你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
Azure 元数据服务:适用于 Windows VM 的计划事件
适用于: ✔️ Windows VM ✔️ 灵活规模集 ✔️ 统一规模集
计划事件是一个 Azure 元数据服务,可提供应用程序时间用于准备虚拟机 (VM) 维护。 它提供有关即将发生的维护事件的信息(例如重新启动),使应用程序可以为其准备并限制中断。 它可用于 Windows 和 Linux 上的所有 Azure 虚拟机类型(包括 PaaS 和 IaaS)。
有关 Linux 上的计划事件的信息,请参阅适用于 Linux VM 的计划事件。
计划事件提供有关即将发生的事件的主动通知。有关已发生的事件的被动信息,请参阅 Azure Resource Graph 中的 VM 可用性信息和为 Azure 虚拟机创建可用性警报规则。
注意
计划事件在所有 Azure 区域中正式发布。 有关最新版本信息,请参阅版本和区域可用性。
为何使用计划事件?
许多应用程序都可以受益于时间来准备 VM 维护。 时间可以用于执行应用程序的特定任务的提高可用性、可靠性和可维护性,包括:
- 检查点和还原。
- 连接清空。
- 主要副本故障转移。
- 从负载均衡器池删除。
- 事件日志记录。
- 正常关闭。
使用计划事件,应用程序可以发现维护的发生,并触发任务以限制其影响。
预定事件提供以下用例中的事件:
- 平台启动的维护(例如,VM 重新启动、实时迁移或主机的内存保留更新)。
- 虚拟机在预计很快将出现故障的降级后的主机硬件上运行。
- 虚拟机在遭受硬件故障的主机上运行。
- 用户启动的维护(例如,用户重启或重新部署 VM)。
- 现成 VM 和现成规模集实例逐出。
基础知识
元数据服务公开在 VM 中使用可访问的 REST 终结点运行 VM 的相关信息。 该信息通过不可路由的 IP 提供,并且不会在 VM 外部公开。
范围
计划事件将传送到以下目标,可由其进行确认:
- 独立虚拟机。
- Azure 云服务(经典)中的所有 VM。
- 可用性集中的所有 VM。
- 规模集位置组中的所有 VM。
整个可用性集中或虚拟机规模集放置组中的所有虚拟机 (VM) 的 Scheduled Events 都传送到同一组或集中的所有其他 VM,而不考虑可用性区域使用情况。
因此,检查事件中的 Resources 字段可确定哪些 VM 受到了影响。
注意
使用 1 个容错域 (FD = 1) 的规模集中的 GPU 加速虚拟机将仅接收受影响资源的计划事件。 事件并不会广播到同一放置组中的所有 VM。
终结点发现
对于启用了 VNET 的 VM,元数据服务可通过不可路由的静态 IP (169.254.169.254) 使用。 最新版本的计划事件的完整终结点是:
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents?api-version=2020-07-01
如果不是在虚拟网络中创建 VM(云服务和经典 VM 的默认情况),则需使用额外的逻辑以发现要使用的 IP 地址。 若要了解如何发现主机终结点,请参阅此示例。
版本和区域可用性
计划事件服务受版本控制。 版本是必需的,当前版本为 2020-07-01。
| 版本 | 发布类型 | 区域 | 发行说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-07-01 | 正式版 | 全部 | |
| 2019-08-01 | 正式版 | 全部 | |
| 2019-04-01 | 正式版 | 全部 | |
| 2019-01-01 | 正式版 | All | |
| 2017-11-01 | 正式版 | All | |
| 2017-08-01 | 正式版 | 全部 | |
| 2017-03-01 | 预览 | 全部 |
注意
支持的计划事件的前一预览版 {latest} 发布为 api-version。 此格式不再受支持,并且将在未来弃用。
启用和禁用 Scheduled Events
首次为事件发出请求时,为服务启用了计划事件。 第一个调用的延迟响应预计最长应为 2 分钟,并将在 5 分钟内开始收到事件。 如果 Scheduled Events 在 24 小时内没有向终结点发出请求,则会为服务禁用它。
用户启动的维护
用户通过 Azure 门户、API、CLI 或 PowerShell 启动的 VM 维护会生成计划事件。 然后,可以在应用程序中测试维护准备逻辑,并可以通过应用程序准备用户启动的维护。
如果重启 VM,将计划 Reboot 类型的事件。 如果重新部署 VM,将计划 Redeploy 类型的事件。 通常,可以立即批准具有用户事件源的事件,以避免用户启动的操作发生延迟。 建议让主 VM 和辅助 VM 通信并批准用户生成的计划事件,以防主 VM 变得无响应。 立即审批事件可以防止在将应用程序恢复到良好状态的过程中出现的延迟。
只有支持内存保留更新的常规用途 VM 大小支持针对虚拟机规模集来宾 OS 升级或重置映像的计划事件。 它不适用于 G、M、N 和 H 系列。 默认情况下,虚拟机规模集来宾操作系统升级或重置映像的计划事件处于禁用状态。 要在支持的 VM 大小上为这些操作启用计划事件,请首先使用 OSImageNotificationProfile 启用它们。
使用 API
综合概述
处理 Scheduled Events 有两个主要组件:准备和恢复。 可通过 IMDS Scheduled Events 终结点读取所有影响 VM 的当前计划事件。 当事件达到终止状态后,将会从事件列表中将其移除。 下图显示了单个计划事件可能经历的各种状态转换:
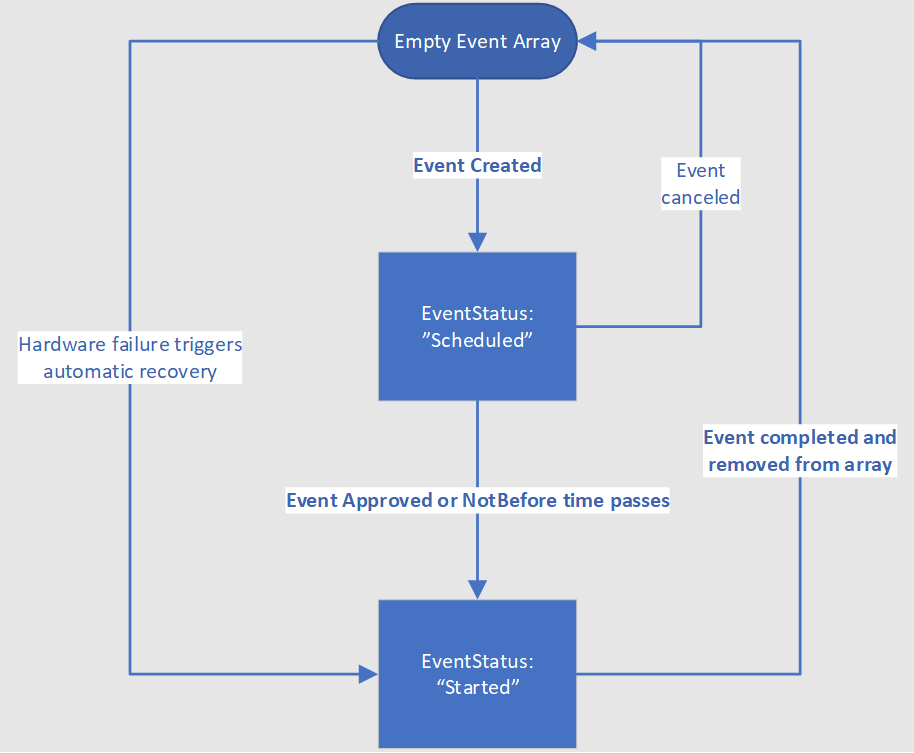
对于 EventStatus 为“Scheduled”状态的事件,需采取措施来准备工作负荷。 准备工作完成后,应使用计划事件 API 来审批事件。 否则,当到达 NotBefore 时间时,事件会自动获得批准。 如果 VM 位于共享基础结构上,则系统会等待同一硬件上的所有其他租户也批准该作业,直至超时。 一旦从所有受影响的 VM 收集审批或到达 NotBefore 时间,Azure 就会生成一个 EventStatus 为“Started”的新计划事件负载,触发维护事件。 当事件达到终止状态后,将会从事件列表中将其移除。 这是客户恢复其 VM 的信号。
下面是伪代码,演示了在应用程序中读取和管理计划事件的具体过程:
current_list_of_scheduled_events = get_latest_from_se_endpoint()
#prepare for new events
for each event in current_list_of_scheduled_events:
if event not in previous_list_of_scheduled_events:
prepare_for_event(event)
#recover from completed events
for each event in previous_list_of_scheduled_events:
if event not in current_list_of_scheduled_events:
receover_from_event(event)
#prepare for future jobs
previous_list_of_scheduled_events = current_list_of_scheduled_events
由于计划事件通常用于具有高可用性要求的应用程序,因此应考虑一些特殊情况:
- 计划事件完成并从数组中删除后,如果没有新事件(包括另一个 EventStatus 为“已计划”的事件),则不会产生进一步的影响
- Azure 会监视整个舰队的维护操作,在极少数情况下会作出维护操作因风险过高而无法应用的判断。 在这种情况下,计划事件将直接脱离“已计划”状态,被系统从事件数组中删除
- 如果出现硬件故障,Azure 会绕过“已计划”状态,立即转为 EventStatus 为“已启动”的状态。
- 虽然事件仍处于 EventStatus 为“已启动”的状态,但可能会有另一个影响:持续时间比计划事件中播发的持续时间要短。
不同容错域中的 VM 不可同时受到日常维护操作的影响,这是为了确保 Azure 的可用性。 但是,可以让这些操作一个接一个地连续进行。 一个容错域中的 VM 可以在另一个容错域的维护完成后不久接收 EventStatus 为“Scheduled”的计划事件。 无论选择哪种体系结构,请始终检查 VM 上是否有待处理的新事件。
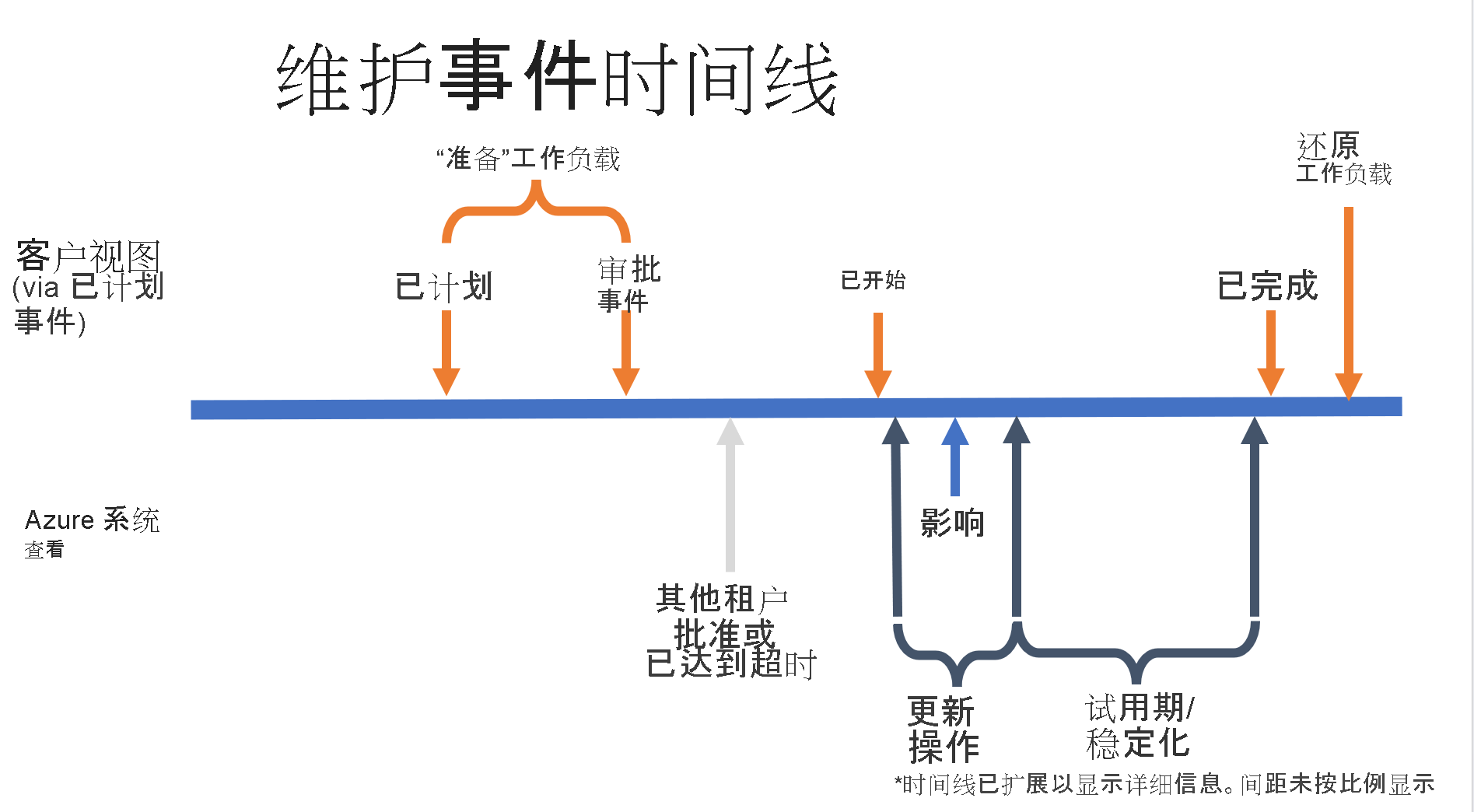
虽然事件的确切时间各不相同,但可以根据下图提供的粗略指南来了解典型的维护操作是如何进行的:
- EventStatus:“Scheduled”到“Approval Timeout”:15 分钟
- 影响持续时间:7 秒
- EventStatus:“Started”到“Completed”(事件从 Events 数组中删除):10 分钟
标头
查询元数据服务时,必须提供标头 Metadata:true 以确保不会在无意中重定向该请求。 Metadata:true 标头对于所有预定事件请求是必需的。 不在请求中包含标头会导致元数据服务发出的“错误的请求”响应。
查询事件
只需进行以下调用即可查询计划事件:
Bash 示例
curl -H Metadata:true http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents?api-version=2020-07-01
PowerShell 示例
Invoke-RestMethod -Headers @{"Metadata"="true"} -Method GET -Uri "http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents?api-version=2020-07-01" | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 64
Python 示例
import json
import requests
metadata_url ="http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents"
header = {'Metadata' : 'true'}
query_params = {'api-version':'2020-07-01'}
def get_scheduled_events():
resp = requests.get(metadata_url, headers = header, params = query_params)
data = resp.json()
return data
响应包含计划事件的数组。 数组为空意味着目前没有计划事件。 如果有计划事件,响应会包含事件的数组。
{
"DocumentIncarnation": {IncarnationID},
"Events": [
{
"EventId": {eventID},
"EventType": "Reboot" | "Redeploy" | "Freeze" | "Preempt" | "Terminate",
"ResourceType": "VirtualMachine",
"Resources": [{resourceName}],
"EventStatus": "Scheduled" | "Started",
"NotBefore": {timeInUTC},
"Description": {eventDescription},
"EventSource" : "Platform" | "User",
"DurationInSeconds" : {timeInSeconds},
}
]
}
事件属性
| Property | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 文档化身 | 当事件数组发生更改时增加的整数。 具有相同化身的文档包含相同的事件信息,当事件发生更改时,化身将递增。 |
| EventId | 此事件的全局唯一标识符。 示例:
|
| EventType | 此事件将导致的预期影响。 值:
|
| ResourceType | 此事件影响的资源类型。 值:
|
| 资源 | 此事件影响的资源列表。 示例:
|
| EventStatus | 此事件的状态。 值:
Completed 或类似状态。 事件完成后,将不再返回该事件。 |
| NotBefore | 在可以启动此事件之前所要经过的时间。 此事件保证在此时间之前不启动。 如果事件已启动,则为空 示例:
|
| 说明 | 此事件的说明。 示例:
|
| EventSource | 事件的发起者。 示例:
|
| DurationInSeconds | 事件导致的中断的预期持续时间。 在影响窗口期间,可能会产生持续时间较短的二次影响。 示例:
|
事件计划
将根据事件类型为每个事件计划将来的最小量时间。 此时间反映在某个事件的 NotBefore 属性上。
| EventType | 最小通知 |
|---|---|
| 冻结 | 15 分钟 |
| 重新启动 | 15 分钟 |
| 重新部署 | 10 分钟 |
| 终止 | 用户可配置:5 - 15 分钟 |
这意味着,可至少在事件发生前的最小通知时间检测到事件的未来计划。 计划了事件后,它将在获批或 NotBefore 时间过去后进入 Started 状态。 但是,在极少数情况下,Azure 会在操作开始之前将其取消。 在这种情况下,事件会从 Events 数组中删除,不会像以前计划的那样产生影响。
注意
在某些情况下,由于硬件降级,Azure 能够预测主机故障,并会尝试通过对迁移进行计划来缓解服务中断。 受影响的虚拟机会收到计划事件,该事件的 NotBefore 通常是将来几天的时间。 实际时间因预测的故障风险评估而异。 Azure 会尽可能提前 7 天发出通知,但实际时间可能会有变化,如果预测硬件即将发生故障的可能性很大,则实际时间可能更早。 为了在系统启动迁移之前硬件出现故障时将服务风险降至最低,我们建议你尽快自行重新部署虚拟机。
注意
如果主机节点遇到硬件失败,Azure 将绕过最短通知期,立即开始受影响虚拟机的恢复过程。 这减少了受影响 VM 无法响应情况下的恢复时间。 在恢复过程中,将为所有受影响的 VM 创建一个带有 EventType = Reboot 和 EventStatus = Started 的事件。
轮询频率
可根据需要频繁或偶尔轮询终结点以进行更新。 但是,两次请求之间的时间越长,你拥有的对即将发生的事件做出响应的时间就越少。 大多数事件都会提前 5 到 15 分钟通知,尽管在某些情况下,可能只会提前 30 秒通知。 为确保有尽可能多的时间采取缓解措施,我们建议你每秒轮询一次服务。
启动事件
了解即将发生的事件并完成正常关闭逻辑后,可以通过使用 EventId 对元数据服务进行 POST 调用来批准未完成的事件。 此调用指示 Azure 可以缩短最小通知时间(如可能)。 事件可能不会在获得批准后立即启动,在某些情况下,Azure 会要求节点上托管的所有 VM 都获得批准,然后才能继续该事件。
下面是 POST 请求正文中所需的 JSON 示例。 请求应包含 StartRequests 列表。 每个 StartRequest 包含想要加速的事件的 EventId:
{
"StartRequests" : [
{
"EventId": {EventId}
}
]
}
如果服务传递了某个有效的事件 ID,则即使另一个 VM 已批准该事件,服务也会始终返回成功代码 200。 400 错误代码指示请求标头或有效负载格式不正确。
注意
除非事件通过 POST 消息获得批准或 NotBefore 时间过去,否则事件不会继续。 这包括用户触发的事件,例如从 Azure 门户重启 VM。
Bash 示例
curl -H Metadata:true -X POST -d '{"StartRequests": [{"EventId": "f020ba2e-3bc0-4c40-a10b-86575a9eabd5"}]}' http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents?api-version=2020-07-01
PowerShell 示例
Invoke-RestMethod -Headers @{"Metadata" = "true"} -Method POST -body '{"StartRequests": [{"EventId": "5DD55B64-45AD-49D3-BBC9-F57D4EA97BD7"}]}' -Uri http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents?api-version=2020-07-01 | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 64
Python 示例
import json
import requests
def confirm_scheduled_event(event_id):
# This payload confirms a single event with id event_id
payload = json.dumps({"StartRequests": [{"EventId": event_id }]})
response = requests.post("http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents",
headers = {'Metadata' : 'true'},
params = {'api-version':'2020-07-01'},
data = payload)
return response.status_code
注意
确认事件后,即可允许事件针对事件中所有的 Resources 继续进行,而不仅仅是确认该事件的 VM。 因此,可以选择一个指挥计算机来协调该确认,为简单起见,可选择 Resources 字段中的第一个计算机。
示例响应
以下事件是实时迁移到另一个节点的两个 VM 看到的内容的示例。
每次 Events 中有新信息时,DocumentIncarnation 都会发生更改。 事件的批准将允许继续对 WestNO_0 和 WestNO_1 进行冻结。 DurationInSeconds 为 -1 表示平台不知道操作需要多长时间。
{
"DocumentIncarnation": 1,
"Events": [
]
}
{
"DocumentIncarnation": 2,
"Events": [
{
"EventId": "C7061BAC-AFDC-4513-B24B-AA5F13A16123",
"EventStatus": "Scheduled",
"EventType": "Freeze",
"ResourceType": "VirtualMachine",
"Resources": [
"WestNO_0",
"WestNO_1"
],
"NotBefore": "Mon, 11 Apr 2022 22:26:58 GMT",
"Description": "Virtual machine is being paused because of a memory-preserving Live Migration operation.",
"EventSource": "Platform",
"DurationInSeconds": 5
}
]
}
{
"DocumentIncarnation": 3,
"Events": [
{
"EventId": "C7061BAC-AFDC-4513-B24B-AA5F13A16123",
"EventStatus": "Started",
"EventType": "Freeze",
"ResourceType": "VirtualMachine",
"Resources": [
"WestNO_0",
"WestNO_1"
],
"NotBefore": "",
"Description": "Virtual machine is being paused because of a memory-preserving Live Migration operation.",
"EventSource": "Platform",
"DurationInSeconds": 5
}
]
}
{
"DocumentIncarnation": 4,
"Events": [
]
}
Python 示例
下例将查询计划事件的元数据服务器并审核所有未完成的事件。
#!/usr/bin/python
import json
import requests
from time import sleep
# The URL to access the metadata service
metadata_url ="http://169.254.169.254/metadata/scheduledevents"
# This must be sent otherwise the request will be ignored
header = {'Metadata' : 'true'}
# Current version of the API
query_params = {'api-version':'2020-07-01'}
def get_scheduled_events():
resp = requests.get(metadata_url, headers = header, params = query_params)
data = resp.json()
return data
def confirm_scheduled_event(event_id):
# This payload confirms a single event with id event_id
# You can confirm multiple events in a single request if needed
payload = json.dumps({"StartRequests": [{"EventId": event_id }]})
response = requests.post(metadata_url,
headers= header,
params = query_params,
data = payload)
return response.status_code
def log(event):
# This is an optional placeholder for logging events to your system
print(event["Description"])
return
def advanced_sample(last_document_incarnation):
# Poll every second to see if there are new scheduled events to process
# Since some events may have necessarily short warning periods, it is
# recommended to poll frequently
found_document_incarnation = last_document_incarnation
while (last_document_incarnation == found_document_incarnation):
sleep(1)
payload = get_scheduled_events()
found_document_incarnation = payload["DocumentIncarnation"]
# We recommend processing all events in a document together,
# even if you won't be actioning on them right away
for event in payload["Events"]:
# Events that have already started, logged for tracking
if (event["EventStatus"] == "Started"):
log(event)
# Approve all user initiated events. These are typically created by an
# administrator and approving them immediately can help to avoid delays
# in admin actions
elif (event["EventSource"] == "User"):
confirm_scheduled_event(event["EventId"])
# For this application, freeze events less that 9 seconds are considered
# no impact. This will immediately approve them
elif (event["EventType"] == "Freeze" and
int(event["DurationInSeconds"]) >= 0 and
int(event["DurationInSeconds"]) < 9):
confirm_scheduled_event(event["EventId"])
# Events that may be impactful (for example reboot or redeploy) may need custom
# handling for your application
else:
#TODO Custom handling for impactful events
log(event)
print("Processed events from document: " + str(found_document_incarnation))
return found_document_incarnation
def main():
# This will track the last set of events seen
last_document_incarnation = "-1"
input_text = "\
Press 1 to poll for new events \n\
Press 2 to exit \n "
program_exit = False
while program_exit == False:
user_input = input(input_text)
if (user_input == "1"):
last_document_incarnation = advanced_sample(last_document_incarnation)
elif (user_input == "2"):
program_exit = True
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
后续步骤
- 在 Azure 实例元数据计划事件 GitHub 存储库中查看计划事件代码示例。
- 在 Azure 示例 GitHub 存储库中查看 Node.js Scheduled Events 代码示例。
- 详细了解实例元数据服务中提供的 API。
- 了解 Azure 中 Windows 虚拟机的计划内维护。
- 了解如何通过 Log Analytics 监视 VM 的计划事件。
- 在 Azure 示例 GitHub 存储库中了解如何使用 Azure 事件中心记录计划事件。