你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
Azure Maps 是一系列集成到 Azure 中的地理空间服务 API,使开发人员能够针对 IoT、移动性和资产跟踪等各种方案创建位置感知应用程序。
Azure Maps REST API 支持使用 Python 和 R 等语言进行地理空间数据分析和机器学习,从而提供可靠的路由 API,用于根据车辆类型或可抵达区域等条件计算路线。
本教程指导用户使用 Azure Maps API 以及 VS Code 中的 Jupyter Notebook 和 Python 为电动汽车规划路线,以在电池电量不足时找到最近的充电站。
在本教程中,将:
- 创建并运行 VS Code 中的 Jupyter Notebook。
- 在 Python 中调用 Azure Maps REST API。
- 根据电动车的耗电模型搜索可抵达的范围。
- 在可达距离范围(或等时线)内搜索电动车充电站。
- 在地图上呈现可抵达范围的边界和充电站。
- 基于驾驶时间查找并直观显示最近的电动车充电站的路线。
先决条件
- Azure Maps 帐户
- 订阅密钥
- Visual Studio Code
- VS Code 中的 Jupyter Notebook 的实践知识
- 已设定环境以在 Jupyter Notebook 中使用 Python。 有关详细信息,请参阅设置环境。
注意
有关 Azure Maps 中身份验证的详细信息,请参阅在 Azure Maps 中管理身份验证。
安装项目级包
“EV 路由和可抵达范围”项目依赖于 aiohttp 和 IPython python 库。 可使用 pip 在 Visual Studio 终端中安装这些项:
pip install aiohttp
pip install ipython
在 Visual Studio Code 中打开 Jupyter Notebook
下载并打开本教程中使用的 Notebook:
在 GitHub 的 AzureMapsJupyterSamples 存储库中打开文件 EVrouting.ipynb。
选择屏幕右上角的“下载原始文件”按钮,在本地保存文件。

在 Visual Studio Code 中打开已下载的 Notebook,可以通过右键单击文件并选择“用 Visual Studio Code 打开”,或者通过 VS Code 的文件资源管理器打开。
加载所需的模块和框架
添加代码后,可使用单元格左侧的“运行”图标运行单元格,输出显示在代码单元格下方。
运行以下脚本,加载全部所需的模块和框架。
import time
import aiohttp
import urllib.parse
from IPython.display import Image, display

请求可抵达的范围边界
一家包裹递送公司运营着一支车队,其中包括一些电动汽车。 这些车辆需要在白天无需返回仓库便可充电。 如果剩余电量低于一小时使用时间,则会进行搜索以查找可抵达范围内的充电站。 然后获取这些充电站范围的边界信息。
所请求的 routeType 是 经济型,以平衡经济性和速度。 以下脚本使用与车辆的耗电模型相关的参数调用 Azure Maps 路线服务的获取路线范围 API。 然后,该脚本分析响应以创建 GeoJSON 格式的多边形对象来表示汽车的最大可抵达范围。
subscriptionKey = "Your Azure Maps key"
currentLocation = [34.028115,-118.5184279]
session = aiohttp.ClientSession()
# Parameters for the vehicle consumption model
travelMode = "car"
vehicleEngineType = "electric"
currentChargeInkWh=45
maxChargeInkWh=80
timeBudgetInSec=550
routeType="eco"
constantSpeedConsumptionInkWhPerHundredkm="50,8.2:130,21.3"
# Get boundaries for the electric vehicle's reachable range.
routeRangeResponse = await (await session.get("https://atlas.microsoft.com/route/range/json?subscription-key={}&api-version=1.0&query={}&travelMode={}&vehicleEngineType={}¤tChargeInkWh={}&maxChargeInkWh={}&timeBudgetInSec={}&routeType={}&constantSpeedConsumptionInkWhPerHundredkm={}"
.format(subscriptionKey,str(currentLocation[0])+","+str(currentLocation[1]),travelMode, vehicleEngineType, currentChargeInkWh, maxChargeInkWh, timeBudgetInSec, routeType, constantSpeedConsumptionInkWhPerHundredkm))).json()
polyBounds = routeRangeResponse["reachableRange"]["boundary"]
for i in range(len(polyBounds)):
coordList = list(polyBounds[i].values())
coordList[0], coordList[1] = coordList[1], coordList[0]
polyBounds[i] = coordList
polyBounds.pop()
polyBounds.append(polyBounds[0])
boundsData = {
"geometry": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates":
[
polyBounds
]
}
}
在可抵达范围内搜索电动车充电站
确定电动汽车的可抵达范围(等时线)后,可以搜索该区域内的充电站。
以下脚本使用 Azure Maps 发布在几何图形中的搜索 API 查找车辆最大可抵达范围内的充电站。 然后,它将响应分析成一系列可抵达的位置。
# Search for electric vehicle stations within reachable range.
searchPolyResponse = await (await session.post(url = "https://atlas.microsoft.com/search/geometry/json?subscription-key={}&api-version=1.0&query=electric vehicle station&idxSet=POI&limit=50".format(subscriptionKey), json = boundsData)).json()
reachableLocations = []
for loc in range(len(searchPolyResponse["results"])):
location = list(searchPolyResponse["results"][loc]["position"].values())
location[0], location[1] = location[1], location[0]
reachableLocations.append(location)
在地图上呈现充电站和可抵达范围
运行以下脚本,调用 Azure Maps 获取地图图像服务,在静态地图图像上呈现充电站和最大可抵达边界:
# Get boundaries for the bounding box.
def getBounds(polyBounds):
maxLon = max(map(lambda x: x[0], polyBounds))
minLon = min(map(lambda x: x[0], polyBounds))
maxLat = max(map(lambda x: x[1], polyBounds))
minLat = min(map(lambda x: x[1], polyBounds))
# Buffer the bounding box by 10 percent to account for the pixel size of pins at the ends of the route.
lonBuffer = (maxLon-minLon)*0.1
minLon -= lonBuffer
maxLon += lonBuffer
latBuffer = (maxLat-minLat)*0.1
minLat -= latBuffer
maxLat += latBuffer
return [minLon, maxLon, minLat, maxLat]
minLon, maxLon, minLat, maxLat = getBounds(polyBounds)
polyBoundsFormatted = ('|'.join(map(str, polyBounds))).replace('[','').replace(']','').replace(',','')
reachableLocationsFormatted = ('|'.join(map(str, reachableLocations))).replace('[','').replace(']','').replace(',','')
path = "lcff3333|lw3|la0.80|fa0.35||{}".format(polyBoundsFormatted)
pins = "custom|an15 53||{}||https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/AzureMapsCodeSamples/e3a684e7423075129a0857c63011e7cfdda213b7/Static/images/icons/ev_pin.png".format(reachableLocationsFormatted)
encodedPins = urllib.parse.quote(pins, safe='')
# Render the range and electric vehicle charging points on the map.
staticMapResponse = await session.get("https://atlas.microsoft.com/map/static?api-version=2024-04-01&subscription-key={}&pins={}&path={}&bbox={}&zoom=12".format(subscriptionKey,encodedPins,path,str(minLon)+", "+str(minLat)+", "+str(maxLon)+", "+str(maxLat)))
poiRangeMap = await staticMapResponse.content.read()
display(Image(poiRangeMap))
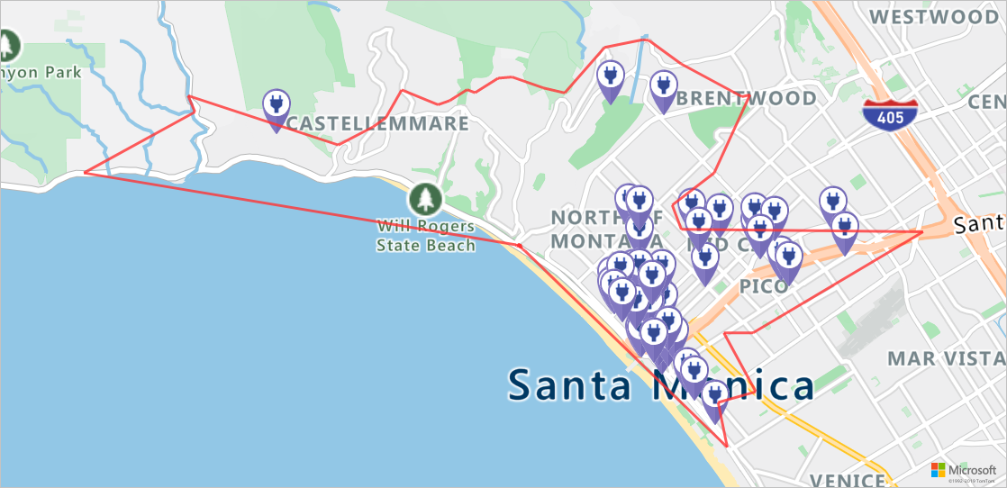
查找最佳充电站
首先,找出车辆可抵达范围内的所有潜在充电站。 接下来,确定在最短时间内可以通往哪些工作站。
以下脚本调用 Azure Maps 的矩阵路线 API。 它会返回车辆的位置、行程时间,以及与每个充电站之间的距离。 后续脚本会分析此响应,以确定可在最短时间内抵达的最近充电站。
locationData = {
"origins": {
"type": "MultiPoint",
"coordinates": [[currentLocation[1],currentLocation[0]]]
},
"destinations": {
"type": "MultiPoint",
"coordinates": reachableLocations
}
}
# Get the travel time and distance to each specified charging station.
searchPolyRes = await (await session.post(url = "https://atlas.microsoft.com/route/matrix/json?subscription-key={}&api-version=1.0&routeType=shortest&waitForResults=true".format(subscriptionKey), json = locationData)).json()
distances = []
for dist in range(len(reachableLocations)):
distances.append(searchPolyRes["matrix"][0][dist]["response"]["routeSummary"]["travelTimeInSeconds"])
minDistLoc = []
minDistIndex = distances.index(min(distances))
minDistLoc.extend([reachableLocations[minDistIndex][1], reachableLocations[minDistIndex][0]])
closestChargeLoc = ",".join(str(i) for i in minDistLoc)
计算到最近充电站的路线
找到最近的充电站后,使用获取路线导航 API 获取以车辆当前位置为起点的详细导航。 运行下一个单元格中的脚本,以生成并分析表示路线的 GeoJSON 对象。
# Get the route from the electric vehicle's current location to the closest charging station.
routeResponse = await (await session.get("https://atlas.microsoft.com/route/directions/json?subscription-key={}&api-version=1.0&query={}:{}".format(subscriptionKey, str(currentLocation[0])+","+str(currentLocation[1]), closestChargeLoc))).json()
route = []
for loc in range(len(routeResponse["routes"][0]["legs"][0]["points"])):
location = list(routeResponse["routes"][0]["legs"][0]["points"][loc].values())
location[0], location[1] = location[1], location[0]
route.append(location)
routeData = {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": route
}
直观显示路线
若要可视化路线,请使用获取地图图像 API 在地图上呈现路线。
destination = route[-1]
#destination[1], destination[0] = destination[0], destination[1]
routeFormatted = ('|'.join(map(str, route))).replace('[','').replace(']','').replace(',','')
path = "lc0f6dd9|lw6||{}".format(routeFormatted)
pins = "default|codb1818||{} {}|{} {}".format(str(currentLocation[1]),str(currentLocation[0]),destination[0],destination[1])
# Get boundaries for the bounding box.
minLon, maxLon = (float(destination[0]),currentLocation[1]) if float(destination[0])<currentLocation[1] else (currentLocation[1], float(destination[0]))
minLat, maxLat = (float(destination[1]),currentLocation[0]) if float(destination[1])<currentLocation[0] else (currentLocation[0], float(destination[1]))
# Buffer the bounding box by 10 percent to account for the pixel size of pins at the ends of the route.
lonBuffer = (maxLon-minLon)*0.1
minLon -= lonBuffer
maxLon += lonBuffer
latBuffer = (maxLat-minLat)*0.1
minLat -= latBuffer
maxLat += latBuffer
# Render the route on the map.
staticMapResponse = await session.get("https://atlas.microsoft.com/map/static?api-version=2024-04-01&subscription-key={}&&path={}&pins={}&bbox={}&zoom=16".format(subscriptionKey,path,pins,str(minLon)+", "+str(minLat)+", "+str(maxLon)+", "+str(maxLat)))
staticMapImage = await staticMapResponse.content.read()
await session.close()
display(Image(staticMapImage))
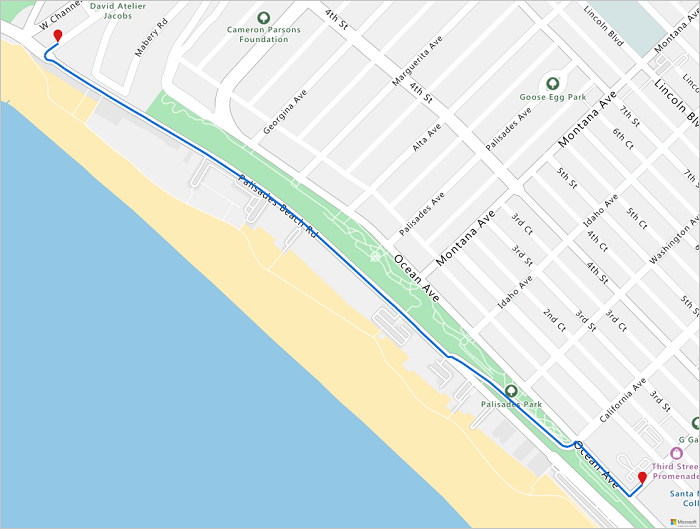
本教程已介绍如何使用 Python 直接调用 Azure Maps REST API 和直观显示 Azure Maps 数据。
有关本教程中使用的 Azure Maps API 的详细信息,请参阅:
有关 Azure Maps REST API 的完整列表,请参阅 Azure Maps REST API。