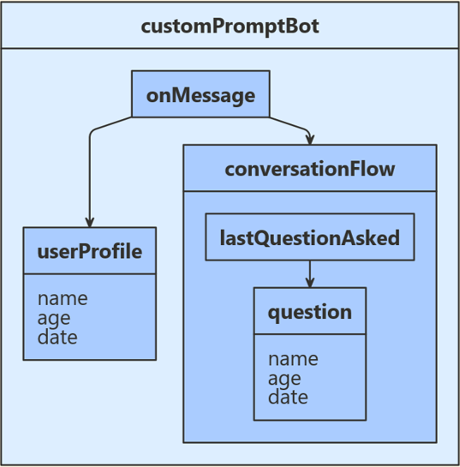
机器人与用户之间的聊天通常涉及到请求(提示)用户输入信息、分析用户的响应,然后对该信息采取措施。 机器人应该跟踪聊天上下文,以便可以管理聊天行为并记住先前问题的回答。 机器人的状态是它为了正确响应传入消息而跟踪的信息。
在启动时创建用户和聊天状态对象,并通过在机器人构造函数中进行依赖项注入来使用它们。
Startup.cs
// Create the Bot Adapter with error handling enabled.
services.AddSingleton<IBotFrameworkHttpAdapter, AdapterWithErrorHandler>();
// Create the storage we'll be using for User and Conversation state. (Memory is great for testing purposes.)
services.AddSingleton<IStorage, MemoryStorage>();
// Create the User state.
services.AddSingleton<UserState>();
// Create the Conversation state.
services.AddSingleton<ConversationState>();
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
private readonly BotState _userState;
private readonly BotState _conversationState;
public CustomPromptBot(ConversationState conversationState, UserState userState)
{
_conversationState = conversationState;
_userState = userState;
}
在 index.js 中创建用户和聊天状态对象,在机器人构造函数中使用它们。
index.js
const bot = new CustomPromptBot(conversationState, userState);
// Catch-all for errors.
adapter.onTurnError = async (context, error) => {
机器人/customPromptBot.js
// Defines a bot for filling a user profile.
class CustomPromptBot extends ActivityHandler {
this.userProfile = userState.createProperty(USER_PROFILE_PROPERTY);
// The state management objects for the conversation and user.
使用 Spring 容器提供的 ConversationState 和 UserState 实例在 getBot 方法中构造 CustomPromptBot。 CustomPromptBot 的构造函数将存储对启动期间提供的 ConversationState 和 UserState 的引用。
Application.java
警告
您正在寻找的示例似乎已经被移动了! 放心,我们正在努力解决此问题。
CustomPromptBot.java
警告
您正在寻找的示例似乎已经被移动了! 放心,我们正在努力解决此问题。
在 app.py 中创建用户和聊天状态对象,在机器人构造函数中使用它们。
app.py
CONVERSATION_STATE = ConversationState(MEMORY)
# Create Bot
BOT = CustomPromptBot(CONVERSATION_STATE, USER_STATE)
# Listen for incoming requests on /api/messages.
bots/custom_prompt_bot.py
class CustomPromptBot(ActivityHandler):
def __init__(self, conversation_state: ConversationState, user_state: UserState):
if conversation_state is None:
raise TypeError(
"[CustomPromptBot]: Missing parameter. conversation_state is required but None was given"
)
if user_state is None:
raise TypeError(
"[CustomPromptBot]: Missing parameter. user_state is required but None was given"
)
self.conversation_state = conversation_state
self.user_state = user_state
为用户配置文件和聊天流属性创建属性访问器,然后通过调用 GetAsync 从状态检索属性值。
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
protected override async Task OnMessageActivityAsync(ITurnContext<IMessageActivity> turnContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var conversationStateAccessors = _conversationState.CreateProperty<ConversationFlow>(nameof(ConversationFlow));
var flow = await conversationStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new ConversationFlow(), cancellationToken);
var userStateAccessors = _userState.CreateProperty<UserProfile>(nameof(UserProfile));
var profile = await userStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new UserProfile(), cancellationToken);
在本回合结束之前,调用 SaveChangesAsync 将所有状态更改写入存储器。
await _conversationState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
await _userState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
}
为用户配置文件和聊天流属性创建属性访问器,然后通过调用 get 从状态检索属性值。
机器人/customPromptBot.js
this.userState = userState;
this.onMessage(async (turnContext, next) => {
在本回合结束之前,调用 saveChanges 将所有状态更改写入存储器。
}
/**
* Override the ActivityHandler.run() method to save state changes after the bot logic completes.
*/
async run(context) {
await super.run(context);
// Save any state changes. The load happened during the execution of the Dialog.
await this.conversationState.saveChanges(context, false);
为用户配置文件和聊天流属性创建属性访问器,然后通过调用 get 从状态检索属性值。
CustomPromptBot.java
警告
您正在寻找的示例似乎已经被移动了! 放心,我们正在努力解决此问题。
在本回合结束之前,调用 saveChanges 将所有状态更改写入存储器。
警告
您正在寻找的示例似乎已经被移动了! 放心,我们正在努力解决此问题。
在构造函数中,请创建状态属性服务器,并设置用于聊天的状态管理对象(已在上面创建)。
bots/custom_prompt_bot.py
async def on_message_activity(self, turn_context: TurnContext):
# Get the state properties from the turn context.
profile = await self.profile_accessor.get(turn_context, UserProfile)
flow = await self.flow_accessor.get(turn_context, ConversationFlow)
在本回合结束之前,调用 SaveChangesAsync 将所有状态更改写入存储器。
# Save changes to UserState and ConversationState
await self.conversation_state.save_changes(turn_context)
await self.user_state.save_changes(turn_context)
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
protected override async Task OnMessageActivityAsync(ITurnContext<IMessageActivity> turnContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var conversationStateAccessors = _conversationState.CreateProperty<ConversationFlow>(nameof(ConversationFlow));
var flow = await conversationStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new ConversationFlow(), cancellationToken);
var userStateAccessors = _userState.CreateProperty<UserProfile>(nameof(UserProfile));
var profile = await userStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new UserProfile(), cancellationToken);
await FillOutUserProfileAsync(flow, profile, turnContext, cancellationToken);
// Save changes.
await _conversationState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
await _userState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
}
机器人/customPromptBot.js
this.userState = userState;
this.onMessage(async (turnContext, next) => {
const flow = await this.conversationFlow.get(turnContext, { lastQuestionAsked: question.none });
const profile = await this.userProfile.get(turnContext, {});
await CustomPromptBot.fillOutUserProfile(flow, profile, turnContext);
// By calling next() you ensure that the next BotHandler is run.
CustomPromptBot.java
警告
您正在寻找的示例似乎已经被移动了! 放心,我们正在努力解决此问题。
bots/custom_prompt_bot.py
async def on_message_activity(self, turn_context: TurnContext):
# Get the state properties from the turn context.
profile = await self.profile_accessor.get(turn_context, UserProfile)
flow = await self.flow_accessor.get(turn_context, ConversationFlow)
await self._fill_out_user_profile(flow, profile, turn_context)
# Save changes to UserState and ConversationState
await self.conversation_state.save_changes(turn_context)
await self.user_state.save_changes(turn_context)
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
{
var input = turnContext.Activity.Text?.Trim();
string message;
switch (flow.LastQuestionAsked)
{
case ConversationFlow.Question.None:
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync("Let's get started. What is your name?", null, null, cancellationToken);
flow.LastQuestionAsked = ConversationFlow.Question.Name;
break;
case ConversationFlow.Question.Name:
if (ValidateName(input, out var name, out message))
{
profile.Name = name;
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Hi {profile.Name}.", null, null, cancellationToken);
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync("How old are you?", null, null, cancellationToken);
flow.LastQuestionAsked = ConversationFlow.Question.Age;
break;
}
else
{
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync(message ?? "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.", null, null, cancellationToken);
break;
}
case ConversationFlow.Question.Age:
if (ValidateAge(input, out var age, out message))
{
profile.Age = age;
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"I have your age as {profile.Age}.", null, null, cancellationToken);
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync("When is your flight?", null, null, cancellationToken);
flow.LastQuestionAsked = ConversationFlow.Question.Date;
break;
}
else
{
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync(message ?? "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.", null, null, cancellationToken);
break;
}
case ConversationFlow.Question.Date:
if (ValidateDate(input, out var date, out message))
{
profile.Date = date;
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Your cab ride to the airport is scheduled for {profile.Date}.");
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Thanks for completing the booking {profile.Name}.");
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Type anything to run the bot again.");
flow.LastQuestionAsked = ConversationFlow.Question.None;
profile = new UserProfile();
break;
}
else
{
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync(message ?? "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.", null, null, cancellationToken);
break;
}
}
}
机器人/customPromptBot.js
}
// Manages the conversation flow for filling out the user's profile.
static async fillOutUserProfile(flow, profile, turnContext) {
const input = turnContext.activity.text;
let result;
switch (flow.lastQuestionAsked) {
// If we're just starting off, we haven't asked the user for any information yet.
// Ask the user for their name and update the conversation flag.
case question.none:
await turnContext.sendActivity("Let's get started. What is your name?");
flow.lastQuestionAsked = question.name;
break;
// If we last asked for their name, record their response, confirm that we got it.
// Ask them for their age and update the conversation flag.
case question.name:
result = this.validateName(input);
if (result.success) {
profile.name = result.name;
await turnContext.sendActivity(`I have your name as ${ profile.name }.`);
await turnContext.sendActivity('How old are you?');
flow.lastQuestionAsked = question.age;
break;
} else {
// If we couldn't interpret their input, ask them for it again.
// Don't update the conversation flag, so that we repeat this step.
await turnContext.sendActivity(result.message || "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.");
break;
}
// If we last asked for their age, record their response, confirm that we got it.
// Ask them for their date preference and update the conversation flag.
case question.age:
result = this.validateAge(input);
if (result.success) {
profile.age = result.age;
await turnContext.sendActivity(`I have your age as ${ profile.age }.`);
await turnContext.sendActivity('When is your flight?');
flow.lastQuestionAsked = question.date;
break;
} else {
// If we couldn't interpret their input, ask them for it again.
// Don't update the conversation flag, so that we repeat this step.
await turnContext.sendActivity(result.message || "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.");
break;
}
// If we last asked for a date, record their response, confirm that we got it,
// let them know the process is complete, and update the conversation flag.
case question.date:
result = this.validateDate(input);
if (result.success) {
profile.date = result.date;
await turnContext.sendActivity(`Your cab ride to the airport is scheduled for ${ profile.date }.`);
await turnContext.sendActivity(`Thanks for completing the booking ${ profile.name }.`);
await turnContext.sendActivity('Type anything to run the bot again.');
flow.lastQuestionAsked = question.none;
profile = {};
break;
} else {
// If we couldn't interpret their input, ask them for it again.
// Don't update the conversation flag, so that we repeat this step.
await turnContext.sendActivity(result.message || "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.");
break;
}
CustomPromptBot.java
警告
您正在寻找的示例似乎已经被移动了! 放心,我们正在努力解决此问题。
bots/custom_prompt_bot.py
async def _fill_out_user_profile(
self, flow: ConversationFlow, profile: UserProfile, turn_context: TurnContext
):
user_input = turn_context.activity.text.strip()
# ask for name
if flow.last_question_asked == Question.NONE:
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text("Let's get started. What is your name?")
)
flow.last_question_asked = Question.NAME
# validate name then ask for age
elif flow.last_question_asked == Question.NAME:
validate_result = self._validate_name(user_input)
if not validate_result.is_valid:
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text(validate_result.message)
)
else:
profile.name = validate_result.value
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text(f"Hi {profile.name}")
)
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text("How old are you?")
)
flow.last_question_asked = Question.AGE
# validate age then ask for date
elif flow.last_question_asked == Question.AGE:
validate_result = self._validate_age(user_input)
if not validate_result.is_valid:
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text(validate_result.message)
)
else:
profile.age = validate_result.value
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text(f"I have your age as {profile.age}.")
)
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text("When is your flight?")
)
flow.last_question_asked = Question.DATE
# validate date and wrap it up
elif flow.last_question_asked == Question.DATE:
validate_result = self._validate_date(user_input)
if not validate_result.is_valid:
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text(validate_result.message)
)
else:
profile.date = validate_result.value
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text(
f"Your cab ride to the airport is scheduled for {profile.date}."
)
)
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text(
f"Thanks for completing the booking {profile.name}."
)
)
await turn_context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.text("Type anything to run the bot again.")
)
flow.last_question_asked = Question.NONE
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
private static bool ValidateName(string input, out string name, out string message)
{
name = null;
message = null;
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(input))
{
message = "Please enter a name that contains at least one character.";
}
else
{
name = input.Trim();
}
return message is null;
}
private static bool ValidateAge(string input, out int age, out string message)
{
age = 0;
message = null;
// Try to recognize the input as a number. This works for responses such as "twelve" as well as "12".
try
{
// Attempt to convert the Recognizer result to an integer. This works for "a dozen", "twelve", "12", and so on.
// The recognizer returns a list of potential recognition results, if any.
var results = NumberRecognizer.RecognizeNumber(input, Culture.English);
foreach (var result in results)
{
// The result resolution is a dictionary, where the "value" entry contains the processed string.
if (result.Resolution.TryGetValue("value", out var value))
{
age = Convert.ToInt32(value);
if (age >= 18 && age <= 120)
{
return true;
}
}
}
message = "Please enter an age between 18 and 120.";
}
catch
{
message = "I'm sorry, I could not interpret that as an age. Please enter an age between 18 and 120.";
}
return message is null;
}
private static bool ValidateDate(string input, out string date, out string message)
{
date = null;
message = null;
// Try to recognize the input as a date-time. This works for responses such as "11/14/2018", "9pm", "tomorrow", "Sunday at 5pm", and so on.
// The recognizer returns a list of potential recognition results, if any.
try
{
var results = DateTimeRecognizer.RecognizeDateTime(input, Culture.English);
// Check whether any of the recognized date-times are appropriate,
// and if so, return the first appropriate date-time. We're checking for a value at least an hour in the future.
var earliest = DateTime.Now.AddHours(1.0);
foreach (var result in results)
{
// The result resolution is a dictionary, where the "values" entry contains the processed input.
var resolutions = result.Resolution["values"] as List<Dictionary<string, string>>;
foreach (var resolution in resolutions)
{
// The processed input contains a "value" entry if it is a date-time value, or "start" and
// "end" entries if it is a date-time range.
if (resolution.TryGetValue("value", out var dateString)
|| resolution.TryGetValue("start", out dateString))
{
if (DateTime.TryParse(dateString, out var candidate)
&& earliest < candidate)
{
date = candidate.ToShortDateString();
return true;
}
}
}
}
message = "I'm sorry, please enter a date at least an hour out.";
}
catch
{
message = "I'm sorry, I could not interpret that as an appropriate date. Please enter a date at least an hour out.";
}
return false;
}
机器人/customPromptBot.js
}
// Validates name input. Returns whether validation succeeded and either the parsed and normalized
// value or a message the bot can use to ask the user again.
static validateName(input) {
const name = input && input.trim();
return name !== undefined
? { success: true, name: name, message: '' }
: { success: false, name: null, message: 'Please enter a name that contains at least one character.' };
};
// Validates age input. Returns whether validation succeeded and either the parsed and normalized
// value or a message the bot can use to ask the user again.
static validateAge(input) {
// Try to recognize the input as a number. This works for responses such as "twelve" as well as "12".
try {
// Attempt to convert the Recognizer result to an integer. This works for "a dozen", "twelve", "12", and so on.
// The recognizer returns a list of potential recognition results, if any.
const results = Recognizers.recognizeNumber(input, Recognizers.Culture.English);
let output;
results.forEach(result => {
// result.resolution is a dictionary, where the "value" entry contains the processed string.
const value = result.resolution.value;
if (value) {
const age = parseInt(value);
if (!isNaN(age) && age >= 18 && age <= 120) {
output = { success: true, age: age, message: '' };
return;
}
}
});
return output || { success: false, age: null, message: 'Please enter an age between 18 and 120.' };
} catch (error) {
return {
success: false,
age: null,
message: "I'm sorry, I could not interpret that as an age. Please enter an age between 18 and 120."
};
}
}
// Validates date input. Returns whether validation succeeded and either the parsed and normalized
// value or a message the bot can use to ask the user again.
static validateDate(input) {
// Try to recognize the input as a date-time. This works for responses such as "11/14/2018", "today at 9pm", "tomorrow", "Sunday at 5pm", and so on.
// The recognizer returns a list of potential recognition results, if any.
try {
const results = Recognizers.recognizeDateTime(input, Recognizers.Culture.English);
const now = new Date();
const earliest = now.getTime() + (60 * 60 * 1000);
let output;
results.forEach(result => {
// result.resolution is a dictionary, where the "values" entry contains the processed input.
result.resolution.values.forEach(resolution => {
// The processed input contains a "value" entry if it is a date-time value, or "start" and
// "end" entries if it is a date-time range.
const datevalue = resolution.value || resolution.start;
// If only time is given, assume it's for today.
const datetime = resolution.type === 'time'
? new Date(`${ now.toLocaleDateString() } ${ datevalue }`)
: new Date(datevalue);
if (datetime && earliest < datetime.getTime()) {
output = { success: true, date: datetime.toISOString(), message: '' };
return;
}
});
});
return output || { success: false, date: null, message: "I'm sorry, please enter a date at least an hour out." };
} catch (error) {
return {
success: false,
date: null,
CustomPromptBot.java
警告
您正在寻找的示例似乎已经被移动了! 放心,我们正在努力解决此问题。
bots/custom_prompt_bot.py
def _validate_name(self, user_input: str) -> ValidationResult:
if not user_input:
return ValidationResult(
is_valid=False,
message="Please enter a name that contains at least one character.",
)
return ValidationResult(is_valid=True, value=user_input)
def _validate_age(self, user_input: str) -> ValidationResult:
# Attempt to convert the Recognizer result to an integer. This works for "a dozen", "twelve", "12", and so on.
# The recognizer returns a list of potential recognition results, if any.
results = recognize_number(user_input, Culture.English)
for result in results:
if "value" in result.resolution:
age = int(result.resolution["value"])
if 18 <= age <= 120:
return ValidationResult(is_valid=True, value=age)
return ValidationResult(
is_valid=False, message="Please enter an age between 18 and 120."
)
def _validate_date(self, user_input: str) -> ValidationResult:
try:
# Try to recognize the input as a date-time. This works for responses such as "11/14/2018", "9pm",
# "tomorrow", "Sunday at 5pm", and so on. The recognizer returns a list of potential recognition results,
# if any.
results = recognize_datetime(user_input, Culture.English)
for result in results:
for resolution in result.resolution["values"]:
if "value" in resolution:
now = datetime.now()
value = resolution["value"]
if resolution["type"] == "date":
candidate = datetime.strptime(value, "%Y-%m-%d")
elif resolution["type"] == "time":
candidate = datetime.strptime(value, "%H:%M:%S")
candidate = candidate.replace(
year=now.year, month=now.month, day=now.day
)
else:
candidate = datetime.strptime(value, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
# user response must be more than an hour out
diff = candidate - now
if diff.total_seconds() >= 3600:
return ValidationResult(
is_valid=True,
value=candidate.strftime("%m/%d/%y"),
)
return ValidationResult(
is_valid=False,
message="I'm sorry, please enter a date at least an hour out.",
)
except ValueError:
return ValidationResult(
is_valid=False,
message="I'm sorry, I could not interpret that as an appropriate "
"date. Please enter a date at least an hour out.",
)