Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Caution
Most cross-certificates expired in July 2021. You can't use code-signing certificates that chain with expired cross-certificates to create new kernel mode digital signatures for any version of Windows.
The Microsoft Trusted Root Program no longer supports root certificates that have kernel mode signing capabilities.
For policy requirements, see [Windows 10 kernel mode code signing requirements] (/security/trusted-root/program-requirements#f-windows-10-kernel-mode-code-signing-kmcs-requirements).
Existing cross-signed root certificates with kernel-mode code-signing capabilities continue to work until expiration. All software publisher certificates, commercial release certificates, and commercial test certificates that chain back to these root certificates also become invalid on the same schedule.
To get your driver signed, first Register for the Windows Hardware Dev Center program.
Frequently asked questions
How can I find the expiration schedule of the trusted cross-certificates?
Are there alternatives to cross-signed certificates for testing drivers?
Is there a way to run production driver packages without exposing it to Microsoft?
Does every new production version of a driver package require a Microsoft signature?
Can I sign nondriver code with existing certificates issued by a third party?
Can I continue to use EV certificate for signing submissions to Hardware Dev Center?
How do I know if scheduled expirations can affect my signing certificate?
How can I automate Microsoft Test Signing to work with my organization's build processes?
Is Microsoft the sole provider of production kernel-mode code signatures?
How can I have my drivers run in Windows XP when Hardware Dev Center doesn't provide driver signing?
How do production signing options differ by Windows version?
How can I find the expiration schedule of the trusted cross-certificates?
All cross-signed trusted root certificates are now expired.
Are there alternatives to cross-signed certificates for testing drivers?
The following procedures are available. For all methods, the TESTSIGNING boot option must be enabled.
- MakeCert test certificate process
- Windows Hardware Quality Labs (WHQL) test signature program
- Enterprise CA test certificate
For testing drivers at boot, see How to install a test-signed driver required for Windows setup and boot.
For more information, see the Introduction to signing drivers during development and test.
How are my existing signed driver packages affected?
As long as driver packages are timestamped before the expiration date of the leaf-signing certificate, the packages continue working.
Is there a way to run production driver packages without exposing it to Microsoft?
No, all production driver packages must be submitted to, and signed by Microsoft.
Does every new production version of a driver package require a Microsoft signature?
Yes, every time a Production level driver package is rebuilt, Microsoft must sign the package.
Can I sign nondriver code with existing certificates issued by a third party?
Yes, these certificates continue to work until they expire. Code signed by using these certificates runs only in user mode unless it has a valid Microsoft signature.
Can I continue to use EV certificate for signing submissions to Hardware Dev Center?
Yes, extended validation (EV) certificates continue to work until they expire. If you sign a kernel-mode driver with an EV certificate after the issuing cross-certificate expires, the resulting driver doesn't load, run, or install.
How do I know if scheduled expirations can affect my signing certificate?
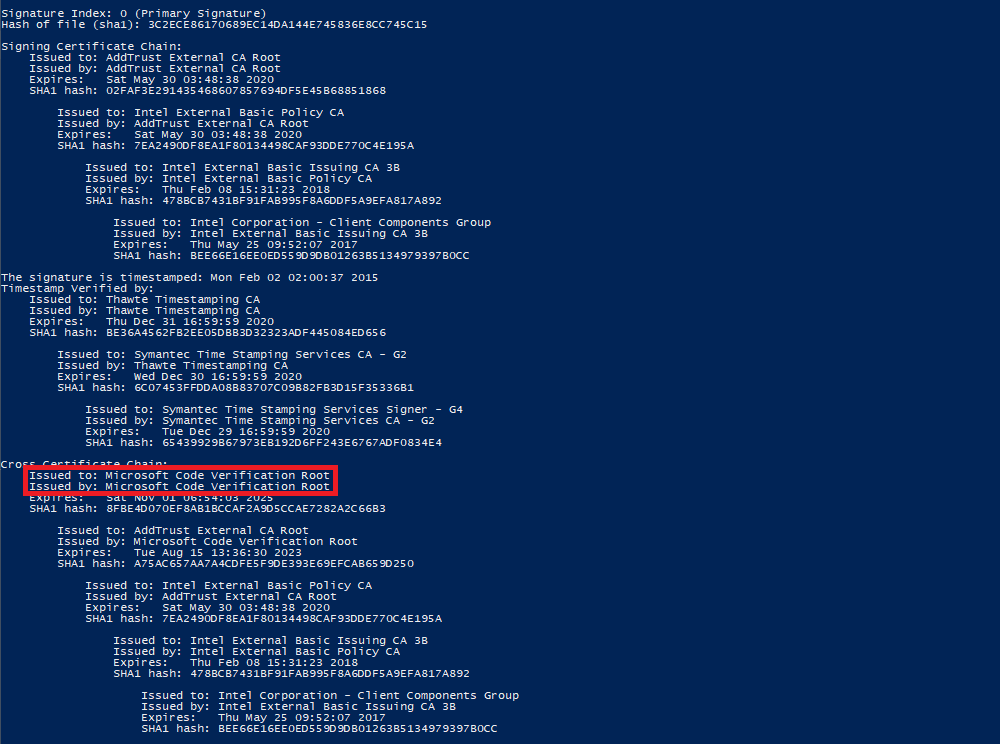
If your cross certificate chain ends in Microsoft Code Verification Root, your signing certificate is affected.
To view the cross certificate chain, run the signtool verify /v /kp <mydriver.sys> command. For example:
How can I automate Microsoft Test Signing to work with my organization's build processes?
Your build processes can call the Hardware Dev Center API.
For samples that show usage, see the Surface Dev Center Manager (SDCM) repository on GitHub.
Is Microsoft the sole provider of production kernel-mode code signatures?
Yes.
How can I have my drivers run in Windows XP when Hardware Dev Center doesn't provide driver signing?
Drivers can still be signed with a third-party issued code-signing certificate. However, the certificate that signed the driver must be imported into the Local Computer Trusted Publishers certificate store on the target computer. For more information, see Trusted publishers certificate store.
How do production signing options differ by Windows version?
Warning
Cross-signing is no longer accepted for driver signing. Using cross certificates to sign kernel-mode drivers is a violation of the Microsoft Trusted Root Program (TRP) policy. The TRP no longer supports root certificates that have kernel mode signing capabilities. Certificates in violation of Microsoft TRP policies will be revoked by the CA.
If your driver runs on Windows 7, 8, or 8.1, your driver must be signed through the Windows Hardware Compatibility Program. To get started, see Create a new hardware submission.
Starting in Windows 10, use either Windows Hardware Compatibility Program (WHCP) or attestation signing.
If you have challenges signing your driver with WHCP, report the specifics using one of the following options:
Use the Microsoft Collaborate portal available through the Microsoft Partner Center Dashboard and create a feedback bug.
Go to Windows developer support and select the Contact us tab. In the Technical support box, next to Driver Development and Testing/Certification, select Submit an incident.