分析 Bot 的遙測數據
適用於: SDK v4
分析 Bot 行為
下列查詢集合可用來分析 Bot 行為。 您可以使用集合在 Azure 監視器 Log Analytics 中撰寫自定義查詢,以及建立監視和 Power BI 視覺效果儀錶板。
必要條件
對下列概念有基本瞭解很有説明:
- Kusto 查詢
- 如何在 Azure 入口網站 中使用Log Analytics來撰寫 Azure 監視器記錄查詢
- Azure 監視器中記錄查詢的基本概念
儀表板
Azure 儀錶板提供絕佳的方式,可讓您檢視和共用從查詢產生的資訊。 您可以建置自定義儀錶板,藉由將查詢與您新增至儀錶板的磚建立關聯,以協助監視 Bot 活動。 如需儀錶板的詳細資訊,以及如何將查詢與其產生關聯,請參閱 建立和共用Log Analytics資料的儀錶板。 本文的其餘部分顯示一些查詢範例,這些查詢在監視 Bot 行為方面可能很有用。
範例 Kusto 查詢
注意
建議您針對本文中的所有查詢,在不同的維度上進行樞紐分析,例如期間、通道和地區設定。
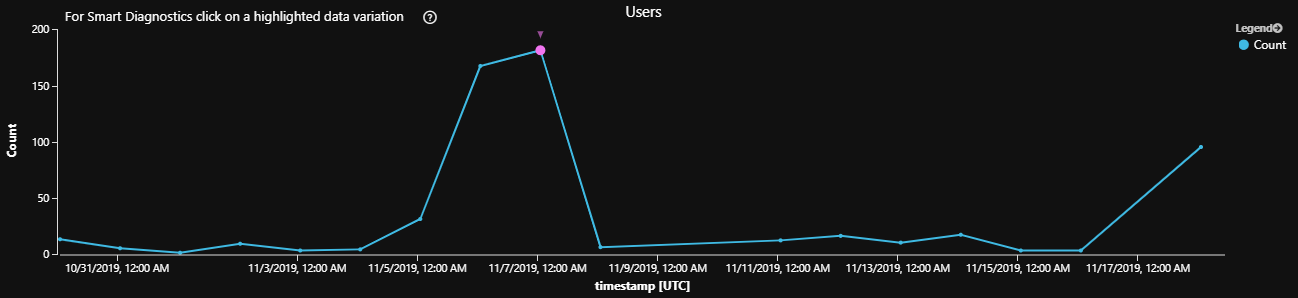
每個期間的用戶數目
此範例會產生折線圖,其中顯示過去 14 天內每天與 Bot 通訊的相異用戶數目。 藉由將不同的值指派給 queryStartDate、 queryEndDate 和 interval 變數,即可輕鬆地變更時間週期。
重要
如果使用者經過驗證,您只會取得此查詢中唯一使用者的正確計數,而結果也可能取決於通道功能。
// number of users per period
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let groupByInterval = 1d;
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| summarize uc=dcount(user_Id) by bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)
| render timechart
提示
Kusto summarize 運算子 可用來產生匯總輸入數據表內容的數據表。
Bin 函式是 Kusto 純量函式,與搭配 summarize operator 使用時,會將查詢結果分組至指定的值。 在上述範例中,這會依天分組,Kusto 也會接受 h=hours、m=minutes、s=seconds、ms=milliseconds、microsecond=microseconds。
轉 譯運算符 可讓您輕鬆地轉譯圖表,例如 時間圖、x 軸是日期時間的折線圖,而任何其他數值數據行都可用於Y軸。 即使您的數據每次未指定,它仍會自動保持 X 軸間距。 如果未使用轉譯語句,它會預設為 table。
每個期間使用者查詢結果的範例數目
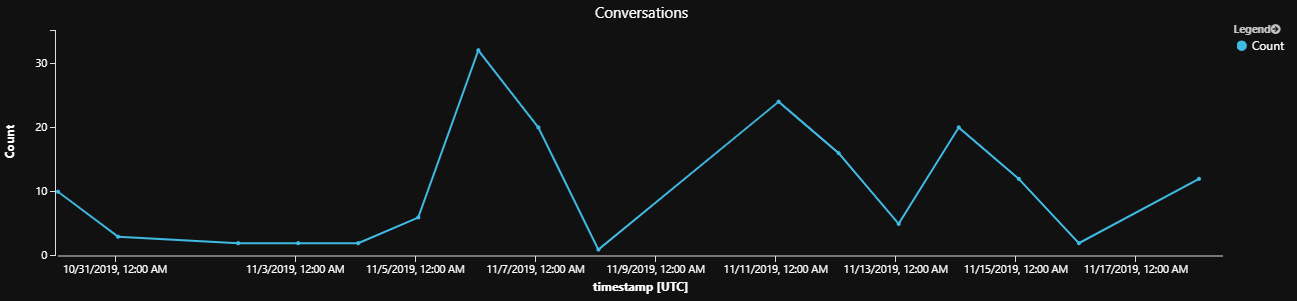
每個期間的活動數
此範例說明如何測量每個所需維度的活動量,例如過去 14 天內交談、對話或訊息數目的計數。 藉由將不同的值指派給 querystartdate、 queryEndDate 和 interval 變數,即可輕鬆地變更時間週期。 所需的維度是由extend下列範例中的 子句所定義,metric可以設定為 InstanceId、DialogId 或 activityId。
將計量指派給您想要顯示的維度:
// Measures the number of activity's (conversations, dialogs, messages) per period.
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let groupByInterval = 1d;
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| extend ActivityId = tostring(customDimensions['activityId'])
| where DialogId != '' and InstanceId != '' and user_Id != ''
| extend metric = InstanceId // DialogId or ActivityId
| summarize Count=dcount(metric) by bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)
| order by Count desc nulls last
| render timechart
提示
Kusto 擴充運算符 可用來建立導出數據行,並將其附加至結果集。
每個期間的活動範例查詢結果
每個使用者每個期間的活動
此範例示範如何計算每個使用者每個期間的活動數目。 此查詢會向下切入每個期間查詢的活動,以專注於每個使用者每個期間的活動。 活動包括對話、交談或訊息。 此查詢會測量使用者與 Bot 的互動,以協助找出潛在問題,例如:
- 單一用戶有許多活動的日子可能表示攻擊或測試
- 與很少互動的日子可能表示服務健康情況問題
提示
您可以藉由user_Id移除,以取得可在時間和對話、訊息或交談上樞紐處理的一般 Bot 活動磁碟區。
// number of users per period per dialogs
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let interval = 6h;
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| extend ActivityId = tostring(customDimensions['activityId'])
| where DialogId != '' and InstanceId != '' and user_Id != ''
| extend metric = ActivityId // InstanceId // DialogId // or InstanceId for conversation count
| summarize Count=dcount(metric) by user_Id, bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)
| order by Count desc nulls last
每個週期的範例活動查詢結果
| user_Id | timestamp | Count |
|---|---|---|
| User-8107ffd2 | 2019-09-03T00:00:00Z | 14 |
| User-75f2cc8f | 2019-08-30T00:00:00Z | 13 |
| User-75f2cc8d | 2019-09-03T00:00:00Z | 13 |
| User-3060aada | 2019-09-03T00:00:00Z | 10 |
對話框完成
設定對話框的遙測客戶端之後,對話框(及其子系)將會發出一些預設遙測數據,例如 已 啟動和 完成。 這個範例可用來測量相對於已啟動對話的已完成對話框。 如果啟動的對話框數目大於完成的數目,則部分使用者未完成對話流程。 您可以使用此查詢來協助您識別並針對任何潛在的對話邏輯進行疑難解答。 它也可以用來識別哪些對話最常使用且最不常使用。
瀑布式對話完成
// % Completed Waterfall Dialog: shows completes relative to starts
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| where name=="WaterfallStart"
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| join kind=leftouter (
customEvents
| where name=="WaterfallComplete"
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
) on InstanceId
| summarize started=countif(name=='WaterfallStart'), completed=countif(name1=='WaterfallComplete') by tostring(DialogId)
| where started > 100 // filter for sample
// Show starts vs. completes
| project tostring(DialogId), started, completed
| order by started desc, completed asc nulls last
| render barchart with (kind=unstacked, xcolumn=DialogId, ycolumns=completed, started, ysplit=axes)
提示
Kusto 聯結運算子 可用來合併兩個數據表的數據列,藉由比對每個數據表中指定數據行的值來形成新的數據表。
項目 運算子 可用來選取您想要顯示在輸出中的欄位。 類似於 extend operator 新增欄位的 , project operator 可以選擇現有的欄位集或新增欄位。
自適性對話已啟動和完成
// % Completed adaptive dialog: shows completes relative to starts. This type is the default dialog type when using Power Virtual Agents or Composer.
customEvents
| where name=="AdaptiveDialogStart" or name == "AdaptiveDialogComplete"
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| summarize started=countif(name=='AdaptiveDialogStart'), completed=countif(name=='AdaptiveDialogComplete') by DialogId
| project DialogId, started, completed
| order by started desc, completed asc nulls last
| render barchart with (kind=unstacked, xcolumn=DialogId, ycolumns=completed, started, ysplit=axes)
範例對話框完成查詢結果
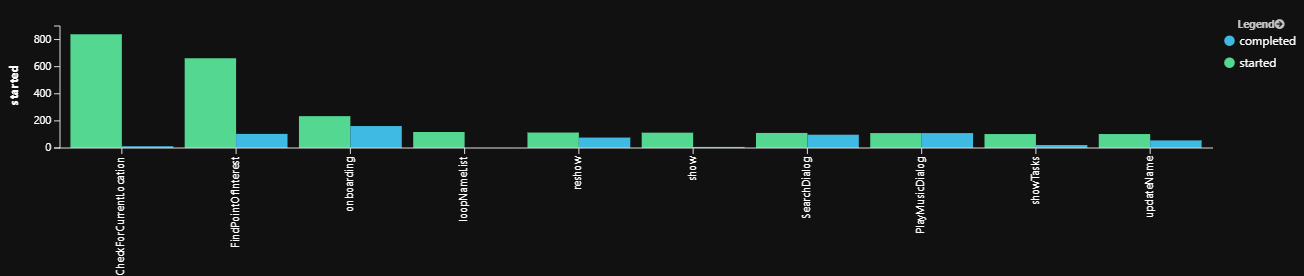
對話框完成
這個範例可用來計算在指定時段內因取消或放棄而未完成但從未完成的對話流程數目。 您可以使用它來檢閱不完整的對話,並檢查他們是否因為使用者混淆而主動取消,或因為使用者分心或失去興趣而放棄。
瀑布式對話未完成
// Show incomplete dialogs when using waterfall dialogs.
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| where name == "WaterfallStart"
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| join kind=leftanti (
customEvents
| where name == "WaterfallComplete"
| extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
) on instanceId
| summarize cnt=count() by tostring(DialogId)
| order by cnt
| render barchart
調適型對話未完成
// Show incomplete dialogs for adaptive dialogs; this type is the default dialog type when using Power Virtual Agents or Composer.
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where name == "AdaptiveDialogStart"
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| join kind=rightanti (
customEvents
| where name == "AdaptiveDialogComplete"
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
) on name, DialogId
| summarize cnt=count() by DialogId
| order by cnt
| render barchart
提示
Kusto 順序運算子 (與 sort operator相同) 可用來依一或多個數據行排序輸入數據表的數據列。 注意:如果您想要從任何查詢的結果中排除 Null 值,您可以在語句中where篩選出這些值,例如,您可以新增 “and isnotnull(Timestamp)”,或在開頭或結尾傳回 Null 值,將 或 nulls first 新增nulls first至 order 語句的結尾。
範例對話框完成查詢結果

對話框順序向下切入
交談中對話的瀑布開始/步驟/完成
此範例顯示對話步驟順序,依交談 (instanceId) 分組,這在判斷哪些步驟會導致對話中斷時很有用。
執行此查詢,輸入所需的 DialogId 值以取代 <SampleDialogId>
// Drill down: Show waterfall start/step/complete for specific dialog
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let DialogActivity=(dlgid:string) {
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend StepName = customDimensions['StepName']
| extend InstanceId = customDimensions['InstanceId']
| where DialogId == dlgid
| project timestamp, name, StepName, InstanceId
| order by tostring(InstanceId), timestamp asc
};
// For example see SampleDialogId behavior
DialogActivity("<SampleDialogId>")
提示
此查詢是使用 查詢定義函數撰寫的,這是用戶定義的函數,該函數是在單一查詢的範圍內定義及使用,而且是透過 let 語句來定義。 此查詢未使用 query-defined function所撰寫:
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend StepName = customDimensions['StepName']
| extend InstanceId = customDimensions['InstanceId']
| where DialogId == "<SampleDialogId>"
| project timestamp, name, StepName, InstanceId
| order by tostring(InstanceId), timestamp asc
範例查詢結果
| timestamp | NAME | StepName | InstanceId |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-08-23T20:04... | WaterfallStart | null | ...79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:04... | WaterfallStep | GetPointOfInterestLocations | ...79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:04... | WaterfallStep | ProcessPointOfInterestSelection | ...79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:04... | WaterfallStep | GetRoutesToDestination | ...79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:05... | WaterfallStep | ResponseToStartRoutePrompt | ...79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:05... | WaterfallComplete 1 | null | ...79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-28T23:35... | WaterfallStart | null | ...6ac8b3211b99 |
| 2019-08-28T23:35... | 瀑布圖 2 | GetPointOfInterestLocations | ...6ac8b3211b99 |
| 2019-08-28T19:41... | WaterfallStart | null | ...8137d76a5cbb |
| 2019-08-28T19:41... | 瀑布圖 2 | GetPointOfInterestLocations | ...8137d76a5cbb |
| 2019-08-28T19:41... | WaterfallStart | null | ...8137d76a5cbb |
1 已完成
2 已放棄
解譯:使用者似乎在 GetPointOfInterestLocations 步驟放棄交談。
注意
瀑布式對話會執行序列(開始、多個步驟、完成)。 如果序列顯示開頭未完成,表示對話因為使用者放棄或取消對話框而中斷。 在此詳細分析中,人們可以看到此行為(請參閱已完成與已放棄的步驟)。
瀑布式開始/步驟/完成/取消步驟匯總總計
此範例顯示對話框序列啟動的總次數、瀑布步驟的總總數、已成功完成的次數、已取消多少個,以及瀑布圖和瀑布圖加瀑布圖的總和總計之間的差異,都會提供放棄的總數。
// Drill down: Aggregate view of waterfall start/step/complete/cancel steps totals for specific dialog
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let DialogSteps=(dlgid:string) {
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| where DialogId == dlgid
| project name
| summarize count() by name
};
// For example see SampleDialogId behavior
DialogSteps("<SampleDialogId>")
範例瀑布匯總查詢結果
| name | 計數 |
|---|---|
| WaterfallStart | 21 |
| WaterfallStep | 47 |
| WaterfallComplete | 11 |
| WaterfallCancel | 1 |
解譯:在對話順序的 21 個調用中,只有 11 個已完成,9 個已放棄,一個被使用者取消。
對話框中的平均持續時間
此範例會測量使用者在指定對話框中花費的平均時間量。 您的 Bot 可能受益於簡化需要用戶長時間完成的對話。
// Average dialog duration
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| where name=="WaterfallStart"
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| join kind=leftouter (customEvents | where name=="WaterfallCancel" | extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])) on instanceId
| join kind=leftouter (customEvents | where name=="WaterfallComplete" | extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])) on instanceId
| extend duration = case(not(isnull(timestamp1)), timestamp1 - timestamp,
not(isnull(timestamp2)), timestamp2 - timestamp, 0s) // Abandoned aren't counted. Alternate: now()-timestamp
| extend seconds = round(duration / 1s)
| summarize AvgSeconds=avg(seconds) by tostring(DialogId)
| order by AvgSeconds desc nulls last
| render barchart with (title="Duration in Dialog")
範例平均持續時間查詢結果
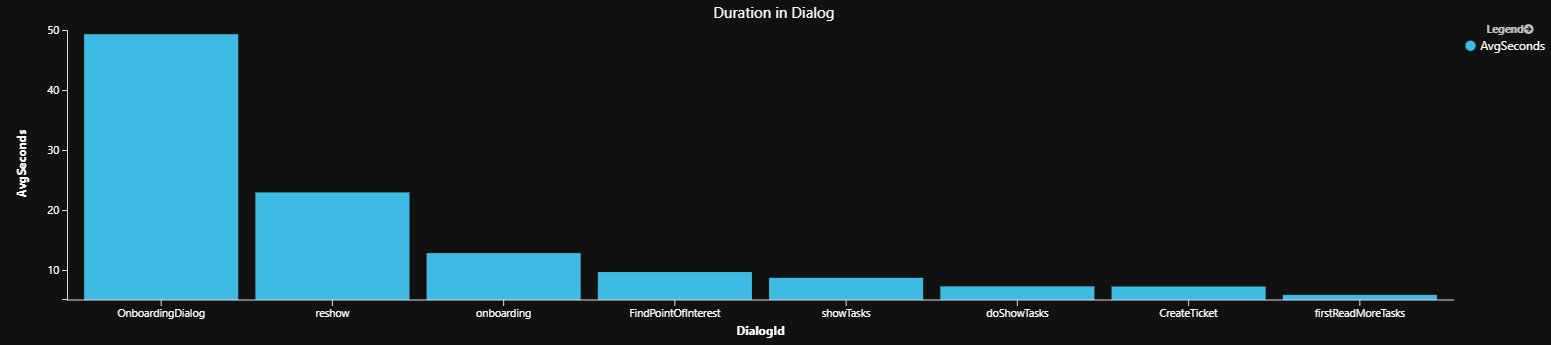
對話框中的平均步驟
此範例顯示每個叫用對話方塊的「長度」,依平均值、最小值、最大值和標準偏差計算。 這有助於分析對話品質。 例如:
- 應該評估具有太多步驟的對話,以簡化商機。
- 在最小值/最大值/平均值之間有較大差距的對話,可能表示用戶嘗試完成工作時停滯不前。 您可能需要評估有較短路徑完成工作的可能性,或減少對話複雜度的方法。
- 具有大型標準偏差的對話會建議複雜的路徑或中斷的體驗(放棄/取消)。
- 具有幾個步驟的對話框可能是因為從未完成過。 分析完成/放棄率可能有助於做出該決定。
// min/max/std/avg steps per dialog
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| extend StepName = tostring(customDimensions['StepName'])
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| where name == "WaterfallStart" or name == "WaterfallStep" or name == "WaterfallComplete"
| order by InstanceId, timestamp asc
| project timestamp, DialogId, name, InstanceId, StepName
| summarize cnt=count() by InstanceId, DialogId
| summarize avg=avg(cnt), minsteps=min(cnt),maxsteps=max(cnt), std=stdev(cnt) by DialogId
| extend avgsteps = round(avg, 1)
| extend avgshortbysteps=maxsteps-avgsteps
| extend avgshortbypercent=round((1.0 - avgsteps/maxsteps)*100.0, 1)
| project DialogId, avgsteps, minsteps, maxsteps, std, avgshortbysteps, avgshortbypercent
| order by std desc nulls last
範例平均步驟查詢結果
| 對話框識別碼 | avg steps | 最小步驟 | 最大步驟 | std | avg short by steps | avg short by percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FindArticlesDialog | 6.2 | 2 | 7 | 2.04 | 0.8 | 11.4% |
| CreateTicket | 4.3 | 2 | 5 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 14% |
| CheckForCurrentLocation | 3.9 | 2 | 5 | 1.41 | 1.1 | 22% |
| BaseAuth | 3.3 | 2 | 4 | 1.03 | 0.7 | 17.5% |
| 上架 | 2.7 | 2 | 4 | 0.94 | 1.3 | 32.5% |
__Interpretation:例如,FindArticlesDialog 在最小值/最大值之間有廣泛的分佈,而且應該進行調查,並可能重新設計並優化。
依活動計量的通道活動
此範例會測量 Bot 在指定期間內每個通道接收的活動量。 它會計算下列任何一個計量,以執行這項作業:傳入訊息、使用者、交談或對話。 這對於服務健康情況分析或測量通道受歡迎程度很有用。
// number of metric: messages, users, conversations, dialogs by channel
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let groupByInterval = 1d;
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| extend ActivityId = tostring(customDimensions['activityId'])
| extend ChannelId = tostring(customDimensions['channelId'])
| where DialogId != '' and InstanceId != '' and user_Id != ''
| extend metric = user_Id // InstanceId or ActivityId or user_Id
| summarize Count=count(metric) by ChannelId, bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)
| order by Count desc nulls last
| render barchart with (title="Users", kind=stacked) // or Incoming Messages or Conversations or Users
提示
您可能想要考慮嘗試這些變化:
- 在沒有時間戳貯體的情況下執行查詢:
bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)。 - 您也可以針對不同的使用者與
count所有使用者事件活動使用dcount。 這也適用於重複使用者。
範例 channel-activity-by-activity 查詢結果
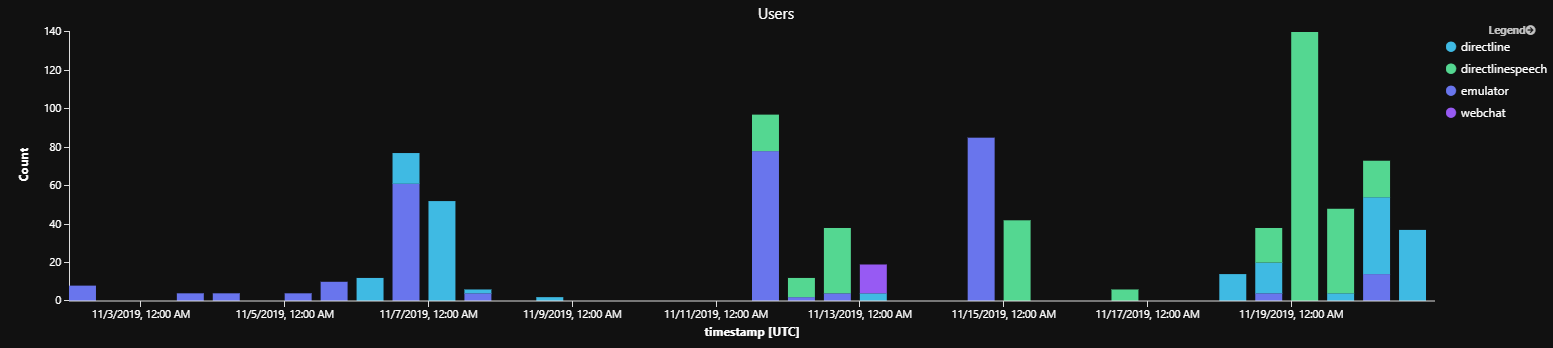
解譯:模擬器測試過去最常使用,但一旦上線,DirectLineSpeech 是最受歡迎的頻道。
依熱門程度的總意圖
此範例適用於已啟用 LUIS 的 Bot。 它會依熱門程度顯示所有意圖的摘要,以及對應的意圖偵測確定性分數。
注意
Language Understanding (LUIS) 將於 2025 年 10 月 1 日淘汰。 從 2023 年 4 月 1 日起,您將無法建立新的 LUIS 資源。 新版的語言理解現在已提供作為 Azure AI 語言的一部分。
對話式語言理解(CLU)是 Azure AI 語言的一項功能,是 LUIS 的更新版本。 如需 Bot Framework SDK 中語言理解支援的詳細資訊,請參閱 自然語言理解。
- 實際上,檢視應該針對每個計量分隔。
- 熱門意圖路徑應針對用戶體驗進行優化。
- 低平均分數表示辨識不佳, 可能遺漏實際的使用者意圖。
// show total intents
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| where name startswith "LuisResult"
| extend intentName = tostring(customDimensions['intent'])
| extend intentScore = todouble(customDimensions['intentScore'])
| summarize ic=count(), ac=avg(intentScore)*100 by intentName
| project intentName, ic, ac
| order by ic desc nulls last
| render barchart with (kind=unstacked, xcolumn=intentName, ycolumns=ic,ac, title="Intents Popularity")
範例意圖逐熱門查詢結果
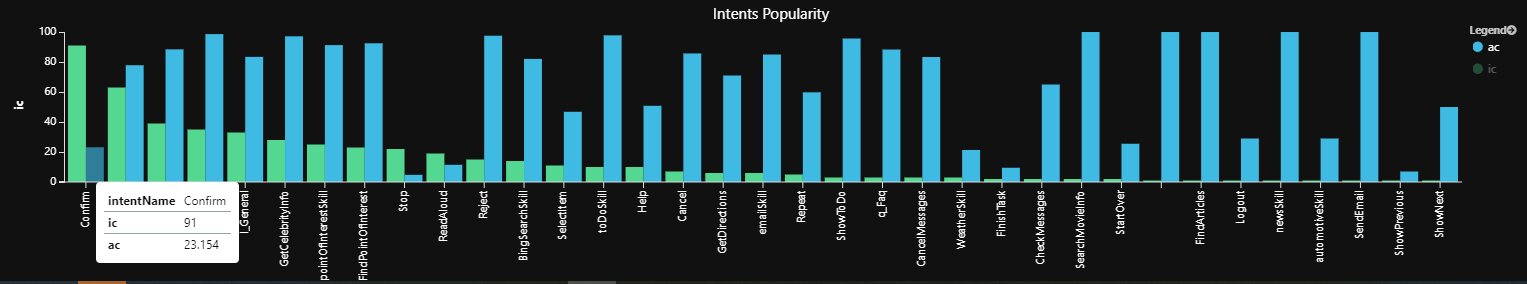
解譯:例如,最受歡迎的意圖,只偵測到平均信賴度為 23% 的確認。
提示
條形圖是 Kusto 查詢可用的十幾個選項之一。 其他一些選項包括:anomalychart、areachart、columnchart、linechart、散佈圖。 如需詳細資訊,請參閱 轉譯運算符 主題。
Bot Analytics Instrumentation 的架構
下表顯示 Bot 將記錄遙測數據的最常見欄位。
一般信封
Application Insights 檢測中的常見記錄分析字段。
| 欄位 | 說明 | 範例值 |
|---|---|---|
| NAME | 訊息類型 | BotMessageSend、BotMessageReceived、LuisResult、WaterfallStep、WaterfallStart、SkillWebSocketProcessRequestLatency、SkillWebSocketOpenCloseLatency、WaterfallComplete、QnaMessage、WaterfallCancel、SkillWebSocketTurnLatency、AuthPromptValidatorAsyncFailure |
| customDimensions | SDK Bot 分析 | activityId=<id>, activityType=message, channelId=emulator, fromId<=id>, fromName=User, locale=en-us, recipientId=<id>, recipientName=Bot, text=find a coffee shop |
| timestamp | 事件時間 | 2019-09-05T18:32:45.287082Z |
| instance_Id | 交談識別碼 | f7b2c416-a680-4b2c-b4cc-79c0f03d8711 |
| operation_Id | 回合識別碼 | 084b2856947e3844a5a18a8476d99aaa |
| user_Id | 唯一通道使用者標識碼 | emulator7c259c8e-2f47... |
| client_IP | 用戶端IP位址 | 127.0.0.1 (可能因為隱私權封鎖而缺席) |
| client_City | 用戶端城市 | 雷德蒙德(如果偵測到,可能不存在) |
注意
Azure AI QnA Maker 將於 2025 年 3 月 31 日淘汰。 從 2022 年 10 月起,您將無法建立新的 QnA Maker 資源或知識庫。 較新版的問題和解答功能現在隨附於 Azure AI 語言。
自定義問題解答是 Azure AI 語言的一項功能,是 QnA Maker 服務的更新版本。 如需 Bot Framework SDK 中問答支援的詳細資訊,請參閱 自然語言理解。
注意
Language Understanding (LUIS) 將於 2025 年 10 月 1 日淘汰。 從 2023 年 4 月 1 日起,您將無法建立新的 LUIS 資源。 新版的語言理解現在已提供作為 Azure AI 語言的一部分。
對話式語言理解(CLU)是 Azure AI 語言的一項功能,是 LUIS 的更新版本。 如需 Bot Framework SDK 中語言理解支援的詳細資訊,請參閱 自然語言理解。
自訂維度
大部分的 Bot 特定活動數據會儲存在 customDimensions 字段中。
| 欄位 | 說明 | 範例值 |
|---|---|---|
| activityId | 訊息識別碼 | <id>: 8da6d750-d00b-11e9-80e0-c14234b3bc2a |
| activityType | 訊息類型 | message, conversationUpdate, event, invoke |
| channelId | 管道識別碼 | emulator, directline, msteams, webchat |
| fromId | 寄件者識別碼 | <id> |
| fromName | 來自用戶端的使用者名稱 | 約翰·博納姆、基思·穆恩、史蒂夫·史密斯、史蒂夫·加德 |
| locale | 用戶端來源地區設定 | en-us、zh-cn、en-GB、de-de、zh-CN |
| recipientId | 收件者識別碼 | <id> |
| recipientName | 收件者名稱 | 約翰·博納姆、基思·穆恩、史蒂夫·史密斯、史蒂夫·加德 |
| text | 訊息中的文字 | 尋找咖啡店 |
自定義維度:LUIS
注意
Language Understanding (LUIS) 將於 2025 年 10 月 1 日淘汰。 從 2023 年 4 月 1 日起,您將無法建立新的 LUIS 資源。 新版的語言理解現在已提供作為 Azure AI 語言的一部分。
對話式語言理解(CLU)是 Azure AI 語言的一項功能,是 LUIS 的更新版本。 如需 Bot Framework SDK 中語言理解支援的詳細資訊,請參閱 自然語言理解。
LUIS 檢測會將其資料儲存在下列 [自定義維度] 字段中。
| 欄位 | 說明 | 範例值 |
|---|---|---|
| 意圖 | LUIS 偵測到的意圖 | pointOfInterestSkill |
| intentScore | LUIS 辨識分數 | 0.98 |
| 實體 | LUIS 偵測到的實體 | FoodOfGrocery = [[“coffee”]], KEYWORD= [“coffee shop”] |
| 問題 | LUIS 偵測到的問題 | 尋找咖啡店 |
| sentimentLabel | LUIS 偵測到情感 | positive |
自定義維度:QnAMaker
注意
Azure AI QnA Maker 將於 2025 年 3 月 31 日淘汰。 從 2022 年 10 月起,您將無法建立新的 QnA Maker 資源或知識庫。 較新版的問題和解答功能現在隨附於 Azure AI 語言。
自定義問題解答是 Azure AI 語言的一項功能,是 QnA Maker 服務的更新版本。 如需 Bot Framework SDK 中問答支援的詳細資訊,請參閱 自然語言理解。
QnAMaker 檢測會將其資料儲存在下列 [自定義維度] 字段中。
提示
若要啟用如問題和解答等個人信息記錄功能,記錄個人資訊參數應該在QnA Maker類別的建構函式中設定為 true。
| 欄位 | 說明 | 範例值 |
|---|---|---|
| 問題 | QnA 偵測到的問題 | 你能做什麼? |
| answer | QnA 答案 | 你有問題,我可能有答案。 |
| articleFound | QnA | true |
| questionId | QnA 問題標識碼 | 488 |
| knowledgeBaseId | QnA KB 識別碼 | 2a4936f3-b2c8-44ff-b21f-67bc413b9727 |
| matchedQuestion | 相符問題的陣列 | [“你能向我解釋你的角色是什麼?”,“你能告訴我一點關於你嗎?”,“你能告訴我你嗎?”,“你能幫我嗎?”,“你怎麼能幫我?”,“你怎麼能幫我?”,“你怎麼能幫我?”,“我該怎麼在我的專案中使用你呢??”,“跟我談談你的能力”,“你有能力嗎?,...] |
另請參閱
- 如需撰寫記錄查詢的教學課程,請參閱 開始使用 Azure 監視器中的記錄查詢
- 將來自 Azure 監視器的資料視覺化 (機器翻譯)
- 瞭解如何 將遙測新增至 Bot
- 深入瞭解 Azure 監視器記錄查詢
- Bot Framework Application Insights 事件的完整清單
- 建立和共用 Log Analytics 資料的儀表板