继承与封装和多态性一起是面向对象的编程的三个主要特征之一。 通过继承,可以创建新的类,以便重复使用、扩展和修改在其他类中定义的行为。 其成员继承的 类称为基类,继承这些成员的 类称为派生类。 派生类只能有一个直接基类。 但是,继承是可传递的。 如果ClassC派生自ClassB,并且ClassB派生自ClassA,ClassC则继承在ClassB和ClassA声明的成员。
注释
结构不支持继承,但它们可以实现接口。
从概念上讲,派生类是基类的专用化。 例如,如果你有一个基类 Animal,则可能有一个命名 Mammal 的派生类和另一个命名 Reptile的派生类。
Mammal 是一个 Animal,而 Reptile 是一个 Animal,但每个派生类表示对基类的不同专用化。
接口声明可以为其成员定义默认实现。 这些实现由派生接口和实现这些接口的类继承。 有关默认接口方法的详细信息,请参阅有关 接口的文章。
定义要从另一个类派生的类时,派生类会隐式获取基类的所有成员,其构造函数和终结器除外。 派生类重用基类中的代码,而无需重新实现它。 可以在派生类中添加更多成员。 派生类扩展基类的功能。
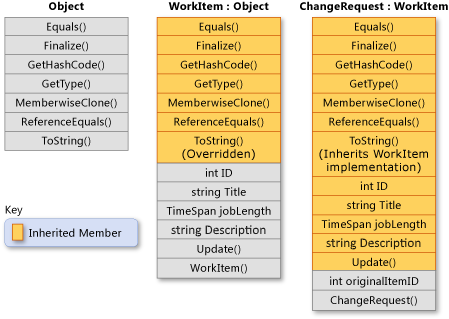
下图显示了一个类 WorkItem ,表示某些业务流程中的工作项。 像所有类一样,它从System.Object派生并继承了其所有方法。
WorkItem 会添加其自己的六个成员。 这些成员包括构造函数,因为构造函数不会继承。 类 ChangeRequest 继承自 WorkItem 并表示特定类型的工作项。
ChangeRequest 从 WorkItem 和 Object 中继承的成员之外再添加两个新成员。 它必须添加自己的构造函数,并且还会添加 originalItemID。 属性 originalItemID 使 ChangeRequest 实例能够与更改请求应用到的原始 WorkItem 实例相关联。
下面的示例演示如何用 C# 表示上图中所示的类关系。 该示例还演示了如何 WorkItem 重写虚拟方法 Object.ToString,以及类如何 ChangeRequest 继承 WorkItem 该方法的实现。 第一个块定义类:
// WorkItem implicitly inherits from the Object class.
public class WorkItem
{
// Static field currentID stores the job ID of the last WorkItem that
// has been created.
private static int currentID;
//Properties.
protected int ID { get; set; }
protected string Title { get; set; }
protected string Description { get; set; }
protected TimeSpan jobLength { get; set; }
// Default constructor. If a derived class does not invoke a base-
// class constructor explicitly, the default constructor is called
// implicitly.
public WorkItem()
{
ID = 0;
Title = "Default title";
Description = "Default description.";
jobLength = new TimeSpan();
}
// Instance constructor that has three parameters.
public WorkItem(string title, string desc, TimeSpan joblen)
{
ID = GetNextID();
Title = title;
Description = desc;
jobLength = joblen;
}
// Static constructor to initialize the static member, currentID. This
// constructor is called one time, automatically, before any instance
// of WorkItem or ChangeRequest is created, or currentID is referenced.
static WorkItem() => currentID = 0;
// currentID is a static field. It is incremented each time a new
// instance of WorkItem is created.
protected int GetNextID() => ++currentID;
// Method Update enables you to update the title and job length of an
// existing WorkItem object.
public void Update(string title, TimeSpan joblen)
{
this.Title = title;
this.jobLength = joblen;
}
// Virtual method override of the ToString method that is inherited
// from System.Object.
public override string ToString() =>
$"{this.ID} - {this.Title}";
}
// ChangeRequest derives from WorkItem and adds a property (originalItemID)
// and two constructors.
public class ChangeRequest : WorkItem
{
protected int originalItemID { get; set; }
// Constructors. Because neither constructor calls a base-class
// constructor explicitly, the default constructor in the base class
// is called implicitly. The base class must contain a default
// constructor.
// Default constructor for the derived class.
public ChangeRequest() { }
// Instance constructor that has four parameters.
public ChangeRequest(string title, string desc, TimeSpan jobLen,
int originalID)
{
// The following properties and the GetNexID method are inherited
// from WorkItem.
this.ID = GetNextID();
this.Title = title;
this.Description = desc;
this.jobLength = jobLen;
// Property originalItemID is a member of ChangeRequest, but not
// of WorkItem.
this.originalItemID = originalID;
}
}
下一个块演示如何使用基类和派生类:
// Create an instance of WorkItem by using the constructor in the
// base class that takes three arguments.
WorkItem item = new("Fix Bugs",
"Fix all bugs in my code branch",
new TimeSpan(3, 4, 0, 0));
// Create an instance of ChangeRequest by using the constructor in
// the derived class that takes four arguments.
ChangeRequest change = new("Change Base Class Design",
"Add members to the class",
new TimeSpan(4, 0, 0),
1);
// Use the ToString method defined in WorkItem.
Console.WriteLine(item.ToString());
// Use the inherited Update method to change the title of the
// ChangeRequest object.
change.Update("Change the Design of the Base Class",
new TimeSpan(4, 0, 0));
// ChangeRequest inherits WorkItem's override of ToString.
Console.WriteLine(change.ToString());
/* Output:
1 - Fix Bugs
2 - Change the Design of the Base Class
*/
抽象和虚拟方法
基类将方法声明为 virtual 时,派生类可以使用其自己的实现override该方法。 如果基类将成员声明为 abstract,则必须在直接继承自该类的任何非抽象类中重写该方法。 如果派生类本身是抽象类,则它继承抽象成员而不实现它们。 抽象和虚拟成员是多态性的基础,这是面向对象的编程的第二个主要特征。 有关详细信息,请参阅 多态性。
抽象基类
如果要使用新运算符防止直接实例化,则可以将类声明为抽象类。 仅当新类派生自抽象类时,才能使用抽象类。 抽象类可以包含一个或多个本身声明为抽象的方法签名。 这些签名指定参数和返回值,但没有实现(方法正文)。 抽象类不必包含抽象成员;但是,如果类确实包含抽象成员,则必须将类本身声明为抽象成员。 不是抽象本身的派生类必须为抽象基类中的任何抽象方法提供实现。
接口
接口是定义一组成员的引用类型。 实现该接口的所有类和结构都必须实现该成员集。 接口可能为其中任何成员或全部成员定义默认实现。 即使类只能从单个直接基类派生,也可以实现多个接口。
接口用于为不一定具有“是”关系的类定义特定功能。 例如, System.IEquatable<T> 接口可由任何类或结构实现,以确定该类型的两个对象是否等效(但类型定义等效性)。
IEquatable<T> 不表示基类和派生类之间存在的同一种“是”关系(例如,Mammal 是 Animal)。 有关详细信息,请参阅 接口。
防止进一步派生
类可以通过将自身或成员声明为 sealed 来防止其他类继承自它或其任何成员。
基类成员的派生类隐藏
派生类可以通过声明具有相同名称和签名的成员来隐藏基类成员。
new 修饰符可以用于显式指示成员不应作为基类成员的重写。 未必需要使用 new,但如果不使用 new,则会生成编译器警告。 有关详细信息,请参阅 使用重写和新关键字进行版本控制 以及 了解何时使用重写和新关键字。
