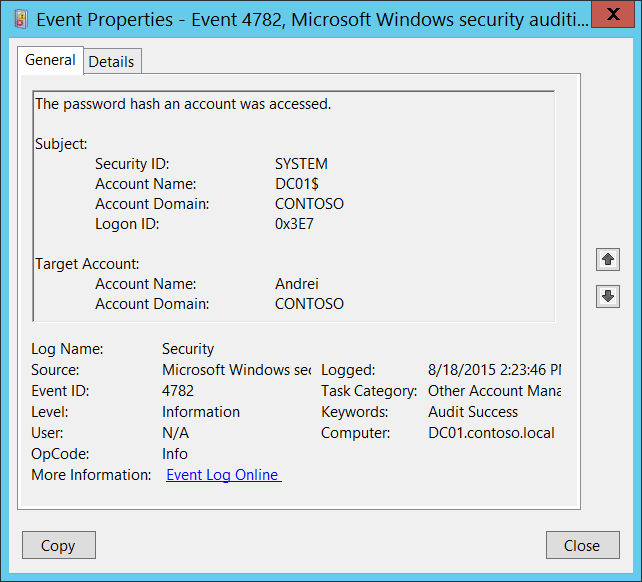
4782(S): The password hash of an account was accessed.
Subcategory: Audit Other Account Management Events
Event Description:
This event generates on domain controllers during password migration of an account using Active Directory Migration Toolkit.
Typically “Subject\Security ID” is the SYSTEM account.
Note For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
- <Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event">
- <System>
<Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" />
<EventID>4782</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>13829</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8020000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2015-08-18T21:23:46.435367800Z" />
<EventRecordID>174829</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID="512" ThreadID="1232" />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>DC01.contoso.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
- <EventData>
<Data Name="TargetUserName">Andrei</Data>
<Data Name="TargetDomainName">CONTOSO</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectUserSid">S-1-5-18</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectUserName">DC01$</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectDomainName">CONTOSO</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectLogonId">0x3e7</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Required Server Roles: Active Directory domain controller.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Subject:
- Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of account that requested hash migration operation. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
Note A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers.
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that requested hash migration operation.
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: subject’s domain name. Formats vary, and include the following:
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
For ANONYMOUS LOGON you will see NT AUTHORITY value for this field.
Logon ID [Type = HexInt64]: hexadecimal value that can help you correlate this event with recent events that might contain the same Logon ID, for example, “4624: An account was successfully logged on.”
Target Account:
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account for which the password hash was migrated. For example: ServiceDesk
User account example: Andrei
Computer account example: DC01$
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: domain name of the account for which the password hash was migrated. Formats vary, and include the following:
Domain NETBIOS name example: FABRIKAM
Lowercase full domain name: fabrikam.local
Uppercase full domain name: FABRIKAM.LOCAL
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 4782(S): The password hash of an account was accessed.
- Monitor for all events of this type, because any actions with account’s password hashes should be planned. If this action was not planned, investigate the reason for the change.