trying to connect using WinRM. It can happen for the following reasons:
If the service couldn't resolve DNS, make sure you entered the correct server name.
If the service couldn't reach the server name at all, this is likely due to a network connection issue, such as a network disruption.
If the firewall rules aren't configured for the WinRM service, you must reconfigure them for domain and private profiles.
If the WinRM service isn't running or disabled, enable the service and make sure it keeps running.
Authentication error
When you encounter this error, the following error message appears:
Connecting to remote server ack failed with the following error message:
WinRM cannot process the request. The following error with error code 0x8009030e occurred while
using Negotiate authentication: A specified logon session does not exist. It may already have been
terminated. \r\n This can occur if the provided credentials are not valid on the target server, or
if the server identity could not be verified. If you trust the server identity add the server name
to the TrustedHosts list, and then retry the request. User winrm.cmd to view or edit the
TrustedHosts list. Note that computers in the TrustedHosts list might not be authenticated. For
more information about how to edit the TrustedHosts list, run the following command: winrm help
config. For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
This error usually occurs on cluster connections when WinRM can't connect because of the following reasons:
The user is trying to remotely connect to a domain-connected machine while signed in as a local user administrator account.
The user trying to sign in is in the domain but can't contact the domain even though they can reach the server. When this happens, WinRM treats the user like they aren't in the domain but are connecting to a domain account.
You can try the following methods to resolve this issue:
Make sure users can always contact the domain, especially after a network operation.
You should add all computers you're connecting to into the trusted hosts (FQDNS), such as
@{TrustedHosts="VS1.contoso.com,VS2.contoso.com,my2012cluster.contoso.com"}.The General connection error should pass all validations.
WinRM service
When you encounter this error, the following error message appears:
We cannot display the changes right now:
Connecting to remote server localhost failed with the
following error message : The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request.
Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs
and documentation for the WS-Management services running on the destination, mostly commonly IIS or
WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to
analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig". For more information, see the
about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
You can encounter this error for the following reasons:
The WinRM service isn't running. The service could be temporarily disabled or completely shut down. To resolve this issue, make sure the WinRM service is always running.
The WinRM listener isn't configured or is corrupted. The quickest way to solve this problem is to run
WinRM quickconfigin PowerShell, which creates a listener. WinRM also has two built-in listeners for HTTPS and HTTP connections. The HTTPS server and client should both have the same valid certificates.
Security error
When you encounter this error, the following error message appears:
Connecting to remote server dc1.root.contoso.com failed with the following error message:
WinRM cannot process the request. The following error with errorcode 0x80090322 occurred while
using Kerberos authentication. An unknown security error occurred. At line:1 char:1 +
Enter-PSSession dc1.root.contoso.com + ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ + CategoryInfo
:InvalidArgument:(dc1.root.contoso.com:String)[Enter-PSSession], PSRemotingTransportException +
FullyQualifiedErrorId : CreateRemoteRunspaceFailed
This error is uncommon. You usually encounter this area when an account tries to create a remote connection. In most cases, one or more default HTTP SPNs are registered to a service account, causing Kerberos authentication to fail. This issue usually happens because some software installed on the server needs one or more SPNs to function properly, such as SQL Server Reporting Services, Microsoft Dynamics, SharePoint, and so on.
In some cases, one of the SPNs is registered to a service account while the other one isn't. In that case, the WinRM connection succeeds when trying to start a session with the server name, but fails when it tries to start a session using the FQDN.
To resolve this issue, check if one or more default HTTP SPNs are registered to a service account by running the following command in PowerShell:
setspn -q HTTP/servername.or.fqdn
If the service finds the SPN but the server name isn't in the highlighted field of the error message, run the following command to set up dedicated SPNs for WinRM by specifying the port number and the machine account:
setspn -s HTTP/servername.or.fqdn:5985 servername
If you're connecting remotely using PowerShell, make sure to also use the IncludePortInSPN parameter, as shown in the following example command:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName servername.or.fqdn -SessionOption (New-PSSessionOption -IncludePortInSPN)
WinRM status 500
When you encounter this error, the following error message appears:
Error: Connecting to remote server YAZSHCISIIH01.ad.yara.com failed with the following error message:
The WinRM client received an HTTP server error status (500), but the remote service did not include
any other information about the cause of the failure. For more information, see the
about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
This error is very rare. When you see this error message, it usually means WinRM couldn't process the request. The reason why this error appears varies based on context.
To resolve this issue, make sure remoting is enabled and that you configure the WinRM listener to accept requests. We also recommend you check the event logs for other errors, such as if WinRM can't access certain files in the file system due to the files only having read permissions.