适用于: SQL Server 2017 (14.x) 及更高版本
Azure SQL 托管实例
本教程系列由四个部分组成。在第四部分中,你将使用机器学习服务或大数据群集将在 Python 中开发的线性回归模型部署到 SQL Server 数据库中。
本教程系列由四个部分组成,在第四部分中,你将使用机器学习服务将在 Python 中开发的线性回归模型部署到 SQL Server 数据库中。
本教程系列由四个部分组成,在第四部分中,将使用机器学习服务将在 Python 中开发的线性回归模型部署到 Azure SQL 托管实例数据库。
本文将指导如何进行以下操作:
- 创建生成机器学习模型的存储过程
- 将模型存储在数据库表中
- 创建使用模型进行预测的存储过程
- 使用新数据执行模型
在第一部分中,你了解了如何还原示例数据库。
在第二部分中,你了解了如何将数据从数据库加载到 Python 数据帧中,并在 Python 中准备数据。
在第三部分中,你了解了如何在 Python 中定型线性回归机器学习模型。
先决条件
- 本教程的第四部分假设你已完成了第一部分和其中的必备条件。
创建生成模型的存储过程
现在,使用你开发的 Python 脚本来创建存储过程 generate_rental_py_model,此存储过程使用 scikit-learn 中的 LinearRegression 来训练和生成线性回归模型。
在 Azure Data Studio 中运行以下 T-SQL 语句,从而创建存储过程来定型模型。
-- Stored procedure that trains and generates a Python model using the rental_data and a linear regression algorithm
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS generate_rental_py_model;
go
CREATE PROCEDURE generate_rental_py_model (@trained_model varbinary(max) OUTPUT)
AS
BEGIN
EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script
@language = N'Python'
, @script = N'
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import pickle
df = rental_train_data
# Get all the columns from the dataframe.
columns = df.columns.tolist()
# Store the variable well be predicting on.
target = "RentalCount"
# Initialize the model class.
lin_model = LinearRegression()
# Fit the model to the training data.
lin_model.fit(df[columns], df[target])
# Before saving the model to the DB table, convert it to a binary object
trained_model = pickle.dumps(lin_model)'
, @input_data_1 = N'select "RentalCount", "Year", "Month", "Day", "WeekDay", "Snow", "Holiday" from dbo.rental_data where Year < 2015'
, @input_data_1_name = N'rental_train_data'
, @params = N'@trained_model varbinary(max) OUTPUT'
, @trained_model = @trained_model OUTPUT;
END;
GO
将模型存储在数据库表中
在 TutorialDB 数据库中创建一个表,然后将模型保存到表中。
在 Azure Data Studio 中运行以下 T-SQL 语句来创建名为 dbo.rental_py_models 的表,用于存储模型。
USE TutorialDB; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS dbo.rental_py_models; GO CREATE TABLE dbo.rental_py_models ( model_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT('default model') PRIMARY KEY, model VARBINARY(MAX) NOT NULL ); GO将模型作为二进制对象保存到表中,模型名为 linear_model。
DECLARE @model VARBINARY(MAX); EXECUTE generate_rental_py_model @model OUTPUT; INSERT INTO rental_py_models (model_name, model) VALUES('linear_model', @model);
创建进行预测的存储过程
创建存储过程 py_predict_rentalcount,此过程会使用已定型的模型和一组新数据来进行预测。 在 Azure Data Studio 中运行以下 T-SQL。
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS py_predict_rentalcount; GO CREATE PROCEDURE py_predict_rentalcount (@model varchar(100)) AS BEGIN DECLARE @py_model varbinary(max) = (select model from rental_py_models where model_name = @model); EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script @language = N'Python', @script = N' # Import the scikit-learn function to compute error. from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error import pickle import pandas rental_model = pickle.loads(py_model) df = rental_score_data # Get all the columns from the dataframe. columns = df.columns.tolist() # Variable you will be predicting on. target = "RentalCount" # Generate the predictions for the test set. lin_predictions = rental_model.predict(df[columns]) print(lin_predictions) # Compute error between the test predictions and the actual values. lin_mse = mean_squared_error(lin_predictions, df[target]) #print(lin_mse) predictions_df = pandas.DataFrame(lin_predictions) OutputDataSet = pandas.concat([predictions_df, df["RentalCount"], df["Month"], df["Day"], df["WeekDay"], df["Snow"], df["Holiday"], df["Year"]], axis=1) ' , @input_data_1 = N'Select "RentalCount", "Year" ,"Month", "Day", "WeekDay", "Snow", "Holiday" from rental_data where Year = 2015' , @input_data_1_name = N'rental_score_data' , @params = N'@py_model varbinary(max)' , @py_model = @py_model with result sets (("RentalCount_Predicted" float, "RentalCount" float, "Month" float,"Day" float,"WeekDay" float,"Snow" float,"Holiday" float, "Year" float)); END; GO创建用于存储预测的表。
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS [dbo].[py_rental_predictions]; GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[py_rental_predictions]( [RentalCount_Predicted] [int] NULL, [RentalCount_Actual] [int] NULL, [Month] [int] NULL, [Day] [int] NULL, [WeekDay] [int] NULL, [Snow] [int] NULL, [Holiday] [int] NULL, [Year] [int] NULL ) ON [PRIMARY] GO执行此存储过程来预测租赁计数
--Insert the results of the predictions for test set into a table INSERT INTO py_rental_predictions EXEC py_predict_rentalcount 'linear_model'; -- Select contents of the table SELECT * FROM py_rental_predictions;可得到类似于下面的结果。
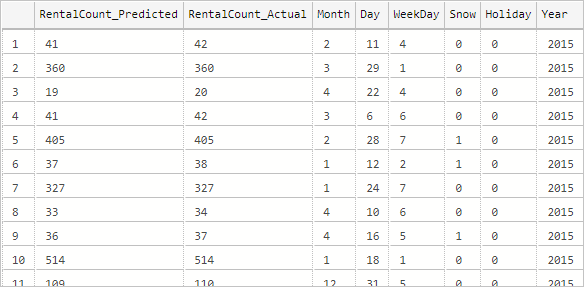
你已成功创建、训练并部署了一个模型。 然后,你在存储过程中使用了该模型来基于新数据对值进行预测。
后续步骤
在本教程系列的第四部分中,你完成了这些步骤:
- 创建生成机器学习模型的存储过程
- 将模型存储在数据库表中
- 创建使用模型进行预测的存储过程
- 使用新数据执行模型
若要详细了解如何通过 SQL 机器学习使用 Python,请参阅: