只需执行几个步骤,即可在 Python、.NET 或 Java 中使用语义内核生成第一个 AI 代理。 本指南将介绍如何...
- 安装所需的包
- 使用 AI 创建来回对话
- 使 AI 代理能够运行代码
- 观看 AI 动态创建计划
安装 SDK
语义内核有多个 NuGet 包可用。 但是,对于大多数方案,通常只需要 Microsoft.SemanticKernel。
可以使用以下命令安装它:
dotnet add package Microsoft.SemanticKernel
有关 Nuget 包的完整列表,请参阅 支持的语言文章。
此处SemanticKernel有关访问 Java 包的说明。 它非常简单:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.semantic-kernel</groupId>
<artifactId>semantickernel-bom</artifactId>
<version>${sk.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.semantic-kernel</groupId>
<artifactId>semantickernel-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.semantic-kernel</groupId>
<artifactId>semantickernel-aiservices-openai</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
快速开始使用笔记本
如果你是 Python 或 C# 开发人员,则可以快速开始使用我们的笔记本。 这些笔记本提供了有关如何使用语义内核生成 AI 代理的分步指南。

要开始,请按照以下步骤操作:
- 克隆语义内核存储库
- 在 Visual Studio Code 中打开存储库
- 导航到 _/python/samples/getting_started
- 打开 00-getting-started.ipynb 以开始设置环境并创建第一个 AI 代理!
要开始,请按照以下步骤操作:
- 克隆语义内核存储库
- 在 Visual Studio Code 中打开存储库
- 导航到 _/dotnet/notebooks
- 打开 00-getting-started.ipynb 以开始设置环境并创建第一个 AI 代理!
编写第一个控制台应用
- 使用以下命令创建新的 .NET 控制台项目:
dotnet new console
- 安装以下 .NET 依赖项:
dotnet add package Microsoft.SemanticKernel
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Logging
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Console
- 将
Program.cs文件的内容替换为以下代码:
// Import packages
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.ChatCompletion;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Connectors.OpenAI;
// Populate values from your OpenAI deployment
var modelId = "";
var endpoint = "";
var apiKey = "";
// Create a kernel with Azure OpenAI chat completion
var builder = Kernel.CreateBuilder().AddAzureOpenAIChatCompletion(modelId, endpoint, apiKey);
// Add enterprise components
builder.Services.AddLogging(services => services.AddConsole().SetMinimumLevel(LogLevel.Trace));
// Build the kernel
Kernel kernel = builder.Build();
var chatCompletionService = kernel.GetRequiredService<IChatCompletionService>();
// Add a plugin (the LightsPlugin class is defined below)
kernel.Plugins.AddFromType<LightsPlugin>("Lights");
// Enable planning
OpenAIPromptExecutionSettings openAIPromptExecutionSettings = new()
{
FunctionChoiceBehavior = FunctionChoiceBehavior.Auto()
};
// Create a history store the conversation
var history = new ChatHistory();
// Initiate a back-and-forth chat
string? userInput;
do {
// Collect user input
Console.Write("User > ");
userInput = Console.ReadLine();
// Add user input
history.AddUserMessage(userInput);
// Get the response from the AI
var result = await chatCompletionService.GetChatMessageContentAsync(
history,
executionSettings: openAIPromptExecutionSettings,
kernel: kernel);
// Print the results
Console.WriteLine("Assistant > " + result);
// Add the message from the agent to the chat history
history.AddMessage(result.Role, result.Content ?? string.Empty);
} while (userInput is not null);
import asyncio
from semantic_kernel import Kernel
from semantic_kernel.utils.logging import setup_logging
from semantic_kernel.functions import kernel_function
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.open_ai import AzureChatCompletion
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.function_choice_behavior import FunctionChoiceBehavior
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.chat_completion_client_base import ChatCompletionClientBase
from semantic_kernel.contents.chat_history import ChatHistory
from semantic_kernel.functions.kernel_arguments import KernelArguments
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.open_ai.prompt_execution_settings.azure_chat_prompt_execution_settings import (
AzureChatPromptExecutionSettings,
)
async def main():
# Initialize the kernel
kernel = Kernel()
# Add Azure OpenAI chat completion
chat_completion = AzureChatCompletion(
deployment_name="your_models_deployment_name",
api_key="your_api_key",
base_url="your_base_url",
)
kernel.add_service(chat_completion)
# Set the logging level for semantic_kernel.kernel to DEBUG.
setup_logging()
logging.getLogger("kernel").setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# Add a plugin (the LightsPlugin class is defined below)
kernel.add_plugin(
LightsPlugin(),
plugin_name="Lights",
)
# Enable planning
execution_settings = AzureChatPromptExecutionSettings()
execution_settings.function_choice_behavior = FunctionChoiceBehavior.Auto()
# Create a history of the conversation
history = ChatHistory()
# Initiate a back-and-forth chat
userInput = None
while True:
# Collect user input
userInput = input("User > ")
# Terminate the loop if the user says "exit"
if userInput == "exit":
break
# Add user input to the history
history.add_user_message(userInput)
# Get the response from the AI
result = await chat_completion.get_chat_message_content(
chat_history=history,
settings=execution_settings,
kernel=kernel,
)
# Print the results
print("Assistant > " + str(result))
# Add the message from the agent to the chat history
history.add_message(result)
# Run the main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
OpenAIAsyncClient client = new OpenAIClientBuilder()
.credential(new AzureKeyCredential(AZURE_CLIENT_KEY))
.endpoint(CLIENT_ENDPOINT)
.buildAsyncClient();
// Import the LightsPlugin
KernelPlugin lightPlugin = KernelPluginFactory.createFromObject(new LightsPlugin(),
"LightsPlugin");
// Create your AI service client
ChatCompletionService chatCompletionService = OpenAIChatCompletion.builder()
.withModelId(MODEL_ID)
.withOpenAIAsyncClient(client)
.build();
// Create a kernel with Azure OpenAI chat completion and plugin
Kernel kernel = Kernel.builder()
.withAIService(ChatCompletionService.class, chatCompletionService)
.withPlugin(lightPlugin)
.build();
// Add a converter to the kernel to show it how to serialise LightModel objects into a prompt
ContextVariableTypes
.addGlobalConverter(
ContextVariableTypeConverter.builder(LightModel.class)
.toPromptString(new Gson()::toJson)
.build());
// Enable planning
InvocationContext invocationContext = new InvocationContext.Builder()
.withReturnMode(InvocationReturnMode.LAST_MESSAGE_ONLY)
.withToolCallBehavior(ToolCallBehavior.allowAllKernelFunctions(true))
.build();
// Create a history to store the conversation
ChatHistory history = new ChatHistory();
// Initiate a back-and-forth chat
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String userInput;
do {
// Collect user input
System.out.print("User > ");
userInput = scanner.nextLine();
// Add user input
history.addUserMessage(userInput);
// Prompt AI for response to users input
List<ChatMessageContent<?>> results = chatCompletionService
.getChatMessageContentsAsync(history, kernel, invocationContext)
.block();
for (ChatMessageContent<?> result : results) {
// Print the results
if (result.getAuthorRole() == AuthorRole.ASSISTANT && result.getContent() != null) {
System.out.println("Assistant > " + result);
}
// Add the message from the agent to the chat history
history.addMessage(result);
}
} while (userInput != null && !userInput.isEmpty());
以下来回聊天应类似于你在控制台中看到的内容。 下面添加了函数调用,以演示 AI 如何在后台利用插件。
| 角色 | 消息 |
|---|---|
| 🔵 用户 | 请切换灯 |
| 🔴 助手(函数调用) | LightsPlugin.GetState() |
| 🟢 工具 | off |
| 🔴 助手(函数调用) | LightsPlugin.ChangeState(true) |
| 🟢 工具 | on |
| 🔴 助手 | 灯现在打开 |
如果有兴趣了解有关上述代码的详细信息,我们将在下一部分中将其分解。
了解代码
为了更轻松地开始使用语义内核构建企业应用,我们创建了一个分步指导你完成创建内核的过程,并使用它与 AI 服务交互。

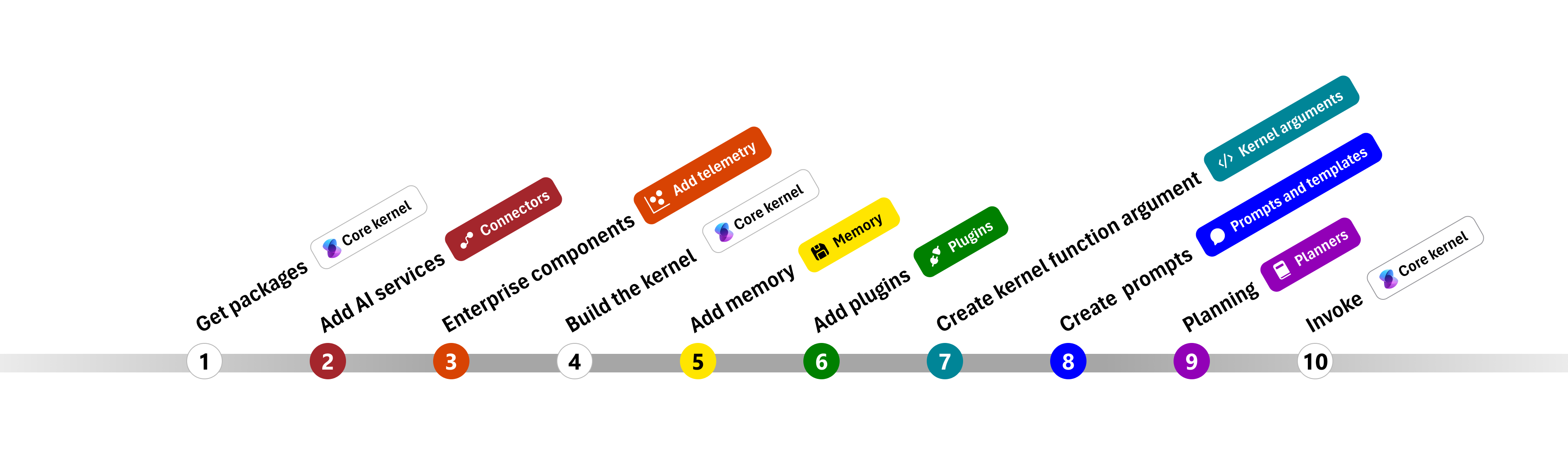
在以下部分中,我们将通过演练步骤 1、2、3、4、6、9 和 10 来解包上述示例。 构建由 AI 服务提供支持且可以运行代码的简单代理所需的一切。
1) 导入包
对于此示例,我们首先导入以下包:
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.ChatCompletion;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Connectors.OpenAI;
import asyncio
from semantic_kernel import Kernel
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.open_ai import AzureChatCompletion
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.function_choice_behavior import FunctionChoiceBehavior
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.chat_completion_client_base import ChatCompletionClientBase
from semantic_kernel.contents.chat_history import ChatHistory
from semantic_kernel.functions.kernel_arguments import KernelArguments
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.open_ai.prompt_execution_settings.azure_chat_prompt_execution_settings import (
AzureChatPromptExecutionSettings,
)
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.Kernel;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.aiservices.openai.chatcompletion.OpenAIChatCompletion;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.contextvariables.ContextVariableTypeConverter;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.contextvariables.ContextVariableTypes;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.orchestration.InvocationContext;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.orchestration.InvocationReturnMode;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.orchestration.ToolCallBehavior;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.plugin.KernelPlugin;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.plugin.KernelPluginFactory;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.services.chatcompletion.AuthorRole;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.services.chatcompletion.ChatCompletionService;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.services.chatcompletion.ChatHistory;
import com.microsoft.semantickernel.services.chatcompletion.ChatMessageContent;
2) 添加 AI 服务
之后,我们将添加内核最重要的部分:要使用的 AI 服务。 在此示例中,我们向内核生成器添加了 Azure OpenAI 聊天完成服务。
注意
在此示例中,我们使用了 Azure OpenAI,但可以使用任何其他聊天完成服务。 若要查看受支持的服务的完整列表,请参阅 支持的语言文章。 如果需要创建其他服务的帮助,请参阅 AI 服务文章。 你将在此处找到有关如何将 OpenAI 或 Azure OpenAI 模型用作服务的指南。
// Create kernel
var builder = Kernel.CreateBuilder()
builder.AddAzureOpenAIChatCompletion(modelId, endpoint, apiKey);
# Initialize the kernel
kernel = Kernel()
# Add Azure OpenAI chat completion
kernel.add_service(AzureChatCompletion(
deployment_name="your_models_deployment_name",
api_key="your_api_key",
base_url="your_base_url",
))
// Create your AI service client
ChatCompletionService chatCompletionService = OpenAIChatCompletion.builder()
.withModelId(MODEL_ID)
.withOpenAIAsyncClient(client)
.build();
// Create a kernel with Azure OpenAI chat completion and plugin
Kernel kernel = Kernel.builder()
.withAIService(ChatCompletionService.class, chatCompletionService)
.withPlugin(lightPlugin)
.build();
3) 添加企业服务
使用语义内核的主要优点之一是它支持企业级服务。 在此示例中,我们已将日志记录服务添加到内核,以帮助调试 AI 代理。
builder.Services.AddLogging(services => services.AddConsole().SetMinimumLevel(LogLevel.Trace));
import logging
# Set the logging level for semantic_kernel.kernel to DEBUG.
logging.basicConfig(
format="[%(asctime)s - %(name)s:%(lineno)d - %(levelname)s] %(message)s",
datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",
)
logging.getLogger("kernel").setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
4) 生成内核并检索服务
添加服务后,我们生成内核并检索聊天完成服务供以后使用。
Kernel kernel = builder.Build();
// Retrieve the chat completion service
var chatCompletionService = kernel.Services.GetRequiredService<IChatCompletionService>();
配置内核后,我们将检索聊天完成服务供以后使用。
注意
在 Python 中,无需显式生成内核。 相反,可以直接从内核对象访问服务。
chat_completion : AzureChatCompletion = kernel.get_service(type=ChatCompletionClientBase)
// Create a kernel with Azure OpenAI chat completion and plugin
Kernel kernel = Kernel.builder()
.withAIService(ChatCompletionService.class, chatCompletionService)
.withPlugin(lightPlugin)
.build();
6) 添加插件
借助插件,AI 代理可以运行代码,从外部源检索信息或执行操作。 在上面的示例中,我们添加了一个插件,允许 AI 代理与灯泡交互。 下面,我们将演示如何创建此插件。
创建本机插件
下面可以看到,创建本机插件与创建新类一样简单。
在此示例中,我们创建了一个可以操作灯泡的插件。 虽然这是一个简单的示例,但此插件快速演示了如何支持这两者...
在自己的代码中,可以创建与任何外部服务或 API 交互的插件,以实现类似的结果。
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel;
public class LightsPlugin
{
// Mock data for the lights
private readonly List<LightModel> lights = new()
{
new LightModel { Id = 1, Name = "Table Lamp", IsOn = false },
new LightModel { Id = 2, Name = "Porch light", IsOn = false },
new LightModel { Id = 3, Name = "Chandelier", IsOn = true }
};
[KernelFunction("get_lights")]
[Description("Gets a list of lights and their current state")]
public async Task<List<LightModel>> GetLightsAsync()
{
return lights;
}
[KernelFunction("change_state")]
[Description("Changes the state of the light")]
public async Task<LightModel?> ChangeStateAsync(int id, bool isOn)
{
var light = lights.FirstOrDefault(light => light.Id == id);
if (light == null)
{
return null;
}
// Update the light with the new state
light.IsOn = isOn;
return light;
}
}
public class LightModel
{
[JsonPropertyName("id")]
public int Id { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("name")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("is_on")]
public bool? IsOn { get; set; }
}
from typing import Annotated
from semantic_kernel.functions import kernel_function
class LightsPlugin:
lights = [
{"id": 1, "name": "Table Lamp", "is_on": False},
{"id": 2, "name": "Porch light", "is_on": False},
{"id": 3, "name": "Chandelier", "is_on": True},
]
@kernel_function(
name="get_lights",
description="Gets a list of lights and their current state",
)
def get_state(
self,
) -> str:
"""Gets a list of lights and their current state."""
return self.lights
@kernel_function(
name="change_state",
description="Changes the state of the light",
)
def change_state(
self,
id: int,
is_on: bool,
) -> str:
"""Changes the state of the light."""
for light in self.lights:
if light["id"] == id:
light["is_on"] = is_on
return light
return None
public class LightsPlugin {
// Mock data for the lights
private final Map<Integer, LightModel> lights = new HashMap<>();
public LightsPlugin() {
lights.put(1, new LightModel(1, "Table Lamp", false));
lights.put(2, new LightModel(2, "Porch light", false));
lights.put(3, new LightModel(3, "Chandelier", true));
}
@DefineKernelFunction(name = "get_lights", description = "Gets a list of lights and their current state")
public List<LightModel> getLights() {
System.out.println("Getting lights");
return new ArrayList<>(lights.values());
}
@DefineKernelFunction(name = "change_state", description = "Changes the state of the light")
public LightModel changeState(
@KernelFunctionParameter(name = "id", description = "The ID of the light to change") int id,
@KernelFunctionParameter(name = "isOn", description = "The new state of the light") boolean isOn) {
System.out.println("Changing light " + id + " " + isOn);
if (!lights.containsKey(id)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Light not found");
}
lights.get(id).setIsOn(isOn);
return lights.get(id);
}
}
将插件添加到内核
创建插件后,可以将其添加到内核,以便 AI 代理可以访问它。 在本示例中,我们已将 LightsPlugin 类添加到内核。
// Add the plugin to the kernel
kernel.Plugins.AddFromType<LightsPlugin>("Lights");
# Add the plugin to the kernel
kernel.add_plugin(
LightsPlugin(),
plugin_name="Lights",
)
// Import the LightsPlugin
KernelPlugin lightPlugin = KernelPluginFactory.createFromObject(new LightsPlugin(),
"LightsPlugin");
9) 规划
语义内核利用 函数调用(大多数 LLM 的本机功能)来提供 规划。 使用函数调用,LLM 可以请求(或调用)特定函数以满足用户的请求。 然后,语义内核将请求封送至代码库中的相应函数,并将结果返回给 LLM,以便 AI 代理可以生成最终响应。
若要启用自动函数调用,首先需要创建适当的执行设置,以便语义内核知道在 AI 代理请求函数时自动调用内核中的函数。
OpenAIPromptExecutionSettings openAIPromptExecutionSettings = new()
{
FunctionChoiceBehavior = FunctionChoiceBehavior.Auto()
};
execution_settings = AzureChatPromptExecutionSettings()
execution_settings.function_choice_behavior = FunctionChoiceBehavior.Auto()
// Enable planning
InvocationContext invocationContext = new InvocationContext.Builder()
.withReturnMode(InvocationReturnMode.LAST_MESSAGE_ONLY)
.withToolCallBehavior(ToolCallBehavior.allowAllKernelFunctions(true))
.build();
10) 调用
最后,我们使用插件调用 AI 代理。 示例代码演示如何生成非流式处理响应,但也可以使用该方法生成流式处理响应GetStreamingChatMessageContentAsync。
// Create chat history
var history = new ChatHistory();
// Get the response from the AI
var result = await chatCompletionService.GetChatMessageContentAsync(
history,
executionSettings: openAIPromptExecutionSettings,
kernel: kernel
);
使用以下命令运行程序:
dotnet run
# Create a history of the conversation
history = ChatHistory()
# Get the response from the AI
result = (await chat_completion.get_chat_message_contents(
chat_history=history,
settings=execution_settings,
kernel=kernel,
arguments=KernelArguments(),
))[0]
userInput = scanner.nextLine();
// Add user input
history.addUserMessage(userInput);
// Prompt AI for response to users input
List<ChatMessageContent<?>> results = chatCompletionService
.getChatMessageContentsAsync(history, kernel, invocationContext)
.block();
后续步骤
本指南介绍了如何通过构建可与 AI 服务交互并运行代码的简单 AI 代理快速开始使用语义内核。 若要查看更多示例并了解如何构建更复杂的 AI 代理,请查看我们的 深入示例。