將 HTTP 處理常式和模組遷移至 ASP.NET Core 中介軟體
本文說明如何將現有 ASP.NET HTTP 模組和處理常式從 system.webserver 移轉到 ASP.NET Core 中介軟體。
重新檢視模組和處理常式
在繼續討論 ASP.NET Core 中介軟體之前,讓我們先回顧一下 HTTP 模組和處理常式的運作方式:
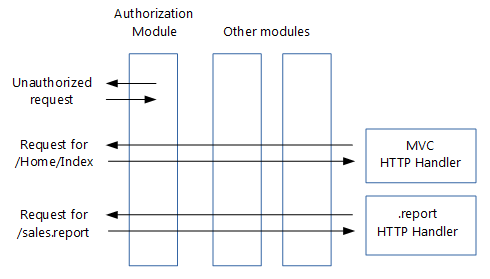
處理常式是:
實作 IHttpHandler 的類別
用來處理具有指定檔名或副檔名 (例如 .report) 的要求
在 Web.config 中設定
模組是:
實作 IHttpModule 的類別
針對每個要求叫用
能夠短路 (停止進一步處理要求)
能夠新增到 HTTP 回應,或建立自己的 HTTP 回應
在 Web.config 中設定
模組處理傳入要求的順序取決於:
ASP.NET 所引發的一系列事件 (例如 BeginRequest 和 AuthenticateRequest)。 如需完整的清單,請參閱 System.Web.HttpApplication。 每個模組都可以為一或多個事件建立一個處理常式。
對於相同的事件,它們在 Web.config 中設定的順序。
除了模組之外,您還可以將生命週期事件的處理常式新增至 Global.asax.cs 檔案。 這些處理常式會在設定的模組中的處理常式之後執行。
從處理常式和模組到中介軟體
中介軟體比 HTTP 模組和處理常式更簡單:
模組、處理常式、
Global.asax.cs、Web.config (IIS 組態除外) 和應用程式生命週期已消失模組和處理常式的角色都已由中介軟體接管
中介軟體是使用程式碼 (而不是在 Web.config 中) 設定
- 管線分支可讓您不僅可以基於 URL,還可以基於要求標頭、查詢字串等向特定中介軟體傳送要求。
- 管線分支可讓您不僅可以基於 URL,還可以基於要求標頭、查詢字串等向特定中介軟體傳送要求。
中介軟體與模組非常類似:
原則上針對每個要求叫用
能夠透過不將要求傳遞給下一個中介軟體來讓要求短路
能夠建立自己的 HTTP 回應
中介軟體和模組會以不同的順序處理:
中介軟體的順序是基於它們插入要求管線的順序,而模組的順序主要是基於System.Web.HttpApplication事件。
中介軟體對於回應的順序與對於要求的順序是相反的,而模組對於要求和回應的順序都是相同的
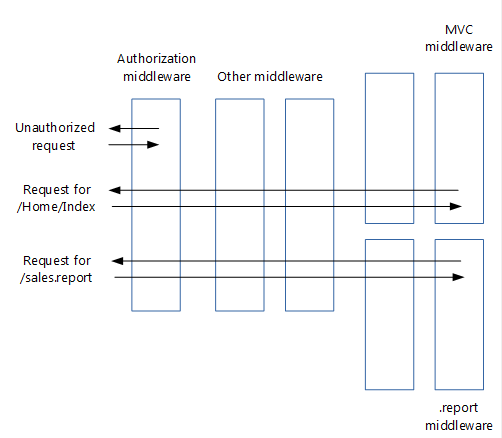
請注意在上圖中,驗證中介軟體如何讓要求短路。
將模組程式碼移轉至中介軟體
現有的 HTTP 模組看起來會像這樣:
// ASP.NET 4 module
using System;
using System.Web;
namespace MyApp.Modules
{
public class MyModule : IHttpModule
{
public void Dispose()
{
}
public void Init(HttpApplication application)
{
application.BeginRequest += (new EventHandler(this.Application_BeginRequest));
application.EndRequest += (new EventHandler(this.Application_EndRequest));
}
private void Application_BeginRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpContext context = ((HttpApplication)source).Context;
// Do something with context near the beginning of request processing.
}
private void Application_EndRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpContext context = ((HttpApplication)source).Context;
// Do something with context near the end of request processing.
}
}
}
如中介軟體頁面所示,ASP.NET Core 中介軟體是一個公開 Invoke 方法的類別 (該方法採用 HttpContext 並傳回 Task)。 您的新中介軟體看起來會像這樣:
// ASP.NET Core middleware
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyApp.Middleware
{
public class MyMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public MyMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
// Do something with context near the beginning of request processing.
await _next.Invoke(context);
// Clean up.
}
}
public static class MyMiddlewareExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMyMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder builder)
{
return builder.UseMiddleware<MyMiddleware>();
}
}
}
上面的中介軟體範本取自撰寫中介軟體上的區段。
MyMiddlewareExtensions 協助程式類別可讓您更輕鬆地在 Startup 類別中設定中介軟體。 UseMyMiddleware 方法會將您的中介軟體類別新增至要求管線。 中介軟體所需的服務會被插入中介軟體的建構函式中。
您的模組可能會終止要求,例如如果使用者未獲得授權:
// ASP.NET 4 module that may terminate the request
private void Application_BeginRequest(Object source, EventArgs e)
{
HttpContext context = ((HttpApplication)source).Context;
// Do something with context near the beginning of request processing.
if (TerminateRequest())
{
context.Response.End();
return;
}
}
中介軟體會透過不對管線中的下一個中介軟體呼叫 Invoke 來處理此狀況。 請記住,這不會完全終止要求,因為當回應透過管線返回時,仍會叫用先前的中介軟體。
// ASP.NET Core middleware that may terminate the request
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
// Do something with context near the beginning of request processing.
if (!TerminateRequest())
await _next.Invoke(context);
// Clean up.
}
當您將模組的功能移轉至新的中介軟體時,您可能會發現您的程式碼不會編譯,因為 HttpContext 類別在 ASP.NET Core 中已顯著變更。 稍後,您將了解如何移轉至新的 ASP.NET Core HttpCoNtext。
將模組插入移轉到要求管線
HTTP 模組通常會使用 Web.config 來新增至要求管線:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--ASP.NET 4 web.config-->
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<modules>
<add name="MyModule" type="MyApp.Modules.MyModule"/>
</modules>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
透過新增您的新中介軟體至 Startup 類別中的要求管線來轉換它:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
loggerFactory.AddDebug();
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseBrowserLink();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
}
app.UseMyMiddleware();
app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams();
var myMiddlewareOptions = Configuration.GetSection("MyMiddlewareOptionsSection").Get<MyMiddlewareOptions>();
var myMiddlewareOptions2 = Configuration.GetSection("MyMiddlewareOptionsSection2").Get<MyMiddlewareOptions>();
app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams(myMiddlewareOptions);
app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams(myMiddlewareOptions2);
app.UseMyTerminatingMiddleware();
// Create branch to the MyHandlerMiddleware.
// All requests ending in .report will follow this branch.
app.MapWhen(
context => context.Request.Path.ToString().EndsWith(".report"),
appBranch => {
// ... optionally add more middleware to this branch
appBranch.UseMyHandler();
});
app.MapWhen(
context => context.Request.Path.ToString().EndsWith(".context"),
appBranch => {
appBranch.UseHttpContextDemoMiddleware();
});
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
管線中您插入新中介軟體的確切位置取決於它作為模組處理的事件 (BeginRequest、EndRequest 等) 及其在 Web.config 中模組清單中的順序。
如先前所述,ASP.NET Core 中沒有任何應用程式生命週期,且中介軟體處理回應的順序與模組所使用的順序不同。 這可能會讓您的排序決定更具挑戰性。
如果排序成為一個問題,您可以將模組分割成多個可獨立排序的中介軟體元件。
將處理常式程式碼移轉至中介軟體
HTTP 處理常式看起來像這樣:
// ASP.NET 4 handler
using System.Web;
namespace MyApp.HttpHandlers
{
public class MyHandler : IHttpHandler
{
public bool IsReusable { get { return true; } }
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
string response = GenerateResponse(context);
context.Response.ContentType = GetContentType();
context.Response.Output.Write(response);
}
// ...
private string GenerateResponse(HttpContext context)
{
string title = context.Request.QueryString["title"];
return string.Format("Title of the report: {0}", title);
}
private string GetContentType()
{
return "text/plain";
}
}
}
在您的 ASP.NET Core 專案中,您可以將其轉換為類似於以下的中介軟體:
// ASP.NET Core middleware migrated from a handler
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyApp.Middleware
{
public class MyHandlerMiddleware
{
// Must have constructor with this signature, otherwise exception at run time
public MyHandlerMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
// This is an HTTP Handler, so no need to store next
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
string response = GenerateResponse(context);
context.Response.ContentType = GetContentType();
await context.Response.WriteAsync(response);
}
// ...
private string GenerateResponse(HttpContext context)
{
string title = context.Request.Query["title"];
return string.Format("Title of the report: {0}", title);
}
private string GetContentType()
{
return "text/plain";
}
}
public static class MyHandlerExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMyHandler(this IApplicationBuilder builder)
{
return builder.UseMiddleware<MyHandlerMiddleware>();
}
}
}
此中介軟體與對應至模組的中介軟體非常類似。 唯一真正的差別在於這裡沒有呼叫 _next.Invoke(context)。 這很合理,因為處理常式位於要求管線的末尾,因此不會有下一個要叫用的中介軟體。
將處理常式插入移轉至要求管線
設定 HTTP 處理常式是在 Web.config 中完成的,看起來像這樣:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--ASP.NET 4 web.config-->
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<handlers>
<add name="MyHandler" verb="*" path="*.report" type="MyApp.HttpHandlers.MyHandler" resourceType="Unspecified" preCondition="integratedMode"/>
</handlers>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
您可以透過將新的處理常式中介軟體新增至 Startup 類別中的要求管線來轉換它,類似於從模組轉換的中介軟體。 該方法的問題在於,它會將所有要求傳送至新的處理常式中介軟體。 不過,您只想要具有指定副檔名的要求到達您的中介軟體。 這將為您提供與 HTTP 處理常式相同的功能。
一種解決方案是使用 MapWhen 擴充方法為具有指定副檔名的要求來對管線進行分支。 您可以在新增其他中介軟體的相同 Configure 方法中執行此動作:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
loggerFactory.AddDebug();
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseBrowserLink();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
}
app.UseMyMiddleware();
app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams();
var myMiddlewareOptions = Configuration.GetSection("MyMiddlewareOptionsSection").Get<MyMiddlewareOptions>();
var myMiddlewareOptions2 = Configuration.GetSection("MyMiddlewareOptionsSection2").Get<MyMiddlewareOptions>();
app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams(myMiddlewareOptions);
app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams(myMiddlewareOptions2);
app.UseMyTerminatingMiddleware();
// Create branch to the MyHandlerMiddleware.
// All requests ending in .report will follow this branch.
app.MapWhen(
context => context.Request.Path.ToString().EndsWith(".report"),
appBranch => {
// ... optionally add more middleware to this branch
appBranch.UseMyHandler();
});
app.MapWhen(
context => context.Request.Path.ToString().EndsWith(".context"),
appBranch => {
appBranch.UseHttpContextDemoMiddleware();
});
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
MapWhen 會採用下列參數:
一個採用
HttpContext並在要求應沿著分支走下去時傳回true的 Lambda。 這意味著您不僅可以根據要求的副檔名對要求進行分支,還可以根據要求標頭、查詢字串參數等進行分支。一個採用
IApplicationBuilder並為分支新增所有中介軟體的 Lambda。 這意味著您可以在處理常式中介軟體前面的分支中新增額外的中介軟體。
在分支之前新增至管線的中介軟體會在所有要求上被叫用;該分支不會對他們造成任何影響。
使用選項模式載入中介軟體選項
某些模組和處理常式具有儲存在 Web.config 的組態選項。不過,在 ASP.NET Core 中,會使用新的組態模型來取代 Web.config。
新的組態系統會為您提供了以下選項來解決此問題:
建立類別來保存您的中介軟體選項,例如:
public class MyMiddlewareOptions { public string Param1 { get; set; } public string Param2 { get; set; } }儲存選項值
該組態系統可讓您將選項值儲存在任何您想要的地方。 不過,大部分的網站都使用
appsettings.json,因此我們將採用這種方法:{ "MyMiddlewareOptionsSection": { "Param1": "Param1Value", "Param2": "Param2Value" } }這裡的 MyMiddlewareOptionsSection 是一個區段名稱。 它不必與您的選項類別的名稱相同。
將選項值與選項類別相關聯
選項模式會使用 ASP.NET Core 的相依性插入架構,將選項類型 (例如
MyMiddlewareOptions) 與具有實際選項的MyMiddlewareOptions物件相關聯。更新您的
Startup類別:如果您使用
appsettings.json,請將它新增至Startup建構函式中的組態建置器:public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env) { var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder() .SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath) .AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true) .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true) .AddEnvironmentVariables(); Configuration = builder.Build(); }設定選項服務:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { // Setup options service services.AddOptions(); // Load options from section "MyMiddlewareOptionsSection" services.Configure<MyMiddlewareOptions>( Configuration.GetSection("MyMiddlewareOptionsSection")); // Add framework services. services.AddMvc(); }將您的選項與您的選項類別相關聯:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { // Setup options service services.AddOptions(); // Load options from section "MyMiddlewareOptionsSection" services.Configure<MyMiddlewareOptions>( Configuration.GetSection("MyMiddlewareOptionsSection")); // Add framework services. services.AddMvc(); }
將選項插入您的中介軟體建構函式。 這類似於將選項插入控制器。
public class MyMiddlewareWithParams { private readonly RequestDelegate _next; private readonly MyMiddlewareOptions _myMiddlewareOptions; public MyMiddlewareWithParams(RequestDelegate next, IOptions<MyMiddlewareOptions> optionsAccessor) { _next = next; _myMiddlewareOptions = optionsAccessor.Value; } public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) { // Do something with context near the beginning of request processing // using configuration in _myMiddlewareOptions await _next.Invoke(context); // Do something with context near the end of request processing // using configuration in _myMiddlewareOptions } }將您的中介軟體新增至
IApplicationBuilder的 UseMiddleware 擴充方法會處理相依性插入。這不限於
IOptions物件。 您的介軟體所需的任何其他物件都可以透過這種方式插入。
透過直接插入來載入中介軟體選項
選項模式的優點是它會在選項值與其取用者之間建立鬆散的結合。 一旦您將選項類別與實際選項值相關聯後,任何其他類別都可以透過相依性插入架構來存取選項。 不需要傳遞選項值。
不過,如果您想要使用相同的中介軟體兩次 (以不同的選項),則這種情況會失敗。 例如,在允許不同角色的不同分支中使用的授權中介軟體。 您不能將兩個不同的選項物件與一個選項類別相關聯。
解決方案是在 Startup 類別中取得具有實際選項值的選項物件,並將它們直接傳遞給中介軟體的每個實例。
將第二個金鑰新增至
appsettings.json若要將第二組選項新增至
appsettings.json檔案,請使用新的索引鍵來唯一識別它:{ "MyMiddlewareOptionsSection2": { "Param1": "Param1Value2", "Param2": "Param2Value2" }, "MyMiddlewareOptionsSection": { "Param1": "Param1Value", "Param2": "Param2Value" } }擷取選項值,並將其傳遞給中介軟體。
Use...擴充方法 (將中介軟體新增至管線) 是一個傳入選項值的邏輯位置:public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); loggerFactory.AddDebug(); if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); app.UseBrowserLink(); } else { app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); } app.UseMyMiddleware(); app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams(); var myMiddlewareOptions = Configuration.GetSection("MyMiddlewareOptionsSection").Get<MyMiddlewareOptions>(); var myMiddlewareOptions2 = Configuration.GetSection("MyMiddlewareOptionsSection2").Get<MyMiddlewareOptions>(); app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams(myMiddlewareOptions); app.UseMyMiddlewareWithParams(myMiddlewareOptions2); app.UseMyTerminatingMiddleware(); // Create branch to the MyHandlerMiddleware. // All requests ending in .report will follow this branch. app.MapWhen( context => context.Request.Path.ToString().EndsWith(".report"), appBranch => { // ... optionally add more middleware to this branch appBranch.UseMyHandler(); }); app.MapWhen( context => context.Request.Path.ToString().EndsWith(".context"), appBranch => { appBranch.UseHttpContextDemoMiddleware(); }); app.UseStaticFiles(); app.UseMvc(routes => { routes.MapRoute( name: "default", template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); }); }讓中介軟體能夠採用 options 參數。 提供
Use...擴充方法的多載 (此方法採用 options 參數並將其傳遞給UseMiddleware)。 使用參數呼叫UseMiddleware時,它會在具現化中介軟體物件時將參數傳遞給中介軟體建構函式。public static class MyMiddlewareWithParamsExtensions { public static IApplicationBuilder UseMyMiddlewareWithParams( this IApplicationBuilder builder) { return builder.UseMiddleware<MyMiddlewareWithParams>(); } public static IApplicationBuilder UseMyMiddlewareWithParams( this IApplicationBuilder builder, MyMiddlewareOptions myMiddlewareOptions) { return builder.UseMiddleware<MyMiddlewareWithParams>( new OptionsWrapper<MyMiddlewareOptions>(myMiddlewareOptions)); } }請注意這會如何將選項物件包裝在
OptionsWrapper物件中。 這實作了IOptions(正如中介軟體建構函數所預期的)。
移轉至新的 HttpCoNtext
您稍早看到中介軟體中的 Invoke 方法採用 HttpContext 類型的參數:
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
HttpContext 在 ASP.NET Core 中已大幅變更。 本節說明如何將 System.Web.HttpContext 最常使用的屬性轉換為新的 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.HttpContext。
HttpContext
HttpCoNtext.Items 會轉換為:
IDictionary<object, object> items = httpContext.Items;
唯一要求 ID (沒有 System.Web.HttpCoNtext 對應項)
為您提供每個要求的唯一 ID。 包含在您的記錄中非常有用。
string requestId = httpContext.TraceIdentifier;
HttpContext.Request
HttpCoNtext.Request.HttpMethod 會轉換為:
string httpMethod = httpContext.Request.Method;
HttpCoNtext.Request.QueryString 會轉換為:
IQueryCollection queryParameters = httpContext.Request.Query;
// If no query parameter "key" used, values will have 0 items
// If single value used for a key (...?key=v1), values will have 1 item ("v1")
// If key has multiple values (...?key=v1&key=v2), values will have 2 items ("v1" and "v2")
IList<string> values = queryParameters["key"];
// If no query parameter "key" used, value will be ""
// If single value used for a key (...?key=v1), value will be "v1"
// If key has multiple values (...?key=v1&key=v2), value will be "v1,v2"
string value = queryParameters["key"].ToString();
HttpCoNtext.Request.Url 和 HttpCoNtext.Request.RawUrl 會轉換為:
// using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Extensions;
var url = httpContext.Request.GetDisplayUrl();
HttpCoNtext.Request.IsSecureConnection 會轉換為:
var isSecureConnection = httpContext.Request.IsHttps;
HttpCoNtext.Request.UserHostAddress 會轉換為:
var userHostAddress = httpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress?.ToString();
HttpContext.Request.Headers 會轉換為:
IRequestCookieCollection cookies = httpContext.Request.Cookies;
string unknownCookieValue = cookies["unknownCookie"]; // will be null (no exception)
string knownCookieValue = cookies["cookie1name"]; // will be actual value
HttpContext.Request.RequestContext.RouteData 會轉換為:
var routeValue = httpContext.GetRouteValue("key");
HttpContext.Request.Headers 會轉換為:
// using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Headers;
// using Microsoft.Net.Http.Headers;
IHeaderDictionary headersDictionary = httpContext.Request.Headers;
// GetTypedHeaders extension method provides strongly typed access to many headers
var requestHeaders = httpContext.Request.GetTypedHeaders();
CacheControlHeaderValue cacheControlHeaderValue = requestHeaders.CacheControl;
// For unknown header, unknownheaderValues has zero items and unknownheaderValue is ""
IList<string> unknownheaderValues = headersDictionary["unknownheader"];
string unknownheaderValue = headersDictionary["unknownheader"].ToString();
// For known header, knownheaderValues has 1 item and knownheaderValue is the value
IList<string> knownheaderValues = headersDictionary[HeaderNames.AcceptLanguage];
string knownheaderValue = headersDictionary[HeaderNames.AcceptLanguage].ToString();
HttpContext.Request.UserAgent 會轉換為:
string userAgent = headersDictionary[HeaderNames.UserAgent].ToString();
HttpContext.Request.UrlReferrer 會轉換為:
string urlReferrer = headersDictionary[HeaderNames.Referer].ToString();
HttpContext.Request.ContentType 會轉換為:
// using Microsoft.Net.Http.Headers;
MediaTypeHeaderValue mediaHeaderValue = requestHeaders.ContentType;
string contentType = mediaHeaderValue?.MediaType.ToString(); // ex. application/x-www-form-urlencoded
string contentMainType = mediaHeaderValue?.Type.ToString(); // ex. application
string contentSubType = mediaHeaderValue?.SubType.ToString(); // ex. x-www-form-urlencoded
System.Text.Encoding requestEncoding = mediaHeaderValue?.Encoding;
HttpContext.Request.Form 會轉換為:
if (httpContext.Request.HasFormContentType)
{
IFormCollection form;
form = httpContext.Request.Form; // sync
// Or
form = await httpContext.Request.ReadFormAsync(); // async
string firstName = form["firstname"];
string lastName = form["lastname"];
}
警告
只有在內容子類型為 x-www-form-urlencoded 或 form-data 時才會讀取表單值。
HttpContext.Request.InputStream 會轉換為:
string inputBody;
using (var reader = new System.IO.StreamReader(
httpContext.Request.Body, System.Text.Encoding.UTF8))
{
inputBody = reader.ReadToEnd();
}
警告
只有在管線末端的處理常式類型中介軟體中,才會使用此程式碼。
對於每個要求,您只能讀取一次如上所示的原始本文。 第一次讀取後嘗試讀取本文的中介軟體會讀取空白本文。
這不適用於讀取如稍早所示的表單,因為這是從緩衝區完成的。
HttpContext.Response
HttpCoNtext.Response.Status 和 HttpCoNtext.Response.StatusDescription 會轉換為:
// using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
httpContext.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status200OK;
HttpCoNtext.Response.ContentEncoding 和 HttpCoNtext.Response.ContentType 會轉換為:
// using Microsoft.Net.Http.Headers;
var mediaType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/json");
mediaType.Encoding = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8;
httpContext.Response.ContentType = mediaType.ToString();
HttpCoNtext.Response.ContentType 本身也會轉換為:
httpContext.Response.ContentType = "text/html";
HttpCoNtext.Response.Output 會轉換為:
string responseContent = GetResponseContent();
await httpContext.Response.WriteAsync(responseContent);
HttpContext.Response.TransmitFile
在vASP.NET Core 中的要求功能中討論提供檔案。
HttpContext.Response.Headers
傳送回應標頭很複雜,因為如果您在將任何內容寫入回應本文之後加以設定,則不會傳送它們。
解決方案是設定一個回呼方法,該方法會在寫入回應開始之前立即被呼叫。 這最好是在中介軟體中的 Invoke 方法開頭完成。 正是這個回呼方法設定了您的回應標頭。
以下程式碼設定一個名為 SetHeaders 的回呼方法:
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext httpContext)
{
// ...
httpContext.Response.OnStarting(SetHeaders, state: httpContext);
SetHeaders 回呼方法看起來會像這樣:
// using Microsoft.AspNet.Http.Headers;
// using Microsoft.Net.Http.Headers;
private Task SetHeaders(object context)
{
var httpContext = (HttpContext)context;
// Set header with single value
httpContext.Response.Headers["ResponseHeaderName"] = "headerValue";
// Set header with multiple values
string[] responseHeaderValues = new string[] { "headerValue1", "headerValue1" };
httpContext.Response.Headers["ResponseHeaderName"] = responseHeaderValues;
// Translating ASP.NET 4's HttpContext.Response.RedirectLocation
httpContext.Response.Headers[HeaderNames.Location] = "http://www.example.com";
// Or
httpContext.Response.Redirect("http://www.example.com");
// GetTypedHeaders extension method provides strongly typed access to many headers
var responseHeaders = httpContext.Response.GetTypedHeaders();
// Translating ASP.NET 4's HttpContext.Response.CacheControl
responseHeaders.CacheControl = new CacheControlHeaderValue
{
MaxAge = new System.TimeSpan(365, 0, 0, 0)
// Many more properties available
};
// If you use .NET Framework 4.6+, Task.CompletedTask will be a bit faster
return Task.FromResult(0);
}
HttpContext.Response.Cookies
Cookie 會透過Set-Cookie回應標頭傳送到瀏覽器。 因此,傳送 Cookie 需要與用來傳送回應標頭相同的回呼:
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext httpContext)
{
// ...
httpContext.Response.OnStarting(SetCookies, state: httpContext);
httpContext.Response.OnStarting(SetHeaders, state: httpContext);
SetCookies 回呼方法看起來如下:
private Task SetCookies(object context)
{
var httpContext = (HttpContext)context;
IResponseCookies responseCookies = httpContext.Response.Cookies;
responseCookies.Append("cookie1name", "cookie1value");
responseCookies.Append("cookie2name", "cookie2value",
new CookieOptions { Expires = System.DateTime.Now.AddDays(5), HttpOnly = true });
// If you use .NET Framework 4.6+, Task.CompletedTask will be a bit faster
return Task.FromResult(0);
}
