在本教學課程中,您將瞭解如何使用 文字分析 分析 Azure Synapse Analytics 上的非結構化文字。 文字分析是一種 Azure AI 服務,使您能夠使用自然語言處理 (NLP) 功能執行文字採礦和文字分析。
本教學課程示範如何使用文字分析搭配 SynapseML 來:
- 在句子或文件層級偵測情感標籤
- 識別指定文字輸入的語言
- 從具有已知知識庫連結的文字辨識實體
- 從文字擷取關鍵片語
- 識別文字中的不同實體,並將它們分類成預先定義的類別或類型
- 在指定的文字中,識別和修訂敏感性實體
如果您沒有 Azure 訂用帳戶,請在開始前建立免費帳戶。
必要條件
- Azure Synapse Analytics 工作區,其中 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 儲存體帳戶已設定為預設儲存體。 使用 Data Lake Storage Gen2 檔案系統時,您必須是該檔案系統的儲存體 Blob 資料參與者。
- 在您 Azure Synapse Analytics 工作區中的 Spark SQL 集區。 如需詳細資訊,請參閱在 Azure Synapse 中建立 Spark 集區。
- 在 Azure Synapse 中設定 Azure AI 服務教學課程中所述的預先設定步驟。
開始使用
開啟 Synapse Studio 並建立新的筆記本。 若要開始使用,請匯入 SynapseML。
import synapse.ml
from synapse.ml.services import *
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
設定文字分析
使用您在預先設定步驟中設定的連結文字分析。
linked_service_name = "<Your linked service for text analytics>"
文字情感
文字情感分析提供一種方式來偵測情感卷標(例如「負面」、「中性」和「正面」)和句子和檔層級的信賴分數。 如需啟用的語言清單,請參閱文字分析 API 中支援的語言。
# Create a dataframe that's tied to it's column names
df = spark.createDataFrame([
("I am so happy today, it's sunny!", "en-US"),
("I am frustrated by this rush hour traffic", "en-US"),
("The Azure AI services on spark aint bad", "en-US"),
], ["text", "language"])
# Run the Text Analytics service with options
sentiment = (TextSentiment()
.setLinkedService(linked_service_name)
.setTextCol("text")
.setOutputCol("sentiment")
.setErrorCol("error")
.setLanguageCol("language"))
# Show the results of your text query in a table format
results = sentiment.transform(df)
display(results
.withColumn("sentiment", col("sentiment").getItem("document").getItem("sentences")[0].getItem("sentiment"))
.select("text", "sentiment"))
預期的結果
| text | 情感 |
|---|---|
| 今天我很高興,陽光明媚! | positive |
| 我對這個高峰時段的交通感到沮喪 | negative |
| Spark 上的 Azure AI 服務不佳 | neutral |
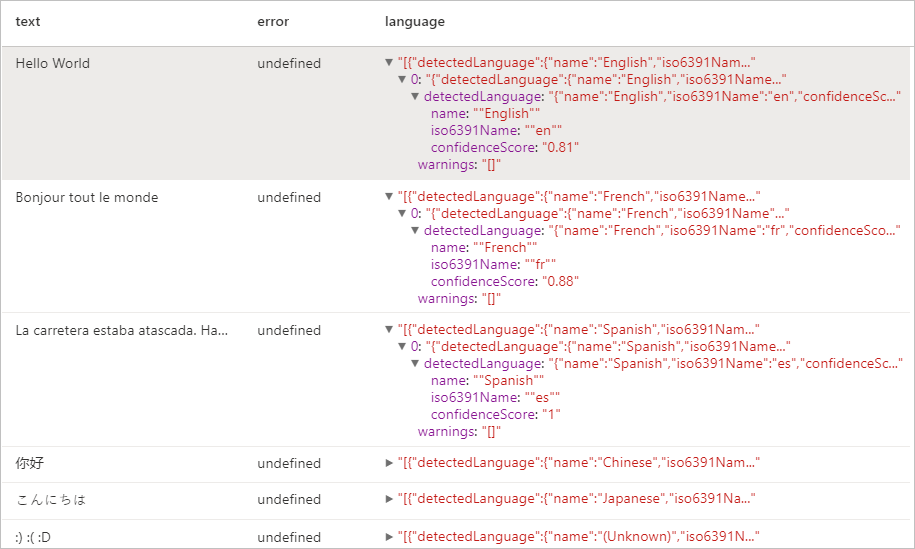
語言偵測器
語言偵測器會針對每份文件評估文字輸入,並傳回語言識別碼,其中含有指出分析強度的分數。 此功能很適合用於收集未知語言任意文字的內容存放區。 如需啟用的語言清單,請參閱文字分析 API 中支援的語言。
# Create a dataframe that's tied to it's column names
df = spark.createDataFrame([
("Hello World",),
("Bonjour tout le monde",),
("La carretera estaba atascada. Había mucho tráfico el día de ayer.",),
("你好",),
("こんにちは",),
(":) :( :D",)
], ["text",])
# Run the Text Analytics service with options
language = (LanguageDetector()
.setLinkedService(linked_service_name)
.setTextCol("text")
.setOutputCol("language")
.setErrorCol("error"))
# Show the results of your text query in a table format
display(language.transform(df))
預期的結果
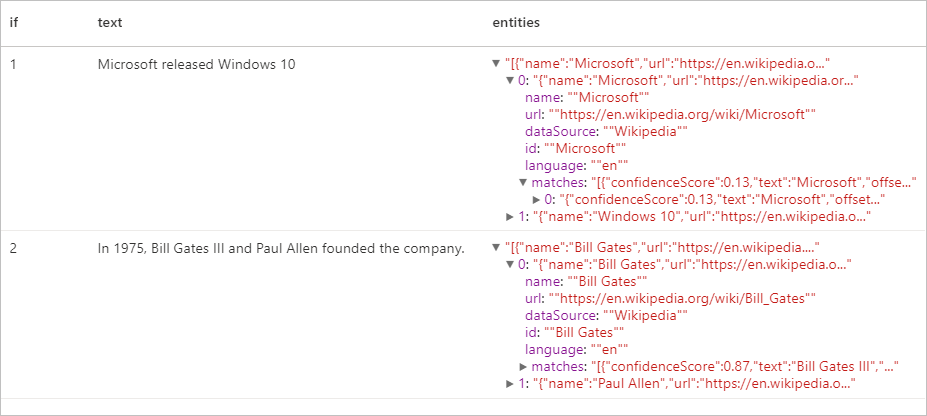
實體偵測器
實體偵測器會傳回具有已知知識庫連結的已識別實體清單。 如需啟用的語言清單,請參閱文字分析 API 中支援的語言。
df = spark.createDataFrame([
("1", "Microsoft released Windows 10"),
("2", "In 1975, Bill Gates III and Paul Allen founded the company.")
], ["if", "text"])
entity = (EntityDetector()
.setLinkedService(linked_service_name)
.setLanguage("en")
.setOutputCol("replies")
.setErrorCol("error"))
display(entity.transform(df).select("if", "text", col("replies").getItem("document").getItem("entities").alias("entities")))
預期的結果
關鍵片語擷取器
關鍵片語擷取會評估非結構化的文字,並傳回關鍵片語的清單。 此功能在您需要快速識別文件集合中的要點時相當有用。 如需啟用的語言清單,請參閱文字分析 API 中支援的語言。
df = spark.createDataFrame([
("en", "Hello world. This is some input text that I love."),
("fr", "Bonjour tout le monde"),
("es", "La carretera estaba atascada. Había mucho tráfico el día de ayer.")
], ["lang", "text"])
keyPhrase = (KeyPhraseExtractor()
.setLinkedService(linked_service_name)
.setLanguageCol("lang")
.setOutputCol("replies")
.setErrorCol("error"))
display(keyPhrase.transform(df).select("text", col("replies").getItem("document").getItem("keyPhrases").alias("keyPhrases")))
預期的結果
| text | keyPhrases |
|---|---|
| Hello World。 這是我喜愛的一些輸入文字。 | "["Hello world","input text"]" |
| Bonjour tout le monde | "["Bonjour","monde"]" |
| La carretera estaba atascada. Había mucho tráfico el día de ayer. | "["mucho tráfico","día","carretera","ayer"]" |
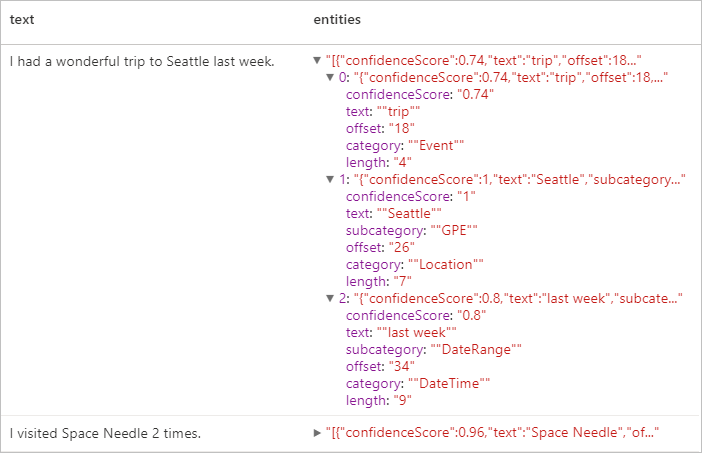
具名實體辨識 (NER)
具名實體辨識 (NER) 能夠識別文字中的不同實體,並將它們分類成預先定義的類別或類型,例如:人員、位置、事件、產品和組織。 如需啟用的語言清單,請參閱文字分析 API 中支援的語言。
df = spark.createDataFrame([
("1", "en", "I had a wonderful trip to Seattle last week."),
("2", "en", "I visited Space Needle 2 times.")
], ["id", "language", "text"])
ner = (NER()
.setLinkedService(linked_service_name)
.setLanguageCol("language")
.setOutputCol("replies")
.setErrorCol("error"))
display(ner.transform(df).select("text", col("replies").getItem("document").getItem("entities").alias("entities")))
預期的結果
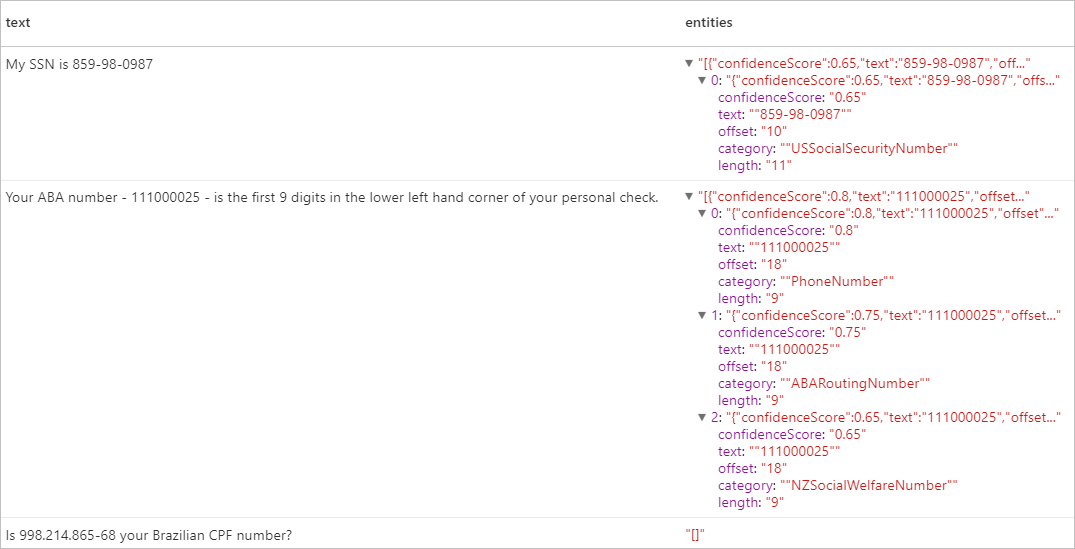
個人識別資訊 (PII) V3.1
PII 功能是 NER 的一部分,可以識別和修訂文字中的與個人相關聯的敏感實體,例如電話號碼、電子郵件地址、郵寄地址、護照號碼。 如需啟用的語言清單,請參閱文字分析 API 中支援的語言。
df = spark.createDataFrame([
("1", "en", "My SSN is 859-98-0987"),
("2", "en", "Your ABA number - 111000025 - is the first 9 digits in the lower left hand corner of your personal check."),
("3", "en", "Is 998.214.865-68 your Brazilian CPF number?")
], ["id", "language", "text"])
pii = (PII()
.setLinkedService(linked_service_name)
.setLanguageCol("language")
.setOutputCol("replies")
.setErrorCol("error"))
display(pii.transform(df).select("text", col("replies").getItem("document").getItem("entities").alias("entities")))
預期的結果
清除資源
為確保 Spark 執行個體已關閉,請結束任何已連線的工作階段 (Notebook)。 當達到 Apache Spark 集區中指定的閒置時間時,集區就會關閉。 您也可以在筆記本右上方的狀態列,選取 [停止工作階段]。
![顯示狀態列上 [停止工作階段] 按鈕的螢幕擷取畫面。](media/tutorial-build-applications-use-mmlspark/stop-session.png)