在C++/CX 程式中,您可以自由使用標準範本程式庫 (STL) 容器,或任何其他使用者定義的集合類型。 但是,當您在 Windows 執行階段應用程式二進位介面 (ABI) 之間來回傳遞集合時 (例如,傳遞到 XAML 控制或 JavaScript 用戶端),您必須使用 Windows 執行階段集合類型。
Windows 執行階段會定義集合和相關類型的介面,C++/CX 會在collection.h 標頭檔中提供具體 C++實作。 下圖顯示集合型別之間的關聯性:
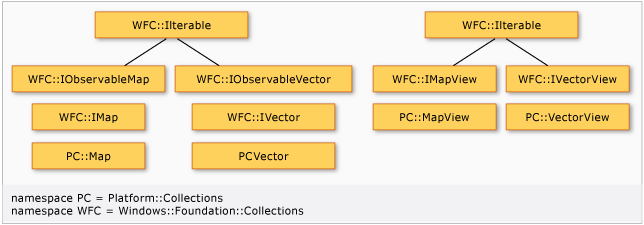
類別 類別是 和 的唯讀版本。 反覆運算器定義於命名空間中
Platform::Collections。 這些迭代器滿足 STL 迭代器的需求,允許在任何std::find、std::count_if介面類型或Windows::Foundation::Collections具體類型上使用Platform::Collections和其他 STL 演算法。 例如,這表示您可以逐一查看以 C# 建立的 Windows 執行階段元件中的集合,並套用 STL 演算法。Important
Proxy 迭代器
VectorIterator和VectorViewIterator會利用 Proxy 物件VectorProxy<T>和ArrowProxy<T>來與 STL 容器搭配使用。 如需詳細資訊,請參閱本文稍後的 VectorProxy 元素 。C++/CX 集合類型支援 STL 容器支援的相同執行緒安全性保證。
Windows::Foundation::Collections::IObservableVector和Windows::Foundation::Collections::IObservableMap定義當集合以各種方式變更時引發的事件。 藉由實作這些介面,Platform::Collections::Map和Platform::Collections::Vector支援與 XAML 集合的資料繫結。 例如,如果您具有資料繫結至Vector的Grid,當您將項目加入至集合時,此變更會反映在 Grid UI。
向量使用方式
當您的類別必須將序列容器傳遞至另一個 Windows 執行時間元件時,請使用 Windows::Foundation::Collections::IVector<T> 做為參數或傳回型別,以及 Platform::Collections::Vector<T> 做為具體實作。 如果您嘗試在公用傳回值或參數中使用 Vector 類型,則會引發編譯器錯誤 C3986。 只要將 Vector 變更為 IVector,就可以修正這個錯誤。
Important
如果您在自己的程式中傳遞序列,則使用 Vector 或 std::vector ,因為這些方法比 IVector更有效率。 只有在透過 ABI 傳遞容器時,才應該使用 IVector 。
Windows 執行階段類型系統不支援不規則陣列的概念,因此您也就不能將 IVector<Platform::Array<T>> 做為傳回值或方法參數傳遞。 若要跨 ABI 傳遞不規則陣列或一組序列中的某個序列,請使用 IVector<IVector<T>^>。
Vector<T> 提供在集合中新增、移除和存取項目的必要方法,此集合可隱含轉換為 IVector<T>。 您也可以在 Vector<T>的執行個體上使用 STL 演算法。 下列範例示範一些基本用法。 這裡的函begin式和end函式來自 Platform::Collections 命名空間,而不是 std 命名空間。
#include <collection.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace Platform;
using namespace Platform::Collections;
using namespace Windows::Foundation::Collections;
void Class1::Test()
{
Vector<int>^ vec = ref new Vector<int>();
vec->Append(1);
vec->Append(2);
vec->Append(3);
vec->Append(4);
vec->Append(5);
auto it =
std::find(begin(vec), end(vec), 3);
int j = *it; //j = 3
int k = *(it + 1); //or it[1]
// Find a specified value.
unsigned int n;
bool found = vec->IndexOf(4, &n); //n = 3
// Get the value at the specified index.
n = vec->GetAt(4); // n = 3
// Insert an item.
// vec = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
vec->InsertAt(0, 0);
// Modify an item.
// vec = 0, 1, 2, 12, 4, 5,
vec->SetAt(3, 12);
// Remove an item.
//vec = 1, 2, 12, 4, 5
vec->RemoveAt(0);
// vec = 1, 2, 12, 4
vec->RemoveAtEnd();
// Get a read-only view into the vector.
IVectorView<int>^ view = vec->GetView();
}
如果您有現有使用 std::vector 的程式碼,而您想要在 Windows 執行階段元件中重複使用它,請使用其中一個 Vector 建構函式,當您透過 ABI 傳遞集合時,此建構函式接受 std::vector 或一組迭代器來建構 Vector。 下列範例示範如何從 Vector 使用 std::vector移動建構函式,以提高初始化效率。 在移動作業後,原始 vec 變數就不再有效。
//#include <collection.h>
//#include <vector>
//#include <utility> //for std::move
//using namespace Platform::Collections;
//using namespace Windows::Foundation::Collections;
//using namespace std;
IVector<int>^ Class1::GetInts()
{
vector<int> vec;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i);
}
// Implicit conversion to IVector
return ref new Vector<int>(std::move(vec));
}
如果您必須在未來透過 ABI 傳遞字串向量,您必須決定最初以 std::wstring 型別或 Platform::String^ 型別建立字串。 如果您必須對字串進行許多處理,則使用 wstring。 否則,請以 Platform::String^ 類型建立字串,以避免稍後進行轉換的成本。 您也必須決定是否要將這些字串放入 std::vector 或 Platform::Collections::Vector 內部。 一般的作法是,只有在您透過 ABI 傳遞容器時,才使用 std::vector ,然後從中建立 Platform::Vector 。
Vector 中的實值類型
任何要儲存在 Platform::Collections::Vector 中的項目都必須隱含支援相等比較,或是使用您提供的自定義 std::equal_to 比較器。 所有參考型別及所有純量型別都隱含支援相等比較。 對於像是 Windows::Foundation::DateTime 這樣的非純量值類型,或針對自定義比較,例如 objA->UniqueID == objB->UniqueID,您必須提供自定義函式物件。
VectorProxy 元素
Platform::Collections::VectorIterator 和 Platform::Collections::VectorViewIterator 使可以在 range for 容器中使用 std::sort 迴圈和像 IVector<T> 的演算法。 但是 IVector 元素無法透過C++指標取值來存取;它們只能透過 GetAt 和 SetAt 方法來存取。 因此,這些反覆運算器使用 Proxy 類別 Platform::Details::VectorProxy<T> 和 Platform::Details::ArrowProxy<T>,依據標準庫的需求,透過 *、-> 和 [] 運算子提供對個別元素的存取權。 嚴格來說,如果指定 IVector<Person^> vec,則 *begin(vec) 的類型就是 VectorProxy<Person^>。 不過,對您的程式碼來說,Proxy 物件永遠都像是不存在一樣。 這些 Proxy 物件沒有記錄在文件中,因為它們僅供迭代器在內部使用,但是了解機制如何運作還是很重要。
當您針對 for 容器使用基於範圍的 IVector 迴圈時,請使用 auto&& 讓迭代器變數能夠正確繫結至 VectorProxy 元素。 如果您使用 auto&,就會引發編譯器警告 C4239,而且警告文字中會提及 VectorProxy。
下圖顯示針對 range for 執行的 IVector<Person^>迴圈。 請注意,程式會執行到第 64 行的中斷點停止。 [ 快速監看式 ] 視窗會顯示迭代器變數 p 就是擁有 VectorProxy<Person^> 和 m_v 成員變數的 m_i 。 但是,當您針對這個變數呼叫 GetType 時,它會將相同的類型傳回給 Person 執行個體 p2。 因此,雖然 VectorProxy 和 ArrowProxy 可能會出現在 [ 快速監看式]、偵錯工具、某些編譯器錯誤或其他位置,但是一般而言,您仍然不必明確為它們撰寫程式碼。
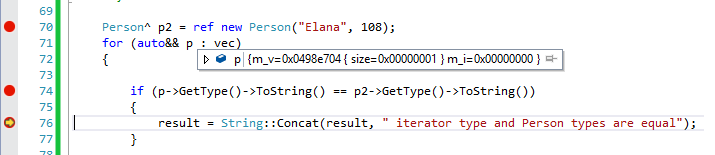
有一種情況下您必須為 Proxy 物件撰寫程式碼,就是必須針對元素執行 dynamic_cast 的時候 (例如,當您在 UIElement 項目集合中尋找特定類型的 XAML 物件時)。 在此情況下,您必須先將元素 Platform::Object轉換成 ^,然後執行動態轉換:
void FindButton(UIElementCollection^ col)
{
// Use auto&& to avoid warning C4239
for (auto&& elem : col)
{
Button^ temp = dynamic_cast<Button^>(static_cast<Object^>(elem));
if (nullptr != temp)
{
// Use temp...
}
}
}
對應使用量
這個範例示範如何插入項目,並在Platform::Collections::Map中查詢這些項目,然後將Map傳回為唯讀Windows::Foundation::Collections::IMapView類型。
//#include <collection.h>
//using namespace Platform::Collections;
//using namespace Windows::Foundation::Collections;
IMapView<String^, int>^ Class1::MapTest()
{
Map<String^, int>^ m = ref new Map<String^, int >();
m->Insert("Mike", 0);
m->Insert("Dave", 1);
m->Insert("Doug", 2);
m->Insert("Nikki", 3);
m->Insert("Kayley", 4);
m->Insert("Alex", 5);
m->Insert("Spencer", 6);
// PC::Map does not support [] operator
int i = m->Lookup("Doug");
return m->GetView();
}
一般而言,基於效能考量,在內部對應功能上最好使用 std::map 型別。 如果您必須透過 ABI 傳遞容器,請從 Platform::Collections::Map 建構 std::map,並將 Map 作為 Windows::Foundation::Collections::IMap 傳回。 如果您嘗試在公用傳回值或參數中使用 Map 類型,則會引發編譯器錯誤 C3986。 只要將 Map 變更為 IMap,就可以修正這個錯誤。 在某些情況下,例如,如果不是進行大量搜尋或插入,且您經常透過 ABI 傳遞集合,則一開始便使用 Platform::Collections::Map 可耗費較少資源,還能避免轉換 std::map時的成本。 在任何情況下,請避免在 IMap 上執行查閱和插入作業,因為這些是效能最低的三個類型。 只有在透過 ABI 傳遞容器時,才應該轉換為 IMap 。
Map 中的實值類型
中的 Platform::Collections::Map 元素是有序的。 任何要儲存在 Map 中的元素必須支援嚴格弱排序的「小於」比較,不論是隱式的方式,還是使用您提供的自定義 std::less 比較器。 純量類型隱含支援此比較。 針對非純量實值類型 (例如 Windows::Foundation::DateTime) 或自訂比較 (例如 objA->UniqueID < objB->UniqueID),您必須提供自訂比較子。
集合類型
集合分成四種分類:序列集合和關聯集合的可修改版本和唯讀版本。 此外,C++/CX 提供三個迭代器類別來簡化集合的存取,藉此增強集合。
您可以變更可修改的集合的元素,但只能讀取唯讀集合的元素,又稱為 檢視 (View)。 您可以使用迭代器,或集合的Platform::Collections::Vector和索引,來存取Platform::Collections::VectorView集合的元素Vector::GetAt。 使用集合的 Map::Lookup 和索引鍵來存取關聯集合的元素。
Platform::Collections::Map 類別
可修改的關聯集合。 對應元素是機碼值組。 支援查閱機碼以擷取其關聯值與逐一查看所有機碼值組。
Map 和 MapView 以 <K, V, C = std::less<K>>為樣板,因此,您可以自訂比較子。 此外, Vector 和 VectorView 以 <T, E = std::equal_to<T>> 為樣板,因此,您可以自訂 IndexOf()的行為。 這對於值結構的 Vector 和 VectorView 而言十分重要。 例如,若要建立 Vector<Windows::Foundation::DateTime>,您必須提供自定義比較子,因為 DateTime 不會多載 == 運算子。
Platform::Collections::MapView 類別
Map的唯讀版本。
Platform::Collections::Vector 類別
可修改的序列集合。
Vector<T> 支援常數時間隨機存取和分攤常數時間 Append 作業。
Platform::Collections::VectorView 類別
Vector的唯讀版本。
Platform::Collections::InputIterator 類別
滿足 STL 輸入迭代器需求的 STL 迭代器。
Platform::Collections::VectorIterator 類別
滿足 STL 可變動隨機存取迭代器需求的 STL 迭代器。
Platform::Collections::VectorViewIterator 類別
滿足 STL const 隨機存取迭代器需求的 STL 迭代器。
begin() 和 end() 函式
為了簡化使用 STL 來處理 Vector、VectorView、Map、MapView 以及任意 Windows::Foundation::Collections 物件,C++/CX 支援多載的 begin 函式 和非成員 end 函式。
下表列出可用的迭代器和函式。
| Iterators | Functions |
|---|---|
Platform::Collections::VectorIterator<T>(內部儲存 Windows::Foundation::Collections::IVector<T> 和 int。) |
begin
/
end(Windows::Foundation::Collections::IVector<T>) |
Platform::Collections::VectorViewIterator<T>(內部儲存 IVectorView<T>^ 和 int。) |
begin
/
end (IVectorView<T>^) |
Platform::Collections::InputIterator<T>(內部儲存 IIterator<T>^ 和 T。) |
begin
/
end (IIterable<T>) |
Platform::Collections::InputIterator<IKeyValuePair<K, V>^>(內部儲存 IIterator<T>^ 和 T。) |
begin
/
end (IMap<K,V>) |
Platform::Collections::InputIterator<IKeyValuePair<K, V>^>(內部儲存 IIterator<T>^ 和 T。) |
begin
/
end (Windows::Foundation::Collections::IMapView) |
集合變更事件
Vector 和 Map 藉由實作變更或重設集合物件時,或者插入、移除或變更集合的任何元素時所發生的事件,來支援 XAML 集合中的資料繫結。 您可以撰寫自己的型別來支援資料繫結,但是您無法繼承自 Map 或 Vector ,因為這些型別是密封型別。
Windows::Foundation::Collections::VectorChangedEventHandler和 Windows::Foundation::Collections::MapChangedEventHandler 委派會指定集合變更事件的事件處理程序簽章。
Windows::Foundation::Collections::CollectionChange公用列舉類別和 Platform::Collections::Details::MapChangedEventArgsPlatform::Collections::Details::VectorChangedEventArgs ref 類別會儲存事件自變數,以判斷造成事件的原因。
*EventArgs 類型在 Details 命名空間中定義,因為當您使用 Map 或 Vector 時,不需要明確建構或使用這些類型。